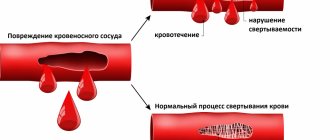
The protein component does not have its own color and dissolves in blood serum. Fibrinogen is the basis of blood clots; it is formed in the liver; its renewal is recorded every 3 days. The amount of the element is regularly checked by laboratory diagnostics. A critical minimum or maximum amount of a component can cause serious disruptions in the functioning of the body, provoke long-term bleeding or the formation of blood clots on the inner walls of blood vessels.
General information and functions of fibrinogen
Protein is one of the primary factors of the blood coagulation system. Indicators of the presence of fibrinogen must be checked in case of hepatic and cardiovascular pathologies, predisposition to bleeding, thrombosis, before surgery and labor.
The list of protein functions is presented:
- participation in the formation of fibrin clots;
- impact on the rate of healing of wound surfaces;
- regulation of fibrinolysis (dissolution of formed clots);
- participation in the production of new vessels;
- influence on arterial walls and blood during inflammation.
Testing for fibrinogen levels is prescribed to patients:
- in the preoperative and postoperative period;
- with pathologies of the heart, blood vessels, liver;
- during pregnancy, suspected hemophilia, inflammation of unknown origin.
The minimum protein content must be above 2 mg/l; if it is lower, then there is a risk of death during surgery. A level greater than 4 mg/l indicates thrombosis (blockage of the lumen of blood vessels with plaques) and related complications.
Fibrinogen is a protein produced in the liver and converted into insoluble fibrin, the basis of the clot during blood clotting.
Synonyms Russian
Factor I (first) of the plasma coagulation system.
English synonyms
Fibrinogen Activity and Fibrinogen Antigen Assays, Factor I, Fibrinogen Activity, Functional Fibrinogen, Fibrinogen Antigen.
Research method
Side scatter detection method, end point percentage determination.
Units
G/L (grams per liter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Avoid physical and emotional stress 30 minutes before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
According to the international nomenclature, fibrinogen is factor I (first) of the blood plasma coagulation system. It is produced by the liver and released into the blood along with several other substances that affect blood clotting.
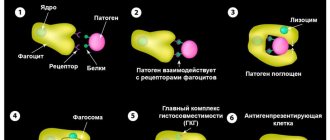
If a blood vessel or tissue is damaged, the body begins hemostasis, or blood clotting, resulting in the appearance of a blood clot (thrombus), which helps slow and then stop bleeding. This process produces strands of protein called fibrin. They intertwine, forming a fibrin mesh, which, together with platelets, contributes to the formation of a blood clot, which remains at the site of damage to the vessel until it is completely healed.
Given a sufficient number of platelets, each of the coagulation factors must act correctly to ensure the formation of a stable blood clot. Insufficient amounts or improper interaction of these factors can lead to bleeding or thrombosis.
Fibrinogen analysis is necessary in preoperative examination, prenatal diagnosis, and for inflammatory and cardiovascular diseases.
Fibrinogen is also one of the blood factors known as rheumatic tests. Levels of fibrinogen and other rheumatic factors rise sharply in the blood when there is inflammation or tissue damage.
The level of fibrinogen in the blood increases during acute inflammatory diseases, as well as during tissue death. In other cases, it can mean acute infectious and inflammatory diseases, strokes, myocardial infarction, hypothyroidism, amyloidosis, pneumonia, and malignant tumors. The reason for the increase in fibrinogen levels is previous operations, burns, or the patient taking estrogens or oral contraceptives.
It is worth noting that treatment for elevated fibrinogen levels may not be necessary in two cases: during pregnancy and the inflammatory process. Then the level of fibrinogen in the blood returns to normal on its own when the body’s condition stabilizes.
What is the research used for?
To assess the body's ability to form blood clots and identify associated disorders, such as hereditary afibrinohemia or hypofibrinohemia, chronic liver disease, exhaustion of the body, inflammatory process.
When is the study scheduled?
- In case of bleeding or thrombotic episode.
- When studying activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) or thrombin time (TT).
- In case of progressive liver disease.
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Reference values |
| 1.8 - 3.5 g/l |
| Week of pregnancy | Reference values |
| 1-13th | 2.12 - 4.33 g/l |
| 13-21st | 2.9 - 5.3 g/l |
| 21st-29th | 3 - 5.7 g/l |
| 29-35th | 3.2 - 5.7 g/l |
| 35-42nd | 3.5 - 6.5 g/l |
Fibrinogen is an acute phase protein of inflammation. This means that the concentration of fibrinogen can increase sharply in any condition caused by inflammatory processes or tissue damage. Elevated fibrinogen alone does not provide the doctor with information about the cause of this change. Usually it is temporary and the level of fibrinogen in the patient's blood returns to normal after the cessation of exposure to the following factors.
Fibrinogen levels increase in the following cases:
- if there are malignant tumors in the body,
- with myocardial infarction,
- for burns,
- after undergoing surgery,
- for hypothyroidism,
- for acute inflammatory and infectious diseases (influenza, tuberculosis),
- in the first days after a stroke,
- with amyloidosis,
- with pneumonia,
- as a result of taking estrogens and oral contraceptives.
Factors that lower fibrinogen levels:
- DIC syndrome (in dynamics),
- liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis),
- toxicosis,
- lack of vitamin C and B12,
- amniotic fluid embolism (in newborns),
- chronic myeloid leukemia,
- polycythemia,
- snake venom poisoning.
What can influence the result?
- A low level of fibrinogen occurs as a result of transfusion of a large amount of blood to the patient.
- Some drugs lower fibrinogen levels: anabolic steroids, phenobarbital, streptokinase, urokinase, and valproic acid.
Normal protein levels
In healthy patients, fibrinogen levels depend on age:
- adult women and men – from 2 to 4 g/l;
- newborns – from 1.25 to 3 g/l;
- pregnant women - from 6 to 7 g/l.
To determine the level, venous blood is taken. Tests are taken 12 hours after the last meal; 2 hours before the procedure, you must avoid any physical activity. The patient should not smoke 40 minutes before the appointment.
During pregnancy, the amount of fibrinogen gradually changes:
- in the first 3 months – 2.98 g/l, reduced results are associated with toxicosis;
- in the second trimester – about 3.1 g/l;
- last quarter – 4.95-6 g/l.
If the protein exceeds the specified results, then the following may occur:
- infertility;
- premature placental abruption;
- thrombosis in vessels located in the umbilical cord;
- gestosis, early miscarriage;
- frozen pregnancy, premature labor;
- thrombosis or thrombophlebitis.
To timely determine developing abnormalities, pregnant women undergo a coagulogram several times throughout the entire period. Primary samples show information about the volume of fibrinogen contained, and final samples show information about the risks of developing thrombosis and the body’s readiness for labor.
Fibrinogen in children
In childhood (up to 18 years), the level of fibrinogen in the blood is slightly different from “adult” levels. Regardless of gender, the normal level of fibrinogen in children is considered to be 1.25-4 g/l. The exception to this group are newborn children, whose fibrinogen value ranges from 1.25 to 3 g/l.
The fibrinogen indicator in children differs from “adult” values because in childhood the homeostasis system is still being formed, like many other systems of the body. Over time, the child’s fibrinogen level approaches “adult” levels.
As you can see, the answer to the question about the importance of fibrinogen for the human body is far from clear-cut, as expected. The level of fibrinogen in human blood depends on many factors, and an increase or decrease in its concentration often becomes the most important marker of the inflammatory process. A laboratory symptom of an increase or decrease in protein is a clear marker that will allow the doctor to suspect certain pathologies in the patient. Doctors actively use fibrinogen testing to assess patients’ homeostasis system, prescribe a treatment regimen and monitor the dynamics of patient therapy.
Increased protein
A large amount of fibrinogen warns of a hidden inflammatory process and the danger of blood clots. Pathological deviation indicates the presence of:
- rheumatism, nephrotic syndrome;
- heart attack, infections;
- diabetes mellitus, pneumonia;
- hepatitis, DIC syndrome, tuberculosis;
- cancer, trauma, burns.
The increase in fibrinogen volume in pregnant women is explained by the physiological norm. Sometimes an unusual increase in protein is associated with age-related changes and the use of oral contraceptives. If a deviation is detected, the patient must be sent for additional diagnostics to identify the root causes of the abnormal condition.
Additional facts about fibrinogen
- The fibrinogen index, as a rule, is deciphered in conjunction with other tests, for example, PT and APTT.
- In the absence of a superficial reason for a decrease in the fibrinogen index and in the presence of some general clinical or medical history data, an immunological analysis of colorless protein is used to determine the basis of the disorders.
- To avoid incorrect results, blood testing for fibrinogen levels should not be performed on old specimens collected within 4 hours after administration of therapeutic doses of unfractionated heparin.
- High concentrations of unfractionated heparin may result in incorrect measurements of true fibrinogen levels.
Low protein
As the amount of fibrinogen decreases, the rate of blood clotting decreases and the risk of spontaneous bleeding increases. The root cause of the anomaly lies in congenital characteristics or individual diseases:
- due to DIC syndrome;
- congenital afibrinogenemia, hypofibrinogenemia;
- deficiency of ascorbic acid and cobalamin;
- treatment with anticoagulants;
- polycythemia, taking androgens or anabolic steroids, fish oil;
- toxicosis of pregnant women - early and late type;
- poisonous snake bites;
- liver cirrhosis;
- amniotic fluid embolism - a problem that occurs in infants.
A decrease in protein units occurs in vegetarians, during therapy with antioxidants, and moderate consumption of alcoholic beverages (with clearly adjusted dosages). When the level drops from 0.5 to 1 g/l, there is a risk of bleeding from the arteries and veins of the internal organs. The condition requires hospitalization and observation by medical personnel.
If fibrinogen is below normal
If your blood fibrinogen content is below the established norm, then its clotting occurs slowly, which will cause prolonged bleeding. This may be an acquired condition as a result of concomitant diseases or congenital.
The main reasons for the decrease in the amount of fibrinogen in the blood:
- thrombohemorrhagic syndrome - acute destruction of hemostasis, leading to the appearance of a huge number of microthrombi in the smallest vessels;
- severe hepatology;
- intoxication of the body during pregnancy;
- hypovitaminosis of group C and B12;
- genetic disorders;
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- use of medications that inhibit blood clotting and prevent blood clots;
- increase in the number of blood leukocytes;
- use of anabolic drugs, steroid sex hormones, valproic acid;
- taking Omega-3.
Low fibrinogen levels also occur:
- in people who have given up food of animal origin;
- when consuming antioxidants,
- with low blood alcohol levels.
If the volume of fibrinogen is less than 0.5–1 g/l, then there is a possibility of bleeding of the vessels of the internal organs.
Actions for low fibrinogen
As with increased fibrinogen, the first priority is to contact a qualified specialist who will promptly detect the causes of low protein and prescribe quality treatment. In addition, additional treatment can be carried out aimed at increasing the amount of fibrinogen, the essence of which is to take the following drugs:
- 6-aminohexanoic acid;
- transescam;
- ethamsylate;
- dicasol.
It is also necessary to change your diet and add more high-protein foods to it.
Solution
Deviation from the norm of fibrinogen does not allow us to draw conclusions about a hidden disease. The indicators make it possible to identify increased or decreased results, but not to detect the original source of the disease. To make a correct diagnosis, the patient must undergo additional laboratory diagnostic examination. Correct identification of existing pathologies will solve the problem.
Doctors warn that ignoring the altered level of fibrinogen and refusing to undergo therapeutic procedures provokes external and internal bleeding (with reduced results) or accelerated formation of blood clots (with an increased amount).
The attending physician makes the final diagnosis and selects a treatment regimen. By seeking professional help in a timely manner, the chances of complications and consequences are significantly reduced.
What to do if there is elevated fibrinogen?
The first thing to do if you have high levels of fibrinogen protein 0 is to immediately consult a doctor for further examination of the body. The specialist’s responsibility in this case is to prescribe high-quality therapy to eliminate the underlying disease, which will lead to a gradual independent decrease in protein levels to an acceptable level.
If there is an urgent need, fibrinogen levels can return to normal by taking medications that prevent blood clotting and the formation of blood clots. These include antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, thrombolytics, fibrinolytics.
Filling your diet with fresh vegetables, seafood, red berries, dark chocolate or cocoa helps reduce the amount of protein in the blood. If all the specialist’s instructions are followed, increased fibrinogen does not pose a threat to the life and health of the patient.
Complexes with this research
Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure RUR 23,020 Composition
Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators 6,630 R Composition
Expanded hospital complex Expanded infectious screening for prevention and hospitalization RUR 7,700 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Miscarriage RUB 40,070
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 16,690 RUR
- Preventive check-up RUB 11,960
- Women's check-up No. 1 RUB 19,290
- For those at risk of COVID-19 RUB 4,510
Other Important Recommendations
Normalization of fibrinogen levels can be achieved by following the above tips and recommendations. At the same time, maintaining its acceptable level, achieving the content of all substances in the blood at the proper level, ensuring the health of the heart, blood vessels and the whole body can only be achieved by using an integrated approach, which includes, in addition to proper nutrition, the following components:
- playing sports - in addition to the general strengthening effect, some sports especially stimulate getting rid of anticoagulants (aerobics, water sports);
- environmental situation - the quality of inhaled air inevitably affects the state of the body;
- giving up bad habits - alcohol in small doses (dry red wine, cognac) can improve the overall blood picture, but excessive consumption significantly worsens the situation, and smoking has an even worse effect;
- consumption of clean water - a feeling of thirst, manifested in dry oral mucosa, already indicates a significant degree of dehydration. Insufficient water intake can inevitably increase the risk of blood clots, while drinking 1 – 2 liters of water daily helps thin the blood.
Thus, to normalize fibrinogen levels it is necessary:
- establish the root cause of the condition (if the root cause is the presence of a disease, then, first of all, it is necessary to fight it);
- adjust nutrition, take additional nutrients;
- exclude from the diet foods whose consumption critically increases the level of fibrinogen;
- provide support for treatment using traditional medicine methods (if possible and necessary);
- support treatment by giving up bad habits, exercising, and breathing.
It is important to consolidate the obtained result. In some cases, the level of various substances in the blood must be monitored especially carefully (for example, during pregnancy or planning it, in the presence of chronic diseases, etc.), in others there is no need for strict constant monitoring.
However, you must visit your doctor regularly and get tested. Prevention is not only cheaper, but is also more likely to produce positive results than treatment.
Folk remedies to reduce it
To support efforts to normalize blood composition, in some cases it is advisable to use proven folk methods. Among them, you should pay attention to the following:
- Let's take nattoginase , an enzyme extracted from boiled fermented beans. The essence of taking nattoginase is to reach the limit values of coagulation, at which nattoginase will begin to break down fibrin formed from fibrinogen. Should be taken on an empty stomach, up to 300 mg daily.
- Drinking kombuccia , a natural fermented tea produced using kombucha. It should be taken with caution and should be discontinued a week before menstruation or a few weeks before planned surgery. Potential side effects include: headaches, rashes, diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain.
- Other recipes based on decoctions and infusions of herbs, willow and birch bark - the number of recipes is huge, however, it is recommended to use them with great caution, after consulting with a specialist.
- Taking raw onion and garlic on an empty stomach.
In addition, it is very important to ensure sufficient magnesium content, which helps oxygenate the blood.
Among the vitamins that you should pay attention to and, with the consent of your doctor, take as additional nutrition, include:
- E;
- B (especially B12);
- C.