What is a heart murmur and how does it happen?
Thanks to the work of the cardiovascular system, tissues and organs receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen.
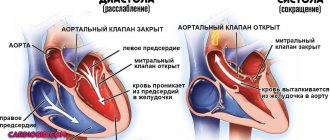
After birth, a significant restructuring of blood circulation in the pulmonary vessels occurs in the child’s body, the dominant of the right ventricle is replaced by the left, physiological closure of the ductus arteriosus is observed, and the pressure in the pulmonary trunk increases to facilitate the work of the left ventricle. Such changes cause cardiac murmurs. During the examination, the doctor conducts auscultation using a phonendoscope, listening to the heart valves in turn:
- mitral;
- aortic;
- pulmonary valve;
- tricuspid valve.
The auscultation method helps to assess the frequency and rhythm of tones, their melody and timbre.
How to prevent problems?
A timely ultrasound of a child’s heart is an opportunity to diagnose the disease at an early stage and begin timely treatment. You should not engage in “self-medication”, since some medications can only relieve symptoms and pain, but the problem itself will remain, and the disease will progress.
On the official website of the Heratsi Medical Center, you can make an appointment with an experienced cardiologist who will be able to recognize the problem,, if necessary, prescribe additional tests and draw up a treatment plan that will be aimed at eliminating the problem, and not relieving symptoms. For additional information and answers to any questions, the medical center’s 24-hour telephone number is 8-863-333-20-11.
Causes
The most common sources of heart murmurs in a child are associated with impaired blood flow and the occurrence of turbulence in the supravalvular aorta, pulmonary trunk or organ cavities. The causes of this hemodynamic disorder are a defect in the valve apparatus or septum, vascular aneurysm, decreased blood viscosity due to anemia, and the following cases:
- if the child is premature, the source of the noise is an insufficiently formed heart, incomplete closure of the aortic duct after birth;
- when a soft systolic murmur is heard in the first three days after birth, this indicates anatomical obstruction of the ventricular outlets, which requires daily monitoring over time;
- mixed systolic-diastolic murmur often occurs when the aortic duct is incompletely closed, which closes upon completion of the transition from fetal blood flow after birth;
- the most common cause of heart murmur in a newborn is a patent aortic duct (the turbulence is quiet, blowing, more audible between the second and first heart sounds);
- listening to murmurs in a child during systole is convenient on the third or fourth day in case of cardiomyopathy and impaired transitional circulation, the formation of a pathological shunt from the right side of the heart to the left and vice versa;
- the main sign of pathology of the cardiovascular system and congenital valve defects is hemodynamic disturbances, cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin), arterial hypoxemia and decreased saturation (oxygen saturation in the blood) less than 75%;
- in older children, the source of noise is a past illness, cold, sore throat or acute respiratory viral infection. As a result, the inflammatory process and bacterial culture provoke damage to the heart valves, endocarditis (inflammation of the endocardium);
- If a child is over five years old and a murmur is heard during auscultation, the cause is often an anomaly of the left ventricle, an accessory chord, which can only be detected by ultrasound of the heart. When there is no hemodynamic disturbance, treatment is not required.
Unlike pathological noise, functional noise is always heard during systole, it is less intense. In newborns, auscultation reveals a greater spread of vortices beyond the boundaries of the heart. If the child does not have a rapid heartbeat, cyanosis or signs of heart failure, then such a noise is not dangerous, but requires observation. It is enough to have an assessment of functional noise over time, recording cardiogram data, and ultrasound of the heart.
What do parents need to remember?
In order for a child to have a healthy heart, it is necessary to carefully monitor his daily routine, nutrition, general health and correctly distribute loads. Psycho-emotional as well. The heart does not need increased stress, but the child must train his heart, that is, lead an active lifestyle: spend enough time outside, regularly be in nature, and play sports. In your diet, you need to pay attention to complete proteins (meat, fish, cottage cheese, eggs), because the heart is a muscle like all the others, and it needs to be nourished. Fresh fruits and vegetables, as well as dried fruits rich in potassium and magnesium, and decoctions from them are useful. Be careful and do not trigger foci of chronic infection in a child: even the notorious caries that is not cured in time can reduce immunity and trigger a mechanism that indirectly “backfires” on the functioning of the heart. Therefore, regularly take your child for routine examinations not only with a cardiologist and neurologist, but also with other specialized specialists, to whom your local pediatrician will give you a referral.
Olga Chubukova-Reutskaya
The Right Action
The basis for the prevention of heart disease in children is compliance with regular medical examinations by a neonatologist and pediatrician according to the following algorithm:
- The primary examination is carried out by a neonatologist in the maternity hospital, when he evaluates cardiac activity using auscultation.
- Screening to diagnose congenital heart defects is done if murmurs are observed in the organ.
- Based on saturation data and ultrasound of the heart, the doctor confirms or removes the diagnosis.
- After discharge from the maternity hospital, the child is supervised at home by a general practitioner for up to a month. Normally, after the third or fourth week, the venous duct closes and the circulatory system begins to fully function. A medical examination helps to identify the slightest deviation from the norm, diagnosing murmurs in newborns.
- Particularly important is the child's infancy (infant up to one year), when the complete restructuring of blood circulation is completed and the doctor makes a conclusion about the nature of the noise.
- Blueness of the skin is the main symptom of hemodynamic disturbances. In combination with severe weakness, dizziness and low hemoglobin - these are indications for examination.
- In addition to auscultation, all children with signs of a heart murmur should be referred for phonocardiography, echocardiography, ultrasound of the heart and great vessels.
- Refusal to examine and treat a child with a heart murmur leads to serious hemodynamic disturbances and heart failure. Regular examinations with a pediatrician help prevent the development of organ pathology.
Causes of heart murmurs in newborns and older children
The symptom occurs due to the structural features of the organ. Anatomical anomalies can be harmless, then the child quickly outgrows them. Such noises are called physiological, innocent or functional. They are provoked by:
- anemia;
- developmental features, uneven growth of blood vessels and heart;
- increased blood pressure caused by external circumstances, for example, fatigue, stress, illness, for example, acute respiratory infections;
- minor pathologies, for example, dysfunction of the papillary muscles, dystrophy or inflammation of the myocardium.
An alarming symptom is organic noise. They indicate a serious illness, congenital or acquired. The most common ailments:
- Congenital heart defect;
- acute myocarditis;
- open oval window;
- benign and malignant tumors;
- mitral valve prolapse.
With physiological noises, the child appears healthy. He feels good, is gaining weight normally, and plays willingly. If the noises are organic, the baby becomes quiet and lethargic. He avoids outdoor games, eats poorly, and loses weight. Sometimes a child lags behind his peers in development. When the baby moves actively, his lips and nails turn blue, his skin turns pale, and he sweats profusely. The child is choking, complaining of palpitations and dizziness. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
Development factors
A special place is occupied by a persistent increase in blood pressure. With FKP, they attach importance to figures of more than 140/90 mmHg. If the cause of such manifestations is not cardiac pathology, then other forms may develop. More often, signs of hypertrophic or dilated cardiomyopathy appear.
With a significant increase in pressure, the load on the myocardium and blood vessels increases. The walls lose their former elasticity, and over time the process of blood circulation becomes difficult.
All heart cells are rich in various proteins. If there is a defect in any of them, the work of the muscle walls changes. If the examination fails to establish the exact cause of the symptoms, then they are inclined to think of a genetic predisposition to cardiomyopathy.
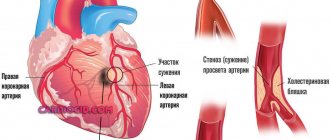
With oxygen deficiency in tissues, ischemia gradually develops. In most patients, the disorder occurs due to pathology of the arteries of the heart. Older people are prone to atherosclerosis. The lumen of the vascular walls narrows due to the deposition of cholesterol.
Pathology becomes a predisposing factor for the development of functional cardiopathy. Age over 50 years, smoking, obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure are important.
Pathology appears not only in children and older people. Pregnant women, being in the third period, or in the first months after childbirth, are also at risk of getting sick. This is due to hormonal changes and temporary changes in hemodynamics.
Normally, women have an increase in circulating blood volume. Additionally, stress and blood pressure affect the body. When a newborn baby is born, secondary cardiopathy occurs. They are reversible. Timely treatment of diseases that cause symptoms leads to restoration of health.
Forecast
In the case of functional noise, the prognosis is always favorable. This is not a disease or a manifestation of a pathological process. There are no disturbances in the activity of cardiac structures or hemodynamic problems.
Outside of organic disorders, anatomical defects are also positive. It is possible to achieve complete recovery in 90-95% of cases.
Compensated defects (not all) can be cured in 80% of situations by surgical methods.
In the most severe cases, the survival rate is 30-40%, which is still quite high. The main thing that parents need to remember is that they should closely monitor the child’s well-being and, if necessary, urgently contact a cardiologist for a full diagnosis.
Etiology
The causes of heart problems in children are conventionally divided into large subgroups. Let's look at each one separately.
Mother's side
If during pregnancy a woman has suffered from rubella, systemic lupus erythematosus, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, if she has diabetes mellitus or other chronic diseases, then all this is reflected in the fetus.
The list of approved drugs for pregnant women is strictly limited; most antibiotics, warfarin and other drugs (they are called teratogenic) are too toxic for the fetus. Taking them increases the risk of spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) or various abnormalities in the development of the child.
Drinking alcohol, smoking and using drugs during pregnancy also leads to congenital pathologies in children.
Genetic disorders
Most often these are chromosomal abnormalities. But genetic predisposition and mutations are not considered the only cause of cardiac pathologies. In 90% of cases, the cause of heart problems is multifactorial.
Bad habits
We have already talked about how the state of the mother’s body affects children. But the risk factors for developing heart problems in children are similar to those in adults:
- Smoking;
- Alcohol;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Narcotic substances;
- Stress;
- Infections;
- High cholesterol levels.
This list is more relevant for teenagers 14-17 years old than for kids. However, we must understand that nicotine and ethanol metabolism products destroy the myocardium and vascular wall in a child in the same way as in an adult. “Pampering” behind garages can result in a heart attack at age 30.
Statistics show that over the last decade the percentage of children with excess body weight has increased, which also negatively affects the heart. Myocardial infarction, due to obesity and other risk factors, has become “younger” and is already occurring in girls and boys aged 20-30 years, which was considered casuistry back in the 2000s.
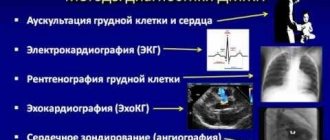
Diagnostics
- Electrocardiography (ECG).
- Chest X-ray.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the heart.
- Echocardiography. At the moment, it is the most informative and safest diagnostic method, allowing one to determine pathology with high accuracy. In this study, the doctor observes not only a three-dimensional picture of the heart, but also monitors the pressure in the chambers and the speed of blood movement in them.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT).
- Angiocardiography is the study of the condition of the heart vessels.
- Blood tests. Depending on the type and method of taking and testing blood, other diseases that negatively affect the functioning of the heart can be diagnosed. Infections, kidney and immune system diseases are detected in this way.
Treatment
Therapy depends entirely on the specific nosology. Infectious endocarditis and pericarditis are treated with drugs, but tumors or defects require surgical intervention, otherwise the child will grow, and with it pathological holes (or neoplasms) in the organ, which will lead to death.
Conservative treatment
Non-drug methods are recommended for all patients with a predisposition to or presence of cardiac problems. They include:
- normalization of work and rest regimes;
- 8 hours sleep;
- regular moderate physical activity;
- control of salt intake;
- weight loss (if you are overweight);
- avoiding alcohol and smoking;
- changing your diet towards proper nutrition.
Specific drug therapy depends on the cause of cardiac dysfunction. Main groups of drugs:
- Antibiotics (for bacterial etiology);
- Antihypertensives (Beta blockers, diuretics, ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers dilate blood vessels to lower blood pressure);
- Cardiac glycosides (to restore cardiac conduction and contractility);
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (suppress inflammation);
- Immunosuppressors (for autoimmune processes), etc.
Surgery
The surgeon restores the heart rhythm by implanting a pacemaker. The batteries for it are changed every 5-7 years during repeated surgery.
All affected valves are replaced with artificial ones. In severe cases, a heart transplant is required.
Symptoms
A child who has heart problems may complain of:
- Chest pain (in the area of the heart, possibly radiating to the arm, hypochondrium, or armpit);
- Shortness of breath;
- Rapid heartbeat or noticeable pauses;
- Interruptions in heart function;
- Dizziness;
- Darkening of the eyes and fainting;
- Paleness or cyanosis (bluish coloration of the skin and mucous membranes);
- Acceleration of the pulse or its difference in the hands;
- Poor appetite and short stature;
- Frequent respiratory infections;
- Swelling and pulsation of neck vessels;
- High or low blood pressure;
- Chest deformation, etc.
Symptoms usually begin or worsen after exercise. At first, the child usually does not attach any importance to this, then his endurance begins to suffer, and his condition worsens, which becomes the reason for contacting a cardiologist.