Stroke is a clinical syndrome represented by general cerebral and focal neurological disorders. It develops suddenly as a result of an acute cerebrovascular accident, persists for at least 24 hours or ends in death at this or earlier time. There are ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes. Ischemic strokes occur 5 times more often than hemorrhagic strokes. In addition, so-called complex strokes (mixed strokes, hemorrhagic infarctions) are possible.
Coma during stroke mainly develops in the case of hemorrhagic stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital provide emergency care to patients admitted in a coma, using individual treatment regimens with modern drugs.
For the effective treatment of patients with stroke, the neurology clinic has all the conditions:
- modern diagnostic equipment with high resolution;
- the high scientific potential of the clinic, which employs professors and doctors of the highest category;
- effective high-class life-support equipment;
- comfortable conditions for patients’ stay and European service;
- psychological assistance to relatives and patients after recovery from a coma;
- innovative rehabilitation techniques.
All cases of patients with stroke entering a coma are discussed at the Expert Council. The decision on treatment methods is made collectively. All this together increases the chances of recovery for patients with stroke admitted in a coma to the Yusupov Hospital. Thanks to the early start of rehabilitation measures, many patients completely restore lost functions and return to normal life.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose stroke in 3 stages:
- initially distinguish stroke from other conditions associated with brain damage;
- at the second stage, the nature of the stroke itself is determined - hemorrhagic or ischemic;
- in conclusion, the area of vascular damage and the pathogenesis of cerebral infarction in ischemic stroke or the localization of hemorrhage and possible mechanisms of its development in hemorrhagic stroke are clarified.
Difficulties in diagnosing a stroke arise in cases where the patient has a pronounced disorder of consciousness - coma, which does not allow conducting a survey and finding out how the disease developed. In this case, the diagnosis at the first stage is based solely on the data of the neurological examination. Of the focal neurological symptoms in a patient in a comatose state caused by a stroke, the following symptoms are often found:
- paresis of gaze or floating movements of the eyeballs;
- anisocoria (different pupil sizes in the right and left eyes)
- strabismus (squint);
- “flabby” upper eyelid;
- suppression of the corneal reflex;
- facial asymmetry;
- sail sign (“bloating” of the cheek when breathing);
- hemiparesis or hemiplegia (complete or partial impairment of the motor function of the limbs on one side of the body according to the central type).
There is no contact with a patient in a coma; the detection of a rotated foot in a patient lying on his back, decreased tone or muscle spasm in the extremities is of certain importance in the diagnosis of hemiparesis. Neurologists determine the following symptom: in a patient lying on his back, passive flexion of the head is accompanied by flexion of the lower limb in the hip and knee joints on the side of the pathological focus, and on the side of hemiplegia the leg remains in the same position.
The most difficult and responsible task of the second stage is the accurate and rapid diagnosis of the nature of the stroke, since in the acute period of the disease, further treatment tactics and the prognosis for the patient largely depend on this. After ensuring the functioning of vital organs, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital perform magnetic resonance imaging on a patient with a stroke. It is especially informative in case of hemorrhagic stroke, as it allows you to quickly determine the nature of the stroke, the location of the hemorrhage and the size of the affected area.
What is coma and stupor?
Coma is a disorder of the central nervous system. A person has no consciousness, reflexes or reactions to external stimuli. There is a failure in all the most important life processes.
There are primary and secondary coma. The first occurs with focal brain damage. These could be injuries, tumors, apoplexy. The second is a consequence of some pathological process.
Stupor is one of the stages of coma. It is also characterized by depression of the central nervous system. The patient's reflexes are preserved, but he does not react in any way to the environment. In fact, stupor is an intermediate state between stunned consciousness and coma.
Why do people fall into a coma?
The main reason for the development of coma after a stroke is cerebral hemorrhage or apoplexy. Several factors can provoke it:
- Heavy bleeding.
- Insufficient or completely absent blood circulation in the brain.
- Brain swelling.
- Atheroma. This is a disease associated with blood vessels.
- Poisoning with chemicals or other substances hazardous to the body.
- Callagenosis. Represents pathological changes in connective tissue.
- Angiopathy. This is a condition characterized by the accumulation of a specific protein in the blood vessels of the brain.
- Acute stage of vitamin deficiency.
- Infectious and autoimmune diseases of the circulatory system.
- Most often, the listed pathologies develop with hemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic stroke very rarely leads to coma. Even if a coma does occur, the chance that a person will come out of it is great. In the hemorrhagic form, the death of brain tissue occurs, which entails serious complications.
Degrees of coma
Depending on how damaged the brain is after a stroke, there are 5 stages of coma:
Prekoma. This is a state when there is no coma yet, but brain functions are weakening. Its duration ranges from 2 hours to several days. The patient's consciousness is confused, his mood often changes, and coordination of movements is impaired. However, all the reflexes necessary for life are preserved. The body reacts to stimuli. A person feels touch.
Coma of the first degree of severity is considered to be stupor. It is characterized by lethargy, difficulties with communication and establishing contact, and increased muscle tone. The patient has difficulty eating. He can only eat liquid meals or drink water.
- Diabetic coma in children: types, symptoms, emergency care
Second degree. Brain activity is greatly reduced. The patient does not respond to attempts to establish contact with him. However, there is a reaction to loud sounds and bright light (the pupils are constricted). Muscle tone either increases or decreases. Muscle fibers contract chaotically. Reflexes are also inconsistent. In some cases, spontaneous urination and defecation occur. Experts consider the second degree to be a borderline state.
The third degree is the coma itself. The person is in an unconscious state. He has no reaction to stimuli, reduced muscle tone, and muscle twitching is observed, for example, as a response to pain. The functioning of almost all organs and systems is disrupted. Blood pressure drops, heart rate decreases, and breathing slows down.
Stages of medical care for patients in a coma after a stroke
Patients in a state of coma that has developed as a result of a stroke are provided with medical care at the prehospital stage by emergency physicians:
- restore airway patency;
- provide oxygen through an air duct or transfer the patient to artificial ventilation;
- prevent aspiration (foreign bodies entering the respiratory tract).
When there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure, drugs are used that have a vasopressor effect (alpha-adrenergic agonists) and improve myocardial contractility (cardiac glycosides), drugs that replenish the volume of circulating fluid (crystalloid solutions and low molecular weight dextrans). If the patient develops seizures, tranquilizers and antipsychotics are used. If necessary, barbiturates and inhalation anesthesia are used.
When a patient is admitted to the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, doctors take emergency measures:
- maintaining an optimal level of oxygen supply;
- monitoring of blood pressure and correction of cardiac activity;
- administration of pressor amines (1 ml of 1% mesotone solution intramuscularly or subcutaneously, caffeine, corticosteroids;
- constant monitoring and correction of acid-base balance in the body;
- control of swallowing (in the presence of dysphagia, a nasogastric tube is inserted to prevent aspiration bronchopneumonia and ensure adequate nutrition for the patient);
- control of the condition of the bladder and intestines.
There are currently no specific drug treatments for hemorrhagic stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are taking measures aimed at reducing the usually high intracranial pressure. At the same time, they normalize blood pressure, the state of the blood coagulation system and the permeability of the vascular wall, and support the activity of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. In the absence of contraindications, surgical interventions are performed at partner clinics. In the case of an ischemic stroke, patients are brought out of a coma and the restoration of lost functions is immediately begun using methods of drug therapy and physical rehabilitation.
If signs of coma appear, the patient should be placed on a horizontal surface, turn his head to the side and call an ambulance. Call and alert the clinic staff about the current situation. The Yusupov Hospital employs professors and doctors of the highest category who use modern equipment and medications that allow them to do everything possible to bring a patient out of a coma after a stroke.
Causes
Who can be called:
- High pressure in any part of the brain, which can lead to hemorrhage;
- Lack of blood supply to any organ;
- Degeneration of vascular walls;
- Defect in the development of vascular walls;
- Deposits in blood vessels;
- Intoxication;
- Blood diseases;
- Acute lack of vitamins.
- In addition, high blood pressure, old age, severe emotional shock and atherosclerosis can increase the risk.
Signs of a stroke
1. Facial asymmetry
The sign that first catches your eye. If you have a stroke, you may experience sudden numbness and tingling on one side of your face.
2. Numbness of the limbs
Most often, muscle numbness occurs on only one side. The muscles do not obey, the person cannot lift an arm or leg.
3. Speech impairment
Speech becomes incoherent, confused, and a person may not understand what is being said to him.
4. Loss of coordination
You need to be wary of sudden dizziness, accompanied by imbalance, loss of balance. The person loses the firmness of his gait and has problems with coordination.
5. Severe headache
It is unbearable and may be accompanied by vomiting. The pain occurs for no reason and does not decrease when taking painkillers.
6. Vision problems
Clarity is lost, objects begin to appear double. One or both eyes can lose good vision at once.
Recommendations for relatives of patients
A person emerging from a coma requires increased attention.
To avoid the recurrence of apoplexy, the following recommendations must be observed:
- inspire hope for recovery;
- create a favorable psychological climate and comfortable environment;
- motivate for daily exercise and praise for success;
- master manual massage skills.
Only love, care and attention can work miracles. Love and take care of yourself and your loved ones, and a favorable prognosis will not be long in coming.
- Nutrition for stroke and diabetes: what can a diabetic eat?
Brain hemorrhage and its causes
Hemorrhagic stroke is a hypertensive hemorrhage in the brain , characterized by acute circulatory disorders and necrosis (death) of one or another part of the brain.
Most often, pathology occurs as a result of high blood pressure, which remains stably (or increases even more) at a high level.
But there are other factors that contribute to hemorrhagic stroke. Here are some of them:
- Diabetes;
- Bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking);
- Cardiovascular diseases;
- Excess weight;
- Old age (over 60 years old);
- Sedentary lifestyle, etc.
Reference! According to statistics, in approximately 15% of cases the causes of stroke remain unclear.
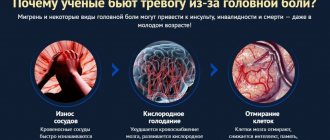
Mechanism of coma development
Damage to neurons is accompanied by changes in the metabolism of nervous tissue. Intracellular fluid exits into the intercellular space. As it accumulates, it compresses the capillaries, causing the nutrition of nerve cells to deteriorate even more and their work to be disrupted. A comatose state can develop very quickly (several seconds or minutes) or gradually (up to several hours, less often days). Most often, coma occurs after a massive or brainstem stroke caused by hemorrhage, less often by blockage of the cerebral arteries.
Symptoms of coma in older people
- Body temperature. If coma in older people is caused by overheating, it is accompanied by high temperature up to +43 ° C and dry skin. In case of poisoning with alcohol or medications, a low temperature of +32…+34 °C is diagnosed.
- Respiratory frequency. Slow breathing is diagnosed in older people in coma caused by a lack of thyroid hormones or poisoning with drugs containing morphine. If the pathology develops against the background of bacterial intoxication, brain tumor, renal failure, diabetes mellitus, then the patient will experience deep breathing.
- Heart pressure and rhythm. In cases where coma in an elderly person is provoked by heart pathologies, a decrease in heart rate is observed. If the cause of the coma is high intracranial pressure, then the patient is diagnosed with a rapid heartbeat in combination with high blood pressure.
- High blood pressure is common in patients in a coma due to a stroke. Low blood pressure is typical for patients in a coma caused by diabetes, poisoning with sleeping pills, extensive internal hemorrhage, or myocardial infarction.
- Color of the skin. The rich red color of the skin indicates that the patient has been poisoned by carbon monoxide. Blueness of the fingertips and nasolabial triangle indicates a lack of oxygen in the blood. If an elderly person in a coma has hematomas, bleeding from the ears and nose, and bruises around the eyes, then this condition has developed as a result of a traumatic brain injury. If there is unnatural paleness of the skin, this may indicate extensive blood loss.
- Contact with others. If an elderly person in a coma or stupor makes involuntary sounds, this is a positive sign, since this ability disappears as the coma deepens.
Read the material on the topic: Medicines for the elderly: 13 tips for taking medications
Recovery from coma
Removal from an induced coma is also carried out with the help of medications and takes a certain time. Rehabilitation can last from several weeks to several years. Patients often complain of hallucinations and nightmares, this is explained by the fact that doctors, when inducing a coma, try to preserve the ability to react to certain stimuli, as a result, the brain begins to interpret all the information that was available to it.
Important information According to neurologists, relatives should definitely talk to the patient when leaving, this allows him to more calmly experience the way out of the condition.
Prognosis and consequences of coma
Coma after a stroke is a dangerous condition; the prognosis of patients is disappointing and depends on the patient’s condition, the degree and timely response of doctors. It is extremely rare for older people to regain consciousness. The chances of recovery are reduced if the duration of coma exceeded 14 days. Patients with stage 1 have the most favorable prognosis, stage 2 gives questionable results, and with stage 3-4 the person does not recover from coma. If the patient manages to regain consciousness, it will take a long time to recover.
The risk of complications increases in parallel with the length of time a person remains in this condition. The patient may develop heart failure, nervous system disorders, infections, and bedsores. The result of mechanical ventilation is often:
- pneumonia;
- tracheobronchitis;
- stenosis.
Fistulas often form on the walls of the esophagus, gastrointestinal functions are disrupted, renal failure, sepsis develop, and blood circulation is impaired. Urinary retention can cause peritonitis and bladder rupture. Symptoms of heart failure and nervous system disorders often persist long after recovery from a coma. The following are considered fatal risk factors:
- recurrent stroke of any type;
- excess of more than 15 mg/l of creatine in the blood;
- complete loss of response to treatment and pain;
- existing brain damage;
- presence of twitching for more than 3 days;
- The patient's age is over 65 years.
If the patient ends up in the hospital in a timely manner, doctors will have the opportunity to stop the comatose process and reduce the severity of possible consequences.
- How many days does a coma last after a stroke and is there a chance of survival?
When to see a doctor
If a person falls into a coma, you should immediately consult a doctor. There can be no exceptions here. First of all, the patient will need the help of a resuscitator who will try to quickly remove the patient from the pathological condition. If resuscitation measures have no effect, treatment of the patient must be started.
Which specialist will treat the patient depends on the cause that caused the disturbance in the state of consciousness. You can seek qualified medical help at our clinic. We have specialists who understand how to work with people who have fallen into a coma. The choice of a doctor who will treat coma in the Central Administrative District depends on the cause that led to the development of the pathology.
How to call a resuscitator
If you decide to go to our clinic in the center of Moscow for medical help, dial the ambulance number -. A team of our specialists will arrive at the address you specified to transport the patient to a medical facility and provide him with first aid.
All our specialists are highly qualified and have extensive medical experience. All diagnostic measures are carried out promptly. This is also due to the availability of modern equipment. Our doctors choose the most optimal treatment method, taking into account the characteristics of the disease and the patient’s body.
Our clinic is located at the address: Moscow, Central Administrative District, 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, building 10. The nearest metro station is Mayakovskaya (5 min walk).
Remember that if a person falls into a coma, he requires emergency assistance from specialists. The slightest delay can lead to the death of the patient.
Forecast
As mentioned above, recovery from a coma is not always possible.
A certain percentage of victims emerge from a comatose state without restoration of motor and cognitive functions, i.e., they remain disabled for the rest of their lives.
The risk of death increases in the following cases:
- Over the age of 60-70 years .
- If the hemorrhage occurs in the brain stem .
- When a large area of the brain is damaged.
- If the person had bad habits (abused drinking alcohol and smoking).
In all other cases, especially at a young age, recovery from a coma is possible, but the rehabilitation process will still take some time.