Gastroenterologist
Neronov
Vladimir Alexandrovich
23 years of experience
Gastroenterologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences
Make an appointment
Gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the stomach, during which the mucous membrane is affected due to the influence of various factors. Gastritis of the stomach belongs to the category of common diseases that currently occur not only in adults, but also in children (superficial gastritis). Adult gastritis of the stomach is more common in middle-aged and elderly people.
Experts identify the following forms of the disease:
- acute form, which occurs suddenly against the background of irritants;
- a chronic form that occurs over time due to improper lifestyle and diet.
Depending on many factors, erosive gastritis, biliary, hypertrophic or peaty gastritis can be diagnosed. Acute forms of the disease are divided into purulent, necrotic, diphtheric, and simple. Depending on the acidity of the stomach during gastritis, the following are distinguished:
- gastritis with high acidity;
- gastritis with low acidity.
Symptoms and signs of gastritis
They help identify gastritis symptoms depending on the type of disease:
- acute gastritis begins suddenly, often after food poisoning; sharp pain with gastritis is felt in the solar plexus area. The pain may intensify when taking foods that irritate the gastric mucosa. The main symptoms of gastritis of the stomach: heartburn, vomiting, belching, frequent release of gas, bloating, headache, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, increased salivation or extreme thirst;
- Chronic gastritis is sluggish. If chronic gastritis is diagnosed, the symptoms in adults may vary, but generally this pathology is characterized by belching with a characteristic odor, constant heartburn, a feeling of pain and heaviness, loss of appetite, diarrhea or constipation, coating on the tongue, and weight loss. Due to the fact that the signs of gastritis of the stomach depend on the type of pathology, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. In the chronic form, nutrition plays an important role in gastritis.
Depending on the form and type of gastritis, symptoms and treatment vary significantly, so the best solution for the patient is to immediately consult a doctor.
Are you experiencing symptoms of gastritis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
The main disease of the stomach is chronic gastritis
And here you can’t do without the help of a doctor, and much more serious help will be needed. Each of us knows from our own experience what abdominal pain is. Sometimes the discomfort goes away on its own; other times we habitually reach for pills. However, if the pain comes back again and again, you should not self-medicate, because you need to look for the cause, and not relieve the symptoms, in which case it is better to trust a specialist. After all, pain in the stomach can be a sign of a number of diseases. The most common of these is gastritis.
Chronic gastritis is an inflammatory process of the gastric mucosa, one of the most common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
How to recognize the manifestations of gastritis? Chronic gastritis is an inflammatory process of the gastric mucosa, one of the most common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
With increased acidity, the aggressive properties of hydrochloric acid increase; with low acidity (hypoacid and anacid gastritis), food is retained in the stomach and fermentation processes intensify. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa causes the body to disrupt the process of digesting food. And this worsens the general condition of the body, reduces performance, causeless fatigue, weakness and other symptoms appear, which even the person himself for some reason ignores, not caring about the possible consequences.
The main manifestations of gastritis may be pain or discomfort, burning in the upper abdomen, heaviness after eating a small amount of food, an unpleasant taste in the mouth or belching “sour” or “rotten egg”, usually in the morning. However, after consuming food or liquid, symptoms may decrease somewhat. Other symptoms (which indicate involvement of the esophagus in the inflammatory process) include heartburn (a burning sensation behind the sternum), belching of air or recently eaten food, and sometimes nausea. If unpleasant sensations bother you constantly and do not go away for more than a week, you need to consult a doctor in order to determine the cause, establish a diagnosis and begin adequate treatment, which can help avoid unpleasant complications. Chronic gastritis can occur without symptoms - this picture is observed in approximately half of the people suffering from this disease.
To the question “What causes gastritis?” most will answer quite easily: poor diet, too much spicy food, smoking, drinking alcohol. Some will name stress and the use of certain medications. All this really influences the appearance of the disease. However, recent studies prove that most often all these factors are not the main ones. In approximately 85% of cases, the disease occurs “thanks to” the bacterium Helicobacter Pylori (Helicobacter) that lives in the stomach. This discovery at the end of the 20th century became one of the turning points in gastroenterology - after all, it was traditionally believed that it was impossible to “get infected” with gastritis.
Infection more often occurs within a family or other closely communicating groups, since the infection spreads when using the same utensils, failure to comply with hygiene rules, and overcrowding. Often the infection is transmitted from mother to child (through saliva that gets on the pacifier, spoon and other objects). You can become infected with Helicobacter pylori even by kissing. Bacteria in the stomach “sleep” indefinitely, and then at some point they begin to “act”, causing illness. Moreover, the probability of developing chronic gastritis if a person is infected before the age of 20 is more than 50%; in this case, he develops the so-called “Helicobacter gastritis”. Its peculiarity is that it is difficult to treat, provokes an increase in exacerbations of gastritis, and is highly likely to cause various complications, primarily ulcers and stomach cancer. If such an ulcer is treated with conventional means without destroying the bacteria, then the probability that it will occur again is extremely high and is close to 90% within the first year after the end of therapy. Therefore, it is necessary to approach the treatment, and therefore the removal from the body of the main enemy of the stomach - Helicobacter, very carefully and with all seriousness.
How to cope with gastritis?
First of all, you should remember: in the fight against Helicobacter pylori gastritis, almagel alone will not help, it is only a symptomatic remedy that will relieve discomfort for a short time: more serious remedies are needed here, moreover, prescribed by a doctor after a thorough examination.
It is desirable that this examination include all the necessary tests - instrumental (fibrogastroscopy - which allows you to fully determine the condition of the gastric mucosa and reliably detect the presence or absence of bacteria) and laboratory (breath test and blood test from a vein). Diagnosis of infection by blood test is less reliable, because it only determines the presence of antibodies to the bacterium - immune cells, and not Helicobacter itself. You need to perform either fibrogastroscopy or 2 methods, a breath test and a blood test. If the result is positive, it is necessary to eradicate the pathogen, that is, to cleanse the body of it. In this case, treatment regimens specially developed by the Society of Gastroenterologists are used.
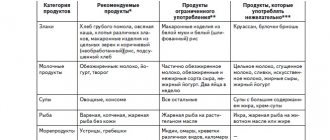
In addition, the doctor will recommend a suitable diet - both during treatment and after it. A good addition to the tablets would be, in case of high acidity, the habit of not eating citrus fruits or drinking their juices, you should temporarily forget about chocolate and coffee, and do not abuse spicy foods and alcohol. With low acidity, food should not be very hot or cold, it should be chewed thoroughly. They recommend products that have a juice-containing effect (meat and vegetable decoctions, lean meat, fish, herring in small quantities, black caviar, herbs, vegetables, fruits, lactic acid products, for example, cottage cheese, preferably homemade, cheese, as well as juices, jam, etc. .).
It is easier to cure any disease in the early stages - before something serious happens. Therefore, if abdominal pain, even infrequently occurring and not severe, bothers you again and again, it’s time to contact a gastroenterologist who will help solve this problem. The sooner you start treatment, the better the effect you can get.
Causes
Gastritis of the stomach occurs and develops for a variety of reasons, the main ones being non-microbial and bacterial factors. Experts call the main cause of the disease the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, detected in 80% of cases, fungi and other bacteria. When bacteria enter the mucous membrane, they release substances that lead to the onset of the inflammatory process.
Other causes of pathology include:
- unhealthy diet: incorrect eating regimen, incorrectly selected diet, frequent consumption of spicy, fatty, refined foods, lack of plant fiber;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- uncontrolled use of medications, including non-hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- infection of the body with worms;
- frequent stressful situations;
- allergic reactions to foods and substances;
- metabolic disease.
Gastritis can also appear in adults due to excessive physical and emotional stress. One of the conditions for recovery is following the menu prescribed by the doctor for gastritis.
Duodenitis
Duodenitis is an inflammatory disease of the duodenum . There are acute and chronic forms. Acute duodenitis often occurs in combination with acute inflammation of the stomach and intestines (acute gastroenteritis, gastroenterocolitis).
Causes of the disease:
- heredity;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- excessive consumption of spicy, rough foods in combination with strong alcohol, etc.
Symptoms:
- pain in the epigastric region;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- general weakness.
Acute duodenitis most often goes away on its own within a few days, but can become chronic. In some forms, complications are possible (intestinal bleeding, perforation of the intestinal wall, development of acute pancreatitis).
In the treatment of diseases of the stomach and duodenum, timely diagnosis and professional medical care are very important. Our clinic specialists work for you seven days a week and on holidays, using the most modern techniques.
Complications
The main cause of complications is the chronic form of the disease. If signs of chronic gastritis appear, but the patient does not consult a doctor, the following complications may occur:
- anemia;
- atrophic gastritis;
- leptic ulcers;
- benign or malignant tumors on the mucosa.
The only way to restore health is to promptly consult a qualified doctor who will give recommendations on how to treat gastritis. Taking pills for gastritis on your own is not recommended, so as not to provoke an exacerbation of the disease and its transition to a severe form. The likelihood of complications depends on what patients with chronic gastritis eat.
When to see a doctor
You should consult a doctor if you feel severe pain with gastritis of the stomach, since exacerbation of gastritis can cause a serious deterioration in health with an increase in the area of mucosal damage and transition to an ulcerative state. Gastritis is especially dangerous if there is increased acidity, since the juice tends to corrode the mucous membrane of the organ, resulting in the formation of ulcers. If, based on a number of signs, the patient has identified an exacerbation of gastritis, the symptoms of which are nausea to vomiting, complete loss of appetite, fever up to 39 degrees Celsius and severe pain, you should make an appointment with a specialist as quickly as possible.
Gastritis, the symptoms and treatment of which may vary in adults, is diagnosed by a gastroenterologist. The Center for Modern Medicine JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) in Moscow offers diagnostic and treatment services for all types of gastritis using modern medical devices and drugs. More complete information on the topic “gastritis and its treatment in adults” can be obtained by clicking on the link. Our clinic is located at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, building 10, a 5-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station.
What diseases of the cardiovascular system do cardiologists treat?
The treatment of cardiovascular diseases is carried out by various specialists - cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, arrhythmologists, neurologists, rheumatologists, angiosurgeons.
Cardiologists treat patients with damage to the heart and its blood vessels, as well as peripheral artery disease.
Such diseases include:
- coronary heart disease (CHD);
- angina pectoris
- myocardial infarction
- chronic heart failure;
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- inflammatory lesions of the heart muscle and pericardium;
- cardiomyopathies (hereditary and secondary);
- arterial hypertension (hypertension);
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- disturbances of heart rhythm and conduction.
Treatment
When gastritis is diagnosed, treatment and medications are prescribed by a specialist, taking into account the course of the disease and the patient’s condition. A gastroenterologist selects a medicine for gastritis based on the examination results strictly individually. A prerequisite for recovery is a properly selected diet for gastritis; the menu for patients is developed by the doctor, taking into account the age and condition of the patient, and lifestyle. During the consultation, the doctor will tell you in detail about what you can eat with gastritis and what you cannot eat with gastritis.
Diagnosis of gastritis
Today, the main way to determine gastritis is fibrogastroduodenoendoscopy or FGDS, which consists of studying the condition of the inner surface of the stomach using a probe, as well as a biopsy - removing a small fragment of tissue for examination.
FGDS makes it possible not to confuse gastritis and ulcer and to determine the type of disease: erosive or non-erosive.
Also, a gastroenterologist, to make a correct diagnosis, may prescribe the following tests:
- General blood analysis.
- Fecal occult blood test.
- Histological examination of a biopsy specimen of the gastric mucosa.
- Cytological examination of a biopsy specimen of the gastric mucosa.
- Two tests for the determination of H. pylori.
- Blood chemistry.
- General urine analysis.
How to make an appointment with a gastroenterologist
You can make an appointment with a gastroenterologist at our multidisciplinary medical center at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, building 10 in the following ways:
- use the form on the website;
- use the phone +7 (495) 775-73-60 around the clock.
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) also offers services to call a gastroenterologist at home and by phone +7 (495) 775-73-60 around the clock.
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located a 5-minute walk from the "Mayakovskaya" metro station.