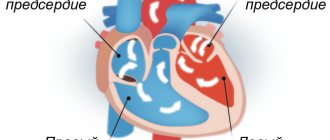
Open oval window - what is it?
Due to increased blood pressure in the left atrium (the pressure is lower in the right atrium), the oval window valve closes tightly.
Over time, it becomes overgrown with connective tissue. However, there are situations when the hole between the right and left atria closes partially or does not close at all. Then, when sneezing, coughing, screaming, or significant tension in the anterior abdominal wall, blood is thrown through it from the right chamber to the left. If such a pathology is detected, the patient is diagnosed with an open oval window.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
The famous pediatrician and TV presenter, Evgeniy Olegovich Komarovsky, claims that a window in the heart is characteristic of virtually all newborns. In every second case it does not heal until 2 years. Closer to 5 years, the anomaly mostly disappears without causing any harm to the child. The doctor also emphasizes that a hole in the septum is not a life-threatening defect. It is considered an individual developmental feature, and in most cases it closes without the intervention of doctors.
Causes of an open oval window in the heart in newborns and adults
The reasons why the oval window does not close completely are still not clear. It is believed that the occurrence of the disease is contributed to by:
- prematurity;
- hereditary predisposition;
- connective tissue dysplasia;
- Congenital heart defect;
- drinking alcohol and smoking during pregnancy;
- the impact of unfavorable environmental factors on the expectant mother’s body.
Also, due to genetic factors, the size of the valve may be smaller than the diameter of the oval opening. Then complete closure of the oval window in the child’s heart becomes impossible.
It has been noted that the pathology accompanies:
- defects of the tricuspid and mitral valves;
- open ductus arteriosus.
An open foramen ovale in the heart can form in athletes due to severe physical exertion. Thus, persons involved in athletic gymnastics, wrestling, and weightlifting are at risk. The disease is especially common among divers and divers who regularly dive to great depths.
In patients with thrombophlebitis of the pelvis or lower extremities with a history of episodes of pulmonary embolism, pressure in the right side of the heart increases due to contraction of the vascular bed of the lungs. As a result, a functioning open oval window is formed.
In other words, the disease is not necessarily congenital. It can develop due to exposure to adverse factors on the body.
How to treat pathology?
Drug therapy does not provide a 100% cure for the disease. No medicine can remove the cavity formed in the heart. The drugs are intended only to minimize the manifestation of symptoms of VSD (shortness of breath, pallor, nosebleeds). In addition, drug therapy reduces the risk of complications after surgery, if one is required.
Below is a list of medications used as part of complex therapy for VSD:
- regulators of muscle heart rate (Digoxin and beta blockers - Inderal and Anaprilin);
- blood clotting regulators (Aspirin, Warfarin).
Surgery for VSD is necessary only in extreme cases. According to Dr. Komarovsky, the need for operations of this kind arises very rarely. However, many pediatricians recommend surgery in childhood to prevent possible exacerbations in adulthood. The advisability of surgical intervention is decided in each case individually.
Advertising:
- Cardiac catheterization is the most common and least traumatic method of surgery. The catheter is inserted into the defect site through the patient's femoral vein. A mesh patch is attached to the end of the boat, with the help of which the defect is closed. It is performed under local anesthesia.
- Open surgery. It is considered a more aggressive method, requires long rehabilitation and is associated with risks of complications. In open surgery, the surgeon makes an incision into the heart and places a synthetic patch into the cavity of the interventricular septum. It is performed under general anesthesia.
A video will tell you about the surgical treatment of VSD in infants.
Symptoms of the defect
A patent foramen ovale is a heart defect that has no specific external manifestations. Usually the disease occurs in a latent form. Sometimes accompanied by scant symptoms.
Indirect signs of the disease include:
- cyanosis and severe pallor of the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle, lips (the symptom becomes noticeable when crying, screaming, straining, coughing, while bathing);
- child's lagging behind in physical development (low weight gain, poor appetite);
- tendency to bronchopulmonary and colds;
- increased fatigue when performing physical work;
- respiratory failure that occurs when running, walking, or physical labor;
- signs of impaired cerebral circulation;
- sudden fainting;
- migraine, frequent headaches;
- postural hypoxemia syndrome.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Course of therapy
Treatment of an abnormal window in the heart muscle, which does not manifest itself with a characteristic clinical picture and does not contribute to the development of complications, is usually not carried out. The doctor will only give the following recommendations:
- Engage in physical therapy to strengthen the heart muscle and keep the body in good shape.
- Rest more, taking breaks at work every hour (5-10 minutes) and observing a sleep schedule (sleep at least 7-8 hours).
- Avoid conflicts and stressful situations. It is advisable for the patient to devote more time to hobbies and listen to his favorite music in order to relax and not overstrain the heart.
- Competently create a diet, removing fatty foods from it and filling it with vegetables and fruits. It is necessary to cook by steaming or boiling, and eat small portions 5-6 times a day.
If the patient complains of attacks of tachycardia and other disorders of the cardiovascular system, the doctor may advise combining the above measures with drug treatment. It is based on taking pills to stabilize the condition:
- Antiarrhythmic medications (sodium, calcium and adrenaline blockers, cardiac glycosides, diuretics, sedatives) intended to eliminate arrhythmia.
- Vitamin complexes based on magnesium, potassium and B vitamins (Panangin, Magne B6) improve the condition of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Surgical intervention is possible only in the case of a pronounced clinical picture, which significantly reduces the patient’s quality of life. It is no less relevant if there is a high chance of blood clots. The specialist will recommend endovascular treatment. Its essence is to insert a catheter into the femoral artery. Next, it is advanced into the right atrium and a special patch is applied to the hole, which stimulates the area to become overgrown with connective tissue. After 3-4 weeks it will resolve on its own without repeated intervention.
The operation must be combined with the use of antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants to reduce the risk of blood clots. During the recovery period, the patient should undergo antibacterial therapy to prevent the development of myocarditis. A successful surgical intervention will allow the patient to live without any restrictions, since the anomaly will be completely eliminated.
Diagnosis of the disease in children and adults
Diagnosis of the disease includes the following procedures:
- Analysis of the patient's medical history. During a conversation with the patient, the doctor finds out whether he suffers from dizziness, fainting, low endurance for physical activity, cyanosis of the extremities, and colds. It is also clarified whether there is a hereditary predisposition to diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Skin examination, blood pressure measurement, weighing, auscultation.
- General blood and urine analysis, coagulogram (blood test for clotting), blood biochemistry.
- Ultrasound of the heart.
- Electrocardiography.
- Echocardiography, Dopplerography (aimed at determining the presence of a hole in the interatrial septum, studying the direction of blood movement through the heart and determining the volume of blood passing through the defect).
- Contrast echocardiography (makes it possible to detect an open oval window even of a small size). During the examination, the patient is given shaken saline solution intravenously. If he has an open foramen ovale, then small air bubbles almost immediately pass through it from the right atrium to the left.
- Transesophageal echocardiography (to identify the hole in the septum of the heart and the patent foramen ovale valve, a probe equipped with an ultrasound sensor at the end is inserted into the esophagus).
- Chest X-ray.
Diagnostics
Ultrasound of the heart is of primary clinical significance. The doctor clearly sees a small hole in the projection of the left atrium, as well as the direction of blood flow.
When listening to a heart murmur, the pediatrician will definitely refer your baby for this type of examination.
According to new standards, at 1 month all newborns must undergo ultrasound screening, including the heart.
As a rule, there are no pathological changes on the ECG with LLC.
Treatment of open oval window
Children and adults diagnosed with a patent foramen ovale should follow non-drug measures:
- Limit physical stress.
- Sleep at least 8 hours a day (children should sleep 10-12 hours).
- Maintaining a daily routine.
- Balanced diet.
- Taking vitamins.
If there are no symptoms of a patent oval window, there is no need for specific treatment. If signs of illness appear, a high risk of blood clots, or significant discharge of blood from one atrium to another (this does not normally occur), the cardiologist may recommend the patient:
- Take anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents - medications that prevent the formation of blood clots (thrombi).
- Perform endovascular treatment of an existing open foramen ovale. A tube (catheter) is inserted into the artery, at the end of which there is an occluder. Getting into the oval window, it completely clogs it. Surgical intervention is performed under X-ray and echocardioscopic control.
Army
Examination of conscripts with an open foramen ovale is carried out according to Article 42 of the Schedule of Diseases. The presence of an open foramen ovale, even without bleeding, according to government decree, allows a conscript to be classified in category B4, when military service is possible but in military units where there is no serious physical activity and, accordingly, high health requirements are not required. If there is a discharge of blood with an open oval window, then the young man is assigned category B, and he is exempt from military service.
Sources:
- Preetham Kumar. The Connection Between Patent Foramen Ovale and Migraine, - data from the US National Library of Medicine PubMed, 2019.
- Sharykin A.S. Clinical observation of an increase in the diameter of the patent foramen ovale in adolescence, Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2013.
- Brian H West. Relation of Patent Foramen Ovale to Acute Mountain Sickness, - US National Library of Medicine PubMed, 2021.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 4, 2013 N 565 (as amended on June 1, 2020) “On approval of the Regulations on military medical examination”
Why is an open oval window dangerous?
For newborns, an open oval window is considered normal. If it does not heal and persists into adulthood, serious health problems may arise:
- Kidney infarction (the organ dies due to impaired blood supply).
- Myocardial infarction (heart muscle tissue dies due to the fact that the required amount of blood does not flow into it).
- Stroke (cerebral circulation disorder causes damage to brain tissue).
- Transient disturbance of cerebral blood supply (due to a disturbance in the blood supply to certain structures of the brain, there is a temporary disruption of its activity).
Complications
They are quite rare. Associated with embolism and impaired blood flow. These are heart attacks, strokes and kidney infarctions.
These complications can already occur in adults. And such a patient should always warn the doctor that he has a functioning foramen ovale.
Minor heart anomalies for the most part do not harm the health of children. Some famous athletes have this pathology and become Olympic champions. Many doctors consider LLC normal. But it should be remembered that annual supervision by a specialist is necessary.
Prevention
There is no special prevention for an open oval window. To prevent pathology from occurring in newborns, during pregnancy a woman should lead a healthy lifestyle, give up alcohol and smoking. She also needs to avoid contact with:
- chemicals (paints, varnish vapors, some medications);
- ionizing radiation (thermonuclear reactions, X-ray machine);
- patients with infectious diseases (if infected with rubella in the first trimester, the risk of heart disease in a child increases significantly).
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Possible consequences and treatment
People with an LLC have fairly favorable prognoses for the future.
To avoid the development of complications, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- periodically undergo a medical examination by specialists, which includes an echocardiogram;
- limiting heavy physical activity;
- engaging in professional activities that do not involve heavy physical exertion or nervous strain;
- Avoid extreme sports.
If the pathology is not accompanied by symptoms and does not affect the normal state of health and life of the child, it is not recommended to carry out any treatment.
In the same case, when the closing valve does not completely close the oval window, which leads to the development of diseases such as stroke, coronary heart disease or heart failure in the child, experts give preference to a preventive course of treatment.
Its main focus is the prevention of thromboembolic complications.
For this, Aspirin or Warfarin is usually used.
Surgical treatment is resorted to only if the blood discharge reaches a large volume. As a rule, a low-traumatic operation, X-ray endovascular occlusion of the LLC, is performed.
If the pathology of the open oval window is detected in a timely manner, as well as if all recommendations of specialists are followed, this anomaly does not pose any threat to the child’s life.
I just found good information on the Internet. Now this diagnosis is made by 80% of children, and up to two years of age it is normal and is considered a minor anomaly of heart development.
“YOUR CHILD HAS AN OPEN FORANA OVAL” - this diagnosis is heard today by about 80% of parents some time after the birth of the child. WHAT IS AN OPEN OVAL WINDOW?
oval, arterial and venous. The foramen ovale is located between the right and left atria, and blood passes through it, bypassing the lungs. The blood entering through the open oval window nourishes, first of all, the brachiocephalic region, ensuring rapid development of the brain. After birth, with the baby’s first breath, the pulmonary circulation begins to function.
Due to the increase in incoming blood, the pressure in the left atrium increases, and the oval foramen closes with a special valve, like a door. This functional closure occurs in the first 3-5 hours of life, and complete anatomical closure, due to the fusion of the edges of the valve flap and the edges of the hole, in 2-12 months. Sometimes the overgrowth process lasts up to two years, which is also considered normal. ☆☆☆
But this does not happen for everyone. The foramen ovale can close in utero, which leads to overload of the right parts of the heart and simultaneous underdevelopment of the left ones. A child in such a situation dies either in utero or in the first hours of life.
In some children, the hole does not close completely, or does not close at all. This often happens in premature babies, and there is also an opinion that it occurs in those children whose mothers abused alcohol or smoked. Due to genetics, the flap that closes the window may be slightly smaller than the hole and may not be able to completely cover it.
Some diseases accompanied by increased pressure in the right side of the heart can contribute to non-closure of the foramen ovale, which serves as a compensatory message. The right parts of the heart are unloaded, which improves the patient’s condition. Such situations arise with primary and secondary pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary stenosis, abnormal drainage of the pulmonary veins, and tricuspid valve defects.
In most cases, the presence of a patent oval window does not cause serious concern. Due to the fact that the pressure in the left atrium is slightly higher than in the right, the valve between the atria is kept closed, which prevents the discharge of blood from the right atrium to the left. This usually happens with small hole sizes: up to 5-7 mm.
In newborns, a temporary increase in pressure in the right atrium may occur against the background of crying, straining, and prolonged anxiety. This is accompanied by the discharge of venous blood through the foramen ovale and is manifested by short-term cyanosis (blue). In older children, blood discharge may occur during paroxysmal coughing, diving, or exercises accompanied by straining and holding their breath.
With large sizes of the foramen ovale (more than 7-10 mm), disturbances characteristic of an atrial septal defect occur. This open oval window is called a “gaping” window. The child should be consulted by a cardiac surgeon to decide on surgical correction. Recently, closure of the defect through the femoral vein using a special device - OCCLUDER - has been more often used.
One of the most severe complications that arises against the background of a functioning open oval window is paradoxical embolism. Emboli, blood clots, gas bubbles, pieces of tumor, foreign bodies, from the right atrium to the left, and continuing their journey further, can reach the vessels of the brain and cause a stroke, or be localized in any other organ with the development of thrombosis and heart attacks.
A patent foramen ovale is not considered a heart defect. It is rather classified as MARS (minor anomalies of cardiac development). Many people, having such an anomaly, lead a normal human lifestyle, living peacefully into old age. Sometimes, in older children with a hemodynamically significant PFO, there is fatigue and shortness of breath during physical exertion, pallor, slight cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, and less often, a tendency to faint.
The main method for diagnosing PFO is echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart). It is better if the device on which the study is carried out has a color Doppler cardiography attachment. This will allow you to see the presence of even a small discharge of blood through the open oval window.
The presence of PFO in children under 2 years of age is normal and, in the absence of other heart diseases, should not be a cause for concern. If the window has not closed after 2 years, this is also no reason to panic. Regular visits to the cardiologist and periodic repetition of heart ultrasound will help parents not let the situation get out of control and monitor the size of the hole. In a certain percentage of children, it nevertheless heals completely. If this does not happen, you need to decide with your doctor what to do next.
★★★★★★★In general, the main thing is what size it is and whether it will be overgrown by the age of 2 years. Beware of coughing and physical exertion - that’s what I understand.
The oval window in the heart is a hole developed in utero, covered with a special fold-valve, which is located on the septum between the atria. This window communicates between the right and left atria of the fetus during the embryonic period. Thanks to it, part of the oxygenated placental blood can flow from the right atrium to the left, bypassing the non-functioning lungs of the unborn baby. This ensures normal blood supply to the head, neck, brain and spinal cord.
During the first breath, the child’s lungs and pulmonary circulation begin to function, and the need for communication between the right and left atria loses its relevance. When the baby inhales and first cries, the pressure created in the left atrium becomes higher than in the right, and, in most cases, the valve slams and closes the oval window.
The oval window in 40-50% of full-term healthy newborns is anatomically closed by a valve already in the first 2-12 months of life, and its functional closure occurs at 2-5 hours of life. Sometimes it remains partially open or, under certain conditions (valve defect, severe crying, screaming, tension in the anterior abdominal wall, etc.)
) does not close. The presence of a patent foramen ovale after 1-2 years is considered a minor anomaly of cardiac development (MARS syndrome). In some cases, the oval window can close at any other time and completely spontaneously. Among adults, it is observed in 15-20% of cases. This prevalence of this anomaly has become an urgent problem for cardiology and requires monitoring.
The exact reasons that the oval window does not close on time are unknown to modern medicine, but, according to some studies, the presence of this anomaly can be provoked by a number of predisposing factors:
- heredity;
- infectious diseases of the mother during pregnancy;
- smoking and alcohol abuse on the part of the mother or father;
- parental drug addiction;
- maternal phenylketonuria or diabetes mellitus;
- taking certain medications during pregnancy (some antibiotics, lithium preparations, phenobarbital, insulin, etc.);
- prematurity of the child;
- connective tissue dysplasia, etc.