There is probably no person who, at least once in his life, has not felt pain in his chest on the right. For some reason, this symptom is not considered alarming: many people are guided by the fact that the “motor” of our body - the heart - is located on the left, which means there is no danger to life. Some people completely ignore the problem until the symptoms expand, preferring to relieve pain with medications available at home. Medical experts strongly disagree with such an irresponsible approach - after all, sharp, severe pain in the chest on the right is often a very alarming signal.
Diseases of the cardiovascular system
With pain in the chest on the right side, almost every doctor will first suspect the presence of cardiac pathologies, especially if the patient is no longer young, and the patient himself leads a sedentary, unhealthy lifestyle and has a history of cardiovascular and endocrine diseases.
Aortic aneurysm
An aneurysm is a weak section of the wall of the main artery in our body. In this place the wall stretches, bulges, and at some point it can either burst or tear. This condition is life-threatening, therefore, at the first suspicion of an aneurysm, the patient will be prescribed an X-ray or MRI, where the pathology will be identified and a decision will be made on the need for surgical treatment.
Angina pectoris
If there is pain in the upper right side of the chest, this may indicate the presence of angina pectoris: it occurs due to impaired blood supply to the myocardium and is often a consequence of atherosclerosis (the formation of plaques on the inner walls of blood vessels).
Pericarditis
The pathology is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the heart muscle (pericardium), as a result of which its function is impaired. This condition is most often observed in men, and at a young age - from 20 to 50 years.
Myocardial infarction
Sudden acute pain in the chest on the right, more often in women and less often in men, which does not go away even after taking strong painkillers, indicates myocardial infarction. This is a deadly condition caused by impaired blood supply to the heart muscle.
What can hurt your chest?
Chest pain is familiar to people of all ages. Painful sensations occur in the middle of the chest, left, right, lower or upper. They can be aching, burning, sharp, growing. They last for several minutes or for a long time, returning periodically, accompanying some specific actions: coughing, inhaling, increased stress.
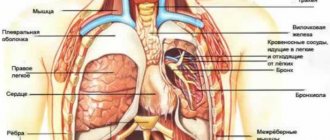
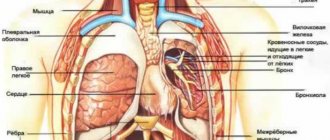
Inside the chest cell are large vessels, the heart, lungs, esophagus, muscles and ligaments. All this can cause pain of various types.
It is customary to classify two types of chest pain :
- Vertebrogenic – associated with spinal pathology.
- Nonvertebrogenic – caused by diseases of blood vessels and internal organs, as well as those of a psychogenic nature.
But it is often very difficult to determine what exactly hurts and in what place in the chest. After all, pain can occur near the problem area from pinched nerves or an inflammatory process, be radiating or wander.
Digestive diseases
Quite often, a patient’s complaints that he has pain on the right side of the chest can signal problems with the gastrointestinal tract. As a rule, such diseases are accompanied by a number of very characteristic additional symptoms - nausea and vomiting, increased body temperature, and upset stool.
Hepatitis
A dangerous disease that affects the liver develops as a result of transfusion of infected blood into the human body (forms B and C), and is also transmitted through dirty hands (form A). A characteristic symptom of hepatitis is not only pain, but also yellowing of the whites of the eyes, associated with an increase in the amount of bilirubin in the blood.
Stomach ulcer
It may appear as the body’s response to the abuse of spicy, fatty and fried foods, as well as alcohol. Often, peptic ulcer disease is preceded by other gastrointestinal lesions. The pathology is characterized by the formation of a perforation in the wall of the stomach, through which its contents enter the abdominal cavity. As a rule, with an ulcer, the patient complains that the pain is most intense on the right side (including in the chest) during or after eating.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) in our country is not treated very responsibly, believing that it is enough to relieve pain symptoms. In fact, such a careless attitude towards the disease can lead to a number of more serious problems that will require urgent surgical intervention.
Chest pain
Chest pain is described as pulling, pressing, burning, stabbing, a feeling of tightness or burning.
These symptoms do not always indicate a heart attack. In addition to the heart, there are many other organs in our chest that can cause discomfort. The pain can be harmless or indicate a serious illness. And such pains are not always very different from each other.
A burning sensation in the chest can be caused by stomach irritation. But the most dangerous chest pain is caused by a heart attack. They are usually accompanied by shortness of breath, severe tight pain on the left side of the chest and fear of death. Even an experienced doctor cannot always immediately determine the source of pain, since each person perceives and describes pain symptoms differently. Thus, the burning sensation on the left side of the chest can be attributed to costal neuralgia, but in reality it turns out that it was a heart attack. And sometimes people call an ambulance for heartburn because it was painful and scary. It is important to be careful, especially when the first symptoms of illness occur.
The rib cage is protected on all sides by the ribs and spine. The ribs protect vital and sensitive organs. The most important organs are the heart and lungs. The esophagus runs approximately in the middle and ends at the entrance to the stomach. In addition, the chest cavity is filled with a network of large blood vessels, such as the aorta, which pumps blood into the body. The muscles of the chest stretch the ribs during inhalation. Thus, the breasts are constantly in motion, even during sleep. In general, the chest is the scene of many well-coordinated processes of various organs.
Chest pain is as varied as the anatomical causes that cause it. Heart pain is life-threatening, such as angina pectoris, a temporary disturbance in the circulation of the heart. Such pain intensifies during exercise. The heart does not supply the body with enough blood, and typical symptoms of angina pectoris appear: burning pain in the chest, sweating, difficulty breathing, nausea, vomiting. Sometimes, with angina, pain can radiate to the shoulder of the left arm or to the jaw.
With increased blood clotting, clots can completely or partially clog the arteries. Blood does not flow through and the heart muscle dies. This is accompanied by severe pain, sometimes behind the chest, a burning sensation on the left side of the chest and shortness of breath.
An aura of pain in the left shoulder and upper abdomen, back, neck or lower jaw also indicates a heart attack. Symptoms last for at least twenty minutes and do not improve. Taking nitroglycerin does not always help; you need to call an ambulance.
High blood pressure can cause symptoms similar to angina (shortness of breath and chest pain, sometimes also heart pain).
Pulmonary embolism - a detached blood clot (thrombus) causes pulmonary vascular obstruction. The result may be sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, coughing, even loss of consciousness.
Typical signs of pneumonia include cough, burning and chest pain, difficulty breathing, fever and expectoration.
Lung cancer is characterized by increasing chest pain, accompanied by cough, shortness of breath, and bloody sputum.
Pericarditis caused by viruses causes a burning sensation in the chest that gets worse with deep breathing and coughing. If a person experiences discomfort while lying on his left side, then one should talk about pericarditis. The feeling of discomfort in such cases is accompanied by a cardiac cough.
Narrowing of the aortic valve impedes blood flow and leads to recurring symptoms of angina that improve over time.
Acute and chronic mediastinitis causes severe chest pain, accompanied by fever and loss of consciousness. Acute mediastinitis is usually caused by bacteria. Sometimes infections take purulent forms. The disease is life-threatening.
Pleurisy is also caused by infections, manifested by sharp pain in the chest, which intensifies with breathing, and a cough that does not bring relief is added to this. Fever and shortness of breath also accompany this disease.
The most severe pain in the chest, radiating to the back, legs and stomach, is caused by aortic rupture .
Esophageal rupture is very rare and is caused by physical injury, but can sometimes be caused by extreme pressure during vomiting.
Heartburn , the rise of stomach acid into the esophagus, can cause severe pain behind the chest, often accompanied by regurgitation. Sometimes heartburn is accompanied by attacks of angina.
Spinal diseases can also cause chest pain. Such pain usually occurs suddenly and resembles the pain of angina pectoris.
Rib fractures and bleeding cause severe chest pain, especially when breathing, laughing, or coughing. Even bruising in this area is often extremely painful and uncomfortable for several weeks.
Stress and anxiety can also cause fluttering and chest pain. By the way, they are often mistaken for symptoms of angina pectoris.
With diseases such as cholelithiasis or pancreatitis, pain in the upper abdomen often radiates into the chest and causes a strong feeling of chest tightness.
Here are some reasons that cause chest pain. In any case, it is not always possible to make a diagnosis yourself. And if you experience severe or recurring feelings of discomfort, you should be examined by a doctor. These can range from simple respiratory diseases to severe forms of the disease that require immediate hospitalization.
Section: Articles Tags: cardiology
Spinal problems
The back is also often able to “give” under the ribs or into the chest. This occurs if there is an injury, sprain after intense physical activity, and as the main concomitant symptom of some pathological conditions.
Intercostal neuralgia
This term refers to compression of the roots of the intercostal nerves. As a result, the latter become irritated and respond with intense pain in the chest on the right or left, often radiating under the shoulder blade.
Intervertebral hernia
This is a musculoskeletal disease in which there is a gradual thinning of the wall of the fibrous ring and, as a result, its rupture.
Scoliosis
The “sickness” that our parents and school teachers used to scare us as children is not as harmless as it might seem. Deforming over time, the spine often produces more or less intense pain and various pathologies.
Ankylosing spondylitis
A situation in which pain in the back and/or chest on the right is a frequent companion to this pathology, manifested by inflammation of the intervertebral joints. The disease is chronic, limits joint mobility, stunts growth and ultimately leads to disability.
Diagnostics
In case of pain in the chest on the right, a consultation with a therapist is indicated; in the future, the doctor can refer the patient to specialized specialists. A diagnostic search involves performing instrumental methods of visualizing the organs of the chest and abdominal cavities; to clarify the cause of thoracalgia, specific laboratory examination methods are performed. The most informative ones are:
- Radiography
. A plain radiograph of the lungs is recommended if pneumonia is suspected: attention is paid to focal heterogeneous darkening of the pulmonary parenchyma, expansion of the roots of the lungs and increased bronchial pattern. If a rounded shadow with a path to the root is detected at the apex of the lung on the right, a preliminary diagnosis of tuberculosis is made. - Ultrasonography
. If there is pain on the right side, not only in the chest, but also in the hypochondrium, an abdominal ultrasound is prescribed. During sonography, the anatomical position and structure of the gallbladder, liver, and bile ducts are assessed. The method also helps to identify gallstones and inflammation as possible causes of thoracic pain syndrome. - Endoscopy
. Bronchoscopy is indicated for severe respiratory diseases of unknown etiology, suspected malignant tumor of the bronchi. Wash water and areas of affected tissue are taken for laboratory diagnostics. Extensive inflammatory processes in the pleura are the basis for thoracoscopy - examination of the pleural cavity with an endoscope through a puncture in the chest wall. - ECG
. To exclude a cardiac cause of pain, an electrocardiogram is recorded in 12 standard leads to detect typical signs of “pulmonary heart”: deviation of the electrical axis of the heart to the right, high P wave, conduction disturbance of the right bundle branch. To clarify the diagnosis, echocardiography and duplex scanning of blood vessels are used. - Laboratory analysis
. To establish the etiological factor of pneumonia and bronchitis, morning sputum is collected for bacterial culture on enriched nutrient media. To confirm gallbladder damage, cholesterol, direct and indirect bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase levels are measured. Additionally, a blood test is performed to determine the level of tumor markers.
X-ray of the chest organs
Treatment
It can be conservative or surgical, depending on the diagnosis. Some types of pathologies - for example, hepatitis - require long-term use of antibiotics and strong antiviral drugs, others are based on normalizing the diet and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The specialists of the Energo clinic, who are true professionals in their field, will definitely identify the causes of back and chest pain, select a method that is suitable for you to solve the problem, and give useful recommendations regarding the period of recovery or remission in the case of a chronic illness.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis and its prevention
Conservative treatment of osteochondrosis in the thoracic spine is intended to stop or at least slow down degenerative changes, restore normal back mobility and eliminate symptoms that cause discomfort to the patient.
Therapeutic treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis involves the simultaneous use of:
- medications
(chondroprotectors, neuroprotectors, muscle relaxants, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics); - methods of physiotherapeutic complex
; - therapeutic exercises
; - orthopedic regime
.
Patients are also advised to change their diet and lifestyle.
In case of severe irreversible changes in the intervertebral joints , in which pain and nerve conduction disorders are not relieved by medications,
surgery is recommended for patients
. It helps stop the death of nerve tissue and prevent life-threatening or disabling consequences of thoracic osteochondrosis. Depending on the situation, complete or partial resection of the intervertebral disc or its replacement with an artificial one, narrowing of the spinal canal or other surgery may be indicated.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
Physiotherapy
The objectives of physiotherapy for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region are to reduce pain and inflammation, relieve spasms, strengthen the muscle corset, restore the function of the nerve roots and normal blood circulation.
To relieve the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, the following are successfully used:
- Magnetic therapy
is one of the most effective anti-inflammatory techniques. Improves metabolic processes in tissues and relieves swelling. - Laser therapy
. Promotes biological activation of regenerative processes. Helps eliminate the consequences of trophic disorders and relieve inflammation. - Drug electrophoresis
. Allows you to restore tissue nutrition and relieve inflammation - the effect of the procedure depends on the medications used. - Medicinal phonophoresis
. Ensures deep penetration of the active ingredients of medications into soft tissues. - Massotherapy
. Helps relax muscles, eliminate tension and improve the supply of nutrients to the tissues of the spine. In the early stages, it eliminates the main symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis - a feeling of pain in the sternum - in a few sessions. - Acupuncture
. Stimulation of muscles and nerve endings helps relieve pain, restore sensitivity and eliminate swelling. - Ultrahigh frequency therapy
. Increases the permeability of capillary walls, improves blood flow and ensures the flow of protective cells into the site of inflammation. - Shock wave therapy
. It starts the processes of restoration of bone and cartilage tissue, prevents the deposition of calcium salts on the vertebral surfaces. - Balneotherapy
. As a rule, mud and ozokerite applications are used, less often paraffin. Radon and hydromassage baths are also recommended for patients. They help improve metabolism and restore sensitivity in affected tissues. - Amplipulse therapy
. It has a neurostimulating, analgesic and trophic effect, activates metabolic processes, and facilitates breathing. - Kinesiotherapy
(physical therapy, massage, traction therapy, kinesiotaping). Allows you to strengthen ligaments and skeletal muscles, restore mobility in the back and eliminate even persistent spasticity. Prevents the formation of osteophytes and narrowing of the canals in which the spinal roots are located.
In addition to physical therapy sessions, for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, patients may be recommended an orthopedic corset, which allows them to relieve the load on the spine.
Exercise therapy and massage
Therapeutic exercises and massage help strengthen the back muscles and relieve stress on the spine. With daily sessions, they help achieve stable drug-free remission, increase range of motion, and eliminate neurological manifestations of the disease. These treatment methods also prevent complications of osteochondrosis.
. For example, congestion in the lungs (with thoracic osteochondrosis it is difficult to breathe deeply), due to which patients are susceptible to pneumonia, as well as coronary heart disease.
Dosed physical activity helps relieve compression of the nerve roots, improve blood circulation and nutrition of the intervertebral discs. The optimal frequency and duration of gymnastic classes is determined by the exercise therapy instructor. As a rule, 3-4 exercises of 10-15 minutes a day are enough.
.
The exercises recommended for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis include the following:
- Stand straight, feet together, hands at your sides. As you exhale, raise your arms up and bend back, then inhale deeply. Lower your arms and lean forward, slightly arching your back in a dome-shaped manner (to do this, lower your head and shoulders as you exhale).
- Sit on a chair and, while inhaling, place your hands behind your head. Bend back and rest your shoulder blades on the back of the chair, exhaling.
- Get on all fours and arch your back. After maintaining the position for 3 seconds, bend your back with a crampon.
- Lying on the floor on your stomach, place your palms on the floor and, raising yourself on your arms, try to move your head as far back as possible, lifting your chest off the floor.
- Lie on your stomach and extend your arms at your sides. Perform the “yoke” exercise, trying to simultaneously raise your head and legs.
- Sit on the floor and stretch your legs in front of you. Reach the fingers of your right hand to the toe of your left foot and vice versa.
- Do a plank exercise (about 30 seconds).
- Perform hangs on the horizontal bar (or, in the absence of a horizontal bar, secure your fingers on the door frame and try to stretch your back as much as possible).
Bends to the side while raising your arm will also be helpful. All exercises should be performed 8 to 10 times
.
To treat thoracic osteochondrosis, various massage techniques are used, incl. acupressure and vacuum massage. For self-massage at home, patients are recommended the following movements:
- stroking the cervical-collar, scapular and axillary areas
; - squeezing with the thumb and index finger
(grabbing the skin and soft tissues); - trituration
; - kneading
(it should be done extremely carefully, it is advisable to entrust this technique to a specialist).
Massage should not be performed during exacerbations of the disease or during severe inflammation.
Drug treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
To treat the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- help relieve pain, calm inflammation and disperse swelling. They can be used both systemically (in the form of tablets, capsules and injections) and locally (in the form of ointments, gels, creams, compresses and solutions for medicinal electrophoresis). - Hormonal drugs
- to eliminate acute and chronic neurological pain. Used in cases where NSAIDs demonstrate insufficient effectiveness. - Muscle relaxants
are prescribed to reduce muscle tone and eliminate spasms of skeletal muscles. This helps alleviate pain and has a positive effect on tissue trophism. - Blood circulation correctors
- strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation in small capillaries that nourish the periosteum and other structural elements of the vertebral joints. Reduce discomfort and reduce the risk of complications. - Neuroprotectors
- to preserve and restore sensitivity during compression of nerve roots and relieve neurological symptoms. This group also includes cholinesterase inhibitors, which improve nerve impulse transmission and help restore normal muscle tone.
For structural restoration of tissues affected by the degenerative process, the following are used in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- chondroprotectors (Artracam)
are essential bioactive substances that trigger the processes of regeneration of cartilage and bone tissue. Serves to prevent the growth of osteophytes and narrowing of the spinal canal. They help a weakened body grow stable and resilient cartilage cells. Taking Artracam significantly improves the shock-absorbing properties of intervertebral discs, making them more elastic and resistant to damage; - vitamin complexes
- help normalize metabolic processes and prevent excess oxidation in tissues.
To relieve excruciating pain that interferes with the patient’s daily activities, the doctor may recommend a medical blockade with anesthetics. Diuretics are used to eliminate swelling and relieve compressed nerves and blood vessels.
Prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis
To prevent symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, you should:
- Take care to maintain healthy posture. This is facilitated by walking, swimming and therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscles of the back, chest, abs, and shoulder complex.
- When working sedentarily, properly arrange your workplace and perform physical warm-up whenever your back and neck begin to become stiff (ideally, bend to the sides, stretch, and rotate your shoulders every 2 hours).
- Avoid back injuries and promptly seek help from an orthopedic traumatologist, even in the case of a seemingly insignificant bruise. Other diseases of the musculoskeletal system should not be triggered, especially in the joints of the lower extremities.
- If possible, unload the spine during the day (to do this, just lie on the floor for 40 minutes).
- Protect yourself from hypothermia and stress.
- Take chondroprotectors to protect joints for at least 3 months a year. Regardless of the strength of the muscular corset, the human spine is anatomically not adapted to vertical loads, and therefore requires additional support.
- Adjust weight if it is overweight. In addition to maintaining a low-carb diet, you should eat a diet high in vitamins and minerals. In the spring-autumn period they can be taken in tablet form.
- Sports activities that involve jumping from heights or lifting heavy weights should be limited.
- It is advisable to sleep on a semi-rigid bed, and for prolonged sitting, choose hard furniture. This helps maintain muscle tone and relieve stress on the spine. If possible, you should purchase an orthopedic mattress and shoe insoles.
- Do not lift loads weighing more than 10 kg. The load should be distributed evenly, with muscle tension and without transferring to one side. If necessary, use a special sports corset. It is undesirable to hold loads in outstretched arms for a long time.
- Women should avoid wearing high-heeled shoes. The optimal heel height is 2-4 cm.
These recommendations will also be useful for those who are already sick - they will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the spine and will help to significantly slow down pathological changes.
And remember: the main thing in the prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis is consistent adherence to healthy habits.
Let chest pain never bother you!
Treatment of pain on the right side of the shoulder blade
Pain treatment must begin with diagnosis, since effective pain management is only possible if you know its cause. Symptomatic therapy based on the use of analgesics does not treat the cause of pain, but only temporarily alleviates the most severe symptom. After making an accurate diagnosis, it is possible to treat the underlying disease by influencing the factors that led to it.
This is also important because without knowing the cause of the pain, it is difficult to choose the right treatment. Thus, attempts to treat pain in the scapula on the right side with analgesics in acute cholecystitis can lead to complications in the form of gangrene of the gallbladder, its perforation and extensive peritonitis, with a high risk of death. Painkillers are strictly contraindicated for acute surgical diseases of the abdominal organs.
How to relieve pain under the right shoulder blade
If pain in the scapula area is associated with diseases of the spine, muscles or injury, then painkillers should be taken as first aid. For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs are most often used. They effectively fight pain of any origin, suppressing inflammatory reactions. However, uncontrolled and long-term use of NSAIDs increases the risk of side effects of this group of drugs, such as stomach ulcers, gastric bleeding or kidney failure. Therefore, without a doctor’s prescription, it is permissible to take analgesics for no more than 5 days, after which you must consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Local remedies in the form of distracting and analgesic ointments, gels and patches do not have such side effects, since this dosage form is limited to the area of application. They help especially well with myositis, muscle strain, attacks of neuralgia and other diseases with chronic pain syndrome. In diseases of the spine, pain can be relieved by rest, limiting physical activity and prohibiting heavy lifting.
It is strictly forbidden to use painkillers if you suspect acute cholecystitis, pancreatitis and other diseases of the abdominal organs that require emergency surgery. Taking painkillers in such patients can lead to temporary relief of symptoms and a false sense of improvement, which ultimately contributes to late presentation and serious condition of the patient due to extensive inflammation of the peritoneum or peritonitis.
If pain in the area of the shoulder blade on the right occurs against the background of severe abdominal pain, accompanied by fever, nausea, and vomiting, you must seek medical help as quickly as possible.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience