A heart attack can be detrimental to a person’s life, and after that the body needs rehabilitation.
An attack involves a rapid blockage of the blood supply to the heart through a spasm or thrombus. Due to the lack of normal blood circulation, the heart is seriously damaged, leading to serious health problems (disease of the cardiovascular system and internal organs, cardiogenic shock).
No one knows how long people can live after a heart attack. Everything depends on the importance of providing first aid, suffering and subsequent illnesses of people and the correctness of treatment. Renewal after a heart attack brings about drastic changes in eating habits and way of living.
What is a heart attack?
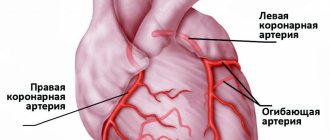
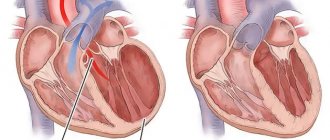
Blood enters the heart through the coronary arteries.
If they become clogged, the blood flow stops, a section of the heart muscle stops receiving oxygen and dies—a heart attack develops. In this case, the person experiences characteristic symptoms. Chest pain, cold sweat, shortness of breath, and fear of death appear. According to WHO, 17.5 million people die from cardiovascular diseases every year worldwide. These diseases also include heart attack, which is a form of coronary artery disease.
According to WHO, 80% of heart attacks are preventable.
In coronary artery disease, the blood supply to the heart muscle is disrupted due to blockage of the coronary arteries. The disturbance can be relative (partial blood flow is preserved) or absolute (blood supply stops). Coronary arteries become blocked due to the formation of plaque made from fat, cholesterol and other substances.
Myocardial infarction. What it is?
The myocardium is the heart muscle. Blood flows to it through arteries called coronary arteries. If any of these arteries is blocked by a blood clot, then the area of the heart that it supplies is left without blood supply, and therefore without oxygen. “On a starvation diet,” myocardial cells can survive for 20-30 minutes at best. Then they die - this is a heart attack, an area of necrosis in the tissue of the heart. A scar remains on the affected area.
Why does this happen?
The main cause of the disease is atherosclerosis, which almost all of us have. In addition, we will name the circumstances of life (both those that depend on us and those that do not) in which the likelihood of getting sick is highest: male gender; for women, the dangerous age comes after 50 years; heredity (IHD) heart attack, cerebral stroke, in at least one of the direct relatives: parents, grandparents, brother, sister, especially if the disease began before the age of 55); elevated blood cholesterol (more than 5 mmol/l or more than 200 mg/dl); smoking (one of the most significant risk factors!); excess body weight and sedentary lifestyle; increased blood pressure (more than 140/90 mm Hg at any age); diabetes mellitus.
The presence of at least one of these factors actually increases the risk of “acquaintance” with myocardial infarction. Moreover, the addition of each new risk factor increases the likelihood of getting sick exponentially. They also say that baldness in men is a kind of harbinger of a heart attack, since one of the factors in the appearance of baldness is an increased level of androgens, and in the case of hormonal fluctuations, the body reacts to changes in hormone levels by raising blood pressure pressure and increased cholesterol levels in the blood.
What happens?
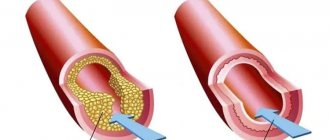
Atherosclerosis is a process in which certain fats (cholesterol and other lipids) are deposited in the walls of large arteries if they are found in excess in the blood. Those places on the vascular wall where there are especially many lipid accumulations are called atherosclerotic plaques.
Plaque is the most vulnerable place in the vascular wall. Especially if it is “young” and calcium has not yet had time to be deposited in it. At the most unexpected moment, the wall of the plaque, and therefore the inner lining of the artery of the heart, can crack and tear. This is an alarm signal for the body. He tries to heal the crack with a blood clot. Therefore, blood immediately begins to clot at the damaged area. The formation of a blood clot resembles a snowball rolling down a mountain. If nothing interferes with it, the thrombus grows very quickly until it closes the entire lumen of the artery. Then the blood flow through it stops, cell death begins and myocardial infarction develops. The larger the artery that the thrombus has closed, the more myocardial cells will die.
The integrity of the atherosclerotic plaque can be disrupted by rapid heartbeat and increased blood pressure. A heart attack can begin during severe physical or emotional stress, but often it develops for no apparent reason, as if out of nowhere. Perhaps even in a dream. But his most “favorite” time is early morning. Depending on the size, infarctions are divided into large-focal, in which necrosis spreads throughout the entire thickness of the heart muscle, and small-focal. Large focal infarctions of the anterior wall of the myocardium are more dangerous. With an infarction of the posterior or lateral walls, especially a small-focal one (not of the full thickness), its consequences are not so traumatic. The scar on the heart muscle remains for life. It cannot resolve, and the heart always “remembers” the heart attack.
Symptoms and diagnosis of heart attack
The first sign to suspect a heart attack is usually severe pain behind the sternum, that is, in the middle of the chest. Usually at rest; presses, burns, squeezes, can radiate to the arm, shoulder, back, jaw, neck. With (angina pectoris, similar pain occurs during exercise, and with a heart attack it is more severe and often begins at rest and does not go away after taking 3 nitroglycerin tablets one after another (1 tablet under the tongue every 5 minutes). If these signs are present, call immediately "Ambulance". The ability to endure in this case is a dangerous enemy. Sometimes the disease manifests itself with vomiting or discomfort in the stomach, interruptions in the heart or difficulty breathing, loss of consciousness or... nothing.
Yes, this also happens: a person suffers a heart attack without even noticing it. The so-called painless form of myocardial infarction is more often observed in people with diabetes. The changes that occur during a heart attack are clearly visible on the electrocardiogram. To clarify the area and extent of the lesion, an ultrasound of the heart, echocardiography, which makes it possible to see structural changes, may be prescribed, the doctor may recommend scintigraphy.
Treatment
To play it safe, at the slightest suspicion of a heart attack, doctors send the person to the intensive care unit of the hospital. And the sooner the better. After all, only during the first few hours, by introducing special drugs, can a “fresh” blood clot be dissolved and blood flow in the coronary artery restored. The formation of new blood clots should then be prevented. For this purpose, medications that slow down blood clotting are used. One of the most reliable remedies is acetylsalicylic acid, that is, regular aspirin. It reduces the number of complications and prolongs the life of people who have had a heart attack. Beta blockers are often used in treatment. These drugs reduce the myocardium's need for oxygen, which means they save heart muscle cells from death and reduce the size of necrosis. At the same time, they make the heart work more economically, which is very important during a heart attack. In recent years, not only medications have been used to treat heart attack. Angioplasty is indicated when drug therapy is ineffective. In another case, a cardiac surgeon may suggest surgery (coronary artery bypass grafting). In the first days, strict bed rest is required. At this time, the damaged heart may not withstand even minimal stress. Previously, a person who had a heart attack did not get out of bed for several weeks. Today, the period of bed rest has been significantly reduced. But all the same, at least three days after a heart attack you need to lie in bed under the supervision of doctors. Then you are allowed to sit, later get up, walk... Recovery begins, adaptation to a new, “post-heart attack” life.
Rehabilitation; after a heart attack
Is it possible to return to normal life after a heart attack? It is difficult to say firmly “yes” or “no”. After all, everyone has their own: one works as a loader, and the other spends his days at a desk. It will not be easy for the first to engage in usual activities, and for the second there will be little to interfere. In addition, complications, and the heart attacks themselves, are different for everyone. Recovery after a heart attack takes several months. After all, the disease is not a joke, it requires you to reconsider your lifestyle and change something in it. Rehabilitation begins in the hospital, where the intensity of physical exercise is gradually increased along with medications and physiotherapeutic procedures. (Particular attention to the word “gradually”). Do not force things under any circumstances. Exercise therapy, walking first on a flat surface, then on stairs... By the way, stairs are a good test of readiness for an active life. If the patient can climb to the fourth floor at an average pace without feeling chest pain or shortness of breath, then recovery is successful. For a more accurate assessment of the condition, a dosed load test is often used. It is usually performed on a special bicycle - a bicycle ergometer or on a treadmill.
How long should I take the medicine? There is only one answer: all your life! Even if you feel great. That’s why it’s wonderful, because medications taken constantly help the heart.
Is it possible to have sex after a heart attack? Feel free to ask your doctor this question. Everything will depend on how you tolerate physical activity (and sexual intercourse is a load, and a considerable one). But there are also rules that are common to everyone, which must be remembered so that sexual contact ends in pleasure and not in a new heart attack. Firstly, it should take place with a familiar partner, secondly, in a familiar environment, and thirdly, when choosing a position for sexual intercourse, you should prefer one in which the load is minimal, for example, on your side.
Prevention
There is no escape from some risk factors (gender and heredity). But everyone else is quite amenable to our efforts! Maintain normal blood pressure, and also monitor the weather - for example, heat and geomagnetic storms are dangerous for people with high blood pressure. Normalize your blood sugar levels.
Move more! It is not at all necessary to run, it is enough to walk in the fresh air at least 5-6 kilometers a day. It is very important to quit smoking - this is one of the most “aggressive” risk factors. Try to lose excess weight. What should be a normal weight? Let's do the math: divide your weight in kilograms by your height in meters squared. The resulting number is called the body mass index. We must strive to ensure that it does not exceed 26. The diet should contain a minimum content of animal fats and cholesterol. More vegetables and fruits. Instead of fatty pork, use white poultry, replace butter with sunflower oil, and lard with fish. This diet allows you to reduce not only your cholesterol levels, but also your costs.
Causes
Myocardial infarction occurs when blood flow in one of the coronary arteries is disrupted. The reason for this phenomenon is atherosclerosis. With it, the arteries narrow because deposits (plaques) of cholesterol, a fat that is part of cell membranes and is involved in the synthesis of steroid hormones in the body, accumulate on their walls. Such plaques can form blood clots that completely block blood flow. In this case, the heart tissue will be completely deprived of oxygen and nutrients.
Impairment of blood flow in the coronary artery may occur due to spasm. It can be triggered by drug use or smoking. It is extremely rare that a heart attack develops as a complication of arteritis (inflammation of the artery walls), infective endocarditis (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart walls due to infection), trauma or abnormalities of the coronary artery, and other diseases.
Risk factors
The following factors increase the risk of myocardial infarction (Fig. 1):
- high levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, lipids, low-density lipoproteins in the blood;
- smoking (including long-term exposure to passive smoking);
- excess weight;
- low physical activity;
- prolonged exposure to stress;
- hypertonic disease;
- diabetes;
- age factor. The risk of heart attack is considered increased after age 55, but for men it can be high after age 45;
- family history. A risk factor is considered to be coronary disease or heart attacks at a relatively early age in relatives;
- male gender. According to statistics, heart attacks develop approximately five times more often in men.
Figure 1. Risk factors for heart attack.
Source: CDC gov A number of these factors can be influenced by making lifestyle changes, strengthening the heart and reducing the likelihood of a heart attack.
Important! In clinical practice, the SCORE scale is also used to calculate the risk of cardiovascular pathologies. To quickly calculate your risk of a heart attack or stroke in 10 years, use the calculator.
Classification
There are several classifications of heart attacks:
- by localization of tissue death. Possible infarction of the left or right ventricle, interventricular septum, apex of the heart, or combined localization;
- by the width of the lesion: extensive (large focal) or small focal. This parameter is assessed by ECG;
- by depth: if all layers of the heart are covered, the infarction is transmural. Subendocardial (affects the inner layer of the lining of the heart walls), subepicardial (affects the outer layer of the lining of the heart walls), intramural infarction (small-focal lesions) can also develop;
- according to the course: monocyclic (the attack develops quickly), protracted, recurrent (a new focus of necrosis develops 3-7 days after the first attack), repeated (a heart attack occurs again within up to 1 month).
When diagnosing, the location of necrosis is assessed (localization, depth and width of the focus of tissue necrosis), as well as the etiology and accompanying circumstances. A heart attack can be spontaneous or caused by ischemia, associated with oxygen deprivation, coronary intervention, or other reasons.
Stages
Symptoms associated with a heart attack may appear in the weeks, days, or hours before a heart attack. Usually this is pain, a burning sensation or squeezing during physical activity, weakness, and mild malaise. Such symptoms appear in the prodromal period preceding the attack. If you consult a doctor at this stage, you can prevent the development of a heart attack (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Stages of infarction development. Source: Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. / and Journal of the American College of Cardiology
There are four main stages of a heart attack:
- acute. It continues from the development of ischemia until the necrosis of the heart tissue area. The average duration is from 20 minutes to 2 hours. Normal blood flow must be restored as quickly as possible. To do this, you need to remove the blood clot using thrombolytic therapy. If you suspect a heart attack, you should immediately call an ambulance so that doctors can begin such treatment;
- spicy. It begins when tissue necrosis has already occurred. At this stage, enzymatic melting of necrotic tissue occurs, which can last from 2 to 14 days;
- subacute A scar begins to form at the site of necrosis. It takes 4 to 8 weeks to form;
- post-infarction. At this stage, the scar matures and adaptation of the heart occurs.
What physical activities are necessary during rehabilitation?
Physical instructions after a heart attack must be calm and treated with a gentle doctor. To speed up your renewal, you need to get used to eating, and if you have problems with your diet, follow it so that there is no streak-like or sudden weight loss.
Doctors recommend regularly exercising the right for physical activity: adults must engage in moderate-intensity aerobic activities of no less than 150 minutes (2 years 30 hours) of shave. Blames arise when the doctor selects individual training due to the presence of concomitant illnesses.
Why is a heart attack dangerous? Complications
During a heart attack, heart tissue is damaged and the following complications may develop:
- arrhythmia. The most common complication can develop immediately after a heart attack. Heart rhythm disturbances can lead to ventricular fibrillation, in which they contract uncoordinated, to ventricular tachycardia, in which the heart rate increases, etc.;
- heart failure. If a large volume of tissue is damaged, the heart muscle cannot pump blood in sufficient volume. The condition may be temporary. If the damage to the heart is irreversible, chronic heart failure develops;
- sudden cardiac arrest. Due to arrhythmia, the heart muscle suddenly stops. Without emergency help, this can lead to death.
Do you need to follow the eating regimen after a heart attack?
Eating after a heart attack tends to improve, and the new diet regime is expected to be balanced and healthy. Children should achieve a low-fat, high-cellulose diet that includes whole grains and at least five servings of fruits and vegetables per day. It is also necessary to be careful or to keep the consumption of alcoholic beverages to a minimum.
It is allowed to eat low-fat varieties of meat and fish, vegetables and milk soups, as well as foods rich in potassium (spinach, banana, potatoes, dried apricots, prunes). You cannot eat herbs that promote fermentation processes in the intestinal tract, or drink drinks that stimulate the nervous system (kava, mitsa tea, energy drinks, licorice and carbonated water). It’s best to cook it steamed or in the oven. Also, if possible, turn off the excess salt and turmeric.
Symptoms
General signs of a heart attack are considered (Fig. 3):
- pain, feeling of squeezing, high pressure, heaviness, burning in the chest. These sensations may spread to the arms, the area of the back between the shoulder blades, the jaw or neck;
- fatigue, weakness, dizziness.
Figure 3. Heart attack symptoms.
Source: MedPortal Symptoms of a heart attack are not always the same. Some people experience severe pain, for others it may be mild, and for others it is almost unnoticeable. Pain can spread to the arms, neck and throat, and the area between the shoulder blades. During a heart attack, pain can increase with any, even minor physical activity: when trying to stand up or change position, when walking. Often a heart attack is accompanied by fear, a feeling of intense melancholy, and doom. Because of this, behavior can become anxious and agitated.
The heart rate during a heart attack can increase to 90-100 beats per minute, but blood pressure does not increase or increases slightly. The skin looks pale, becomes damp to the touch, and the nails and nasolabial triangle may turn blue. In some cases, nausea and vomiting may occur.
Men and women experience heart attacks differently. In women, shortness of breath, nausea or vomiting, and pain in the back and jaw are often added to the standard symptoms (Fig. 4).
Figure 4. Symptoms of heart attack in men and women. Source: MedPortal
A few weeks, days or hours before a heart attack, in some cases, warning signs or precursors appear. This is pain or a feeling of compression, pressure in the chest that occurs during physical activity and goes away at rest. You may also feel weak and short of breath.
How to recognize a heart attack?
Symptoms of a heart attack can occur in varying degrees of intensity and speed (either very or quickly) and include:
- pain in the chest area - people may feel that the chest is being pressed or pressed by an important object, the pain syndrome can spread from the breasts to the cleft, neck, arms and back area;
- butt;
- confused, due to other weaknesses, confused;
- Don’t go overboard with fear and anxiety.
Not all people experience severe pain in the chest during a myocardial infarction (heart attack). Often the pain in the breasts is weak or dead and is gently accepted for the unetched schunu. To identify the presence of an attack, it is the combination of symptoms that is important, not the severity or pain in the chest.
The cause of the heart attack is determined by a cardiologist after examining the patient. Among them there are especially bad symptoms and chronic illnesses.
First aid for heart attack
If symptoms of a heart attack appear, you need to act immediately (video 1):
- call emergency medical assistance;
- Chew and swallow 250 mg of acetylsalicylic acid and take nitroglycerin (spray one dose of spray into the mouth or place one tablet under the tongue). It is better to check with your doctor, therapist or cardiologist in advance whether you can take nitroglycerin (it sharply lowers blood pressure, so it is important to control the dose of the medication);
- provide access to fresh air: open a window or window;
- sit or lie down, take a comfortable position, relax, try not to worry, so as not to increase the load on the heart;
- stay warm (wear warm clothes or cover yourself with a blanket if necessary).
Video 1. How to recognize myocardial infarction and what to do before the ambulance arrives. Boris Todurov. Cardiac surgeon, director of the Heart Institute (Ukraine)
Important! Even if there is doubt that it is a heart attack, emergency medical help should be called immediately. A heart attack can develop very quickly, and you need to act without delay.
If another person has a heart attack, you should:
- call emergency medical assistance;
- check breathing and pulse;
- If a pulse cannot be felt or there is no breathing, perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
During cardiopulmonary resuscitation, the airway is checked and cleared, if necessary, artificial respiration is performed and chest compressions are performed.
Important! You can start the heart if it is not beating in a public place (an airport or a shopping mall) using an external defibrillator. Look for a box on the wall with the inscription “AED”, voice instructions will help you attach the electrodes correctly, the device itself will determine the need for defibrillation and allow you to press the button to start the electrical impulse.
Diagnostics
In case of a heart attack, the diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, the results of electrocardiography and laboratory diagnostics. A heart attack develops quickly, and therefore, if its symptoms appear, you should immediately call an ambulance. Later, when the condition is stabilized, you will need to undergo extensive diagnostics with a cardiologist.
Diagnostic signs of a heart attack are:
- long-lasting chest pain that lasts more than 30 minutes (can be felt as a burning sensation, squeezing);
- leukocytosis and increased ESR in the results of a clinical blood test;
- increased levels of sialic acids, fibrinogen and the presence of C-reactive protein in a biochemical blood test;
- the presence in the blood of markers of ischemic necrosis, cardiac muscle (troponin).
Differential diagnosis may be of some importance during a heart attack. Usually, myocardial infarction is easy to distinguish from other diseases accompanied by pain in the heart (intercostal neuralgia, angina pectoris, pulmonary embolism, pleurisy and others). With an atypical course of a heart attack, diagnosis may become more complicated. The abdominal form can be similar to pancreatitis, peptic ulcers or food poisoning, and the cerebral form can be mistaken for a stroke.
What are the stages of rehabilitation after a heart attack?
In most types of cardiac arrest, cardiac rehabilitation proceeds to the following stages:
- adjusting sleep and sleep patterns;
- transition to healthy food;
- good walks in the fresh air;
- reviewing the approach to sexual life of partners (active sex is included);
- sanatorium-resort treatment (for consumption).
Rehabilitation after surgery on the heart or without it (as there is no need) is based on immediate approaches, directly related to the advanced development of ischemic heart disease, atherosclerosis and other complications. For treatment, use drug therapy (Zocrema antiplatelet drugs). Whenever there are physical procedures and other purposes, the doctor selects them individually depending on the diagnosis and condition of the patient. For example, treatment of a microinfarction is carried out with a variety of painkillers, as well as coronary drugs (which expand the blood vessels of the heart).
Treatment
Treatment requires hospitalization. Until the condition becomes stable, the person remains in the intensive care unit or intensive care unit. Then he is transferred to the hospital to complete the main stage of therapy. You need to seek medical help and start treatment as quickly as possible. This will improve the prognosis, simplify rehabilitation, and reduce the risk of serious consequences.
Drug treatment
For cardiac infarction, drug treatment is carried out in the following directions:
- anesthesia. For mild pain, analgesics are used. In case of severe pain, in case of pain syndrome, which is accompanied by anxiety, a feeling of fear, sedation and analgesic drugs can be used;
- restoration of blood flow using thrombolytic therapy. It starts immediately and should be carried out within the first 90 minutes after seeking medical help. If pain and changes in the electrocardiogram persist, therapy is continued for 24 hours. Thrombolytic therapy is carried out with caution, taking into account the risk of possible bleeding and other contraindications.
Additionally applicable:
- acetylsalicylic acid. Accelerates the destruction of formed blood clots, improves blood flow;
- heparin. Administered intravenously, it helps restore arterial patency and normalize blood flow;
- beta blockers. Used after completion of thrombolytic therapy and reduce the risk of recurrent myocardial infarction;
- ACE inhibitors. They help normalize blood flow, reduce the load on the heart, and help reduce mortality. They are used taking into account the risk of a possible decrease in blood pressure.
Drug treatment for myocardial infarction is prescribed by a cardiologist, taking into account possible contraindications, health status, and the risk of complications.
Surgical intervention
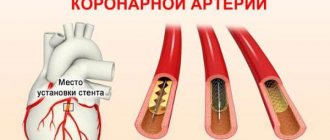
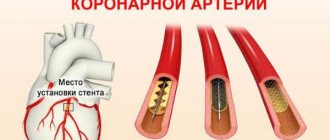
Surgery for myocardial infarction is aimed at increasing coronary blood flow. To do this, two types of operations are used:
- coronary artery bypass surgery. The narrowing of the artery is bypassed by installing a shunt, creating a new “path” for blood flow;
- percutaneous coronary intervention. Interventions that allow you to restore the patency of the coronary artery. To do this, stenting is performed. It involves the installation of a stent, an intravascular prosthesis that helps restore the lumen of the artery in places of its atherosclerotic narrowing.
Rehabilitation after a heart attack
Rehabilitation is carried out to restore normal heart function and improve health. The rehabilitation program is developed taking into account the emotional and physical condition of the patient. It involves control over risk factors for a recurrent heart attack, lifestyle modification, and psychological assistance.
Restoring quality of life after a heart attack
This part of the rehabilitation program is aimed at restoring normal levels of functional health. To do this, your doctor may recommend:
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- following a diet if you need to lose weight or control high blood pressure;
- moderate physical activity. The quantity, intensity and complexity of physical exercises are increased gradually;
- drug therapy: it is possible to continue taking antiplatelet drugs, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, statins for some time;
- reducing stress levels;
- control of concomitant diseases, prevention of their complications.
In consultation with your doctor, additional treatment programs can be used during rehabilitation after a heart attack. New technologies can be used in recovery after a heart attack, such as stem cell treatment.
Psychological support after a heart attack
A heart attack is life-threatening and can cause severe psychological reactions. If it is normal, the person maintains control over emotions, but may experience fear of a second heart attack or death. He worries about the consequences of a heart attack, may be prone to caution, and the feeling of fear can be quite strong. For rehabilitation in this case, consultations with a cardiologist, psychological support, and gradual restoration of health are sufficient.
With a pathological reaction to a heart attack, an anxious, depressed, depressed, and tense state may develop. It has a bad effect on your well-being: sweating, rapid heartbeat, and insomnia. The reaction may be depressive-hypochondriacal. This means that a person becomes overly suspicious, he is too focused on the state of his health. Hysterical manifestations are possible in behavior after a heart attack: demonstrativeness, egocentrism, constant attempts to attract attention to oneself.
If a pathological reaction develops, the rehabilitation program is supplemented with psychotherapy. It is possible to prescribe sedatives and tranquilizers that will help stabilize the mental state. Without psychological rehabilitation, the condition may worsen: psychosis, severe behavioral disorders, and night wanderings are possible (in older people).
Prevention
Prevention of heart attacks is aimed at reducing the risk of heart attacks. The main measures are maintaining a healthy lifestyle and monitoring basic health indicators:
- physical activity. It is increased gradually, after discussing the level of stress with a doctor. Walking, running, swimming, and skiing are especially useful. The intensity of exercise is increased gradually as physical fitness improves;
- rejection of bad habits. Smoking and alcohol abuse increase the load on the cardiovascular system and can provoke myocardial infarction. To reduce the risk of a heart attack, you need to control your drinking and stop smoking;
- weight control. If a person is overweight, the load on the heart increases, and this can provoke a heart attack;
- blood pressure control. If you have hypertension, you need to monitor your blood pressure and ensure that it does not become elevated;
- preventive examinations with a doctor. If you are at increased risk of a heart attack, you should periodically take blood tests, monitor your heart condition, and consult with a physician or cardiologist.
If a heart attack has already occurred, preventing another heart attack is important. In this case, the main preventive measures include taking medications prescribed by a doctor, following a special diet, and performing rehabilitation.
Diet
Diet and diet affect the state of the cardiovascular system. To reduce the risk of heart attack, it is recommended:
- eat more green vegetables, fresh fruits, root vegetables and fresh herbs;
- more often eat low-fat dishes from fish, seafood, and poultry;
- eat animal meat less often;
- reduce the amount of fatty foods;
- limit salt intake;
- eat more foods high in calcium and magnesium.
Such a diet will help reduce cholesterol levels, normalize weight, and improve the condition of the cardiovascular system.
Forecast
The consequences of a heart attack depend on the state of the cardiovascular system, general health, and how quickly a person receives medical help. It is important to call an ambulance immediately at the first sign of a heart attack.
The risk of death increases in old age, in the presence of heart failure, increased heart rate, with anterior localization of the heart attack, in the presence of diabetes mellitus and some other diseases. The mortality rate during the first year after a heart attack ranges from 8 to 10%. A person can reduce the risk of death by taking a responsible approach to treatment, undergoing rehabilitation, and restoring health.
If you have any questions, you can read:
FAQ about myocardial infarction
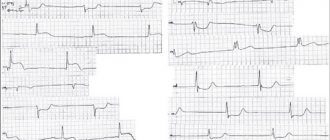
How to determine the focus of a heart attack using an ECG
Each lead displays changes from a specific area of the heart muscle. For a better understanding of the localization of myocardial infarction according to the ECG, let’s consider the correspondence between the heart area and the lead:
- I – left ventricle (LV) from the front and side;
- II – confirms lead I or III;
- III – diaphragmatic surface, posterior;
- aVL – lateral wall of the left ventricle;
- aVF – the same as III;
- V1, V2 – interventricular septum;
- V3 – front wall;
- V4 – apex;
- V5, V6 – LV side;
- V7, V8, V9 – LV posterior.
Lead on the Sky:
- A – anterior wall of the LV;
- I – inferolateral wall;
- D – side and back;
- V3R, V4R – right ventricle (RV).
| Localization | Heart attack on ECG |
| Interventricular septum (IVS) anterior (septal) | For V1 – V3:
|
| Top of the heart | For V4 and A in the Sky:
|
| LV, anterior wall |
|
| Anterolateral |
|
| High sections of the anterolateral wall |
|
| Lateral wall of the left ventricle |
|
| Highly located left side wall MI |
|
| Lower wall of the LV – posterodiaphragmatic (abdominal type of MI) |
|
| Posterolateral (inferolateral) |
|
| pancreas |
|
| Atria |
|
Extensive infarction, in which damage covers large areas of the heart, is common. In this case, the manifestations on the ECG contain a combination of deviations from certain areas at the same time.
You should be careful when detecting a complete block of the left bundle branch, since it hides pathological forms of infarction.
Rice. 6. Anteroseptal MI.
Rice. 7. MI with transition to the apex of the heart.
Rice. 8. MI of the anterior wall of the LV.
Rice. 9. Anterolateral MI.
Rice. 10. Posterior diaphragmatic MI.
Rice. 11. RV infarction.