GGT value
In the test forms, the enzyme gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase is defined as GGT (γ-glutamyl transferase) or GGTP (Gamma glutamyl transpeptidase). This enzyme takes part in the metabolism of amino acids in the body. It can be found in various organs, but most of all it is in the liver, kidneys, pancreas, bile ducts and spleen. It is located in the outer membranes of organs.
GGTP takes part in the process of building protein molecules and stimulates various biological reactions necessary for the functioning of the body. Therefore, the GGT enzyme is determined during a biochemical blood test along with indicators such as bilirubin, AlT, AsT, and alkaline phosphatase.
Attention should be paid to the level of the GGT enzyme when there are symptoms indicating inflammatory processes in the liver, but they are not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. For example, in the early stages of hepatitis. GGT is also of great importance in terms of monitoring the dynamics of the development of chronic diseases affecting the liver parenchyma.
Other possible reasons
Advertising:
Regular examinations and blood tests are recommended for anyone undergoing long-term treatment. Many tablets cause cytolysis (cell death) of the liver. This provokes the release of large amounts of liver enzymes into the blood. In women, this often happens when taking a course of estrogens and corticosteroids. The following gives the same effect:
- drugs for tuberculosis;
- a number of antibiotics, especially tetracyclines;
- barbiturates;
- neuroleptics;
- chemotherapy;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
For treatment, you should take a course of hepatoprotectors - Essentiale, Heptral. All poisons, including alcohol, have a toxic effect on the liver. In chronic alcoholism, the amount of the enzyme can always be increased, and even after quitting alcohol it does not return to normal immediately. Among the rarer reasons for the increase in gamma HT in women are:
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- acute pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- kidney tumors;
- myocardial infarction;
- heart failure.
In some cases, the enzyme is elevated in thyrotoxicosis - hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. All of these pathologies do not occur without additional symptoms and are easily identified during examination.
How the analysis is carried out, GGT norm indicators
To determine a person's GGT level, a blood sample will be required. It is taken in the morning, when the subject has not yet taken food, since after it enters the body, enzymes that can change the blood picture will be activated. It is important to abstain not only from food, but also from water.
The purity of the experiment is influenced by the incubation temperature of the sample, so you can see the temperature in degrees Celsius on the form. This makes it possible to distinguish normal indicators from pathological indicators obtained at different temperatures.
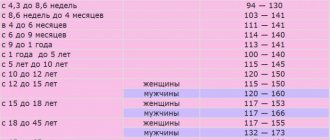
The norm values depend on the person’s age and gender. All of them are presented in the table.
| A person's age and gender | Normal value at a temperature of 37 °C Celsius in U/ I (U/l) |
|
|
|
|
| Newborns in the first 5 days of life | Up to 185 |
Children
|
|
It should be taken into account that in the conditions of one laboratory, the same reference values may be taken as normal indicators, and in the conditions of another laboratory – slightly different indicators. Therefore, the limits of the norm need to be clarified in each specific institution where blood was drawn. Although, as a rule, there is no significant discrepancy in these readings.
How to treat pathology?
Advertising:
As for medications that can normalize gamma HT levels, they should be prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the reasons for the increase in the enzyme. In other words, in order to reduce the concentration of the enzyme, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease, stop taking inducer medications or alcohol. Since an increase in gamma TG is most often associated with choletasis, Urdoxa, Ursosan, Urso, Ursofalk, as well as other drugs based on ursodeoxycholic acid are prescribed. In some cases, vitamin C can reduce gamma-GT levels.
Liver functions are improved by Essentiale, Livolin, Rezalut and other essential phospholipids. If the increase in gamma-GT is associated with stagnation of bile, Alahol, Hofitol and other choleretic drugs are recommended. Alkaline mineral waters can also be prescribed, which will help reduce the viscosity of bile and facilitate its removal.
For pain in the liver area, Besalol, Spasmolitin, No-shpa and other antispasmodics are prescribed.
Skin itching, which often accompanies bile stagnation, is well relieved by Rifampicin or Cholestriamine. The gamma GT test is a very sensitive test that gives the specialist more information than alkaline phosphatase, ALT and AST. Therefore, it is often used not only to assess a person’s health status, but also to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Increase and decrease in GGT
If a person experiences a decrease in the enzyme being studied, then this can indicate only one single condition - decompensated cirrhosis of the liver.
An increase in GGT, on the contrary, is observed against the background of various pathological conditions, including:
- Obstructive jaundice due to blockage of the bile ducts. The patient will also have elevated alkaline phosphatase and 5-nucleotidase levels.
- Cholecystitis.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Viral hepatitis in the acute stage. At the same time, ALT and AST levels will decrease.
- Compensated cirrhosis of the liver.
- Chronic hepatitis.
- Liver damage due to intoxication of the body, or due to its radiation.
- Liver cirrhosis caused by alcoholism.
- Fatty liver hepatosis.
- Cancerous lesions of the liver, or penetration into the organ of metastasis from a tumor of a different location.
- Amyloidosis and chronic glomerulonephritis.
- Myocardial infarction, starting from the 4th day of illness. The enzyme will reach its maximum values 2-3 weeks after a heart attack. The enzyme content in the blood increases due to the fact that the body launches mechanisms aimed at its own restoration.
- Alcohol abuse. After completely giving up alcohol, the indicators will return to normal, but this will not happen earlier than in 14-21 days.
- Taking Phenobarbital or Phenytoin to treat epilepsy.
- Taking Rafampicin for the treatment of tuberculosis.
- Taking hormonal contraceptives.
- Taking drugs that can have a damaging effect on the liver parenchyma: steroids, thiazide diuretics, antidepressants, cytostatics, anti-tuberculosis drugs, anticonvulsants, anabolics, thyreostatic drugs.
GGT increases due to damage to the liver parenchyma and bile ducts. A variety of factors that negatively affect the health of the organ can lead to a jump in the enzyme. Also, the level of GGT indicates the degree of alcoholic liver damage, as well as the course of chronic liver diseases.
How to detect an increase in gamma GT?
With a number of symptoms, one can suspect that the gamma-GT level in women is increased. Only a slight increase in it may not give a clinical picture. Typically, with all pathologies of the hepatobiliary system that accompany the growth of gamma-HT, there is stagnation of bile. This condition can manifest itself:
- jaundice of the skin, yellowing of the sclera;
- heaviness, pain in the liver area;
- sharp pain after eating;
- weakness, decreased performance.
Advertising:
No less often, the patient develops dyspeptic disorders - nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. Sometimes constipation occurs instead of diarrhea. Since even heart disease can be the cause of an increase in GGTP, they may be accompanied by chest pain, pallor, fainting, and shortness of breath.
Results
The liver is an intermediary between the gastrointestinal tract, which receives various substances, and the human body as a whole. The liver is the organ that is directly involved in metabolism.
Liver enzymes AlT, GGT, AST help it cope with various harmful substances, neutralizing them. While the liver is healthy, people do not try to help it maintain its normal condition. They begin to pay attention to the organ only after it is damaged to one degree or another. Until that point in time, a person poisons his liver for many years.
If liver tests and enzymes increase, you should think about the state of your health and continue the examination in order to try to eliminate the pathology in time.
Author of the article:
Shutov Maxim Evgenievich |
Hematologist Education: Graduated from Kursk State Medical University in 2013 and received a diploma in General Medicine. After 2 years, he completed his residency in the specialty “Oncology”. In 2021, she completed postgraduate studies at the National Medical and Surgical Center named after N.I. Pirogov. Our authors
What can lead to improved results, besides diseases?
Elevated gamma-glutamyltransferase levels can be caused by alcohol abuse on the eve of a blood test. It was also previously mentioned that some drugs can affect the results of the study, inflating the actual values.
Such medicines include:
- barbiturates;
- statins are a group of drugs used to lower blood cholesterol levels;
- antidepressants;
- some types of antibiotics;
- oral contraceptives and some other hormonal drugs;
- Aspirin, Paracetamol.
Also noted is the fact that in obese individuals the level of the enzyme will be higher than normal. The doctor should take this into account when interpreting the study results.
Why are the numbers falling?
A decrease in such an indicator as glutamine aminotransferase is quite rare. And it is due to one of three reasons:
- What are triglycerides in a biochemical blood test?
- Hypothyroidism is a pathological condition of the thyroid gland in which it produces an insufficient amount of hormones - thyroxine and triiodothyronine - which leads to a malfunction in the body's metabolic processes,
- Use of certain medications
- GGT is reduced in patients undergoing treatment for alcohol addiction after a month of therapy.
Complexes with this research
Preventive check-up Universal annual preventive screening RUR 11,960 Composition
Biomarkers of liver functional capacity RUR 2,760 Composition
Women's check-up No. 1 38 studies for annual preventive examination RUB 19,290 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Liver and pancreas RUB 3,050
- Biochemistry of blood. 13 indicators 3,490 RUR
- Healthy interest 4,250 RUR
- Check-up No. 1 for children and teenagers 10,950 RUR
- Biomarkers of liver functional capacity. Extended examination RUB 3,900
References
- Ivashkin, V.T., Shirokova, E.N., Mayevskaya, M.V. and others. Clinical recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association and the Russian Society for the Study of the Liver for the diagnosis and treatment of cholestasis. - Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Coloproctology, 2015. - V. 2. - P. 41-57.
- Uspenskaya, Yu.B., Sheptulin, A.A. Clinic, diagnosis and treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnant women, 2021. - V. 27(4). — P. 96-101.
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: The diagnosis and management of patients with primary biliary cholangitis. J Hepatol., 2021. - Vol.67(1). — P. 145-172.
- Alcoholic liver disease: Clinical guidelines - Scientific Society of Gastroenterologists of Russia, Russian Scientific Medical Society of Therapists, 2021. - 38 p.
Indications for the study
A blood test for GGT—the level of gamma-glutamine transferase—is prescribed if there is suspicion of liver cell damage. The causes of such damage can be different (for example: a number of diseases, poisoning with toxic substances, alcoholism, drug use). This test is currently the most sensitive indicator of liver damage.
The analysis is prescribed if the following symptoms are present:
- yellowing of the skin and sclera;
- decreased appetite;
- skin itching;
- nausea and vomiting;
- abdominal pain;
- change in color of stool and urine;
- fast fatiguability.
Also, a GGT test is prescribed at certain intervals to patients who are being treated for alcoholism. Based on its results, the doctor can judge how much the patient follows his recommendations (whether the patient has given up alcohol or not).