Anaprilin is a drug that is often prescribed for hypertension, pathological heart rhythm disturbances, migraines, alcohol withdrawal, anxiety, and panic attacks. The active substance of the drug is propranolol - a selective beta-blocker that normalizes heart rate, lowers blood pressure, reduces tremor, and has a moderate sedative effect. Anaprilin and alcohol are prohibited for joint use due to a decrease in the effectiveness of treatment, as well as the risk of side effects and complications.
Compatibility of Anaprilin and alcohol
? Alcohol has a bad effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular system: it interferes with the conduction of cardiac and nerve impulses, increases or decreases blood pressure, and increases the risk of heart pathologies.
Mixing substances is strictly prohibited. Drinking alcohol while taking the drug will lead to a high risk of death for the patient. The interaction of ethanol with propranol (the active ingredient of the drug) will cause a critical decrease in blood pressure.
It will decrease in proportion to the amount of alcohol consumed. The rate of absorption of the drug into the blood is disrupted, and an overdose occurs.
The interaction of the drug with alcohol-containing drinks will cause arrhythmia. The drug enhances the effect of ethanol. Intoxication will occur much faster. The hangover will be longer and more severe.
There is an increased reaction from the nervous system. Depressive and alcoholic psychosis, along with confusion of thinking, will lead to a loss of consciousness of a person’s actions.
Consequences of combination
The likelihood of developing pathological symptoms, the influence and consequences of combining Anaprilin with alcohol for the body depend on many factors: the individual characteristics of the patient, the dose of alcohol, etc. The most dangerous complications for health are those from the cardiovascular system, manifested by a sharp decrease in blood pressure, and increased side effects, which already provoke life-threatening conditions.
Pressure drop
Anaprilin with alcohol causes a sharp drop in blood pressure in hypertensive patients. This is a serious symptom that requires emergency care. With sudden onset of hypotension, blood vessels quickly dilate, while the blood flow does not have time to increase. Brain vessels react to an extreme situation with a sharp narrowing, which can lead to hemorrhage and stroke.
The outcome of this condition will depend on the speed of assistance.
The danger of taking blood pressure pills and alcohol at the same time also lies in the fact that with a rapid drop in indicators, a person begins to behave inappropriately: he gets confused in his words, does not recognize loved ones, staggers, and falls. Others may mistake this for signs of alcohol intoxication and not call an ambulance.
Increased side effects
Anaprilin has a large list of side effects from all body systems. Combining it with alcohol only increases the severity of unwanted symptoms. The sedative, toxic, diuretic, and irritating effects of alcohol aggravate the side effects, leading to the development of complications, sometimes life-threatening:
- bradycardia, tachycardia, heart failure;
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, toxic liver damage;
- headaches, depression, hallucinations, memory loss;
- shortness of breath, bronchospasm, laryngospasm;
- hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia due to diabetes mellitus;
- impaired visual acuity;
- decreased potency;
- skin itching and rashes.
Propranolol sometimes relieves withdrawal symptoms in alcoholism, which creates a false impression of the safety of simultaneous use of the drug and alcoholic beverages.
It should be borne in mind that withdrawal syndrome is a condition different from intoxication or a hangover. It occurs against the background of a sharp cessation of alcohol in people suffering from alcohol addiction. During this period, ethanol is absent or contained in minimal quantities in the body.
Loss of effectiveness from treatment
Anaprilin after alcohol loses its properties due to difficult passage through the digestive tract. Ethanol slows down the absorption of the drug in the stomach and changes the rate of metabolic reactions occurring in the liver. As a result, only part of the drug penetrates the bloodstream and has a therapeutic effect.
In addition, with the systematic combination of alcohol and Anaprilin, the lack of effectiveness of therapy forces the doctor to look for alternative methods of treatment (in the event that the patient hides the fact of alcohol abuse from him), sometimes less effective.
Brief characteristics of the drug
The drug is available in tablet form. The active substance is propranolol. The dosage in one tablet is 40 milligrams. The medicine is dispensed according to a doctor's prescription.
A beta blocker has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart muscle. Helps reduce arterial hypertension. Restores the natural rhythm of the heart and heart rate.
Affects the functioning of the central nervous system. Relieves attacks of limb tremors. Reduces the intensity of pain in the head area.
With maximum impact on the body, the bronchi expand. The oxygen in the patient's blood increases. The saturation of organs and tissues improves. Metabolism increases.
The body absorbs up to 90 percent of the healing and nutrients included in the medicine. Metabolism occurs through interaction with liver enzymes. Excretion from the body occurs through the kidneys along with urine. One percent of the medicinal composition is released.
The maximum concentration is achieved within three hours from the moment of oral administration.
Prescribed for:
- High blood pressure.
- Tension unstable angina.
- Tachycardia.
- Extrasystoles.
- Prevention of chronic headaches.
- Diffuse toxic goiter.
- Treatment of psychosomatic anxiety.
- Thyrotoxic crisis.
- Treatment of the consequences of drug and alcohol toxic addictions.
- Treatment of hemangiomas (benign vascular neoplasms).
Usually one to three tablets are prescribed, three times a day.
The product has side effects:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- abdominal pain;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- chronic liver failure;
- decreased sensitivity of taste buds;
- dryness of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- burning and pain in the eyes;
- pressure drops;
- bradycardia;
- pain in the chest;
- heart failure;
- arrhythmia;
- yellowness of the sclera;
- depression;
- sleep disorders;
- anxiety;
- allergic reactions.
During treatment, driving a car or using machinery is prohibited. Take with caution with other medications.
Limited use:
- Children and elderly patients.
- For chronic pathologies of the liver and kidneys.
- For obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Asthma.
- Vascular pathologies.
After starting treatment with this drug, it is prohibited to change the course without permission without consulting a doctor.
It is forbidden to prescribe if the medical history includes:
- acute necrosis of the heart walls (myocardial infarction);
- chronic heart failure of the last stage;
- pulmonary edema;
- atrioventricular heart block;
- low heart rate (less than 50 beats per minute);
- severe peripheral vascular disorders;
- weakness of the sinus node;
- reduction in blood pressure by 20% from normal values.
https://myweak.ru/alkogolizm/lekarstva/anaprilin-sovmestimost.html
How to use Anaprilin: instructions
The treatment regimen depends on age, physical condition, type and severity of the disease. General recommendations:
- Swallow the tablets without chewing with a sufficient amount of water;
- time of administration: on an empty stomach: 20–30 minutes. before meals or 1.5 hours after.
For adults, the recommended initial daily dose is 40 mg: once or in doses of 10 mg. four times a day. If well tolerated, the dosage is increased by taking 40 mg. 2–3 times a day. Depending on the physical condition, the maximum dose of the drug is from 160 to 320 mg.
After a heart attack, therapy with Anaprilin begins in the period from 5 to 21 days:
- the first 4 days take 40 mg. 3–4 times a day;
- in the following days the regimen is changed: the single dosage is doubled: up to 80 mg. At the appointment, take the tablets twice a day.
In acute conditions: attacks of angina pectoris, arrhythmia, high intraocular or intracranial pressure, Anaprilin injections are indicated. Injections of the solution are given once or in short courses of 3–5 days.
For children with cardiovascular diseases, treatment with Anaprilin is allowed from 3 years of age according to individual indications. For them, the dosage is calculated according to body weight: 0.25–0.5 mg. per 1 kg. up to 3 times a day.
The duration of the course of oral administration is several months. If the condition changes, the treatment regimen is adjusted. Therapy is discontinued gradually to avoid potential withdrawal effects.
Consequences of drinking alcohol
The consequences of taking medication together with alcohol are life-threatening for the patient.
The effect of alcohol on the body increases. Toxic effects lead to increased hangover symptoms.
The likelihood of developing side effects from the drug increases. They become more pronounced and last longer.
The combined influence leads to critical blood pressure levels and loss of consciousness. Collapse of the heart muscle occurs and the patient dies.
Side effects of Anaprilin
If the recommendations are followed, the drug is well tolerated. In some cases it is possible:
- dizziness, tinnitus;
- physical weakness;
- asthenia;
- increased drowsiness;
- decreased concentration;
- dyspepsia: loss of appetite, nausea;
- bowel dysfunction: diarrhea, constipation;
- bronchopulmonary spasm, cough;
- dyspnea;
- dry eye syndrome, decreased visual acuity.
The likelihood of side effects increases with smoking.
Anaprilin and beer
Anaprilin is prescribed for arrhythmia and angina. The drug is not compatible with beer, and in combination with it can cause orthostatic collapse.
Its symptoms:
- Rigidity of the limbs.
- Loss of coordination.
- Weakness.
- A sharp drop in blood pressure when trying to stand up.
With a large amount of alcohol, its level drops to a critical level, which will require medical intervention.
Ethyl alcohol increases the side effects of the drug, which is expressed in the following symptoms:
- loss of consciousness;
- hypotension.
A severe drop in pressure can lead to serious problems with the heart and brain. There is a possible risk of vascular collapse.
Organs affected by the toxin
The combined use of pharmacological agents and alcohol has a toxic effect on the internal organs and environments of the body. Alcohol, entering into a chemical reaction with a medicine, leads to poisoning, disrupts physiological processes, enhances or weakens the healing properties of drugs.
The liver suffers more than other organs. She gets hit twice. Many medications have a side effect - hepatotoxicity, destroy cells, and disrupt the physiology of the organ. In the liver, alcohol breaks down to ethanal, a substance 20-30 times more toxic than ethanol, which causes the death of hepatocytes.
Dangerous groups of drugs for the organ in combination with alcohol:
- anti-inflammatory;
- hormonal;
- antibacterial;
- antifungal;
- glucose control agents for diabetes mellitus;
- anti-tuberculosis;
- cytostatics (chemotherapy drugs);
- tranquilizers (anti-epileptic, psychotropic).
In second place among the internal organs exposed to the harmful effects of alcohol together with medications are the heart and vascular system. Strong drinks during drug therapy constrict blood vessels and increase blood pressure. The simultaneous intake of alcohol and chemical substances leads to failure of the myocardium and increases the risk of developing an attack of angina pectoris and a heart attack.
A mixture of ethanol and pharmaceuticals disrupts the quality of the blood and reduces clotting. This is dangerous due to internal bleeding and strokes.
Mechanism of action of Anaprilin
Propranolol reduces the frequency and increases the strength of myocardial contractions. The product works systemically: at the same time it reduces the need for oxygen in the muscular system and improves its tone. As a result, contraction of the walls of the uterus, bronchi, and gastrointestinal tract increases. Anaprilin causes a persistent decrease in systolic and diastolic pressure, prevents the development of a hypertensive crisis, and alleviates the condition during angina attacks. The effectiveness of the medicine is equally high in any position of the patient’s body. The drug reduces the risk of sudden myocardial infarction and allows you to reduce the intake of nitroglycerin. With regular use, Anaprilin helps improve physical performance.
Rules for taking medications and alcohol
Drinking alcohol during treatment minimizes the clinical effect of therapy and creates a risk of developing complications of the disease.
If this cannot be avoided, follow the rules of behavior that will reduce the occurrence of negative consequences:
- Do not drink strong drinks (vodka, cognac, whiskey), choose dry wine (100-150 ml), beer (no more than 300 ml). Don't drink alcohol on an empty stomach.
- The interval between taking the medicine and alcohol should be at least 2 hours.
- To reduce the toxic effect, take medications that protect the liver (hepatoprotectors), pancreas (pancreatin), and stomach (antacids ─ Rennie, Almagel).
If a person takes antiviral medications for colds, anti-inflammatory drugs, alcohol in moderation does not pose a threat to the body.
Alcoholic drinks during treatment are strictly contraindicated in cases of liver cirrhosis, severe infectious diseases, and during a course of chemotherapy.
Medicines, alcohol and chronic diseases
If a person has chronic diseases, simultaneous use of alcohol and medications is potentially dangerous for the functioning of vital organs. Since patients systematically take prescribed medications, the influence of alcohol can lead to negative consequences.
People with chronic heart disease (angina pectoris, heart defects) develop arrhythmias of varying severity. Heart attacks with severe pain syndrome develop, which is not relieved by Nitroglycerin, and the risk of developing myocardial infarction increases significantly.
In case of chronic liver diseases (viral hepatitis, hepatosis), alcohol during treatment can become a trigger in the development of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (cancer).
Drinking alcohol during cirrhosis leads to the following consequences:
- bleeding into the abdominal cavity;
- liver decomposition, infection, peritonitis;
- hepatic coma;
- death.
If a person is on long-term treatment with sedatives, psychotropic drugs, tranquilizers, he is contraindicated in drinking alcohol. This leads to severe depression and the appearance of obsessive states (hallucinations, phobias). Suicidal feelings develop. Such a patient needs constant monitoring and assistance from a psychiatrist.
Who is Anaprilin contraindicated for?
The medication is prohibited for use in the first 4 days after myocardial infarction. Other contraindications:
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- bronchial asthma;
- bradycardia with a decrease in heart rate to 60 beats per minute.
Anaprilin reduces the speed of psychomotor reactions. For this reason, treatment with the drug is incompatible with driving vehicles and performing work that requires intense attention.
The most dangerous combinations and consequences
The combination of alcohol and chemical-based drugs can lead to serious disorders in the body, and in some cases to fatal consequences.
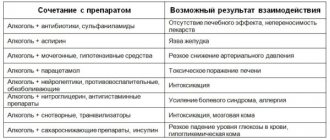
List of medications and their side effects in combination with alcohol:
| Name of group, drug | Negative results of interaction |
| Neuroleptics (tranquilizers, anticonvulsants, hypnotics) | Severe intoxication, up to cerebral coma |
| CNS stimulants (Theophedrine, Ephedrine, Caffeine) | Rapid increase in blood pressure, hypertensive crisis |
| Antihypertensives (Captofrin, Enalapril, Enap-N), diuretics (Indapamide, Furosemide) | Sudden drop in pressure, collapse |
| Analgesics, anti-inflammatory | Increased toxic substances in the blood, general poisoning of the body |
| Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) | Acute gastritis, perforation of gastric ulcer and 12-PC |
| Paracetamol | Toxic liver damage |
| Hypoglycemic (Glibenclamide, Glipizide, Metformin, Phenformin), insulin | A sharp decrease in blood sugar levels, hypoglycemic coma |