Emerging pain in the heart with osteochondrosis can be reflected or true. In the first case, a person experiences unpleasant sensations spreading along the pinched nerve fiber of the roots responsible for the innervation of the intercostal muscles on the left side. In the second case, the situation is much more serious and develops against the background of damage to the radicular or cranial nerves responsible for the innervation of the heart muscle, pacemaker, coronary blood vessels or the formation of the vagus nerve.
More often, pain in the heart is recorded with thoracic osteochondrosis, since the radicular nerves responsible for the innervation of the intercostal muscles and sternum are subject to compression in this type of disease. Also, if the intervertebral disc is damaged in the thoracic region, an inflammatory process may occur that affects the intercostal muscles. The second factor of negative influence is the static tension of the muscular frame of the back, which tries to compensate for the shock-absorbing load that the damaged intervertebral disc cannot cope with.
The pain in the heart that occurs with cervical osteochondrosis is dangerous because it is often associated with damage to the paired cranial nerves. One of these pairs is responsible for the parasympathetic nervous system, which ensures the performance of the myocardial muscle and regulates the work of the pacemaker. The second pair is responsible for the formation of the vagus nerve, which also regulates cardiac activity and controls the volume of arterial blood released into the systemic circulation. If this work is disrupted, a primary form of vascular heart failure may develop.
Damage to the radicular nerves in the lower structures of the cervical spine leads to disruption of the innervation of the coronary vascular bed. This can contribute to the development of coronary heart disease, acute myocardial infarction, etc.
Pain in the heart area that occurs with osteochondrosis is a reason to urgently seek medical help. It is necessary to get an appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist as soon as possible. Only an experienced doctor will be able to exclude the development of cardiac pathology and prevent negative consequences, such as aortic thrombosis, acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery stenosis, etc.
In Moscow, you can make an initial free appointment with a neurologist at our manual therapy clinic. To do this, just call the administrator and agree on a time convenient for your visit. During the free consultation, the doctor will conduct a full examination, make a preliminary diagnosis, and give individual recommendations for subsequent examination and treatment.
Causes and nature of pain in the heart with osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a chronic and slowly progressive disorder that affects the discs between the vertebrae and leads to their destruction.
The causes of development and provoking factors of the disease are well known:
- Traumatization. Violations develop against the background of fractures, bruises, severe concussions, and similar movements.
- Congenital anomalies of the structure of bone and connective tissue.
- Autoimmune connective tissue diseases (systemic collagenoses).
- Vascular lesions with impaired trophism of intervertebral discs.
Provoking factors are:
- excess weight;
- muscle diseases accompanied by atrophy;
- low physical activity;
- improper diet;
- forced stay in one position for a long time.
Pain from pinched nerve endings can vary in intensity, depending on the patient’s pain threshold and the degree of damage to the conductive fibers. It has a pressing, stabbing character, sometimes described as a lumbago. The duration also varies - from a couple of seconds to several days. It intensifies when turning or bending, during breathing movements or coughing. When palpating along the nerve, the problem significantly worsens. After taking analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs, relief occurs.
Many people wonder whether the heart can hurt with osteochondrosis.
This phenomenon occurs in two cases:
- Disruption of the functioning of the nerve endings of the myocardium, when the vegetative nodes are pinched or irritated by a disc that extends beyond the spine.
- Changes in the conduction of impulses in the upper chest and left arm. In this case, cardialgia occurs reflexively.
To understand how the heart hurts with osteochondrosis, you need to understand that the problem is purely neurological in nature, which resembles an attack of radiculitis. For this reason, taking Nitroglycerin does not help, but painkillers provide significant relief.
Risk factors
The main reason for the development of osteochondrosis is improper distribution of the load on the spine, which leads to changes in cartilage tissue in places of excess pressure.
At risk are people suffering from metabolic disorders, as well as various hormonal and vascular disorders, due to which there is a malfunction in the nutrition of the intervertebral discs.
The disease can also be provoked by: spinal injuries, lifting and carrying heavy objects, prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position.
If treatment for thoracic osteochondrosis is not started in time, it will inevitably be accompanied by intercostal neuralgia - compression or irritation of the intercostal nerves with constant severe pain. And then, quite possibly, surgical intervention will be required.
Article on the topic
Osteochondrosis pose. How to avoid spine problems
Heart diseases that need to be excluded
Diseases associated with cardiac dysfunction often manifest themselves in the same way as osteochondrosis. Since some pathologies are acute, and in a neglected state can lead to organ failure and even death of a person, they should be considered in more detail.
IHD
The pain from angina pectoris (“angina pectoris”) lasts 15 minutes. It can be relieved by taking Nitroglycerin and is of a pressing, burning nature. It is provoked by psycho-emotional stress, but can develop as a result of physical activity. It is localized behind the sternum, extends to the arm, under the shoulder blade, left side of the neck, jaw.
A heart attack is characterized by severe pain, sweating, pale skin, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, and shortness of breath develops. The duration of the episode ranges from 1-2 hours to several days. It is not relieved by anti-inflammatory drugs and Nitroglycerin; it causes fear in the patient (which is usually not observed even with severe exacerbation of osteochondrosis).
Pericarditis and myocarditis
With inflammation of the pericardium, the pain tends to increase and can last for several days. It is not relieved by nitrates and NSAIDs. Shortness of breath, cough, and tachycardia gradually develop. Unlike spinal lesions, when trying to assume a horizontal position the patient always experiences a worsening of the condition. You can read more about pericarditis and its symptoms here.
Myocarditis occurs against a background of general weakness: signs of the inflammatory process come first. The pain is often dull, aching, and cannot be relieved by taking painkillers. Tilting the body and turning the body does not change anything in the patient’s sensations.
VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia may resemble symptoms of osteochondrosis. Discomfort in the chest area and lack of air in this case occur both during exertion and at rest. Often an attack is preceded by a stressful situation. Improvement occurs after taking sedatives, or the pain goes away on its own, without any treatment. Often observed in people with a labile nervous system. At the same time, with this pathology, sleep disturbance, irritability, decreased performance, and dependence on weather conditions are noted.
What is VSD and how to live with it: the video at the link below will help you get rid of unnecessary medications and false predictions.
Thromboembolism and aortic aneurysm
When a pulmonary artery is blocked by a thrombus, the symptoms depend on the size of the lumen of the vessel excluded from the circulation. Often the pain resembles angina pectoris or a heart attack with typical irradiation in this case; less pronounced suffering can simulate a herniated nerve being pinched in the spinal column. But the difference from osteochondrosis is the ineffectiveness of anti-inflammatory therapy and accompanying symptoms (bulging neck veins, pallor, tendency to faint).
Acute and unbearable pain is often the main and main symptom of dissecting aortic aneurysm. It arises behind the sternum, spreads to the back, and can radiate to the abdomen and lower extremities, depending on the location of the lesion. Its intensity is not reduced by taking analgesics or NSAIDs, or by rest.
Check yourself!
Determining what kind of pain arose in the left side of the chest is quite simple. With osteochondrosis, the pain usually does not go away for hours. What about hours - weeks and months! At the same time, it either intensifies for 1–3 days, then subsides.
With angina pectoris, the heart pain is short-lived and goes away after 3-5 minutes, especially when taking nitroglycerin. Moreover, it is in no way connected with physical activity, but makes itself felt when taking a deep breath, making sharp turns or changing body position.
But most importantly, if neurological pain is temporarily relieved by analgesics, then for heart patients these drugs are like a poultice for the dead. However, long-term use of analgesics can lead to the development of drug-induced gastritis and even gastric ulcers, so you should not abuse them.
Ointments containing bee or snake venom have a very good effect. They perfectly relax muscles and increase the elasticity of ligaments. After applying the ointment, the chest should be bandaged with a large towel or woolen scarf. Muscle relaxants are prescribed to relax spasmed muscles. In especially severe cases, novocaine or lidocaine blockades are used.
How to recognize the source of pain
When going to see a doctor, I recommend listening to your feelings and answering the following questions:
- how severe the pain is;
- how long does it last;
- what triggered the onset of the attack;
- how can you describe the feeling;
- where does it give;
- after which it becomes stronger;
- what drugs alleviate the condition.
Intensity and duration
How to recognize cardiac problems and distinguish them from osteochondrosis? Prolonged discomfort characterizes advanced destructive changes in the spine, but can occur with inflammation of the heart muscle and pericardium, with blockage of the pulmonary artery, or in the event of a heart attack. Therefore, using these symptoms it is not always possible to determine a preliminary diagnosis. You should pay attention to provoking factors. If the condition worsens after a sharp lifting of a heavy object, as a result of hypothermia or prolonged stay in one position, then this is osteochondrosis. Sudden severe chest pain is a sign of pulmonary embolism, acute aortic aneurysm, or heart attack.
Psycho-emotional stress or a sharp change in temperature often provokes angina pectoris.
Irradiation
Irradiation during angina or heart attack in the classic version is observed on the left: it radiates to the arm, lower jaw, under the shoulder blade, to the neck. But I often saw the same symptoms during exacerbation of osteochondrosis. Therefore, detailed complaints are needed.
If the problem goes away after taking a horizontal position or taking painkillers, cardiac pathology is excluded. But the occurrence of a burning sensation simultaneously with sweating, fear of death, and some relief in a sitting position indicates IHD.
Surveys
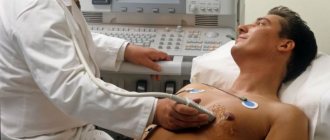
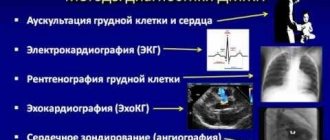
The diagnostic standard here is an electrocardiogram. I always refer patients with chest pain for an ECG, as the most important thing is to rule out cardiac pathology. If necessary, coronary angiography must be done; it helps to clarify the presence and degree of narrowing of the coronary vessels. You can read in detail about the signs of angina on film here.
X-rays can provide some information about changes. To clarify the location of the lesion in the spine and the degree of osteochondrosis, MRI or CT is used. A layer-by-layer image helps to reliably identify all problems with the vertebral bodies and discs between them.
Effective treatment of symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
You can often cope with the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis at home. Many people “save” themselves, without doctors, with over-the-counter painkillers and painkillers, and by applying heat.
However, self-medication is only a temporary reduction in symptoms, and if done incorrectly, the problem can only worsen. During an exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, gymnastics and massage are contraindicated. On the contrary, at this time you should try to unload the spinal muscles as much as possible.
An experienced neurologist will correctly assess your condition and prescribe treatment that will help. The symptoms described in this article do not always indicate thoracic osteochondrosis; competent differential diagnosis is often necessary.
Visit a specialist. The neurological center of the multidisciplinary international clinic Medica24 employs experienced neurologists, uses modern diagnostic equipment, and treats diseases in accordance with the principles of evidence-based medicine. Clinic administrators are on duty at the telephone around the clock, call at any time.
We will call you back
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
The causes of thoracic osteochondrosis are not fully understood, and in general, this disease raises a large number of questions for many doctors. Some even argue that such a disease does not actually exist, and its manifestations are usually caused by completely different pathologies. By the way, in English-speaking medicine this term refers to completely different diseases.
How to relieve pain
To relieve pain in osteochondrosis, the following are used:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac).
- Muscle relaxants (“Mydocalm”).
- Blockades with Novocaine or Lidocaine.
- Physiotherapy (electrophoresis, iontophoresis).
- Spinal traction.
- Wearing a corset.
After the acute condition is relieved, the patient is recommended to undergo a massage course. Sometimes manual therapy helps, but you should be careful here, since it must be carried out by a very experienced specialist. Performing physical therapy exercises allows you to consolidate the results.
To relieve pain due to cardiac pathology, the following are used:
- Nitrates for vasodilation (“Nitroglycerin”).
- “Aspirin” if a heart attack is suspected and narcotic analgesics if it is confirmed.
Expert advice
If there is severe pain behind the sternum, which radiates to the arm, under the shoulder blade and is accompanied by shortness of breath, I advise you not to panic.
You need to sit or lie down and try to relax. If it does not go away after taking Nitroglycerin, Validol or Corvalol, you need to call an ambulance - it could be a heart attack. A few words about osteochondrosis: destructive changes in the spine cannot be cured. But it is quite possible to significantly improve the quality of life and slow down the progression of the disease for many years. To do this I recommend doing the following:
- When sitting, you should choose a hard chair. Your back should rest completely on it.
- If the work involves a forced monotonous position, you should do a light warm-up every 2-3 hours.
- When reading, you need to use a book stand to prevent your head from tilting down.
- Play sports (swimming is best for the spine).
What diseases can cause symptoms resembling thoracic osteochondrosis?
The diagnosis of “osteochondrosis” is not always made justifiably; even the doctor cannot always figure out what is happening to the patient. Back pain often occurs due to other diseases:
- Myofascial pain syndrome. A common condition in which pain occurs as a result of constant spasm of the back muscles.
- Herniated intervertebral discs. They are rare in the thoracic region, but can also be the main cause of pain between the shoulder blades and neurological disorders.
- Injuries. If the injury was relatively mild - for example, a soft tissue bruise, a muscle strain - the symptoms of “osteochondrosis” bother you for some time and then go away on their own, even if no treatment has been carried out. Pain can also be caused by more serious injuries - for example, a compression fracture, vertebral subluxation.
In order to correctly understand the causes of back problems, the patient must be examined by an experienced doctor and a full examination must be carried out. All this can be done at the medical center International Clinic Medica24. In our clinic, high-quality medical care is available around the clock; you can contact the administrator at any time, including holidays and weekends, by calling +7 (495) 230-00-01.
Get a consultation with a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
When the manifestations of “osteochondrosis” begin to bother you, you need to carry out a correct, comprehensive diagnosis and understand the true causes of the symptoms that have arisen. They are not always located in the spine itself. This helps to prescribe the appropriate treatment and deal with the problem as quickly and effectively as possible.
At the Medica24 international clinic, you will be examined by an experienced neurologist, and you will be prescribed all the necessary diagnostic methods.
Clinical case
A 29-year-old patient came to the consultation with complaints of severe pain in the heart.
There is no history of congenital cardiac pathology. A feeling of pressure and burning arose during strength training. The ECG showed no abnormalities; upon palpation, increased pain was noted near the 4-5 vertebrae in the thoracic segment and along the intercostal nerve on the left. X-rays revealed curvature and deformation of the thoracic region, as well as indirect signs of osteochondrosis. He refused an MRI. I took treatment: Diclofenac, Mydocalm. After two weeks of therapy, improvement was noted and the pain stopped. Recommended: reducing stress, a course of massage and physical therapy.
Five steps from osteochondrosis
- Walk 1.5–2 hours a day in the fresh air and perform special exercises that ensure normal mobility of all parts of the thoracic spine (see the following issues of the weekly “AiF. Health”).
- Sleep on a flat, semi-rigid surface that prevents your body from sagging. The thickness of the pillow should be no more, and preferably less than 10 centimeters.
- Sit on a chair with a backrest with a straight back, pressing your lumbar region against the back of the chair.
- Lift weights carefully - with a straight back, slowly straightening your bent legs. When carrying heavy objects, distribute the load evenly between both hands.
- Eat rationally, following a diet with a complete protein content, which is a building material for the spine. First of all, these are animal proteins, beans, peas, beans, and soy. It is also worth including fish products in your daily diet, as well as a sufficient amount of fresh vegetables and fruits.