Bundle branch block is a disorder of intracardiac conduction, characterized by a slowdown or complete cessation of the conduction of excitation impulses along one or more branches of the His bundle. Bundle branch block can be detected only during instrumental examination or symptomatically manifested by rhythm disturbances, dizziness, and attacks of loss of consciousness. Bundle branch block is diagnosed using electrocardiography. Treatment of bundle branch block is reduced to eliminating the causes of conduction disturbances; In some cases, it may be necessary to install an artificial heart pacemaker.
1.General information
The His bundle, as well as blocks of its structural elements, are very often mentioned by cardiologists, especially when interpreting jagged ECG curves. Of course, it would take many years of study of anatomy, neurology, histology, electrochemistry and other complex sciences to thoroughly understand the structure of this intracardiac formation and the features of this or that blockade. However, it is possible and necessary to get a general idea.
If we use standard comparisons of the heart with a “motor” and a “pump,” then this motor is electric (at least with electrical control, since it is the electrical impulses that cause different groups of myocardial muscle fibers to contract in turn).
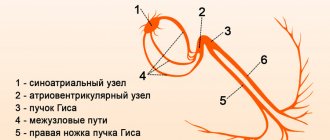
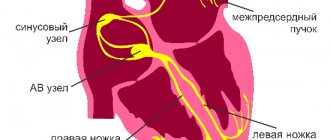
The clock frequency and sequence of phases (contraction-relaxation, depolarization-repolarization) in each cycle must be strictly observed, and any desynchronization is fraught with an emergency stop - and clinical death. Therefore, the critical pacemaker function, i.e. setting the step and rhythm is carried out with multi-stage security for uninterrupted operation. If the main “clock generator” (sinoatrial node, Kis-Flyak sinus node) fails, its role is taken over by the hierarchically located lower atrioventricular node (atrioventricular), which, in turn, gives rise to a switching “harness” consisting of the same atypical electrically conductive cells and branching into two parts.
In case of failure, even at this level, the individual terminal fibers of this cord (Purkinje fibers) try to take on the pacemaker role - in a word, the conduction system of the heart is built by evolution with the expectation of maximum automatism. And yet, mortality from sudden arrhythmias and fibrillations (chaotic, uncoordinated contractions of myocardial elements) remains very high.
The bundle of His is the same “multi-core cable” that comes out of the atrioventricular node, is located in the interventricular septum and conducts control electrical impulses to the ventricles of the myocardium.
One of its legs, the back one, continues the “main vein” and goes down; the other two legs, right and left, represent a paired branching. However, they are located and arranged much less symmetrically than other paired structures of the body (eyes, kidneys, lungs, etc.). Thus, the right bundle branch is a complete “power line” going to the muscle fibers of the right ventricle, and the left bundle is further divided into anterior and posterior branches. A blockade is a decrease or absence of electrical conductivity in one or more segments of this conductive network. This blockage can occur:
- in the anterior branch of the left bundle branch;
- in the posterior branch of the left bundle branch;
- in one of the above branches plus the right leg;
- in both branches of the left leg (complete blockade of the left bundle branch);
- in the right leg in the absence of other blockades;
- in all of the listed legs and branches simultaneously (atrioventricular block).
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of bundle branch block can be established on the basis of a general examination, palpation of the pulse, auscultation (listening) of the heart, general and biochemical blood and urine tests, and analysis of hormonal status - it can reveal causes of blockage not related to heart disease. To make a diagnosis, you will also need electrocardiography (ECG) data, which allows you to identify changes characteristic of each type of blockade. Also necessary are indicators of daily ECG monitoring (Holter monitoring) - a diagnostic procedure that involves the patient wearing a portable ECG device throughout the day. At the same time, a diary is kept in which all the patient’s actions are recorded (getting up, eating, physical activity, emotional anxiety, deterioration in health, going to bed, waking up at night). ECG and diary data are compared, thus identifying intermittent cardiac conduction disturbances associated with physical activity, food intake, stress, or night blockades. Data from an electrophysiological study (stimulation of the heart with small electrical impulses with simultaneous recording of an ECG) can be informative. The procedure is performed through the esophagus (the electrode is inserted through the esophagus; only the atria can be stimulated) or invasively (the electrode is inserted into the heart cavity by inserting a special catheter through a large blood vessel). It is used in cases where ECG results do not provide unambiguous information about the type of blockade, fainting, and also to assess the condition of the conduction system of the heart. Ultrasound examination of the heart can identify cardiac causes of blockade.
2. Reasons
Factors, conditions and causes of blockade of the legs or individual branches of the His bundle include:
- congenital anomalies (in particular, heart defects, abnormalities in the structure of cell membranes permeable to potassium and sodium ions, etc.);
- previous and/or chronic cardiovascular diseases (coronary heart disease, rheumatism, heart attack, arterial hypertension, myocarditis, etc.);
- degenerative-dystrophic processes in myocardial tissues;
- acute conditions that are currently developing (for example, heart attack, blockage of the pulmonary artery by a blood clot, etc.).
Visit our Cardiology page
COMPLETE BLOCK OF THE LEFT BAND BAND
All students know the signs of this blockade: the letter “M” in leads V5-V6. In general, it’s good, but this “M” has more precise characteristics; in particular, we are interested in the duration (width) of the ventricular QRS complex*. For complete blockade of LBP, the criteria are:
- QRS duration is 0.12 s. and more
- The presence in leads V5, V6, I, aVL of widened, deformed ventricular complexes with a split or wide apex (our favorite “M”).
- Presence in leads V5, V6, I, aVL discordant to QRS (now let's see how it is) ST segment displacement and negative or biphasic asymmetric T waves
- Presence of ST elevation in leads V1-V2
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
The possible clinical picture of the blockade varies over a wide range and is determined, firstly, by the localization of the conduction disorder, and secondly, by the degree of its reduction.
Thus, blockade of the right bundle branch is usually detected by chance, on a preventive or “commission” ECG, and is not accompanied by any symptoms. This phenomenon occurs both in absolutely healthy people and in well-trained athletes, but also in people who have suffered a serious cardiac disease in the past.
About the same can be said about partial blockades of one of the branches of the left bundle branch. However, a complete blockade of the left leg is much more often than a blockade of the right one, and is based on a serious pathology.
Finally, combined variants of blockade, especially complete atrioventricular block of the third degree (maximum severity) pose a real risk of developing life-threatening conditions - for example, ventricular and/or atrial fibrillation with sudden cardiac arrest and death within a few minutes in the absence of specialized emergency resuscitation.
The most common symptoms of clinically significant blockades are heart pain of varying nature and intensity, attacks of dizziness, arrhythmias, tachycardia, and syncope.
One of the diagnostic problems is that the presence of left bundle branch block makes it impossible to reliably diagnose (ascertain or exclude) myocardial infarction using an ECG. Blockade of the right bundle branch does not interfere with electrocardiographic diagnosis of a heart attack, but may itself be a symptom of a heart attack, or a symptom of thromboembolism, or simply an epiphenomenon that does not mean anything clinically.
In general, identifying any type of blockade in the structures of the His bundle automatically (regardless of the absence or presence of subjective complaints, their intensity, etc.) requires a more in-depth examination of the condition of the heart muscle and its functioning. For this purpose, various methodological modifications of ECG and EchoCG are prescribed, according to indications - MRI, MSCT, laboratory tests, etc.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Leg block
Leg block is a deviation in the transmission of impulses through one or more branches of the His bundle, which leads to disruption of intracardial conduction.
Basically, the presence of pathology can be detected using special tools. A prerequisite for such an examination is a feeling of movement of one’s own body in space or surrounding objects relative to one’s body, fainting.
In cardiology, branch block is not considered as an independent disease. Because pathology often accompanies other diseases. For example, with a large heart attack, the deviation may appear in 3% of cases.
What are the risk factors?
Leg block is more common in older people than in young people. For the second, the indicator is the presence of a deviation of less than 1%.
8
24/7
Therefore, one of the risk factors for the manifestation of the disease is age. Pathology occurs in 5% of people over 45 years of age. In addition, deviations in the transmission of impulses appear more often in representatives of the stronger sex than in the weaker sex.
Forms of bundle branch block in an adult
Branch blockade, depending on the degree of damage, is divided into two types: incomplete (slowing intracardial conduction) and complete.
In addition, there are forms of pathology depending on the location of the lesion: monofascicular, bifascicular and trifascicular.
Monofascicular blockades are problems when conducting a cardiac impulse through one element of the His bundle:
- right branch;
- left branch (anterior or posterior).
Bifascicular – damage due to the transmission of a cardiac impulse through two channels at once:
- the entire left side of the beam;
- right part and anterior branch;
- right and posterior branches.
Trifascicular - complete lack of functioning of the His bundle.
Causes
Deviations in impulse transmission can appear for a variety of reasons. Basically, the blockade of the right branch manifests itself due to a pathological condition in which the human right ventricle increases in size. Other reasons include:
- body overload;
- narrowing of the left atrioventricular orifice;
- ASD (pathological anastomosis between the right and left atrium);
- tricuspid insufficiency;
- hypertension;
- THEM.
Incomplete blockade of the left branch appears due to:
- closure of the aortic valve or narrowing (stenosis) of the aortic mouth, or a combination thereof;
- primary damage to the heart muscle, not associated with inflammatory manifestations;
- myocardial infarction;
- myocardial inflammation;
- non-inflammatory damage to the heart muscle in the form of disturbances in its metabolism.
Less common causes of heart block of the leg of His include: blockage of the pulmonary artery, abnormally high concentration of potassium in the blood, glycoside intoxication.
8
24/7
Damage to two legs at once manifests itself due to stenosis of the aortic mouth or congenital heart disease.
Since the blockade of the leg of His is accompanied by other diseases and does not exist as an independent one, there is another classification, which identifies eight groups of reasons due to which deviations in the transmission of impulses appear:
- Heart related diseases:
- acute or chronic myocardial damage resulting from a decrease or cessation of arterial blood supply to the heart muscle;
- myocardial necrosis due to insufficient oxygen;
- disturbances in the functioning of the heart with subsequent insufficient blood supply to the organs;
- changes in the structure of the heart muscles;
- heart defects;
- damage to the heart muscle;
- heart surgery or damage;
- dysfunction of the human immune system.
- Pharmacological effects - long-term use of drugs that lead to excessive stress on the heart. These include:
- diuretics (drugs that inhibit the reabsorption of water and salts in the kidney tubules and increase their excretion in the urine);
- a group of drugs used for various heart rhythm disorders;
- SG (a group of herbal medicines that have cardiotonic and antiarrhythmic effects in therapeutic doses and are used to treat heart failure).
- Water and electrolyte disturbances. Manifest due to changes in salt concentration in the body.
- Toxicological. Appear due to smoking or drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Nutrient imbalance.
- Disruptions in the hormonal system. Addison's disease, glandular hyperfunction, adrenal adenoma, elevated blood glucose levels, pancreatitis.
- Oxygen deficiency. Manifests due to inflammation of the bronchi or a disease of the bronchial tree of an inflammatory immune-allergic nature.
- Blockades of unknown origin. The reasons for its appearance are unknown.
Symptoms
In general, signs of bundle branch block do not appear.
Symptoms occur in severe cases and include: loss of consciousness, pain in the head, lack of oxygen, decreased activity, lack of energy.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pedicle block is carried out using data on:
- the patient’s medical history (the doctor carefully examines previous diseases and methods of their treatment);
- the person’s well-being (analysis of the symptoms the patient presented with);
- taking medications and duration of use;
- hereditary diseases.
After collecting this information, the patient is examined, in which generally accepted methods are used: measuring blood pressure and pulse; listening to the heart with a stethoscope or phonendoscope (helps to hear sounds generated in the smallest areas and localize them more accurately), sometimes direct auscultation is used; tapping the heart to determine its boundaries and the degree of damage.
If you suspect a blockade of the His leg, in order to quickly prescribe treatment, the patient needs to undergo tests, which include: a general and biochemical analysis of blood, urine, coprogram, as well as an analysis of the level of hormones in the body (so that they could become cause of impulse transmission disruption).
Diagnosis of branch block directly depends on ECG readings. They provide a complete picture of the work of the heart and its abnormalities. Electrocardiography allows you to determine the type of pathology and location.
8
24/7
Recently, long-term ECG recording has become frequently used. It uses a portable device that a person carries with him throughout the day. In addition, a strict record of all a person’s actions and well-being is kept. Then the doctor examines the cardiography images and the diary kept by the patient and determines the cause of the disturbance in impulse transmission. But, unfortunately, electrocardiography does not always provide accurate information about the presence of the disease.
Therefore, echocardiography is performed. This method makes sense if the blockade of the His leg was caused by cardiac diseases. Studies provide accurate data in the presence of coronary heart disease.
Sometimes there is a consultation with the local attending physician.
Treatment at different stages
Pharmacological therapy usually consists of drugs to strengthen the body (vitamins), as well as doctor’s prescriptions aimed at restricting food intake (excluding fried and excessively peppered foods from the diet) and predominant healthy foods (vegetables, fruits). Basically, the goal of treatment is to reduce the symptoms caused by the bundle branch block.
The second type of treatment is surgery. It is used when conventional therapy is ineffective, as well as when the patient’s condition worsens (more pronounced symptoms). During surgical treatment, an artificial pacemaker is introduced into the body, which regulates the contraction cycle and normalizes the heart rhythm.
Forecast
When the right branch is affected, the treatment and general condition of the patient are much more favorable than when the impulse in the left is disrupted. Complications in the second case can be expressed as acute disruption of the heart, or abnormalities in conduction.
The clinical picture of an impulse transmission disorder is usually quite stable, but when the symptoms disappear, the doctor’s main task is timely prevention of further manifestations.
For patients who do not have any symptoms, it is more beneficial than for people with dizziness and loss of consciousness. The latter, in turn, are more susceptible to unexpected death or the appearance of other diseases.
The consequences of blockade of the pedicles can be:
- tachydependent intraventricular blockades (their peculiarity is that they disappear when the heart rate normalizes and electrocardiography will not show anything);
- development of atrioventricular block;
- change in the shape, parameters and total mass of the heart towards an increase in these parameters;
- hypertonic disease;
- heart failure.
In addition, the harm from impaired impulse transmission consists in the difficulty of differentiating cardiac diseases using an ECG.
Disease prevention
The best treatment is prevention. It consists of:
- correct routine for;
- normal sleep;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- timely visit to the doctor;
- proper nutrition (the diet should contain vegetables and fruits);
- refusal of fast food;
- stress reduction;
- passing a mandatory examination;
Blockade of the legs of His requires the intervention of doctors and timely prevention, so promptly seeking help, as a rule, gives a positive prognosis.
8
24/7
4.Treatment
As shown above, the detection (even accidental) of blockade of the legs or branches of the His bundle requires clarification, but does not necessarily require treatment. In general, such blockades themselves are, strictly speaking, a symptom and not a disease. Therefore, further therapeutic strategy will be completely determined by the results of in-depth diagnostics. When a pathological process or dangerous anomaly is detected, the goal of treatment is to eliminate or relieve the symptoms of the underlying disease, and there are too many options for the therapeutic regimen to list them even briefly. In other, non-pathological cases, no special treatment is required or prescribed.
However, in conclusion, we emphasize once again: normally there should be no decreases, inhibitions, asynchronies, and even more so a complete absence of conduction in the His bundle, and if any blockade occurs, consultation with a cardiologist is strictly required in any case.
Treatment
There is no special course of therapy to treat the pathology. A patient with right bundle block does not require treatment. To a patient who has a single-fascicle or double-fascicular blockade, the cardiologist prescribes antioxidants, vitamins, sedative herbal medicines, antihypertensive drugs for arterial hypertension, ananginal drugs for coronary heart disease, antiplatelet agents to prevent the formation of blood clots in the heart and blood vessels. In severe cases, surgical intervention is required - installation of a pacemaker. With complete right blockade, when myocardial infarction develops, temporary cardiac pacing is required. In this procedure, an electrode is inserted into the right ventricle through a central vein. Permanent pacing is required with a three-fascicular block in the event of a Stokes attack (loss of consciousness).
Prevention of intraventricular block
There are no specific preventive measures! Prevention of intraventricular blockades is aimed at preventing pathologies that accompany the development of the blockade. It is very important to identify all the causes that provoke the development of the underlying disease.
To reduce the risk of any cardiovascular pathologies you should:
- stop smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages;
- avoid stressful situations;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- take medications strictly as recommended by your doctor.
If you have had a heart attack or have other pathologies, you should regularly visit a cardiologist. Make an appointment for preventive appointments at least once every 6 months! This will allow timely detection of the development of complications and elimination of them.
Classification of the disease
There are:
Nonspecific intraventricular block is quite common. It is characterized by the presence of several zones of impaired conductivity.
Also distinguished:
There are no specific signs of pathology. Diagnosed only with an ECG study.
You should pay attention to any symptom and promptly contact a specialist!
Usually the least dangerous is nonspecific blockade. However, even if it is detected, the patient must undergo a full examination.
This will eliminate the possibility of:
- myocarditis, cardiomyopathy
- necrosis.
Important! The disease is dangerous because it can be virtually asymptomatic.
Single-bundle blocks are not dangerous. Two-bundle blockades quickly turn into three-bundle blocks. As a result, impulses from the atrium to the ventricles are not transmitted. Such conditions are called complete blockades. With primary pathology, patients usually simply lose consciousness. Meanwhile, the result of complete blocking of signals can be cardiac arrest. Without prompt medical assistance, it will lead to death.
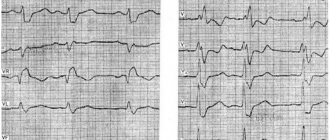
ECG 1
Explanations for ECG 1: There are all the signs of complete blockade of LBP: The presence in leads V5, V6, I, aVL of widened, deformed ventricular complexes with a wide apex (our beloved “M” is better visible in V4). QRS duration is more than 0.12 s. The presence in leads V5, V6, I, aVL of a QRS-discordant ST segment shift and negative or biphasic asymmetric T waves (T+/T-). We see that the ST segment is located under the isoline, that is, it is discordant (opposite) to the high, blockade R.
Causes of intraventricular block
The causes of intraventricular blockade at an early age include:
- myocarditis;
- heart tumors;
- cardiosclerosis;
- cardiomyopathy
- violations of the architectonics of the heart due to acquired or congenital defects.
In adulthood and old age, pathology is provoked by:
- atherosclerotic lesions of the arteries that supply the myocardium;
- arterial hypertension;
- congenital or acquired heart defects.
At any age, blockades can be provoked by:
- poisoning with alcohol and surrogates;
- sternum injuries;
- overdose of antiarrhythmic drugs, drugs with a high potassium content, psychotropic substances, etc.