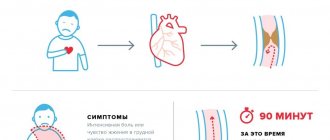
Every day, thousands of people complain of pain syndromes in one organ or another. Pain indicates a dysfunction of the body, the presence of pathology. Unpleasant sensations in the heart area can be caused by a number of reasons and other factors. The appearance of symptoms is associated both with disorders of the cardiovascular system and with pathologies of neighboring organs. They put stress on the heart, thereby causing shooting pains in the heart.
Pain in the heart has different intensity, character, and frequency. Medical experts distinguish this type of heart pain:
- dull aching pain in the heart;
- sharp pain in the heart;
- cutting pain in the heart;
- acute pain in the heart.
The patient feels unpleasant sensations that interfere with normal life and do not allow normal functioning. Most often, pain syndromes in the heart area appear during physical activity. This problem is familiar to athletes and people who are associated with constant physical activity. Emotional stress and constant stress also affect the development of pathologies of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Pressure
40 thousand die every year due to cerebral hemorrhage due to high blood pressure. At the same time, if you follow the rules for controlling blood pressure and do not provoke its increase, you can avoid not only feeling unwell, but also more serious problems.
A persistent increase in blood pressure above 140/90 is a serious factor for concern and suspicion of the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Too rare (less than 50 beats per minute), frequent (more than 90–100 per minute) or irregular pulse should also alert you; such deviations may indicate coronary disease, a violation of the conduction system of the heart and the regulation of cardiac activity.
Treatment of cardiovascular diseases
Carrying out examinations will determine why the heartbeat radiates to the head, after which the doctor will prescribe treatment. For atherosclerosis, it is necessary to use complex therapy aimed not only at strengthening the walls of blood vessels, but also at normalizing blood pressure. The specialist also recommends taking medications that improve blood composition and prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques.
For pathologies of the veins or arteries, treatment is prescribed individually - much depends on the general condition of the patient and the nature of the course of the disease. It is recommended to undergo a course of drug therapy - a stroke may develop against the background of vasoconstriction. Most often, medications are prescribed to prevent the formation of blood clots.
For high or low blood pressure, it is recommended to take medications that stabilize blood pressure. With the permission of a specialist, you can supplement drug therapy with home remedies. Herbal decoctions or tinctures will help normalize blood pressure, strengthen blood vessels, and improve heart function.
Pain resembling osteochondrosis
Pain between the shoulder blades, in the neck, left arm, shoulder, wrist, even in the jaw can be a sure sign of not only osteochondrosis or myositis, but also heart problems.
Article on the topic
Stroke: risk factors, dangerous symptoms, first aid A symptom of angina pectoris may be the occurrence of such symptoms after physical activity or emotional shock. If pain occurs even during rest and after using special heart medications, this symptom may indicate an approaching heart attack.
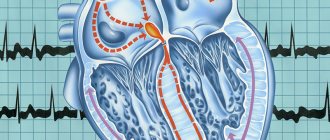
Diagnosis of myocarditis
For diagnostics
of myocardium, instrumental and laboratory methods are used, as well as myocardial biopsy.
Instrumental methods include:
- ECG - rhythm and conduction disturbances may be detected for the first time, sometimes infarction-like changes (especially in the acute phase of inflammation);
- ECHO CG - disturbances in systolic (due to the death of cardiomyocytes) and diastolic (due to swelling of the walls of the left ventricle) myocardial function;
- MRI contrast with gadolinium clearly reveals edema of the heart wall (as one of the stages of inflammation), but can be false negative;
- Myocardial scintigraphy can be informative in cases of suspected sarcoid myocarditis, but in other cases it is not very specific.
Laboratory methods include:
- A clinical blood test that can reveal an increase in ESR, an increase in the number of leukocytes, and in some forms, eosinophils;
- A study of the value of the so-called cardiac-specific enzymes (troponin T and CPK) reveals their increase, but a negative result does not exclude the diagnosis of myocarditis;
- Determination of serum antimyocardial antibodies.
- Routine serological viral testing is not recommended; it may only be useful in diagnosing diphtheria or borreliosis myocarditis
The gold standard for diagnosing myocarditis is endomyocardial myocardial biopsy (EMB), which is performed only in specialized hospitals and according to strict indications. Indications for referral are determined by the attending physician.
Chest pain
A feeling of burning and squeezing, obvious, dull, severe or periodic pain, spasm - all these sensations in the chest are the surest sign of heart problems. With spasm of the coronary vessels, the pain is burning and acute, which is a sign of angina pectoris, which often occurs even at rest, for example at night. An attack of angina is a harbinger of myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease (CHD).
Severe, prolonged pain in the chest, radiating to the left arm, neck and back, is characteristic of a developing myocardial infarction. Chest pain during myocardial infarction can be extremely severe, including loss of consciousness. By the way, one of the most common causes of heart attack is atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels.
Chest pain radiating to the back of the head, back, or groin area is a symptom of an aortic aneurysm or dissection.
Dull and wave-like pain in the heart area, which does not spread to other areas of the body, accompanied by an increase in temperature, indicates the development of pericarditis.
However, acute chest pain may also indicate other diseases, for example, be a symptom of intercostal neuralgia, herpes zoster, sciatica in the neck or chest, spontaneous pneumothorax, or esophageal spasm.
Causes of sharp pain in the heart area
The occurrence of severe pain is influenced by many factors. It is by paying attention to the symptoms that an accurate diagnosis can be made and effective treatment can be prescribed.
- Pain syndrome, which is localized in the chest, indicates pathologies of the cardiovascular system. There are several associated symptoms. Among them, increased heart rate is tachycardia.
- Hypertension and hypotension. With hypertension, a person feels dizzy, feels a sharp stabbing pain in the heart and head, and has migraines for a long time. Pain syndromes are nagging, aching. With hypotension, the patient becomes dizzy, has a feeling of general weakness, fainting, and loss of appetite. It is not life-threatening when taking medications that normalize blood pressure.
- Angina pectoris. Acute pain in the heart area may be a sign of angina. Associated symptoms are headache and tinnitus. Not dangerous to human life if treated correctly.
- Myocarditis and endocarditis.
- Myocardial infarction. When a person breaks into a cold sweat, becomes dizzy and experiences sharp pain in the heart, then we are talking about myocardial infarction. You should call an ambulance immediately.
- Cardiac aneurysm.
- Cardialgia. It causes intense nagging pain, panic and anxiety in the patient.
Non-cardiac causes also influence the patient’s poor health. They are responsible for the condition of other internal organs. Among them:
- Osteochondrosis. With osteochondrosis, a person feels severe pain not only in the spine. The severity also affects the cardiovascular system.
- Tuberculosis and pneumonia. If the respiratory tract is impaired, pain occurs when moving, breathing and laughing.
- Ulcer. Inflammation of the duodenum leads to acute pain in the stomach and heart.
- Gastrointestinal tract disorders. If there is a gastrointestinal tract disorder, the patient's condition may be accompanied by acute pain in the heart area.
- Mastopathy and other pathologies. In women, heart pain is often caused by breast problems. One of them is called mastopathy.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms.
- Musculoskeletal disorders. Inflammatory processes in the musculoskeletal system are caused not only by pain in the joints and muscles, but also by a pulling sensation in the heart area. Such diagnoses include fractures of ribs, joints, cracks, and pits.
- Nervous system disorders. The nervous system is closely connected with the heart, so frequent stress and emotional stress cause pain in the heart area.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. The main symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia are migraine and heart pain.
- Pancreatitis. With the inflammatory process of the pancreas, acute pain in the heart and stomach is observed.
- Toxic poisoning. In case of toxic poisoning with drugs or alcohol, the patient begins to experience tachycardia, increased blood pressure and severe pain in the heart.
- Cholecystitis. When the walls of the gallbladder are inflamed, pain in the heart is observed. The pain is dull.
It is noteworthy that heart pathology develops when the patient feels severe pain in the center of the organ. She is observed behind the sternum. Cardiovascular system disorders are characterized by other symptoms. The patient's condition worsens after stress and emotional stress.
If the pain is associated with other organs, then it intensifies when turning, walking and talking. Sharp pain syndromes appear in the case of angina pectoris, myocardial infarction and stroke. In such cases, you should urgently call an ambulance. With a cardiac aneurysm, the patient cannot tolerate severe attacks and suffers from dizziness and general weakness. The pain also spreads to neighboring organs. Continues for several hours. With pneumothorax, the discomfort increases with every second, especially when breathing. The stabbing pain intensifies with walking and movement.
Palpitations
Palpitations can occur during intense physical activity, as a result of a person's emotional arousal, or due to overeating. But a strong heartbeat is very often an early warning sign of cardiovascular disease.
A strong heartbeat manifests itself as a feeling of disruption in the functioning of the heart; it seems that the heart is almost “jumping out” of the chest or freezing. Attacks may be accompanied by weakness, discomfort in the heart, and fainting.
Such symptoms may indicate tachycardia, angina pectoris, heart failure, or impaired blood supply to organs.
If you have at least one of the listed symptoms, it is important to immediately consult a doctor and undergo tests that will reveal the true cause of the ailment. One of the most effective methods of treating any disease is its early diagnosis and timely prevention.
Diagnosis of cutting pain in the heart
How to diagnose cutting pain in the heart? Make an appointment with a cardiologist at the KDS Clinic. Tell your doctor about the nature, frequency and intensity of pain. Thus, the specialist will determine the exact diagnosis. You will be sent for testing. It is worth undergoing examinations such as ultrasound diagnostics of the heart, electrocardiogram. Once a diagnosis is made, each patient is assigned effective and affordable treatment. If the situation is critical, call an ambulance and take painkillers.
In more advanced cases, the patient remains in the hospital, where KDS Clinic staff monitor the patient’s condition, indicators, improvement or deterioration. Most often, medication treatment is prescribed at home.
Treatment of angina
Since stenography develops against the background of coronary heart disease, it is important to eliminate the root cause of the disease in order to then cope with associated symptoms. At the same time, measures are taken to relieve pain and prevent new attacks.
First aid for angina pectoris is to take nitroglycerin, which reduces pain. A permanent treatment course focuses on taking anti-ischemic drugs, thanks to which the heart continues to work stably in conditions of lack of oxygen. Stenting and coronary artery bypass surgery allow the lumen of blood vessels to expand, restoring the conductive capacity of the arteries. Other clinical recommendations for angina pectoris are selected taking into account the patient’s condition, his age and the severity of cardiac pathology.
Causes of angina
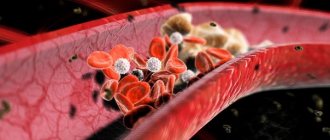
Long-term study of angina pectoris allows us to accurately name the physiological mechanism of the development of the disease. Due to nutritional and metabolic disorders, the lumen of the arteries gradually narrows due to atherosclerotic plaques. Deterioration of blood flow causes oxygen starvation of the heart muscle cells, which causes obvious and quite severe pain. At the same time, vascular spasm may occur, caused by nervous overstrain or hypothermia of the body.
The appearance and accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels is often provoked by:
- symptoms of arterial hypertension;
- smoking;
- obesity;
- symptoms of diabetes;
- physical inactivity, sedentary lifestyle;
- unsatisfactory food quality.
The process of reducing the lumen of the artery occurs gradually. When it narrows by 50% or more, the blood flow noticeably deteriorates, which leads to disturbances in the functioning of the heart muscle. Physical activity and psycho-emotional stress contribute to the aggravation of the situation, forcing the heart to work intensively against the background of oxygen starvation. Lack of oxygen causes malnutrition of muscle tissue, which causes a characteristic pain syndrome with signs of suffocation and pressure in the heart area.
Risk factors that trigger the process of vasoconstriction due to the formation of sclerotic plaques
When making a primary diagnosis, the specialist must take into account the possible effect of one or more of the following factors:
- hyperlipidemia – disorders of cholesterol metabolism with a simultaneous decrease in high-density lipoproteins;
- obesity caused by the predominance of animal fats and high-calorie foods in the diet against the background of a lack of cereals, vegetables, fruits and legumes;
- physical inactivity is a lack of movement that triggers the development of obesity due to the accumulation of cholesterol;
- arterial hypertension is a companion to coronary heart disease due to oxygen deficiency;
- anemia - a decrease in hemoglobin level against the background of general weakness of the body;
- type 2 diabetes mellitus, which is considered one of the most dangerous risk factors;
- tobacco addiction - helps to reduce the volume of oxygen in the blood, increases blood pressure and promotes spasm of arteries narrowed due to the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques.
The action of at least two factors is sufficient for angina to become serious and require immediate intervention by a specialist.
Classification and symptoms of angina
Depending on the symptomatic picture, there are:
- a stable type of disease that occurs in an unchanged form and requires the most serious treatment;
- unstable angina - the most dangerous, of a primary nature or each time making itself felt with new symptoms;
- angina pectoris is an invariable sign of increased physical activity;
- angina at rest has no clear cause and can manifest itself even during sleep, accompanied by a feeling of panic, suffocation, and a set of autonomic disorders.
Characteristic signs allow you to distinguish angina pectoris from other diseases of the heart muscle:
- pressing burning pain;
- recoil under the left shoulder blade, in the neck or arm;
- noticeable fluctuations in pulse and blood pressure.
Any signs of angina pectoris should be a reason to contact a specialized doctor to clarify the diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Are you experiencing symptoms of angina?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call