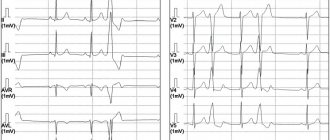
To decipher any electrocardiogram, doctors use a term such as “metabolic changes in the myocardium.” It is believed that it represents a generalized concept expressing the presence of deviations from the isoline of cardiogram segments.
As a rule, these deviations indicate disturbances in metabolic processes in the heart muscle and insufficient supply of nutrition to its cells (cardiomycytes), which means that subsequently a malfunction may occur and the contractility of the heart muscle may be impaired.
Interesting! There are cases when such changes are shown by the cardiogram of a healthy person, and they do not mean anything “terrible”. This is explained by the fact that they can be the consequences of increased workload, severe stress, or excessive alcohol consumption on the eve of the examination. To get rid of them, it is enough to return to a normal lifestyle.
But, most often, metabolic disorders in the myocardium are reflected not only in the electrocardiogram; they are accompanied by patient complaints about general well-being and problems associated with blood circulation (for example, heart rhythm disturbances). Such cases require special attention and appropriate therapy.
General information
Electrocardiography is the simplest diagnostic method for studying the functioning of the heart.
The essence of the examination is to record electrical impulses that accompany the contractile and restorative functions of the myocardium, called “depolarization” and “repolarization.” What do myocardial changes on an ECG mean?
Specific abnormalities in the electrocardiogram can be recorded during a routine medical examination and characterize the condition of the myocardium at the time of the examination. The function of the myocardium is to synthesize by cardiomyocytes , due to which the cavity contracts and ensures normal blood supply to the entire body. This process is carried out due to the cellular exchange of sodium and potassium ions in the cell. The functioning of the cardiac conduction system is recorded on an electrocardiogram using electrodes fixed on the limbs and chest.
Pathogenesis
Changes in the ECG are not a disease, but only a manifestation of some pathological processes occurring in the myocardium. With shifts in the biochemical activity in the heart cells, their contractility changes, which is reflected in the cardiogram when recording the conduction of impulses. Cardiomyocyte function can be impaired during inflammatory processes, for example, with myocarditis . Taking certain medications also affects the functioning of the heart muscle.
Long-term diabetes mellitus can gradually lead to atherosclerosis . Not only large vessels are affected, but also the coronary arteries that supply the myocardium. With inflammatory pathology in the gastrointestinal tract, the absorption of nutrients is impaired, which also negatively affects metabolic processes in cardiomyocytes.
What contributes to the appearance of pathology?
This pathology can be caused by many diseases, mainly those associated with the cardiovascular system.
One of the most common causes of metabolic changes is angina pectoris (the essence of which is the discrepancy between the blood flow entering the heart and the actual need for it in the myocardium). Most often, angina pectoris develops due to the formation of atherosclerotic formations (in other words, plaques) on the walls of blood vessels, which gradually narrow the lumen in them, blocking the passage for blood flow. As a result, myocardial infarction may occur.
Another reason why metabolic changes can occur in the myocardium is hypertension and arterial hypertension. In addition, the following can lead to disturbances: arrhythmia, heart disease, myocardial dystrophy, rheumatic lesions, vasculitis (inflammation of the vessel walls).
Quite often, the described disorders may be a consequence of other pathologies, for example:
- improper metabolism in the body;
- overweight;
- abuse, bad habits (alcohol and nicotine addiction);
- excessive physical activity;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- poisoning of the body with chemicals (household, medicinal);
- infectious diseases (for example, tonsillitis or tonsillitis);
- liver dysfunction;
- anemia;
- allergies.
Classification
Depending on the size and location of the changed cardiomyocytes, the following are distinguished:
- Diffuse changes. Such a widespread lesion indicates the presence of multiple foci of altered cardiomyocytes. Characteristic signs are present in all leads on the ECG.
- Focal changes. Lesions are recorded only in certain leads that correspond to specific areas of the myocardium. Focal changes are a kind of clearly limited areas of connective, scar tissue, which are inert to conduct electricity.
When diagnosing changes on the ECG, a functional diagnostics doctor and cardiologist can state:
- early ventricular repolarization, which is manifested by a negative “T” wave;
- a decrease in the voltage of the r wave, which characterizes the contractility of the myocardium;
- rhythm disturbances;
- conduction disturbances.
Depending on these indicators, the causes of changes in the ECG are determined by nature:
- inflammatory;
- cicatricial;
- dystrophic;
- metabolic.
Causes
Dystrophic changes in the myocardium
Such changes in the ECG are formed due to insufficient nutrition of cardiomyocytes, which inevitably leads to a decrease in the contractility of the left ventricle. Diffuse-dystrophic changes in the myocardium are observed with:
- pathologies of the endocrine system: diabetes mellitus , adrenal dysfunction, disorders of the thyroid gland;
- pathologies of the renal system and liver: excessive amounts of toxic metabolic products negatively affect the functioning of the heart;
- chronic diseases of infectious origin: changes can be observed with tuberculosis , influenza , malaria , etc.;
- chronic iron deficiency anemia : constant oxygen starvation affects the functioning of cardiomyocytes;
- with an unbalanced diet, with vitamin deficiency in the diet;
- with excessive nervous and physical overload;
- with fever and concomitant dehydration;
- in case of poisoning with alcohol, medications or chemical components.
Metabolic changes in the myocardium
What it is? Characteristic nonspecific changes on the ECG are formed as a result of disturbances in intracellular metabolic processes associated with potassium and sodium ions.
Metabolic changes are associated with dystrophy of the heart muscle and appear when:
- ischemia , which is reflected on the cardiogram in the form of deviations of the T wave. Its polarity and shape changes in the leads corresponding to the damaged areas;
- myocardial infarction : the location of the ST segment changes on the ECG, which is located either above or below the isoline;
- death, necrosis of the myocardium, which is characterized by the appearance of an abnormal Q wave.
Scar changes
Areas of scar tissue form at the site of a former inflammatory process, necrosis, as a result of which normal, healthy cardiomyocytes lost their contractility and were replaced by connective tissue that does not have elasticity. Focal cicatricial changes on the ECG indicate a previous myocardial infarction .
- The lower wall of the left ventricle is characterized by changes in leads: II, III and a VF (indicates damage to the right, less often the left circumflex coronary artery).
- The anterior septal region is characterized by changes in leads: V1 and V2 (the left descending septal branch is damaged), or V2-V4 (the left descending coronary artery or its branches is involved).
- The anterior-lateral region is characterized by changes in leads: I, aVL, V4-V6 (the circumflex artery or the left descending artery is damaged).
- Anterior widespread infarction is characterized by changes in leads: I, aVL, V1-V6 (the left descending coronary branch is damaged).
Moderate inflammatory changes in the myocardium
Characteristic changes are observed in myocarditis, in which the voltage of the waves in all leads decreases and rhythm disturbances are recorded. Moderate left ventricular changes may occur after:
- typhus , diphtheria ;
- rheumatism , after streptococcal infection ( tonsillitis , tonsillitis , scarlet fever );
- infections caused by the Coxsackie virus, rubella , influenza , measles ;
- exacerbation of an autoimmune disease ( systemic lupus erythematosus , scleroderma ).
Brown myocardial atrophy
This is what a macropreparation is called during histological examination. Characteristic pathological changes in the myocardium are formed as a result of a long-term lack of blood supply, which is observed in debilitating diseases, cachexia , drug abuse, increased physical activity, and also in old age. lipofuscin, is deposited . Its granules are a product of impaired metabolism in cardiac muscle cells, weakened by insufficient nutrition and blood supply.
Process description
Metabolic changes in the myocardium are a pathological condition accompanied by metabolic disorders:
- proteins,
- carbohydrates,
- fats,
- vitamins,
- electrolytes (potassium, calcium, magnesium).
Such changes are not considered a separate disease, but occur against the background of other pathologies.
Impaired nutrition of myocardial cells leads to a decrease in its contractility, as well as loss of electrical automaticity. Therefore, the condition is often accompanied by various arrhythmias.
Causes
There are many reasons for metabolic changes in the myocardium. Among them are routine conditions (overwork, stress, consumption of energy drinks). In these cases, metabolic disorders in cardiomyocytes do not require urgent medical intervention, as they disappear on their own within a few hours after the factor is eliminated.
The most common causes of metabolic disorders are heart disease or noncardiac pathologies:
- mycardiofibrosis;
- cardiomyopathy provoked by the action of drugs (for example, cardiac glycosides) or toxic substances and allergens;
- myocardial dystrophy;
- cardiac amyloidosis;
- "gouty" heart;
- alcoholic cardiomyopathy;
- endocrine diseases (thyrotoxicosis);
- general metabolic disorders;
- hypovitaminosis;
- malabsorption, atrophic gastritis, pancreatitis with impaired exocrine activity;
- chronic anemia;
- obesity of any degree;
- strict protein-free diets for weight loss, vegetarianism;
- indolent infections;
- pathology of renal excretory function;
- hepatitis, liver failure.
Symptoms
Moderate and minor changes in the ECG may not manifest themselves clinically and may be found on the cardiogram during routine medical examinations and medical examinations. With pronounced changes, special symptoms appear:
- chest pain of a pressing, burning nature, indicating an attack of angina pectoris ;
- swelling of the lower extremities, shortness of breath with minimal physical activity indicate the progression of heart failure ;
- a feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart, arrhythmias ;
- fatigue, pale skin;
- sticky sweat;
- tremors , weight loss in a short time.
What are dysmetabolic changes in the myocardium
Dysmetabolic changes in the myocardium are one of the causes of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
According to statistics, in all countries of the planet, the proportion of people with certain ailments and anomalies of the cardiovascular system in the population structure increases every year. Often these diseases are a consequence of dysmetabolic changes in the myocardium.
Causes of dysmetabolic changes in the myocardium
These types of changes can cause:
- impaired blood supply to the heart muscle;
- energy imbalance, which in turn is caused by insufficient supply of vital elements to cardiomyocytes (heart cells).
Symptoms of an imbalanced energy balance are manifested by an imbalance of ions in cells, as well as in the intercellular space. As a result, protons and lactic acid accumulate in the heart cells. All this occurs against the background of insufficient concentration of high-energy phosphates. The latter are known to provide cells with energy.
Let us note that energy metabolism is one of the most important processes in the body, so its slight disruption leads to the manifestation of various ailments. The consequence of such a violation can be a heart attack, and in extreme cases, death.
Doctors have found that myocardial metabolic disorders are a frequent companion to diseases such as coronary artery disease, angina pectoris, and so on.
Dysmetabolic changes in the myocardium can be a consequence of:
- vitamin deficiency;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- alcohol intoxication;
- dystrophy;
- menopause;
- obesity;
- constant and excessive physical activity;
- acute pancreatitis;
- anemia;
- unfavorable background radiation;
- overheating, hypothermia, vibration and so on.
Treatment
The first thing that may indicate dysmetabolic changes in the myocardium is discomfort in the chest. In this case, physical activity is accompanied by pain in the heart area and shortness of breath. It is even difficult for a person with such a problem to walk.
The main method for diagnosing myocardial metabolic disorders is an ECG.
An integrated approach is used in the treatment of the disease.
In any case, if you suspect a CVD disease, the first thing you need to do is consult a doctor.
The main task in the treatment of such a disease is to restore cardiac conduction, bring the rhythm back to normal, and eliminate heart failure. Patients are prescribed medications that contain potassium salts. It could be “Panangin”, “Trompangin” and so on. Solutions of potassium chloride are effective.
see also
Myocardial hypoxia
Myocardial hypoxia is a violation of the supply of oxygen to organs. In a short period of time, cells die and the organ is damaged. Myocardial hypoxia...
Silent myocardial ischemia
Silent myocardial ischemia is the name of the clinical form of coronary heart disease, when a disturbance in the blood supply to the myocardium passes without an attack of angina, revealing...
What is heart block
One of the serious disorders in the functioning of the heart is blockade. In order to recognize it in time and take the required treatment measures, you need to know what this phenomenon is and what...
Is it possible to go to the bathhouse after myocardial infarction?
Since ancient times, the bathhouse in Rus' has been revered, not only as a means of personal hygiene, but also as a means of promoting health and treating diseases. Bath procedures cleanse the skin of the body well, remove...
Myocardial dystrophy
Myocardial dystrophy arising from physical stress is a rather complex and controversial issue. Not all doctors take this term seriously, although no one...
Tests and diagnostics
To identify the true cause of changes in the myocardium, it is recommended to undergo a full examination, which includes:
- General analysis and biochemical blood test. Based on the results, it will be possible to talk about the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, the functioning of the renal system and kidneys, and the level of cholesterol , which forms plaques in the coronary arteries.
- ECG. Characteristic changes during the examination make it possible to determine further examination tactics. In some cases, it is recommended to perform an ECG with stress, or organize daily ECG monitoring.
- EchoCG. Ultrasound examination of the heart allows you to assess the condition of the valve apparatus of the heart, identify areas of damage, and evaluate the pumping function of the heart.
- Myocardial scintigraphy. The radioisotope research method shows areas of accumulation of a special substance to identify areas of damage and determine their nature.
Changes in the myocardium on the ECG make it possible to determine further tactics for examining the patient to establish an accurate diagnosis and select the correct therapy.
Clinical case
Patient P., 45 years old, was admitted to the emergency department. Delivered by ambulance from the store where she lost consciousness. Complains of weakness, irritability, trembling hands, palpitations. From the anamnesis: a year ago, thyrotoxicosis was diagnosed; he does not take the prescribed therapy. Fainting occurs 1-2 times a month, periodic headaches and dizziness, and increased blood pressure are also disturbing. She did not seek medical help. Objectively: the thyroid gland is enlarged, pressure: 150/90 mm Hg, heart rate 100 beats/min, tremor in the fingers, BMI 18, heart sounds are muffled, the boundaries are expanded by 0.5-0.7 mm. Preliminary diagnosis: “Thyrotoxicosis, thyrotoxic myocardial dystrophy.”
Dynamic ECG, Echo-CG, exercise tests, blood test for TSH and free T4, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, clinical blood and urine tests were performed. The diagnosis was confirmed, after which the patient was sent for treatment to an endocrinologist. After a two-week hospital stay, her condition improved. The patient was discharged for outpatient observation at her place of residence.
Which doctors were prescribed to you for metabolic changes in the myocardium? Share your experience in the comments.