Typically, dizziness, loss of balance, and loss of orientation are symptoms of a simple disease that is easily treatable. Much less often, stroke and severe genetic diseases can manifest themselves this way. But even in the first case, if the doctor does not make the correct diagnosis and starts the wrong treatment, the patient’s quality of life will greatly deteriorate. What to do if you feel dizzy?
You can suspect a diagnosis of dizziness based on the description of the symptoms. There are two types of such complaints:
- Real dizziness, when there is an illusion that everything around is starting to spin (systemic dizziness, vertigo). In this case, certain head movements provoke dizziness. Nystagmus (involuntary oscillatory eye movements) can also be noticed in a person; sometimes this requires special studies. Vertigo also makes it difficult to stay in a straight, upright position when walking or standing. There are three main diseases, the main symptom of which is systemic dizziness:
- benign paroxysmal positional vertigo;
- Meniere's disease;
- vestibular neuronitis.
In none of these situations, the cause of dizziness can be osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, although often this diagnosis can be heard at a doctor’s appointment. Throughout the civilized world they know that degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs (which, in essence, is osteochondrosis) very rarely cause any symptoms - most often you should look for some other disease. Also in Russia they like to diagnose vertebrobasilar (vascular) insufficiency and call it the cause of dizziness. However, vascular problems actually very rarely cause these symptoms.
Mechanism of development of vertigo
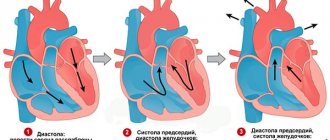
If we consider dizziness from an anatomical point of view, the causes of this condition are quite simple. The vestibular apparatus, responsible for human balance and coordination in space, is located in the inner ear. Vision and muscle reflexes help a person navigate the environment. All received information enters the brain. And it is he who controls the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Sometimes the connection between the inner ear and the brain can become disrupted. A person loses the ability to navigate in space. Dizziness appears. To restore the lost connection, the brain immediately launches several reactions at once. Some of them may affect neighboring centers (for example, emetic). This leads to the appearance of unpleasant accompanying symptoms.
Diagnostics
The doctor clarifies all the symptoms, their frequency, asks about your diet and sleep patterns, and how often you are in stressful situations. Asks about head, hearing, and vision injuries; do you take vitamins and medications, drink alcohol, and about the pace of life.
After all clarifications, the doctor refers to:
- blood analysis;
- echocardiography;
- electrocardiography;
- CT (computed tomography);
- MRI of the brain (magnetic resonance imaging);
- radiography;
- vestibulometry;
- audiography;
- electroencephalogram;
- Ultrasound.
Sudden dizziness: 5 simple reasons
Typically, loss of communication between the brain and the vestibular system is rare and does not last long.
Dizziness that occurs is not considered a pathology in the following cases:
- Ride the carousel. Such entertainment creates a serious load on the vestibular apparatus. And if it is naturally weak and untrained, then it may well fail. Such dizziness usually occurs in women, since they also have psycho-emotional experiences added to the load.
- Stress, anxiety. If dizziness occurs during a speech in front of a large audience or after a reprimand from a boss, then the cause of vertigo is the production of a large amount of adrenaline. This hormone causes vasospasm. And this leads to a temporary deterioration in blood flow in the brain.
- Climbing to heights. In this case, the unpleasant phenomenon is also considered a physiological norm. When rising to a height, a person’s eyes cannot quickly focus on distant and close objects. Abrupt switching between objects causes dizziness.
- Hunger. Similar problems are common to all fans of strict diets. If a person does not receive enough nutrition, then a glucose deficiency occurs in his body. The absence of the main “fuel” leads to deterioration of brain function and the appearance of dizziness.
- Active exercises. Exercise enthusiasts should remember moderation. Excessive exercise can cause low blood pressure. This leads to dizziness and sometimes fainting. The unpleasant condition may be caused by unsuccessful sudden movements of the head, as a result of which the blood supply to the brain is disrupted.
An attack of dizziness may occur in response to taking certain medications. The most common sources of unpleasant symptoms are NSAIDs, antidepressants, antibiotics, and cancer medications. If your head is “turned” by medications, be sure to consult a doctor to change the drug.
Not frequent dizziness
Let's consider situations and diseases in which such symptoms may occur. Dizziness may not be systematic. but only a rare effect. However, this may be a signal of serious illnesses or developing pathologies.
Presyncope
In this state, which lasts no more than a few seconds or minutes, it seems to a person that surrounding objects are moving, he feels hot, sweats profusely, feels nauseous, his eyes become cloudy, vision may even disappear, and the person becomes pale. Presyncope usually occurs when the patient is sitting or standing, but not lying down. The cause may be orthostatic hypotension (a decrease in pressure after moving from a horizontal to a vertical position), arrhythmia and vasovagal crisis (excessive activity of the vagus nerve, leading to a decrease in heart rate).
Mental disorders
Depression, anxiety or panic disorder, alcohol addiction or personality disorder can lead to non-systemic dizziness. For example, if a person, in addition to this symptom, also has shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat and sweating, then most likely we are talking about a panic attack. A psychiatrist works with all these conditions.
Damage due to medication
Some aminoglycosides (for example, gentamicin) can be toxic to the vestibular system: they damage the hair cells of the inner ear, provoke imbalance and cause oscillopsia (the illusion of vibration of surrounding objects) when moving the head. This condition can become chronic.
Antiepileptic drugs, sedatives, and tranquilizers can also cause non-systemic dizziness. Sometimes blood pressure-lowering medications are too effective and blood pressure drops to abnormal levels, causing symptoms similar to dizziness.
Acoustic neuroma
When walking, a person begins to sway, surrounding objects move, his hearing may also deteriorate, and tinnitus may occur - these are the main symptoms of an acoustic neuroma (benign neoplasm). In most cases, such patients are prescribed surgery or radiation therapy.
Stranding syndrome (sea sickness on land)
After traveling on water, in very rare cases, a person may develop this syndrome: the patient feels that he is losing his balance, he is swaying, it seems to him that he is walking on uneven ground. This condition usually goes away within a couple of days. However, in more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe benzodiazepines or the antiepileptic drug clonazepam.
Non-systemic dizziness can also be caused by anemia (accompanied by fatigue, weakness and pallor), hypoglycemia (low blood sugar, which may be manifested by sweating and confusion), inflammation of the ear, heat stroke or dehydration.
Severe dizziness: 6 pathological causes
The causes of dizziness are not always harmless. Sometimes illnesses become sources of unpleasant conditions. In this case, dizziness occurs quite often and can last longer than a few seconds. To cope with this phenomenon, you need to consult a doctor. The severity of a symptom can be reduced (and sometimes completely eliminated) only through proper treatment of the underlying disease.
So, the causes of dizziness may include the following pathologies:
- Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD). A complex disorder in which a person experiences multiple impairments. All these symptoms are associated with malfunctions of the autonomic system. One of the common signs of VSD is dizziness. Such attacks are usually caused by sudden movements and rapid changes in posture. Dizziness does not last long. They go away on their own, without any intervention.
- Disorders in the cervical spine. Various injuries, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias can periodically remind you of themselves with sudden attacks of dizziness. They usually appear after active neck movements. The attack is accompanied by pain in the affected area, sometimes a crunching or crackling sound is heard.
- Anemia. Dizziness may occur due to iron deficiency. Most often this pathology is observed in children and women. With anemia, attacks are accompanied by high fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and pre-fainting conditions.
- Psychogenic dizziness. The reason for this pathology lies in the patient’s increased anxiety (people with an unstable psyche) or in the stress they have endured. Such people usually complain of poor sleep, fear of losing consciousness, a periodic feeling of shortness of breath, and increased heart rate.
- Vertebrobasilar insufficiency. This is a pathology in which blood flow in the vertebral or basilar arteries is weakened. Such problems lead to disruption of brain function. The pathology is characterized by regular attacks of dizziness, which can last up to an hour. In addition, patients complain of nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbances may occur. I often have a headache.
- Hypotension. A decrease in blood pressure is often accompanied by attacks of dizziness. Sometimes lightheadedness may occur.
Conclusion
With high or low blood pressure and dizziness, the causes are poor circulation. In the case of hypertension, blood pressure can be lowered with special medications (hypotensives) and lifestyle changes. Hypotension also requires lifestyle adjustments, sufficient movement, drinking regimen, and a balanced diet. Taking medications is usually not necessary.
If problems with dizziness persist, it is necessary to look for other causes.
Severe dizziness: 6 dangerous reasons
In some cases, vertigo signals the development of severe conditions that require immediate medical attention. Causes of severe dizziness may include:
- Labyrinthitis (internal otitis). A viral infection in the inner ear may be asymptomatic at first. The only sign of otitis media is dizziness, which lasts for several minutes. Such attacks are repeated quite often. In the future, the viral process can affect the nervous system or brain.
- Concussion. Sometimes after a head injury, only dizziness appears. This symptom should not be ignored. It serves as direct evidence of a concussion. To eliminate the risk of swelling or serious brain damage, you should immediately seek medical help.
- Stroke. If dizziness is accompanied by sudden weakness, complaints of numbness of a body part, visual impairment, speech disturbances, then the risk of stroke is high. This is a severe pathology in which blood circulation in the brain is disrupted.
- Migraine. Dizziness accompanied by a severe headache may indicate a migraine. Many people believe that this condition is harmless. But doctors say that migraine, especially in an advanced state, can lead to severe damage (sometimes even to a heart attack or stroke).
- Cardiovascular diseases. Such pathologies are characterized by the appearance of dizziness every time a person gets up. It is caused by a sharp decrease in pressure. Symptoms like these may indicate dehydration, which is causing your blood to thicken. But if the problem is not fluid deficiency, then it may be the development of arrhythmia or heart failure.
- Tumors. Regular attacks of vertigo combined with headaches, usually in one side of the head, can signal the development of a tumor in the brain.
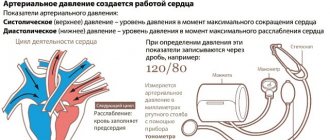
Hypertension and its symptoms
Hypertension syndrome is a condition in which a sustained increase in blood pressure develops.
Each person has their own norm, but high blood pressure has an extremely negative effect on the body. This leads to vascular disorders, the heart works harder, which means the risk of heart attack and stroke increases significantly. Important:
Hypertension can develop even in children.
This is due to common birth injuries. You can learn more about this phenomenon from other videos on Dr. Shishonin’s channel
.
Today, hypertension is not a disease of older people. The disease is getting younger, and every year more and more middle-aged and even young people are becoming chronic hypertensive patients. Bad habits, poor environmental conditions, constant stress and a sedentary lifestyle take their toll.
In the early stages, the disease manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- headache;
- the appearance of “flies” before the eyes;
- noise in ears;
- sleep disorders.
The progressive disease not only damages blood vessels, but also negatively affects the condition of the liver, kidneys, and can destroy the retina. However, dizziness is not among the symptoms of hypertension.
What to do?
It is almost impossible to independently determine the causes of frequent attacks of dizziness. Therefore, those who regularly experience vertigo are advised to go to an appointment with a therapist, or a neurologist. The specialist will carefully examine the patient’s complaints and prescribe diagnostic tests. If necessary, the doctor will refer the patient for consultations with an ENT specialist, an ophthalmologist, a cardiologist, or an endocrinologist.
To identify the causes of vertigo, the patient may be prescribed the following tests:
- Neurological tests. They allow you to assess the functionality of the vestibular apparatus.
- MRI or CT. Such brain studies reveal various disorders (hemorrhages, tumors, vascular pathologies).
- Ultrasound Doppler. Using Doppler ultrasound, the condition of the vessels of the head and neck is studied.
- Audiometry. Diagnostics allows us to assess hearing function.
- EEG. To study the activity of the cerebral cortex, the doctor will prescribe electroencephalography.
To quickly cope with dizziness (of course, if it is not caused by dangerous reasons), you can sit on any surface, relax a little and take 5-6 deep breaths. Be sure to open the window (if you are indoors) to provide fresh air. If the causes of vertigo are harmless, then such actions are quite enough for the dizziness to disappear without a trace.
Dizziness during pregnancy
Pregnant women not only often feel nauseous, but also experience morning vomiting and fatigue. Often during this period weakness and dizziness occur. These problems are caused by low blood pressure and insufficient blood supply to the brain. Such symptoms can affect a woman at any stage of pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the body undergoes many changes. The heart pumps more than twice as much blood throughout the body, the circulatory system expands, which can cause pressure in the arteries and veins to drop. A pregnant woman's blood is primarily oriented towards the fetus, which is why she may suffer from temporary hypotension. These problems usually arise in the first months of pregnancy, when the body is just adapting to a new situation.
In late pregnancy, disproportionately high fetal pressure on the inferior vena cava may occur. This slows down the flow of blood, which can cause the woman to vomit. Another period of risk occurs after the baby is born, during breastfeeding.
How to prevent dizziness:
- Do suitable exercises regularly. Movement strengthens the muscles, heart, and blood vessels, which can more easily compensate for a decrease or increase in pressure.
- Drink enough fluids and sleep well.
- Don't stand in one place for a long time.
- Avoid stuffy rooms and hot environments.
- Slowly get out of bed. First sit down, lower your legs, stand up.
- Eat regularly. A hungry body is much weaker.
- If you feel dizzy while walking, sit down. If necessary, ask others for help.
Dangers of dizziness during pregnancy
Dizziness and low blood pressure itself are not dangerous for a pregnant woman. But fainting and prolonged unconsciousness are fraught with insufficient oxygen supply to the brain.
Constant dizziness threatens to fall, threatening both mother and child (can lead to fetal damage, miscarriage, premature birth).