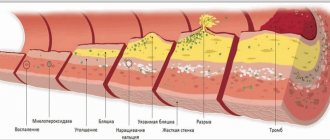
Low hemoglobin is not an independent disease. It is the result of an underlying disease, therefore, if anemia is detected in a patient, the doctor is obliged to prescribe a comprehensive examination.
Concepts of pseudoanemia and hidden anemia
Pseudoanemia is the entry of tissue fluid into the bloodstream during the resorption of edema.
Hidden anemia is the result of the loss of a significant part of the fluid composition of the blood due to dehydration (can be caused by diarrhea, vomiting, hyperhidrosis). In this situation, the blood begins to thicken, so laboratory analysis shows that the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin is normal, even if this is not the case.
Severity of anemia
Based on severity, anemia is classified into:
- light. Hemoglobin level is more than 100 g/l, erythrocytes - more than 3 T/l;
- average Hemoglobin level from 66 to 100 g/l, erythrocytes - from 2 to 3 T/l;
- heavy. Hemoglobin level is less than 66 g/l.
Classification of anemia
All anemias manifest themselves differently. Taking into account the cause of the pathological condition and its symptoms, there are four main types:
- posthemorrhagic anemia (caused by chronic/acute blood loss);
- hemolytic anemia (develops due to the destruction of red blood cells). This group includes hereditary hemolytic anemias: - with a lack of glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase; - thalassemia; - sickle cell; — Minkowski-Shoffar;
- deficiency anemia (caused by a deficiency of microelements/vitamins/iron, that is, any elements that play an important role in the process of hematopoiesis);
- hypoplastic anemia (results from impaired hematopoiesis in the bone marrow, the most dangerous form).
According to the color indicator of blood, anemia can be:
- normochromic (hemoglobin is normal). This group includes hemolytic and posthemorrhagic anemia;
- hyperchromic (hemoglobin increased). These include folate deficiency and B12 deficiency anemia;
- hypochromic (hemoglobin is low). This refers to thalassemia, iron deficiency and chronic posthemorrhagic anemia.
Based on the diameter of red blood cells, anemia can be:
- normocytic (almost all hemolytic and acute posthemorrhagic anemia);
- megaloblastic (B12-deficiency anemia);
- macrocytic (folate deficiency, hemolytic disease of the newborn);
- microcytic (chronic posthemorrhagic anemia).
Based on the iron content in the blood serum, anemia is divided into:
- normosideremic (acute posthemorrhagic anemia);
- hyposideremic (chronic posthemorrhagic and iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia);
- hypersideremic (hemolytic and B12-deficiency anemia).
Causes of anemia
Common causes of low hemoglobin are:
- large blood loss;
- disruption of the formation of new blood cells;
- activation of pathological processes of blood destruction.
Causes of posthemorrhagic anemia
Acute posthemorrhagic anemia is the result of the loss of a large amount of blood in a minimal period of time. The chronic form of this disease is caused by:
- prolonged blood loss;
- polyps, hernias and stomach ulcers;
- kidney diseases;
- malignant tumor neoplasms;
- uterine bleeding;
- disorders of the blood clotting system;
- liver failure, cirrhosis.
What causes hemolytic anemia
All hemolytic anemias occur if “old” red blood cells begin to destroy faster than new ones can form.
The sickle cell form is caused by the synthesis of a defective hemoglobin molecule. The emerging defective molecules form peculiar crystals that stretch the red blood cell, causing the latter to take on the shape of a sickle. Sickle erythrocytes are non-plastic. It leads to increased blood viscosity and blockage of small blood vessels. With their sharp ends they can destroy each other.
Thalassemia is a hereditary disease. It occurs due to a decrease in the rate of hemoglobin formation. Hemoglobin that is not fully formed is unstable. It resembles small inclusions that give the red blood cell the appearance of a target cell.
Deficiency anemias and their causes
Iron deficiency anemia develops for reasons such as:
- lack of iron/increased need for iron (this is why degree 1 anemia is often diagnosed in premature babies and pregnant women);
- chronic blood loss;
- problems associated with the absorption of iron from the gastrointestinal tract, its transportation and disposal.
B12 deficiency anemia is caused by a lack of vitamin B12. The disease can be caused by poor nutrition (refusal to eat meat) or disruption of the absorption of cyanocobalamin in the gastrointestinal tract (parasites, diseases of the small intestine, stomach). Also, symptoms of B12 deficiency anemia can appear while taking hormonal drugs and anticonvulsants.
Folate deficiency anemia is a consequence of a lack of vitamin B9. It is usually observed in pregnant and lactating women, cancer patients, teenage children, premature newborns, liver disease, alcohol abuse, etc.
Causes of hypoplastic anemia
Hypoplastic anemia is manifested by a decrease in the content of all cells in the blood. External and internal factors lead to such a pathological and life-threatening condition:
- vibration and radiation effects on the body;
- serious injuries;
- taking certain medications;
- ingestion of poisons into the body;
- herpes, fungi, bacteria;
- genetic mutations;
- rheumatoid arthritis, lack of elements involved in hematopoietic processes;
- endocrine diseases, etc.
Symptoms of anemia
Conventionally, the symptoms of low hemoglobin are classified into:
- specific (manifest only in specific types of anemia);
- nonspecific (the same for all types of disease).
Nonspecific symptoms of anemia are as follows:
- pallor of the skin/mucous membranes;
- migraine;
- increased fatigue;
- noise in ears;
- refusal of food;
- constant drowsiness;
- feeling of lack of air;
- dizziness;
- cardiopalmus;
- decreased libido, sexual impotence in men;
- disruption of the menstrual cycle;
- heart failure.
Specific signs of different types of anemia
Each type of anemia has its own specific symptoms. Thus, the acute posthemorrhagic form manifests itself:
- increased heart rate;
- fainting;
- cold sweat;
- attacks of dizziness;
- pale skin;
- decrease in body temperature.
In chronic posthemorrhagic anemia the following are observed:
- very white skin;
- craving for or intolerance to certain smells;
- swelling of the face;
- change in taste sensations;
- dry skin;
- brittle nails;
- nausea;
- lack of air;
- sweating;
- involuntary urination when sneezing or laughing;
- temperature increase.
Hemolytic anemias are characterized by:
- yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes (when red blood cells are destroyed, bilirubin enters the bloodstream);
- increased size of the spleen/liver;
- increased levels of bilirubin in the blood;
- darkening of urine and feces;
- high body temperature;
- weakness.
Sickle cell anemia - a type of hemolytic - has the following symptoms:
- jaundice;
- shortness of breath;
- formation of inflamed areas on the legs;
- blurred vision;
- the presence of hemoglobin in the urine.
Doctors diagnose thalassemia if the patient:
- the shape of the skull bones changes;
- the skin becomes very pale with a yellowish/greenish tint;
- eyes become narrow and swollen;
- there is a lag in mental/physical development;
- bones are deformed;
- the spleen/liver enlarges.
Signs of iron deficiency anemia include:
- buzzing in the head;
- lack of oxygen;
- migraine;
- constant desire to sleep, rest;
- dry skin;
- peeling of nails;
- hair section;
- desire to eat chalk, smell paint, etc.;
- violation of the act of urination;
- hyperhidrosis.
Also, during laboratory tests, it is discovered that the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood is significantly lower than the established norm.
B12 deficiency anemia affects the gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system. As a result, the patient experiences:
- swelling of the legs;
- crawling sensation on the arms/legs;
- change in gait;
- memory impairment;
- problems swallowing food;
- enlarged liver/spleen;
- drying of the gastrointestinal mucosa.
In turn, folate deficiency anemia manifests itself:
- inability to eat acidic foods;
- glossitis;
- difficulty chewing and swallowing food;
- enlarged spleen/liver;
- atrophy of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
The symptoms of hypoplastic anemia are:
- the appearance of ulcers in the mouth, on the skin of the face;
- bruising on the skin;
- severe bleeding gums;
- increased fatigue;
- desire to sleep;
- tachycardia;
- decrease in the number of leukocytes, red blood cells and platelets in a blood test.
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor
. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
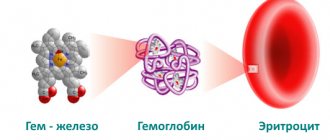
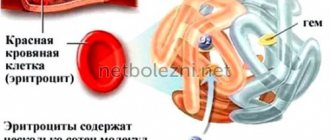
What is hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a complex protein containing iron. Its main task is to add oxygen diffusing into the blood from the lungs and distribute it throughout the body. Giving oxygen to cells, hemoglobin attaches carbon dioxide formed by them in the process of vital activity. Then getting through the bloodstream to the lungs, it gives it away, again making room for oxygen. This is how gas exchange and tissue respiration occur. But, in addition, hemoglobin is involved in maintaining the acid-base balance, in DNA synthesis, and in the occurrence of a number of redox reactions.
To synthesize hemoglobin, the body uses iron, which comes from food and accumulates in the form of ferritin in the liver, lungs, and spleen. There is also a small amount of iron present in the intestinal mucosa. If the diet does not meet the body's iron needs, ferritin is activated. This helps maintain normal hemoglobin levels and organ function. But with prolonged deficiency, its reserves are depleted, and the concentration of hemoglobin decreases.
In men, critically low hemoglobin levels are rare, since they, unlike women, do not experience regular physiological bleeding. For the same reason, the increase in hemoglobin in men occurs faster and more effectively. But if left untreated, there is a serious risk of complications, especially if you have bad habits:
- thrombosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- decreased immunity;
- deterioration of cognitive functions (memory, attention);
- hypoxic coma.
Often, when low hemoglobin persists for a long time, the presence of chronic fatigue syndrome is observed.
Diagnosis of anemia
To identify anemia in a patient, the doctor conducts a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes:
- clarification of the circumstances under which health deteriorated for the first time, the symptoms that are most pronounced;
- studying the patient's life history. The doctor clarifies whether there are chronic diseases, a hereditary predisposition to any pathological conditions, whether there are bad habits, whether the patient has recently taken any medications, or whether there has been contact with poisons or toxic compounds;
- examination of the skin, determination of its color. Measurement of pressure, pulse;
- laboratory tests of blood and urine.
In some situations, the patient is prescribed a bone marrow test. It is necessary to understand whether there are any disturbances in the hematopoietic processes. Also, using special equipment, a trephine biopsy can be performed, during which the doctor correlates the bone marrow with the tissues surrounding it.
An ECG is usually performed to examine the heart. If necessary, the patient is referred to a hematologist.
Laboratory diagnosis of low hemoglobin
In blood biochemistry, if anemia is suspected, the levels of:
- glucose;
- cholesterol;
- uric acid;
- creatinine;
- electrolytes.
This is necessary in order to assess the condition of the patient’s internal organs. A urine test is also performed to exclude the presence of concomitant diseases.
Laboratory signs of different types of anemia:
- posthemorrhagic acute anemia. Reticulocytes more than 11%, the presence of immature red blood cells and red blood cells of abnormal shapes. Leukocytes - 12 g/l (increased), shift in the formula - to the left;
- chronic posthemorrhagic anemia. Presence of tiny, poorly colored and oval red blood cells. Unexpressed lymphocytosis. Iron - below 9 µmol/l. A decrease in the amount of calcium and copper against the background of an increase in the concentration of manganese, nickel and zinc;
- sickle cell anemia. Hemoglobin is reduced to a level of 50 to 80 g/l, red blood cells - from 1 to 2 T/l. Reticulocytes are increased by about a third. The presence of red blood cells, the shape of which resembles a sickle;
- Thalassemia. Detection of target-like red blood cells in a blood sample, an increase in the number of reticulocytes. Hemoglobin - 20 g/l, erythrocytes - 1 T/l. Decreased concentration of platelets and leukocytes;
- B12 deficiency anemia. The presence of giant erythrocytes. Their color is bright, there is no highlighted area in the center. Shape: pear-shaped or oval. Life expectancy is shortened. Detection of huge neutrophils, a decrease in the number of eosinophils (may be completely absent). The concentration of basophils and leukocytes also decreases. Bilirubin, on the contrary, is increased.
Norm
The norm in this situation is considered to be 120-140 g/l. Numbers may vary, it all depends on the physical and mental state. A long decrease or increase in comparison with normal data indicates problems in the body.
In women, an increased rate is rarely observed. It is possible for hemoglobin to increase by 10-20 units; if the values are even higher, then you definitely need to go to the doctor and get tested. The reasons may be different: blood disease, congenital heart pathologies, oncology, cardiopulmonary pathology. This plasma substance is present in red blood cells, which are produced by the bone marrow. These scarlet bloody cells transport air to various organs. Therefore, with an increase in hemoglobin, there is probably an air deficiency in some area of the body. Because of it, the bone marrow forms a lot of red blood cells, and plasma coagulability increases.
| Floor | Age | Hemoglobin norm, g/l |
| Children | 0 – 14 days | 135-200 |
| Up to 1 month | 100-170 | |
| 1-2 months | 95-130 | |
| 2-4 months | 100-140 | |
| 4-6 months | 110-140 | |
| 6-9 months | 100-150 | |
| 9-12 months | 115-145 | |
| 1-5 years | 110-150 | |
| 5-10 years | 115-145 | |
| 10-12 years | 120-160 | |
| Man | 12-15 years | 120-160 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-170 | |
| 18-45 years old | 130-170 | |
| 45-60 years | 140-175 | |
| Over 60 years old | 120-175 | |
| Woman | 12-15 years | 110-150 |
| 15-18 years old | 120-155 | |
| 18-45 years old | 115-160 | |
| 45-60 years | 120-160 | |
| Over 60 years old | 110-170 |
Treatment of anemia in children and adults
To get rid of the symptoms of anemia, you need to eliminate the factor that provoked the decrease in hemoglobin. So, if the pathological condition is associated with the presence of parasites in the body, you need to get rid of them, if with poor nutrition, start following a diet, if with a malignant/benign tumor, it should be removed.
In other words, treatment of low hemoglobin in men, women and children may be conservative or require specialized surgical procedures. Usually, in order to improve the condition of patients and reduce the severity of negative symptoms, doctors adhere to the following therapeutic regimen:
- drugs are prescribed that can compensate for the resulting deficiency - B12 for B12-deficiency anemia, iron for iron deficiency, B9 for folate deficiency, etc.;
- normalize the level of red blood cells. This can be accomplished by transfusion of red blood cells or washing of red blood cells. However, these measures when providing assistance to people with low hemoglobin levels are extreme and are carried out only if the resulting disease is life-threatening.
Treatment of acute and chronic posthemorrhagic anemia
Treatment of the acute form of posthemorrhagic anemia is carried out in a hospital or hematology clinic
. The medications prescribed to the patient help normalize the amount of blood and the level of formed elements, and are also aimed at preventing relapses of the disease. Taking into account the amount of blood lost, the patient may need a transfusion, the introduction of blood substitutes or red blood cells.
As for the chronic form of this type of anemia, it is impossible to get rid of its symptoms without eliminating the cause. After the factor that provoked the pathological condition has been eliminated, the patient will be prescribed a diet that includes eating foods rich in iron. Medicines that can be used are Sorbifer Durules, Ferrum-Lek, vitamins B12 and B9, etc.
Treatment of sickle cell anemia
The main goal of therapeutic measures when it comes to a patient with sickle cell anemia is to prevent the development of hemolytic crises. To do this, the patient must avoid being in places with low oxygen levels. In parallel, blood substitutes and red blood cell infusions can be used.
Elimination of iron deficiency anemia
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia includes eating foods rich in iron and treating existing gastrointestinal diseases. The patient should regularly eat:
- cheeses;
- porridge;
- chicken eggs;
- meat;
- dairy products.
Iron supplements can also help quickly get rid of the symptoms of anemia. The tablets usually used are “Ferrum-Lek”, “Totem”, “Sorbifer Durules”, etc. Injections are prescribed only for severe forms of the disease. It is important that the medicine used does not cause problems with the gastrointestinal tract. If constipation or flatulence occurs, the product needs to be replaced.
Treatment of B12 deficiency anemia
Complex therapy of gastrointestinal diseases and adherence to the principles of proper nutrition help eliminate the manifestations of B12-deficiency anemia. Most often, patients are prescribed vitamin B12 injections. They allow you to quickly restore hematopoietic processes in the bone marrow.
How to get rid of folate deficiency anemia
Folate deficiency anemia is treated by taking vitamin B9 and following a diet. The patient should include foods that contain high amounts of folic acid in their diet. This means citrus fruits, vegetables, herbs, asparagus, nuts, seeds, tomatoes, watermelons, corn, avocados, eggs, animal liver, cod liver, cereals, grain bread.
Treatment of hypoplastic anemia
A hematologist treats hypoplastic anemia. Depending on the age, gender and condition of the patient, he can use different methods - bone marrow transplantation, stimulation of hematopoietic processes, blood transfusion, etc.
Age-related changes in the female body after 60
| CHUZ "RZD-Medicine" Vikhorevka" |
The health of a woman after 60 years largely depends on herself. In order to stay healthy and vigorous for as long as possible, it is necessary to monitor the main indicators of the body’s activity and constantly engage in health improvement. This includes a healthy diet, an active lifestyle, weight control and, if necessary, rehabilitation courses.
Age-related changes in the female body after 60
At 60, a woman is postmenopausal. Her hot flashes and changes in blood pressure (BP) stopped, her mood stabilized, and her overall health improved. But against this background, new problems arise related to age-related changes. All problems are surmountable, you just need to be aware of them and adhere to the generally accepted recommendations of specialists for their correction.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis in women begins late; the most dangerous age in this regard begins after 55-60. The first signs of angina pectoris appear in the form of attacks of acute short-term pain in the heart. The condition is dangerous because blocking the access of arterial blood to the heart muscle (myocardium) can lead to necrosis of its area (myocardial infarction). And the same process in the vessels feeding brain tissue leads to the development of ischemic stroke.
Arterial hypertension
Changes in blood pressure due to hormonal changes at this age are almost no concern. Stably high blood pressure may appear - a threat of developing arterial hypertension and associated hemorrhagic strokes (bleeds in the brain).
Mineral metabolism disorders
Osteoporosis develops: bone tissue, with estrogen deficiency, intensively loses calcium. Bones become brittle and prone to fractures. A fracture of the femoral neck is especially dangerous at this age: the bones hardly heal, and many older people become disabled after this.
A lack of potassium and magnesium negatively affects the condition of the heart muscle: angina attacks intensify and heart rhythm disturbances appear.
Decreased immunity
Immunity (general and local - skin and mucous membranes) is reduced due to metabolic disorders. After 60 people are more likely to suffer from colds, and the risk of acute infections turning into chronic infectious and inflammatory processes increases. Decreased immunity also contributes to the development of tumor processes.
Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine and joints
Metabolic disorders lead to the destruction of cartilage tissue first, and then the bones of the spine (osteochondrosis) and joints (osteoarthrosis) are injured and destroyed. All this is accompanied by pain, first when moving, and then by other disorders. Cervical osteochondrosis, complicated by compression of the vertebral arteries carrying blood to the brain, is especially dangerous. Cervical migraine and fainting appear.
Diabetes
The disorder begins due to the fact that tissues cannot absorb glucose. Type 2 diabetes mellitus develops. If it is not compensated for, severe dehydration develops. Due to glucose deficiency, all types of metabolism and the functioning of internal organs are disrupted. The formation of new cells (including immune cells) is disrupted, and atherosclerosis progresses.
Excess body weight
Age-related changes in fat metabolism and a general slowdown in metabolic processes in women contribute to the development of obesity, which negatively affects the entire body. Maintaining a normal weight is one of the main tasks after 60.
Genitourinary organs
The problems are associated with the increasing dryness of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary organs, which causes thinning of the mucous membranes and suppression of their barrier functions: they are easily injured and do not prevent the penetration of infection. Sometimes this is accompanied by weakness of the sphincter muscles - a circular muscle that prevents involuntary urination. As a result, a woman suffers from urinary incontinence, cystitis, infectious and inflammatory processes of the external genital organs, which, with insufficient general immunity, can spread to the internal genital organs.
Thyroid dysfunction
The thyroid gland in women after 60 gradually reduces the secretion of its hormones, and a tendency to develop hypothyroidism appears. It manifests itself in increased dryness of the skin and mucous membranes, an increase in body weight and a gradual decrease in mental abilities.
How to stay healthy at 60
Health at 60 years old must be constantly maintained at the required level. In order for a woman to stop noticing her age, she needs to lead a healthy lifestyle, adhere to proper nutrition and monitor her weight and basic indicators of the functioning of the body for the timely detection of serious diseases.
The psychological attitude is also very important: you need to remember about age-related changes in your body, but you should not forget about the joys of life. An optimistic attitude helps improve the quality of life.
Regular medical examination is mandatory
Every woman over 60 years of age must undergo an annual medical examination. Medical examination includes examinations by a therapist and specialists, examination of key indicators, changes in which indicate serious disorders in the body. If you carry out medical examinations regularly, you can promptly notice small changes and correct them with the help of diet, therapeutic exercises or drug therapy. This will allow you to stay healthy for a long time.
What tests need to be taken and the norms of indicators
Some vital signs of the body are of great importance during the aging period. They give an idea of how physiologically this process occurs. Small periodic fluctuations in indicators do not play a big role. Sustainable change is important.
Blood sugar
Normally it is 3.3 - 5.5 mmol/l. This indicator needs to be monitored. If there is a suspicion of diabetes mellitus (constant thirst and frequent excessive urination), then blood sugar testing should be done outside of medical examination.
Blood cholesterol
Cholesterol levels can tell a lot about the threat of developing or progressing atherosclerosis. This disease does not threaten everyone; it is mainly associated with family history. But you need to control your cholesterol levels. Three types of cholesterol are studied: total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and NSAID cholesterol. LDL and HDL are lipoprotein (protein-fat) complexes that transport cholesterol from the liver to tissues that need it vitally for metabolism.
Cholesterol is the same everywhere, but the complexes are different: LDL (low-density lipoprotein) is a “leaky” carrier; it loses cholesterol during transportation, which is deposited on the walls of blood vessels in the form of atherosclerotic plaques. It is LDL that is most abundant in the blood. HDL (high density lipoprotein) carries cholesterol without loss, this cholesterol enters into metabolic processes and prevents the development of atherosclerosis. But it is not enough, which is why it is so important to consume foods that maintain high levels of HDL in the blood (vegetable oils).
Cholesterol standards:
- general - 4.45 - 7.7 mmol/l;
- as part of LDL - 2.59 - 5.80 mmol/l;
- as part of HDL - 0.98 - 2.38 mmol/l.
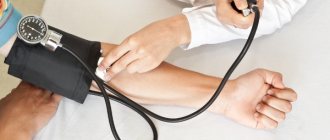
Pressure
Blood pressure is one of the most important health indicators. After 60, changes in blood pressure are rare; pressure stabilizes at 130/80 mm Hg. But these are average numbers, they are individual for each woman: the norm may be 140/85 and 110/80. You should focus on your well-being. A rise in lower (diastolic) pressure and a decrease in pulse pressure (the difference between upper and lower) are dangerous. If your lower blood pressure is consistently above 90 and you are experiencing headaches, you should consult a doctor to maintain your health.
Normal ESR in the blood
ESR or erythrocyte sedimentation rate is an indicator, an increase in which reflects the presence of an inflammatory process or a malignant tumor in the body. The generally accepted standard for ESR is 2 – 15 mm Hg. But there are also age standards. After 60 years, you can have a much higher upper level of ESR, as physiological changes in the body and chronic diseases accumulate. Each individual case of high ESR should be dealt with individually.
Blood creatinine
Creatinine is a residual product of protein metabolism formed in the liver, pancreas and muscle tissue. Its daily content in blood and urine is constant and corresponds to the volume of skeletal muscles. An increase in creatinine in urine indicates kidney disease, injuries or diseases of the muscular system, and dehydration. A temporary increase in this indicator can occur when taking antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, or eating large amounts of animal proteins (meat, fish, dairy products).
Standards for women over 60:
- blood creatinine: 38-70 (µmol/l)
- daily excretion of creatinine in urine: 7.1-15.9 mmol/day. (0.8-1.8 g);
- residual nitrogen: 14.3 - 28.6 mmol/l.
Hemoglobin is normal after 60
Another important indicator is hemoglobin. This iron-containing protein carries oxygen to tissues, so a decrease in its content in the blood will affect the condition of all organs and tissues. The age norm of hemoglobin is 117 – 160 g/l, which is slightly higher than after 50 years. The increase in the norm is associated with the absence of menstrual and intermenstrual bleeding after 60 years.
TSH and its norm in elderly women
The pituitary gland is the main endocrine gland that regulates the work of other glands by secreting its hormones. The pituitary gland itself is under the same control of the hypothalamus.
At the age of 60 years and older, the thyroid gland significantly reduces the secretion of its thyroid hormones (TG) - thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Therefore, the pituitary gland works hard, producing the maximum amount of thyroid-stimulating hormones (TSH), which stimulate the production of thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
The condition of hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function) is very harmful to the body, especially to the brain, as it leads to the development of dementia. Therefore, it is important to monitor the levels of TG and TSH in the blood. The first indicator will be reduced, and the second will be overestimated compared to other age categories.
TSH norm: 1 – 10 mU/l. Exceeding the norm even in the absence of symptoms of the disease indicates the presence of subclinical (asymptomatic) hypothyroidism.
Intraocular pressure and its norm
Aging is often accompanied by an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP) and impaired outflow of intraocular fluid. If you do not pay attention to unpleasant symptoms for a long time, optic nerve dystrophy occurs with the development of blindness. Symptoms of increased IOP are: headache, pain in the eyeballs, blurred vision, flashing “floaters” before the eyes, deterioration of lateral vision.
But low IOP is also bad; it can lead to a significant decrease in vision. Symptoms: rare blinking, sunken eyeballs, decreased vision.
The normal IOP ranges from 10 to 23 mm Hg. Art.
How to maintain health and beauty after 60?
After 60, a woman feels better than at fifty-five, when she was still bothered by hot flashes and changes in blood pressure. The changes taking place are more dangerous, although they do not cause such unpleasant sensations. But all these changes in the body can be corrected, trying to keep aging within physiological limits and suppressing the development of pathological processes.
Hormonal background
After 60 years, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can stimulate the growth of malignant tumors, the risk of which is quite high at this age. The hot flashes have already passed, and there is no urgent need to fix any problems. Therefore, gynecologists-endocrinologists prescribe HRT with caution, trying to replace it with hormone-like substances contained in plants and animals.
Phytohormones are found in soybeans, hop cones, red clover, and licorice roots. Recently, many medications and dietary supplements with these substances have been produced: Estrovel, Feminal, Klimadinon, Klimadinon Uno, Qi-Klim. You can also use homeopathic remedies - Remens, Klimaxan, etc.
Cytamines, biologically active substances obtained from animal organs and tissues, act similarly to phytohormones. An example of a dietary supplement with cytamines is Ovariamine.
You can activate your general metabolism, which will lead to an improvement in hormonal levels, by taking special vitamin and mineral complexes for older women.
Osteoporosis
Advice from a specialist on the prevention of osteoporosis:
- eating foods high in calcium, such as: dairy products, eggs, sardines, shrimp, sesame seeds, cabbage, almonds, chocolate;
- strengthening skeletal muscles that support the musculoskeletal system; muscles protect bones from fractures;
- taking medications and vitamin-mineral complexes that contain calcium - Calcium D3 Nycomed, Kalcemin, etc.
Genitourinary system
Problems with the genitourinary system can increase due to dry mucous membranes. Expert advice: a way out may be to use topical medications with hormones (vaginal suppositories and Ovestin cream). To strengthen the sphincter and pelvic floor muscles, special gymnastics complexes are prescribed.
Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a serious problem in older people. Therefore, you should limit or not consume sweets at all; baked goods are a source of simple carbohydrates. Fatty animal products should also be limited - they can also produce glucose. By following such a diet, diabetes in the initial stages is compensated. If blood sugar does not decrease, hypoglycemic drugs such as metformin (Siofor, Glucophage) are prescribed.
Physical exercise
High physical activity at 60 is contraindicated, but physical activity and feasible sports or gymnastics are vital. It is important to alternate physical activity with rest. Evening walks are very useful: they not only strengthen muscles, but also help you fall asleep quickly.
Cosmetology
It is worth taking care of your face and body, as they determine a woman’s appearance, her age and state of health. To achieve the desired result, you need to adhere to the following expert advice:
- cleanse your face daily, removing decorative cosmetics with special milk;
- clean with a scrub once a week;
- use age-appropriate nourishing creams; Apply day cream with photoprotective properties in the morning, and night cream in the evening; Do not apply the cream in a thick layer; if you do this before bed, swelling may appear on your face in the morning;
- Apply nourishing masks to the skin of the face and neck twice a week; ready-made nourishing masks for your age can be bought in the store; you can also use folk remedies;
- use age-appropriate cosmetic serums in courses;
- Visit a beauty salon 1 – 2 times a year to conduct courses of cosmetic procedures.
Sexual life of women over 60 years of age
Sex life at sixty should continue. Studies have shown that in most cases, married couples at this age retain sexual desire and sexual activity. This strengthens the muscles of the pelvis and perineum (prevention of prolapse of the internal genital organs) and makes life brighter.
The health of a woman in old age requires constant support. But this does not mean that you need to do only examination and treatment. And in your declining years, life should be bright, happy and full of pleasures.
Address: Vikhorevka, st. Komsomolskaya, 1a Contact numbers.
Anemia risk group
Low hemoglobin is most often diagnosed in:
- people with gastrointestinal diseases (oncology, gastritis, stomach and duodenal ulcers, inflammatory process in the large/small intestine, etc.);
- persons with poor nutrition, vegetarians;
- people with a genetic predisposition to a certain type of anemia (the disease can be passed from parent to child).
What are the dangers of low hemoglobin?
Anemia can be simultaneously called both a dangerous and harmless disease. So, if we are talking about a mild degree of the disease in a pregnant woman or a small child, then this is more likely a variant of the norm than a deviation. After taking a course of iron supplements, the baby/future mother will become absolutely healthy.
At the same time, moderate and severe degrees of some forms of anemia can lead to such dangerous conditions as:
- anemic coma (the patient loses consciousness and does not respond to any external stimuli, death may occur);
- malfunctions of internal organs (kidneys and liver are especially often affected by anemia);
- decrease in hemoglobin level to less than 70 g/l (death is also possible).
Signs and consequences of increased hemoglobin
With a high level of hemoglobin in the blood, women may have no symptoms at all, but with a long and high value along with other diseases, the patient may have vague symptoms:
- constant fatigue
- desire to sleep,
- lethargy,
- loss of appetite,
- sleep problems,
- aches in joints and bones,
- high blood pressure,
- itching of the skin, particularly after showering and bathing,
- stomach ache,
- instant bruising and easy bruising.
All these symptoms disappear externally. But the most serious of them take place inside the body. There is an increase in the coagulability of the blood space, an increase in its concentration and a reduction in the speed of movement in the body. Because of this, the internal organs do not receive proper nutrition. If this condition is neglected, blood clots and plaques can form, which cause heart attacks and strokes.
Prevention of anemia
To prevent the development of anemia, it is necessary:
- avoid contact with poisons and toxic substances;
- refuse to visit areas contaminated with radiation;
- do not contact with sources of ionizing radiation;
- do not take medications uncontrollably;
- to harden;
- eat right, include meat, greens, fruits and vegetables in your daily diet;
- spend more time outdoors.
Secondary prevention of low hemoglobin includes:
- blood test once a year;
- seeking qualified medical help in the event of acute infectious and viral diseases;
- annual medical examinations;
- pregnancy planning (for women).
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.