When there is a lack of oxygen, the central nervous system is the first to suffer. Cells in the brain, heart, kidneys and liver are very sensitive to this condition. Oxygen starvation leads to hypoxia. This dangerous disorder can cause coma and death. Since death occurs almost instantly, literally in minutes, it is important to provide timely medical assistance. This will help save the life of the victim.
Kinds
Doctors classify pathology into:
- Respiratory. It occurs due to the impossibility of oxygen supply.
- Exogenous, which develops when inhaling air with a reduced content of this gas. Often develops at low pressure, rise to height, in cramped, closed and crowded rooms.
- Circulatory occurs with pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- Hemic is observed when there is a decrease in oxygen in the blood. This condition is caused by certain diseases, such as anemia.
- Reloading. It is caused by increased physical activity, when the body especially needs oxygen.
- If the ability of tissues to absorb oxygen is impaired, tissue hypoxia begins.
- Mixed - a long-term condition in severe form. A combination of several factors leads to it.
There are different forms of the condition depending on the rate of development. This:
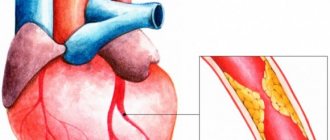
- Chronic, which is observed with heart defects, cardiosclerosis, heart failure.
- The acute form occurs after severe blood loss, heart attacks, and poisoning. In this case, the blood loses its ability to deliver oxygen to the tissues.
- Lightning hypoxia can be rapid. This is the most dangerous form. it develops in a second and causes death within a few minutes.
Prevention
Prevention of AMS should first involve assessing the degree of risk individually for each participant going to high altitude (see table below).
For a low-risk individual, there is no need for prophylactic medications and participants should focus on following a gradual climb schedule. Thus, at altitudes of 3000 meters or more, participants should not increase the altitude of their overnight stop by more than 500 meters/day with a mandatory rest day. If it is impossible to comply with this requirement (relief and other factors do not allow it), it is recommended to arrange a rest day immediately before a large climb or immediately after it at the nearest point with the expectation that the total rate of climb over the period covered will be below 500 meters/day.
A stepped climb/pre-acclimatization significantly reduces the risk of developing mountain sickness, improves oxygenation/ventilation, and reduces the increase in pressure in the pulmonary artery during subsequent climbs.
Individuals at moderate/high risk of developing AMS are recommended to take the mountain sickness tablet Dexamethasone . Doses for adults are 2 mg every 6 hours or 4 mg every 12 hours. Higher doses (4 mg every 6 hours) should only be prescribed in high-risk situations. In this case, the duration of taking dexamethasone in order to avoid suppression of adrenal function/development of glucocorticoid intoxication should not exceed 10 days.
Acetazolamide ( Diacarb ) is also quite effective in preventing AMS (125 mg tablets 2 times a day). However, it is necessary to carefully monitor doses, since increasing them is accompanied by a high risk of side effects. Nifedipine , Tadalafil , Sildenafil are indicated for the prevention of high-altitude pulmonary edema .
The use of other drugs (coca tea, chewing coca leaves, leukotriene receptor blockers, antioxidants, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, Spironolactone / Sumatriptan , salicylic acid ) does not have a positive effect in the prevention of AMS.
Overhydration (increased drinking regimen) also did not demonstrate a positive effect in the prevention of AMS, but at the same time, the risk of hyponatremia .
Some authors believe that resistance to hypoxia is expressed during exercise in special masks, which, in their opinion, imitate hypoxic conditions.
The oxygen deprivation mask restricts the air flow entering the nose/mouth, thereby attempting to simulate the effect of training at high altitudes. At the same time, the mask has a mechanism for regulating the flow of air, which allows for altitudes from 900 to 5500 meters. According to the manufacturer, the use of masks allows you to achieve a significant increase in the key marker of growth in aerobic endurance - VO2max.
However, to date, the effectiveness of using training masks has been studied extremely poorly and many believe that a training mask has nothing to do with hiking in high altitudes. Despite the fact that it is difficult to breathe both at high altitudes and in a mask, the reasons for this are completely different: at high altitudes there is less oxygen in the air, but when using a mask, the oxygen does not become less. It is simply harder for a person to breathe. Therefore, masks cannot be considered a sports accessory that simulates hiking in the highlands. Rather, they can be considered as a simulator used to strengthen the inspiratory muscles involved in the act of inhalation.
Symptomatic picture
Symptoms of oxygen starvation are typical:
- First, the stage of psychomotor agitation occurs. The person feels excess energy. He falls into a state of euphoria. At the same time, he is unable to coordinate movements. Unsteadiness of gait is observed. The skin becomes hyperemic and red. In some cases, on the contrary, the victim’s skin takes on a pale, almost bluish color. Cold, sticky sweat appears.
- The second stage is inhibition. The nervous system becomes less active. Dizziness, nausea, and sometimes profuse vomiting appear. Vision loses clarity and vision becomes dark. The patient loses consciousness.
- Severe forms are accompanied by cerebral edema. Irreversible disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system begin in the body. With severe hypoxia, loss of conditioned and unconditioned reflexes occurs. Human skin loses sensitivity, organs stop working normally. This state progresses to a deep coma.
Hypoxia in newborns
This pathology is diagnosed in children suffering from a lack of oxygen during the perinatal period and during childbirth. This is one of the most common pathologies of newborns. It can occur due to prolonged holding of breath, illness in the infant, fetal asphyxia, and reduced oxygen concentration in the air.
In children, hypoxia leads to irreversible damage to the central nervous system and other vital organs. The lungs, liver, heart, kidneys and brain are primarily affected.
If hypoxia is diagnosed, doctors carry out a set of resuscitation measures:
- The baby is warmed up.
- The airways are cleared of mucus.
- They perform artificial respiration.
- Nutrient solutions are introduced.
- Indirect cardiac massage is performed.
Such children are registered with a neonatologist, and later with a pediatrician. It is very important to carefully monitor the dynamics of development.
To exclude hypoxia in newborns, prevention should begin from the very beginning of pregnancy. The expectant mother needs to be examined and treated for diseases in a timely manner, and try to prevent toxicosis. The correct daily routine, dosed exercise, sufficient sleep and walks in the fresh air are of great importance.
Symptoms
There are many reasons for the appearance of cerebral encephalopathy, and therefore its manifestations differ. They depend on why it develops, where it is localized in the brain and what the nature of the lesion is. However, a common feature is a slow or rapid change in mental status.
For example, hepatitis contributes to a mild change: the patient cannot draw simple designs, that is, he develops apraxia - the inability to make complex movements, purposeful actions. But brain anoxia is a sharp lack of oxygen that leads to death within a few minutes.
Symptoms of encephalopathy include poor coordination of movements, inability to concentrate, inattention, as well as more serious manifestations:
- tremor of the limbs;
- lethargy;
- breathing disorder – it becomes periodic;
- muscle pain, twitching;
- convulsions;
- numbness of the nose, lips, fingertips;
- fainting, dizziness;
- persistent headaches or acute attacks;
- noise in the head;
- sleep disturbance;
- decreased thinking abilities, memory;
- sudden change of mood;
- decreased sex drive;
- apathy;
- fatigue and constant weakness;
- depression;
- sluggishness of speech;
- irritability;
- nausea, vomiting;
- coma.
If treatment is not started in time, the symptoms will intensify, hallucinations, delusions, disorders of consciousness, psychosis, etc. may appear, and there is a risk of death.
Diagnostic methods
The pathology has characteristic symptoms. But for a more accurate diagnosis, instrumental examination methods are used. These include:
- Study of acid-base balance. It includes the gas composition of arterial and venous blood. In this way, the doctor can find out the state of the carbonate and bicarbonate buffer, the partial pressure of oxygen and carbon dioxide. This means establishing quantitative indicators of human homeostasis.
- Pulse oximetry is one of the simplest ways to detect oxygen starvation. A pulse oximeter is placed on the patient's finger. After a few seconds, it shows the degree of oxygen saturation of the blood. Normally, the figure should be above 95%.
- CO-metry and capnography make it possible to determine the composition of inhaled air.
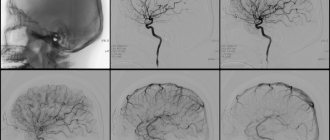
- If a person has suffered hypoxia, it is necessary to make sure that the central nervous system is not damaged. For this purpose, an MRI of the brain is prescribed. This type of diagnosis is the most informative. It will allow you to clarify the condition of soft tissues, blood vessels, neurons, and track the activation of the cortex.
Therapy
To prescribe effective treatment, it is important to correctly determine the root cause of the disorder. Therefore, it is necessary to explain to the patient what preceded the appearance of hypoxia. Do not forget that prolonged consumption of alcoholic beverages and a long stay in a stuffy room can be factors.
Depending on the severity of oxygen starvation of the brain, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. Medicines are prescribed to normalize the functioning of the body, as well as vitamins that restore brain tissue.
For a mild form of pathology, it is enough to take a walk in the fresh air or ventilate the room well. If the disorder is caused by an organic factor, such as a disease of the cardiovascular system, lungs, or blood, it is necessary to treat the primary disease.
- For respiratory hypoxia, antihypoxants, bronchodilators, and respiratory analeptics are prescribed. Oxygen concentrators are used. In difficult cases, artificial ventilation is performed.
- For exogenous, oxygen pillows, masks, and cans are used.
- The histotoxic form of the disease requires antidotes, drugs that improve oxygen utilization by tissues, and mechanical ventilation.
- Treatment of hemic hypoxia is accompanied by blood transfusion and stimulation of hematopoiesis. In case of circulatory disorders, corrective surgery on the blood vessels and heart is required.
Complications
The consequences depend on the duration of the lack of oxygen. This is what determines the degree of brain damage. Brief coma is usually reversible, and lost functions are restored over time. The longer the vegetative state persists, the worse the medical prognosis.
In a vegetative state, a person retains vital functions: the sleep-wake cycle, breathing, blood circulation, nutrition, but there are no conscious reactions to external stimuli. Such patients can live for years, or die within a year.
The consequences of severe forms of hypoxia are:
- Bedsores.
- Dystrophy.
- Lung infections.
- Thromboembolism.
What are we talking about?
The brain coordinates and regulates the functioning of the entire body. It provides a balance of processes, protection from negative influences, and adaptive mechanisms. The brain perceives and processes information, provides a person with thinking and other higher functions.
Nerve cells need a lot of oxygen and nutrients to work. Cerebral circulation is different from blood flow in other tissues of the body. It's much more complicated:
- numerous bends of the brain vessels - to smooth out the pulsation of blood flow and maintain pressure stability;
- the richest network of capillaries - so that all tissue areas and cells without exception receive nutrition;
- developed collateral circulation - brain vessels are connected to each other by collaterals - “bridges”, which help restore blood flow when the main vessel is blocked.
The brain has an autonomous regulation system: with a general increase in blood pressure, it remains stable in the brain for the longest time. But excess or insufficient blood circulation sooner or later leads to negative consequences: fluid accumulation and the development of tissue edema, lack of oxygen, stroke and other complications.