Treatment of AV and SA blockades in Tver (including laser) is carried out by a cardiovascular surgeon, candidate of medical sciences - Ilya Borisovich Lukin.
To make an appointment with a vascular surgeon, as well as to find out the cost of the appointment, you can call:
- 8 (Research Institute “Phlebology”, Tver, 2nd Krasina St. 49)
- 8 (University Clinic, Tver, Peterburgskoye Highway, 115 building 2)
The human heart consists of 2 atria and 2 ventricles (right and left). First, the atria contract and push blood into the ventricles, then the ventricles contract and the blood spreads throughout the body. For this to happen synchronously at regular intervals, there is a conduction system of the heart. The sinus node (SA, SA, sinoatrial, sinoauricular, sinoatrial) generates electrical impulses at a frequency of 60-80 per minute. Electrical impulses are transmitted through nerve fibers like wires to the atria and they contract. At the same time, the impulse is transmitted to the atrioventricular node (AV, AV, atrioventricular), then along the nerve fibers (bundle branches) the impulse passes to the ventricles, as a result of which they contract.
Reasons for the blockade
The human heart beats as a result of electrical impulses that regulate the sequence and frequency of contractions of the chambers of the heart.
Electrical impulses are generated in the sinus node, a structure located in the upper chamber of the heart - the atrium. From the sinus node, impulses propagate down to the ventricles at a certain frequency, thereby setting the heart rate. If, for some reason, the impulses slow down or are blocked, a disease develops - heart block (atrioventricular block).
Heart block is a disease in which a person’s heart contracts with an abnormal frequency and rhythm due to disruption of the conduction system of the heart. As a result of blockades, arrhythmia or other, more serious diseases may develop.
Symptoms at stages 2-3
Phases 2-3 are accompanied by a number of gross changes in condition:
- Chest pain. Pressing or burning. Unlike angina, the episodes are so small that the patient does not have time to pay attention to them. Discomfort is described as a momentary unpleasant sensation that immediately disappears. Duration - from a couple of seconds to several minutes.
- Dyspnea. Against the background of minimal physical activity or at rest. It is extremely difficult to tolerate, the patient is unable to work or perform daily duties. Even going to the store becomes akin to achievement. It is difficult to correct the condition. Usually such patients are given a disability group.
- Heaviness in the chest. It feels like a huge stone has been sewn up.
- Tachycardia and the reverse process. Increase and decrease in heart rate. One may be replaced by another. In parallel, other arrhythmias occur. Ventricular fibrillation. The number of movements reaches 300-400, but they are visible only on electrocardiography.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle.
- Increased sweating, especially at night.
- Paleness of the skin.
- Fainting may occur more than once during the same day.
- Headache.
- Vertigo, inability to navigate in space.
- Weakness, drowsiness. Long-term decline in labor activity.
- Apathy, unwillingness to do anything.
Sinoatrial blockade of the 2nd degree is accompanied by all the described manifestations, but treatment still has promise.
Classification
There are several types of heart block. They are divided based on the location of the area where the conduction function of the heart is difficult or completely blocked. Due to the development of the disease in different parts of the heart, each blockade has its own characteristic features.
Photo: psodaz / freepik.com
Sinoatrial blockade
Sinoatrial block or sick sinus syndrome (SSNS) develops as a result of complete or partial dysfunction of the sinus node. This can occur both as a result of physiological disorders and due to other factors not related to the state of the body (extracardiac factors).
The main cause of SSSS can be considered fibrosis (development of connective tissue and its scarring) of the sinus node tissue. This pathology can be caused by inflammatory processes, increased tone of the vagal nerve, or taking medications.
SSSU can manifest itself:
- shortness of breath;
- general weakness of the body;
- pain in the heart;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- low blood pressure;
- arrhythmia.
Interatrial block
Interatrial block develops when the propagation of electrical impulses is disrupted, both within and between the atria. The propagation of excitation occurs along special conduction pathways, which are circular and longitudinal muscle bundles, usually not described as part of the specialized conduction system of the heart.
One of the mechanisms of changes in the electrophysiological properties of the atrial myocardium, leading to a slowdown in conduction, is the development of fibrosis. There is a violation of the integrity of myocardial cells with the deposition of collagen in the intercellular space, which prevents the movement of impulses throughout the heart.
Accompanied by general weakness, pain in the chest and abnormal heart rate.
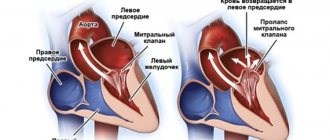
Atrioventricular block
Atrioventricular (AV) block is a partial or complete interruption of the transmission of impulses from the atria to the ventricles, leading to disturbances in heart rate and blood flow rate.
There are 3 types of atrioventricular block:
- 1st degree - due to a slow transition of impulses from the atria to the ventricles;
- 2nd degree - characterized by blocking of some impulses;
- 3rd degree - (complete atrioventricular block), associated with blocking of all impulses coming from the atria to the ventricles.
It occurs due to damage to the most sensitive area of the conduction system of the heart - the atrioventricular junction.
Intraventricular block
Intraventricular block occurs when the His bundle, the conducting region of the heart located in the region of the ventricles, is disrupted. The bundle of His consists of 3 branches: the left and right anterior branches and the posterior branch. The posterior branch is also divided into right and left.
Figure 1. Differences in ECG readings with normal rhythm and with blockades.
Intraventricular block is classified based on damage to 1 of 3 branches:
- Blocking of the anterior right branch - the innervation of the right ventricle is disrupted;
- Blocking of the anterior left branch - in case of disruption of the innervation of the left ventricle;
- Blocking of the posterior branch - the work of the His bundle is disrupted to the greatest extent, since along this branch impulses go from the atria to the ventricles, and are subsequently divided into right and left;
- Three-bundle block is associated with disruption of the conduction of the entire His bundle.
Manifestations and diagnostic methods of SA blockade
The symptoms of sinoatrial block are determined by the severity of disorders in the conductive fibers of the heart. In the first degree, there are no signs of blockade, as well as the patient’s complaints. With bradycardia, the body “gets used” to a rare pulse, so most patients do not experience any worries.
SA blockades of 2 and 3 degrees are accompanied by tinnitus, dizziness, discomfort in the chest, and shortness of breath. Against the background of a slower rhythm, general weakness is possible. If SA blockade has developed due to a structural change in the heart muscle (cardiosclerosis, inflammation), then an increase in heart failure is possible with the appearance of edema, cyanosis of the skin, shortness of breath, decreased performance, and enlarged liver.
In a child, the signs of SA blockade differ little from those in adults. Parents often pay attention to decreased performance and fatigue, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, and fainting in children. This is the reason to contact a cardiologist.
If the interval between heart contractions is too long, then Morgagni-Adams-Stokes (MAS) paroxysms may occur, when the flow of arterial blood to the brain is sharply reduced. This phenomenon is accompanied by dizziness, loss of consciousness, noise, ringing in the ears, possible convulsive muscle contractions, involuntary emptying of the bladder and rectum as a result of severe brain hypoxia.
syncope with MAS syndrome due to sinus node blockade
Suspicion of the presence of a blockade in the heart arises already during auscultation, during which the cardiologist records bradycardia or loss of the next contraction . To confirm the diagnosis of sinoauricular block, the main methods are electrocardiography and 24-hour monitoring.
Holter monitoring can be performed for 72 hours. Long-term ECG monitoring is important in those patients in whom, if the presence of arrhythmia is suspected, no changes could be detected in a regular cardiogram. During the study, a transient blockade, an episode of SA blockade at night or during physical activity may be recorded.
Children also undergo Holter monitoring. The detection of pauses lasting more than 3 seconds and bradycardia of less than 40 beats per minute is considered diagnostically significant.
A test with atropine is indicative. The introduction of this substance to a healthy person will cause an increase in the frequency of heart contractions, and with SA blockade, the pulse will first double, and then just as rapidly decrease - a blockade will occur.
To exclude other cardiac pathologies or search for the cause of the blockage, an ultrasound of the heart can be performed, which will show the defect, structural changes in the myocardium, scarring area, etc.
Degrees and their symptoms
Heart blocks are classified not only by the place of its development, but also by the degree of severity, which reflects the danger of the disease to human health and approaches to treating a particular stage of heart block. There are three main stages of heart block
First degree heart block
The first degree is the mildest form of manifestation. There is a delay of a fraction of a second in the time required for electrical impulses to travel through the atrioventricular junction. Complete blocking does not occur and the impulses reach the desired point.
First-degree heart block usually does not cause any noticeable symptoms and is diagnosed by examining other medical conditions in the person. Treatment may be limited to eliminating risk factors that affect heart health.
Second degree heart block
As the second degree develops, there is a series of increasing delays in the time it takes for the atrioventricular junction to conduct an impulse into the ventricles until the heart beat is missed. Partial blocking of impulses is possible.
The second degree is divided into 2 types:
- The first type of Mobitz. This is a less serious type of second-degree heart block. Characterized by slow conduction of impulses. May cause symptoms of mild dizziness and weakness. Usually does not require treatment.
- Mobitz's second type. Electrical signals reach the ventricles slowly or may be completely blocked. This type of heart block can often progress to third degree heart block. May cause symptoms of dizziness and fainting, accompanied by bradycardia. Requires medical consultation and full treatment.
Third degree heart block
Third degree heart block is the most dangerous degree for a person’s health and life and requires immediate medical attention. It is characterized by complete blocking of the transmission of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles due to the lack of communication between the atrioventricular junction and the ventricles.
In this case, the ventricles can partially take over the function of a pacemaker, but they are not able to ensure full functioning of the heart.
Third degree blocks can be congenital or acquired as a result of other heart diseases or injuries.
Symptoms include:
- shortness of breath;
- weakness;
- fainting conditions;
- chest pain;
- pale skin, spots;
- arrhythmia.
Many cases of third-degree congenital heart block are diagnosed during pregnancy because ultrasound scans can often determine whether the baby has bradycardia.
Important! If the diagnosis is missed during pregnancy, symptoms of third-degree congenital heart block usually do not appear until the baby is older and his heart is more developed.
What are the dangers of heart blocks?
During blockades, bradycardia (slow pulse) develops, because not every impulse passes to the heart, the patient may feel interruptions in the functioning of the heart, weakness, etc. For more information about the symptoms of bradycardia, see “Bradycardia: Symptoms and Treatment.”
The most dangerous condition is when a complete block occurs, in which case the heart stops for a few seconds, this may be enough for the patient to lose consciousness. Usually, the heart “starts” on its own, but sometimes this may not happen. Imagine a light bulb with bad wiring and a rusty socket: You turn it on, and it begins to short out - it’s on, then it’s off, it blinks, then it blinks, i.e. works intermittently. Knock - it will light up, then go out again. But at one moment it can go out forever. It’s the same with the heart: the impulse sometimes passes, sometimes it doesn’t, sometimes the heart works normally, sometimes intermittently, sometimes weakness, sometimes fainting, but at one moment it may stop and not start.
You can always buy a new light bulb. Unfortunately, this does not work with the heart; its failure inevitably leads to the death of the patient.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of heart block begins with an interview and physical examination of the patient. Medical history and family history are studied. The patient's symptoms and lifestyle are examined. Medicines that the patient may have taken are checked.
Testing is carried out using a Holter or event monitor - devices that track heart rhythm over a certain period of time.
Figure 2. Signs of heart block.
A Holter monitor is used to study the heart over 24 or 48 hours. Event monitor - for a month or more. They allow changes in heart rate to be recorded even if they do not occur frequently or predictably.
An implantable loop recorder, a small heartbeat recorder that is placed under the skin over the heart, may be used. Capable of analyzing heart function for up to 2 years.
Basic methods of studying the functioning of the heart are used, such as electrocardiography (ECG) and electrophysiological studies. To diagnose heart diseases of a child in the womb, the ultrasound method is used.
Holter monitor. Photo: yupachingping / freepik.com
Treatment
When diagnosing first-degree heart block and first-degree Mobitz block, treatment as such is not necessary. These types of blockades do not pose any serious danger. The doctor may advise you to lead a healthy and active lifestyle, with moderate physical activity, and give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol.
When diagnosing Mobitz block of the second type and block of the 3rd degree, the patient needs medical attention, since the lack of treatment can lead to death.
The main treatment method for these types of blockades is the installation of a pacemaker. This device is surgically placed near the heart and monitors the correct frequency and rate of generation of electrical impulses.
Pacemaker. Photo: PantherMediaSeller / Depositphotos
Advantages of the clinic
Our clinic employs highly qualified specialists. You can use the help of not only cardiologists, but also therapists and other doctors. They will help diagnose and prescribe effective treatment for the underlying and concomitant pathology. All professionals comply with medical ethics and guarantee high-quality examination and prescription of adequate therapy. Team interaction of staff makes it possible to accompany the patient at all stages of examination and treatment.
Particular attention is paid to a comfortable environment, openness and warmth of the staff, as well as a loyal pricing policy. Anyone can contact our clinic (including patients with limited financial resources). In our clinic you do not spend money on treatment, you invest it in your health.
Contact us!
Our medical center provides the widest range of services. You can always contact us regarding the treatment of diseases in cardiology. We are ready to provide you with ] treatment of angina[/anchor] and treatment of vasospastic angina.
Forecast
Heart block can be congenital) but most often develops after birth. In general, the risk of acquired heart block increases with age, as does the incidence of cardiovascular disease.
First-degree heart block is common in well-trained athletes, adolescents, young adults, and individuals with a highly active vagus nerve. People with various heart conditions, including coronary artery disease, rheumatic heart disease, sarcoidosis, or other structural heart disease, are also at risk of developing first-degree heart block.
Without proper treatment, second-degree Mobitz blocks and third-degree blocks can be accompanied by symptoms that significantly impair the quality of life: constant fatigue, chest pain, severe dizziness and fainting. Without treatment, complete cardiac arrest can result.
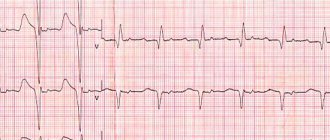
Signs on ECG
At the first stage there are no changes. Problems cannot be detected. Or the features are so nonspecific that they do not give an idea of the nature of the process.
Grade 2 reveals the most pronounced changes on the ECG:
- Passing several pulses in a row at once. Objectively manifested by the complete absence of PQRST complexes on the graph. This is type 1.
For the 2nd, alternating loss of contractions is typical. Yes, no, and so on. Inadequate movements may occur and appear as minor waves.
- PP extension.
- Acceleration or deceleration of the intensity of work of a muscle organ.
SA blockade on the ECG has features of tachycardia or bradycardia and uneven contractile activity.
The third stage is accompanied by impaired functional activity. The graph degenerates almost into a straight line.