Pain under the left sternum often indicates a specific disease and is a symptom of pathologies of the heart and other organs. If this symptom appears repeatedly, it is necessary to promptly seek medical help and carry out diagnostic measures. There may be disturbances in the functioning of not only the heart, but also the lungs, certain parts of the gastrointestinal tract, and the development of an oncological tumor. Pain syndrome may also indicate disturbances in the structure of the mammary gland and nearby tissues.
Causes of pain
If the pain is localized under the left sternum, it is necessary to diagnose the condition of the stomach, heart, and spleen. If you have diseases of the musculoskeletal system, you should diagnose inflammatory reactions. Pay attention to the probable risk of oncological processes.
Spleen disorders:
- With pathologies in the structure of the spleen, a characteristic symptom is radiating pain.
- Spleen cyst, possible abscess formation.
- Traumatic organ damage.
- An increase in organ size, the development of infectious mononucleosis.
Gastrointestinal diseases:
- Pathologies of the small intestine. In this case, the pain becomes aching in nature, and the occurrence of acute pain is excluded.
- Stomach ulcer, characterized by acute symptoms.
- Gastritis, characterized by the appearance of bursting pain.
- Dyspepsia, in which, in addition to pain, persistent nausea is noticeable.
- Diaphragm hernia, signs of which are noted not only under the left sternum, but also from the back.
- Gastropathy developed as a result of ischemia.
- Oncology.
Symptoms indicating the presence of disturbances in the structure of the bronchi and lungs:
- Pneumonia localized on the left side. It is characterized by a dull pain syndrome, unpleasant sensations that are not severe, but spread to the area under the chest and back.
- Left-sided pleurisy, which, in addition to unpleasant symptoms in the form of pain, is characterized by the formation of a severe cough. It intensifies during coughing attacks and radiates to the chest and back.
Diseases developing in the mammary gland:
- Cyst, another tumor accompanied by the formation of an abscess.
- Fibromyalgia.
- Oncology.
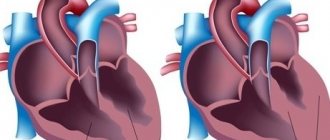
Cardiac disorders:
| Disease | Signs |
| Heart attack or pre-infarction condition resulting from thrombosis or blockage of the splenic artery | Similar disorders occur in rheumatic disease, ischemia, the development of endocarditis, as well as in other acute conditions |
| Angina pectoris, ischemia of the heart muscle | It manifests itself as compressive pain, which is not only localized under the breast, but also radiates to the arm |
| Acute myocardial infarction | In this case there were excessive, often unbearable intensity |
| Aortic aneurysm | Acute pain |
| Pericarditis that has progressed to the acute stage | Shortness of breath combined with pain |
| Valve prolapse | Patients notice aching pain, the location of which constantly moves |
| Osteochondrosis, which in the early stages is often confused with angina pectoris | Characteristic pain under the left sternum |
| Neuralgia | Unpleasant sensations are sharp and excessively intense |
The main causes of pain under the left shoulder blade
There are many causes of pain, but they can all be divided into 2 groups:
- Pain associated with pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Pain under the left shoulder blade can be caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical or thoracic region, intercostal neuralgia, osteomyelitis, bone tuberculosis, scapula injuries, rib fracture or crack, myofascial or scapulocostal syndrome, glenohumeral periarthritis.
- Pain that occurs due to diseases of the internal organs. Pain under the left shoulder blade can be a symptom of heart disease, bronchopulmonary system, gallbladder, stomach ulcers, esophageal spasm, exacerbation of pancreatitis.
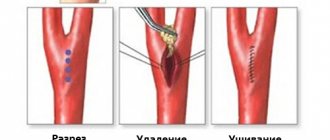
Rare pathologies that cause pain radiating to the shoulder blade include splenic rupture. This pathology requires immediate surgical treatment, since massive abdominal bleeding occurs with a risk of death.
No less dangerous for the body is pain in the back on the left under the shoulder blade, which develops against the background of cardiac diseases:
- dissection of an aneurysm of the ascending aorta;
- cardiac ischemia;
- angina pectoris;
- pericarditis, myocarditis, pericarditis;
- myocardial infarction.
Pain in the left shoulder blade from the back, which radiates to the arm and chest area, may indicate heart disease. Numbness of the limb often occurs. Depending on the disease, accompanying symptoms appear: lack of air, compression of the throat, squeezing of the chest, a feeling of cardiac arrest.
Pain under the left shoulder blade may appear during pregnancy due to increased stress on the back
Let's take a closer look at the main causes of pain under the shoulder blade from the back on the left.
Gallbladder diseases
With cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, heaviness appears in the right side, pain radiating under the shoulder blade on the left. An acute attack of inflammation of the gallbladder causes severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and increased body temperature. If it is provoked by obstruction of the bile ducts by a stone, the pain syndrome occurs as biliary colic.
With chronic inflammation, the nature of the pain is aching. Unpleasant sensations appear after eating fatty foods, with long breaks between meals.
Relapses of attacks can occur after physical or nervous strain, against a background of stress.
Subphrenic abscess
It is an accumulation of pus under the diaphragm. Most often, an abscess forms on the right side, but left-sided localization is also possible. The pathology is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the left side, radiating under the scapula to the sternum;
- acute pain in the chest, which intensifies when inhaling;
- high body temperature;
- hiccups;
- increased sweating;
- nonproductive cough;
- dyspnea.
Without treatment, the disease can cause empyema, pneumonia, and lung abscess.
Bronchopulmonary diseases
Diseases of the lower respiratory tract (bronchi, lungs and pleura) cause both chest and scapular pain, which are always complemented by a specific bronchopulmonary clinical picture:
- increased body temperature;
- weakness, lethargy;
- labored breathing;
- chest pain (usually from the affected lung) of moderate intensity, which intensifies when coughing or inhaling;
- cough;
- wheezing.
Pain syndrome in the back of the back in the area of the left shoulder blade most often occurs with pneumonia, dry pleurisy, pneumothorax, acute bronchitis or abscess of the left lung.
With tumors, back pain in the area of the left shoulder blade is not accompanied by fever and high temperature, but there is a cough and breathing problems
Kidney diseases
Scapular pain may occur due to problems with the right kidney, since it is located close to the scapula. With its inflammation, the formation of purulent infiltrates or stones, the pain is often localized on the right, but can also radiate to the left. The pain is often dull or aching, but can also be sharp. It is paroxysmal, ascending, that is, it rises from the lower back, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and elevated body temperature.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Problems with the spine and neurological disorders associated with them are the main cause of back pain in the area of the left shoulder blade. Pain can occur with any movement, turning the body, sneezing, breathing, or taking a deep breath. They can radiate into the arm, combined with a crunching sound and limited mobility.
Often pain in the scapula area occurs due to the following diseases:
- cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis;
- herniated intervertebral discs;
- protrusion;
- scoliosis;
- radiculitis.
Against the background of degenerative processes in the spine, not only blood vessels and nerve endings are pinched, but also muscles spasm. Muscle spasm provokes the occurrence of scapular-costal syndrome.
One of the most common causes of pain in the scapula is cervical osteochondrosis. At first, the pain syndrome is mild, but as degenerative changes occur, it becomes acute and shooting. The pain is accompanied by dizziness, tinnitus, blurred vision, and increased blood pressure.
With cervical osteochondrosis, pain radiates to the arm
More rare diseases of the musculoskeletal system that can provoke scapular pain include osteomyelitis, bone tuberculosis, and malignant neoplasms.
Muscle strain and inflammation
The back muscles that surround the shoulder blade support the spine in an anatomically correct position and protect the internal organs that are located nearby. Their inflammation or injury is not only accompanied by pain, but also provokes a decrease in muscle tone and the occurrence of instability in the shoulder.
Intercostal neuralgia
The disease is accompanied by inflammation of the intercostal nerves and appears against the background of the following provoking factors:
- injuries to the ribs or spine;
- hypothermia;
- excessive physical activity;
- osteochondrosis.
The intensity of the pain syndrome depends on the severity of the pathology and the timeliness of treatment. The pain can be aching, but sometimes it hurts so much that you can’t stand it.
It is important to contact a neurologist in time, who will provide qualified and, most importantly, timely assistance, otherwise intercostal neuralgia will cause a person severe discomfort:
- the pain becomes shooting, cutting in nature;
- pain increases when moving your hand, coughing or inhaling;
- numbness occurs in the affected area of the body;
- heart rhythm is disturbed.
A neurologist with more than 10 years of experience sees patients in a medical clinic. Only he can correctly determine what causes the sudden pain under the left shoulder blade - neuralgia or cardiac pathology. It is impossible to make a correct diagnosis on your own.
Diseases or injuries of the scapula
Cracks and fractures of the scapula, glenohumeral arthritis are accompanied by pain, limitation of movement, damage to blood vessels and pinched nerve endings.
Injuries to the scapula are more common among athletes, patients with osteoporosis, and cancer of bone tissue.
Aching nature of pain
If the pain syndrome occurs in a mild form, this often indicates the development of chronic inflammatory processes. Possible inflammation of the stomach, which occurs in slow motion, pathologies of the large intestine, disorders of the spleen. In this case, along with such pain, nausea and vomiting appear. This violation indicates the development of a stomach ulcer.
Important!
Often, chronic aching pain signals ischemia or angina. In rare cases, with pathologies of the pancreas, the pain has a girdling character.
If you experience discomfort after stress or physical activity, you may develop cardiac disorders, for example, myocarditis. If even a slight pain syndrome is detected, you should consult a doctor and perform a set of diagnostic examinations.
Sharp pain
If acute pain syndrome develops, measures should be taken immediately to relieve it. If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition may occur. Severe pain indicates the onset of spasm of the coronary arteries, the development of an aortic aneurysm, heart attack, perforation of the stomach and intestines. In this case, along with pain, a person notices a strong increase in temperature, and pancreatitis is likely to occur. When this disease develops, the nature of the pain is unbearable and cannot be relieved with standard analgesics.
Important!
If mediastinal emphysema develops, the pain radiates to the retrosternal space, and a typical crunching sound appears when breathing. In a hospital setting, measures are taken to relieve severe pain, as well as to prevent the worsening of the patient’s general condition.
If the pain becomes stabbing in nature, this disorder indicates the presence of inflammatory processes in the muscles, the development of neuralgia, and in some cases, angina. The patient is not always able to accurately determine the nature of the pain syndrome. You should undergo an examination to exclude perforation of the stomach wall and various traumatic injuries.
Diagnostics
If a patient begins to have pain in the chest on the left, he needs to consult a therapist. First of all, regardless of the patient’s age, the specialist excludes all cardiac causes of pain, after which instrumental examinations of other organs of the chest cavity are performed. To clarify the etiological factor of the disease, advanced laboratory tests are indicated. In diagnostic terms, the most valuable are:
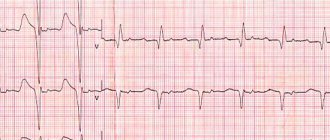
- ECG
. An electrocardiogram is recorded at the time of an attack of pain and signs of myocardial ischemia are revealed - a rise in the ST interval, a widening or change in the shape of the T wave. In the case of myocardial infarction, a typical “cat’s back” pattern is detected on the ECG. To confirm the anginal cause of pain, a troponin test is performed and the level of creatine phosphokinase is determined. - Echocardiography
. Ultrasound diagnostics of the heart allows you to identify signs of inflammatory processes and degenerative changes in the heart valves. Left ventricular contractility and ejection fraction are measured to rule out heart failure. Additionally, Doppler ultrasound and color mapping of the great vessels are prescribed. - Radiography
. If pneumonia is suspected, chest x-rays in the frontal and lateral planes are required. If a suspicious shadow appears on the image, it is informative to perform a CT scan of the chest cavity for detailed visualization of the affected area. X-rays can also help look for signs of a diaphragmatic hernia. - Ultrasonography
. An abdominal ultrasound is necessary to exclude inflammatory processes in the spleen and pancreas. The structure and homogeneity of the organ parenchyma and the presence of focal formations are taken into account. Ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities is required to detect thrombotic masses, a common cause of pulmonary embolism. - Blood
tests . A general blood test is not informative enough; it usually reveals leukocytosis and an increase in ESR, which indicates an acute pathological process in the body. In a biochemical study, attention is paid to the levels of acute phase indicators. To diagnose atherosclerosis and the ischemic cause of left chest pain, the lipid profile is assessed. - Bacteriological research
. In case of pneumonia or bronchitis, sputum samples should be collected for bacterial culture on nutrient media, then the isolated microorganisms are tested for sensitivity to antibiotics. To confirm the diagnosis of infective endocarditis, it is necessary to culture pathogens in two or more blood samples taken 12 hours apart. - Invasive diagnostics
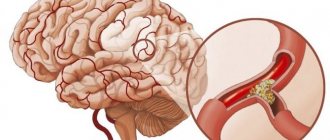
. To clarify the condition of the vessels, coronary angiography with a contrast agent is indicated, during which the patency of the arteries, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques and thrombotic masses are studied. Angiography is used to select the method of myocardial revascularization. In case of pleurisy, a pleural puncture is performed to take exudate for analysis.
Echocardiography
Strong pain
Severe pain is associated with disruption of nerve endings, which indicates the development of pericarditis, pneumonia, as well as deterioration of the patient’s condition with chronic angina. If these symptoms occur during physical activity, such a violation indicates a worsening of osteochondrosis.
Important!
Severe pain is a sign of pulmonary embolism. In this case, the newly appeared painful sensations quickly worsen and radiate to other areas of the body. This disease is often confused with myocardial infarction, but with thromboembolism the patient suffers from severe shortness of breath, blood escaping through the mouth, and possible loss of consciousness.
Myocardial infarction is suspected if pain develops from the middle of the chest and then moves to the left side. As symptoms intensify, it radiates to the arm and back. If you notice similar symptoms in yourself or someone you know, you must seek medical help promptly, since an acute condition requires urgent treatment measures.
Burning behind the sternum
Gastritis
Ulcer
Pancreatitis
22465 May 28
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Burning sensation behind the sternum: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
A burning sensation behind the sternum is a symptom characteristic of many diseases - this is how patients with pathologies of the cardiovascular system, spine, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, neuralgia and panic attacks describe their sensations.
In some cases, this symptom is not dangerous, but some pathological conditions require immediate medical attention.
Types of burning behind the sternum
There is no generally accepted classification of burning behind the sternum. When patients are asked about their sensations, they talk about pressing, pulling, stabbing, burning, and encircling pain.
Thus, the burning sensation is as varied as the causes that cause it.
Possible causes of burning behind the sternum
Burning in the sternum, a feeling of fullness and heaviness, especially in older people, can be a symptom of serious cardiac problems, and all of them equally require seeking medical help.
In diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, the burning sensation is usually diffuse, often radiating to the back. In many patients it occurs during or after eating.
Disruption of the musculoskeletal system often leads to unpleasant sensations in the chest. The burning sensation intensifies when inhaling or exhaling, and changes when changing body position.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine can cause numbness in the hands and decreased sensitivity.
Neuroses and panic attacks are often accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest.
When the neuroendocrine regulation of internal organs is disrupted, patients complain of a burning sensation behind the sternum. The cause may be either insufficient maturity of the body's systems during adolescence, or previous infectious diseases, stress, bad habits, or overwork. Short-term vasospasm directly leads to the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the heart area. The attacks pass at rest and are accompanied by weakness, rapid heartbeat, and cold hands due to deterioration of blood flow.
Diseases leading to a burning sensation behind the sternum
Cardiovascular pathologies:
- Angina pectoris. Impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the heart due to atherosclerosis leads to deterioration in the nutrition of the heart muscle. During physical activity or anxiety, the heart requires more oxygen - if there is not enough oxygen, then the first signal will be discomfort in the chest area. A burning sensation, a feeling of squeezing, a tingling sensation can radiate (radiate) to the left arm, under the shoulder blade, rarely to the lower jaw, lasting no more than 15 minutes and passing with rest and after taking nitroglycerin.
- Myocardial infarction.
During a heart attack, a sharp disruption of the blood supply to the heart muscle occurs due to blockage of most of the lumen of the vessel supplying the heart by thrombotic masses. Most often, intense pain occurs, but a strong burning sensation in the chest may also be present. The attack lasts a long time, is not relieved by nitroglycerin, does not go away with rest, and is accompanied by shortness of breath, severe weakness, and decreased vision. Myocardial infarction is a life-threatening condition, so the patient needs urgent hospitalization. - A sharp rise in blood pressure may occur with a burning sensation in the chest. During a hypertensive crisis, the patient feels weakness, headache, dizziness, nausea, spots appear before the eyes and tinnitus.
- Inflammatory processes in the heart can also be manifested by a burning sensation in the chest. Typically, this condition is preceded by an infectious disease, most often of viral origin, or a severe bruise in the chest area. Unpleasant sensations can spread to the right or left side and intensify with changes in body position.
- A very dangerous condition is pulmonary embolism.
It occurs if blood clots are present in the vessels of the lower extremities - when they break off, they rise up the bloodstream and clog the pulmonary vessels. In addition to a burning sensation behind the sternum, the patient is bothered by severe shortness of breath, coughing (sometimes with blood), and severe cyanosis appears. In such a situation, emergency hospitalization is necessary. At risk are patients with varicose veins, smokers, and patients on the first day after surgery.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Esophageal pathology is considered perhaps the most common cause of burning in the chest. It occurs as a result of the reflux of acidic gastric contents into the esophagus, which leads to damage to its mucous membrane. A burning sensation appears after eating food (especially spicy, fatty, smoked and fried), when wearing tight belts and taking a horizontal position immediately after eating.
- Inflammatory processes in the pancreas and gall bladder are often accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest. This symptom appears a couple of hours after eating and may be accompanied by nausea and heaviness in the stomach.
Respiratory diseases:
In case of inflammation of the bronchi or lungs (bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy), in addition to coughing and fever, the patient may be bothered by a burning sensation in the chest.
In addition, diseases characterized by a burning sensation behind the sternum include intercostal neuralgia, osteochondrosis, intercostal myositis, and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Which doctors should I contact if I have a burning sensation in the chest?
If a burning sensation behind the sternum is accompanied by a sharp deterioration in condition, weakness, an increase in pain, shortness of breath, coughing, or dizziness, you must immediately call an ambulance.
In other cases, you should also not postpone your visit to the doctor. Since this symptom has many causes, it is advisable to first turn to. He will prescribe examinations and, if necessary, refer to other specialists: a cardiologist; gastroenterologist; pulmonologist; neurologist.
Diagnosis and examinations for burning sensation behind the sternum
Making a diagnosis begins with a thorough history taking into account all the patient’s complaints and a physical examination.
To exclude cardiovascular pathology, first of all, a chest x-ray or CT scan of the chest and mediastinum is performed, as well as an electrocardiographic study (ECG) or echocardiography (EchoCG).
Blunt pain
Dull pain indicates osteochondrosis and is a sign of chronic gastrointestinal pathology. With aching pain, patients may suffer from pancreatitis, cholecystitis, but in this case these diseases have atypical symptoms. Unpleasant sensations of a dull nature indicate the development of cardialgia of the vegetative type. Additionally, patients feel a rapid heartbeat and suffer from severe shortness of breath. An increase in blood pressure is diagnosed, which cannot be reduced with validol or other similar medications. With this disease, discomfort can be relieved with the help of sedatives.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis. Part 1 Symptoms of osteochondrosis. Part 2
Important!
Similar signs are present with the development of false angina. In this case, negative manifestations become more pronounced if the patient is exposed to physical activity, stress, or becomes very tired at work.
The dull nature of the pain manifests itself in breast cancer at an early stage. Typically, at the onset of the disease, characteristic manifestations cannot be noticed. When stages 2 and further occur, patients complain of dull pain, characterized by an increasing course. If you notice even minor pain, you should consult a doctor to diagnose and treat possible dangerous pathologies.
Treatment
Features of treatment depend on the disease that was identified during diagnostic measures. If the pain is acute, measures are first taken to relieve it. Subsequently, therapy is carried out aimed at treating a specific disease.
In case of severe pain, follow these rules:
- Elimination of the primary pathology that caused the pain. It is necessary to carry out surgical measures if there is a risk of splenic rupture or aortic aneurysm. A number of therapeutic measures are also carried out if the patient is in a pre-infarction state.
- If the patient is 40 years of age or older, doctors decide on emergency hospitalization to avoid the development of acute or irreversible processes.
- The use of strong analgesics is not recommended. The use of drugs is especially dangerous when disorders in the gastrointestinal tract are detected, since in the case of complete relief of the pain syndrome it is impossible to determine the exact clinical picture.
- Strong painkillers are used if the pain is due to problems with the heart, as well as in case of traumatic injuries.
- First aid involves independently performing the following actions:
- Use of heart medications. You can often find Validol, Nitroglycerin or similar medications in your home medicine cabinet.
- Move the patient to a horizontal position. Turn off the lights, you should also reduce the patient’s nervous excitability, and ensure silence around the patient.
- If the pain does not become moderate, you should immediately call an ambulance.
- If the pain is caused by disorders in the gastrointestinal tract, you must stop eating for a while and call a competent specialist or an ambulance. The hospital undergoes various diagnostic measures to determine the location of the pathology. If the pain is girdling, acute, and localized on the left side, self-treatment of the disease is completely prohibited, since rash actions can provoke a number of serious complications.
- If the pain syndrome has developed as a result of neuralgia, the patient should be provided with complete rest, periodically consult a doctor, and, if necessary, conduct diagnostic tests. In the future, you can select a suitable therapy, thanks to which the general condition of the patient significantly improves.
Video - 3 tests for chest pain. How to find out what hurts behind the sternum
Prevention
Prevention of chest pain syndrome consists of timely contacting a doctor for the first symptoms of the disease, a healthy lifestyle and following all the recommendations of the attending physician. FEATURES OF THE COURSE OF CHEST PAIN SYNDROME
in age groups is that in older people the pain syndrome is usually less pronounced. It can be masked by shortness of breath and weakness, dizziness, and its most common cause is ischemic heart disease.
In younger patients, the list of main causes includes traumatic and inflammatory diseases of the chest, lungs, and gastroenterological pathology.
There are no differences between individuals of both sexes in the characteristics of chest pain. In pregnant women, the clinical picture of chest pain differs little from that in other individuals.
Our clinic at the New Hospital has all the necessary examinations and specialists to conduct a full examination of a patient with chest pain
Prevention of pain under the left sternum
A number of standard measures are used as prevention. A clinical examination is required, carried out at least once a year. Seek medical help if you notice negative symptoms to prevent the development of a dangerous disease. Pain prevention is carried out in conjunction with procedures aimed at preventing the worsening of the underlying disease.
If pain is provoked by the development of cardiopathy, the following activities should be carried out daily:
- Use cardioprotectors, Aspirin Cardio, and other medications prescribed by your doctor. They should not be canceled if an improvement in the general condition is detected. It is advisable to consult with a specialist in advance. Not only observe the frequency of taking medications, but also do not refuse to take the full course.
- Take measures aimed at getting rid of bad habits. First of all, this is excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages, as well as smoking.
- Balance your diet, take time to select the optimal products to normalize your overall health.
- Pay attention to physical activity, but do not overdo it, engage in physical exercise until discomfort appears.
- Be in a positive mood, learn to independently normalize the activity of vital organs, including with the help of breathing exercises.
- When leaving home, take with you a standard set of cardiac medications that help relieve an acute attack.
If the pain under the left sternum is associated with the development of osteochondrosis, you should spend time doing therapeutic exercises every day and ensure moderate physical activity. After going to the doctor, take medications prescribed to strengthen the musculoskeletal system. If possible, take a swimming course.
Important!
If breast diseases are detected, regular visits to a mammologist are required. Do not forget to undergo diagnostic examinations in a timely manner and consult with your doctor. In some cases, surgical treatment of the pathology is indicated.
Pain under the left sternum may indicate both the development of neuralgia and more serious disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Pay attention to the prevention of this deviation; if negative symptoms appear, seek medical help to diagnose and treat dangerous diseases. Read the incubation period of syphilis on our website.