Leukemia is a malignant disease that is often called blood cancer, which is not correct. It has another name - leukemia, which in Greek means “white cells”, hence the word leukemia. The bone marrow itself is responsible for the production of blood cells: red blood cells, platelets and white blood cells.
When affected by a tumor, immature mutated leukocytes begin to be produced in the blood, which constantly divide and completely fill the space, interfering with healthy cells. Also, mutated leukocytes do not perform their protective function.
Is leukemia curable or not?
The first question that arises for people who are faced with suspected blood cancer is whether leukemia can be treated or not.
Everyone knows that this is a serious and serious disease, but until it affects a specific person, few people delve into all the details. This is quite typical of human nature.
But in fact, information on this topic should not be neglected, since this disease is becoming widespread and, unfortunately, young children are often exposed to it.
There are proven medicinal methods, using which you can control the disease and achieve remission
Prevention
As such, there is no prevention of the occurrence of the disease. It is recommended to adhere to a properly balanced diet, walk more in the fresh air, avoid gas pollution, exposure to radiation, etc.
Dear parents!
Remember that only a qualified pediatrician can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-800-700-31-69 Grow up healthy and happy!
Causes of the disease
Possible causes of the disease are:
- disturbances in the chromosomal apparatus and cell structure;
- exposure to elevated levels of radiation over a long period of time;
- interaction with toxic drugs and chemicals;
- bad habits, including smoking;
- after chemotherapy;
- genetic predisposition.
Types of leukemia
Leukemias are acute and chronic. In the acute form, immature white cells begin to divide rapidly, and the disease develops in a short time.
Chronic leukemia progresses more slowly over several years, with white blood cells first maturing and then becoming abnormal.
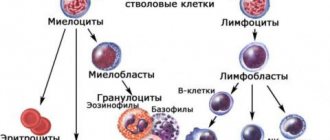
The disease is classified depending on which cells are affected - lymphocytes, which do not contain granules, or myelocytes - young cells with a granular structure.
Thus, there are four types of leukemia:
- Acute myeloid. Both adults and children are susceptible to the disease.
- Acute lymphoblastic. Children are most often affected, although it also occurs in adults.
- Chronic lymphocytic. It usually develops in people over 55 years of age.
Myeloid leukemia. Characterized by rapid growth of myeloid cells, as a result they accumulate in the peripheral system.
Diagnosis of lymphocytic leukemia
To diagnose lymphocytic leukemia, a clinical blood test is performed (code 2 and code 5). It allows the specialist to obtain information about the ratio of blood elements, their quality and quantity.
Leukocytes in acute lymphocytic leukemia can be elevated, decreased, or normal. To determine the leukocyte formula (the ratio of certain types of leukocytes), a blood smear is used, which is applied to a glass slide, stained with special dyes and examined under a microscope. This is how the doctor determines the ratio of leukocytes and identifies immature, pathological cells that differ from normal ones in appearance.
Symptoms of leukemia
Symptoms of leukemia, especially at the beginning, are very nonspecific and these signs are easy to miss. We therefore recommend that you be very careful if you:
- feel severe weakness;
- you get tired quickly;
- suffer from headaches;
- don't want to eat;
- feel bone pain;
- noted that a rash and strange bruises appeared;
- nosebleeds appeared, gums bleed;
- losing weight;
- you often suffer from infectious diseases.
Of course, one or two of these symptoms can simply be attributed to workload, for example. However, do not miss a serious illness, do not risk your life - once you notice the signs, then come to us for diagnosis. The sooner you begin treatment for blood diseases, the greater the chances of your recovery.
Forecast
Significant advances in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia have made it possible to make this disease potentially curable or to support a person’s life for a sufficiently long time without progression of the underlying disease while maintaining its quality.
On the contrary, without treatment, the disease slowly but steadily progresses, which can cause the death of the patient several years after the onset of the disease, so timely consultation with a doctor and initiation of adequate therapy are very important.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Bibliography:
- Clinical recommendations for examination and treatment of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Recommendations of the National Society of Hematology. 2014.
- Volkova M.A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and its treatment. Attending doctor. 2007, No. 4.
- Michael Hallek. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncohematology. 2010, volume 3, no. 1. pp. 181-182.
- Fedorov A.B. B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clinical oncohematology. Basic research and clinical practice. 2008. P.275-277.
- Fiyya A.T., Frenkel B.I. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: diagnosis and treatment. Journal of Grodno State Medical University. 2011. No. 4. P. 93-97.
- Nikitin E.A. Ibrutinib in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clinical oncohematology. 2021. 10(3), p. 282-286.
- Kravchenko D.V., Svirnovsky A.I. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: clinical picture, diagnosis, treatment. Practical guide for doctors. Gomel, 2021.
Stages
Separately, it is necessary to consider the main stages of leukemia.
- Initial. Most often diagnosed in patients who suffer from anemia.
- Expanded. All the symptoms are already showing up here.
- Remission. May be complete or incomplete. It is characterized by an increase in blast cells by a maximum of 5% in the bone marrow (in their absence in the blood).
- Relapse. It can develop both in the bone marrow and other organs. It is worth saying that each subsequent relapse is more dangerous than the previous one.
- The last one. In this case, the patient develops ulcerative-necrotic processes, and suppression of hematopoiesis occurs.
How is this pathology diagnosed?
After the initial examination, the first thing the doctor will prescribe is a blood test for leukemia in children (this includes extensive research and biochemistry). Laboratory testing will show the presence of anemia, thrombocytopenia, and ESR will be increased. The most characteristic blood parameters for leukemia in children are such an anomaly as “leukemic failure”. Its essence is that between immature leukocytes and mature ones there are no obligatory transitional forms (young, segmented).
The pediatric diagnostic program must include:
- sternal puncture;
- bone marrow biopsy;
- trephine biopsy.
In addition, an examination by a pediatric neurologist or ophthalmologist is necessary. Additional are ultrasound of the lymph nodes, and, if necessary, of the liver, salivary glands and other organs (the need is determined by the doctor based on the results of the examination).
Chances of recovery
Currently, the diagnosis of leukemia is not a death sentence, as it was before. The answer to the question whether leukemia is curable depends on certain factors:
- types of disease;
- timely diagnosis;
- the nature of tissue and organ damage;
- age characteristics;
- other possible risks.
Thus, it is important to monitor your health carefully and closely. At the moment, specialists do not have a maximum guarantee that leukemia can be treated, but thanks to modern medicine, there are a considerable number of methods that make it possible to extend the patient’s life by several decades.
About relapses and prognosis after treatment
As a rule, a relapse of this particular disease, if it exists, manifests itself directly during the course of treatment or immediately after its completion. After remission has been achieved and its consolidation (consolidation) has been carried out, after five years relapses are an extremely rare occurrence. After seven years, we can safely talk about a complete recovery.
Modern treatment methods suggest a favorable prognosis for acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children in 60-80% of cases. The indicator is influenced by an adequate therapy program (including the capabilities of a specialized clinic) and the general condition of the body.
Treatment of acute forms of leukemia
Acute lymphocytic leukemia in young children is cured in 95%. Almost 70% of those who have recovered from the disease have no signs of the disease for at least five years.
In the treatment of acute lymphoblastic form, chemotherapy based on three drugs is used. If a relapse of the disease occurs after using chemotherapy, the doctor advises using a stem cell transplant if indicated; the decision depends on the patient.
When treating the myeloid form, strong drug therapy is used in several courses. Bone marrow transplantation is sometimes used. The higher the patient's age, the lower the likelihood of recovery.
What treatment methods are used
The main method of treating leukemia in children is complex chemotherapy. It consists of a combination of several specific anticancer drugs and glucocorticoid hormones in high doses. After the course, immunotherapy (interferon or other drugs) is mandatory.
Particularly important in treatment is a step-by-step approach, which is aimed at:
- achieve stable remission;
- secure it;
- carry out maintenance therapy;
- prevent possible complications.
In complex cases, stem cell transplantation, bone marrow transplantation from a donor, and platelet and red blood cell transfusions may be necessary.
Treatment of chronic leukemia
Unlike the acute form of the disease, the chronic form does not require such urgent intervention. It develops more slowly and treatments vary. First of all, there is an observation period. In the early stages, the symptoms are almost invisible, but medical supervision is a must.
Such patients are also prescribed the usual treatment, but in the case of transplantology, cells can be taken from the patient’s body. Biological therapy is also used to help the body improve its protective functions. Conventional treatment methods are also used for patients.
The danger of leukemia - life prognosis in children
The life prognosis for children with acute leukemia, for whom adequate treatment has not been selected, is unfavorable - death occurs in 100% of cases. With the use of modern chemotherapy, the course of the disease without relapse is observed in 50-60% of children. We can talk about recovery after 6-7 years of life without relapses.
The most dangerous complication of leukemia is infiltration of the brain, nerve trunks and meninges. Signs of neuroleukemia are: nausea, headaches, dizziness, stiff neck, diplopia. Infiltration of the spinal cord substance is manifested by sensory disturbances, paraparesis of the legs, and pelvic disorders.
Treatment methods
The method of combating the disease is selected based on its stage and form. For chronic leukemia, therapy is used that is aimed at stopping the development of the disease, maintaining the body's protective functions and preventing complications. In addition, many patients are interested in whether acute blood leukemia is curable or not. It is worth saying that with a competent approach, the symptoms of this form of the disease can also be eliminated. For this use:
Chemotherapy. It destroys cancer cells.
Radiation therapy. It destroys affected cells using x-ray radiation.
Stem cell transplant. With this method, the formation of healthy cells is restored.
Before proceeding with surgery, chemotherapy is administered. It is necessary to make room for new, healthy bone marrow cells.
What is pathology?
Blood leukemia in children is a malignant disease of leukocytes, i.e. white blood cells. The problem is that with this pathology, the bone marrow produces abnormal (mutated) cells that are unable to perform their protective functions. Instead, diseased white blood cells divide uncontrollably, preventing the body from producing red blood cells (red blood cells) and platelets (nuclear-free, flat cells responsible for blood clotting).
Based on the duration of the disease, two forms are described:
- acute (less than two years);
- chronic (over two years).
In the children's body, the first type occurs predominantly; it accounts for 97% of cases.
According to morphological type, they are distinguished:
- lymphoblastic leukemia in children (in this case, young, immature leukocytes – lymphoblasts) undergo mutations;
- non-lymphoblastic.
The second type includes a malignant lesion of the myeloid blood line (it is also called acute myeloblastic leukemia in children).
The acute form is characterized by dynamic development; as a result of this disease, anemia appears, the immune system is weakened, internal hemorrhages occur, and increased bleeding is observed. All this is accompanied by sensitivity to infections (children get sick very often).
Preventive measures
To avoid pathology it is necessary:
- choose a place of residence with as favorable an environment as possible,
- patients whose relatives had cancer should donate blood for examination every six months;
- the same recommendation applies to people who have genetic defects that exceed the norm.
Leukemia is a malignant disease often called blood cancer. When the disease occurs, the red bone marrow produces leukemia cells - abnormal blood cells. Scientists have not yet established why this happens in the human body.
Related posts:
- Chances of surviving stomach cancer Stomach cancer occurs in the tissues of the mucous membrane of this digestive organ….
- Tumors in the oral cavity Tumors can occur in any type of tissue in the oral cavity...
- Chemotherapy for cancer: can such treatment affect the psyche? The condition of a cancer patient after undergoing a course of chemotherapy is quite serious...
- 6 Superfoods That Reduce Your Risk of Cancer The human body is made up of many different types of cells. Usually they...
Patient care
After diagnosing chronic lymphocytic leukemia, even in the initial stages, the patient is registered with the general public. This is necessary for the purpose of constant monitoring of its parameters.
Such people need to constantly prevent infectious diseases: get vaccinated. Treat inflammatory and autoimmune processes only under the supervision of doctors, as they can progress quite quickly.
During remission, do a blood test every 4-5 months and come for a preventive examination by a doctor.