Pregnancy is a special period in a woman’s life. Her body begins to work at a different pace, so cases of rapid heartbeat are not uncommon. This phenomenon is called tachycardia. A pregnant woman is said to have palpitations when the heart rate exceeds one hundred beats per minute. Most likely, the heartbeat will return to normal. However, if tachycardia occurs too often and does not go away after the recommended actions, then contact a specialist immediately.
Rapid heartbeat: what is it?
A rapid heartbeat (tachycardia) is said to occur when the frequency of contractions of the arteries of the heart exceeds the norm established for a certain age. The human pulse is one of the most important biomarkers that reflects the picture of general health and level of physical fitness, therefore any changes in heart rate should be monitored over time under the influence of various etiological factors.
The heart is a muscle that, when contracting, ensures the circulation of blood enriched with vitamins, nutrients and oxygen and its transport to all tissues and organs. All work of the heart is subject to the cardiac cycle, which consists of systole (periods of tension) and diastole (periods of relaxation). When the cardiac cycle is disrupted, the heart rhythm changes, arrhythmia occurs, and heart rate slows down or speeds up, which is clinically manifested by a change in pulse value.
Pulmonary artery stenosis (PAS) in newborns is a narrowing of the lumen of the outflow tract of the right ventricle. Pathological changes affect the pulmonary valve or part of the vessel in the valve area. Read more in the article: “pulmonary artery stenosis in newborns.”
Rapid heartbeat can be considered a pathology only if a change in pulse is observed at rest, or tachycardia does not go away for a long period of time, occurs at night (and also if a woman is diagnosed with more than 10 attacks of tachycardia per day).
Causes
The main causes of heart palpitations during pregnancy are physiological changes in a woman’s body. In the early stages, hormonal changes occur against the background of increased secretion of sex hormones, which leads to stimulation of the heart muscle and the development of tachycardia. Gradually, with the growth of the fetus and uterus, the volume of circulating blood increases, and the uteroplacental circulation appears. All this creates additional stress on the heart. In the later stages, when the child is already quite large, a displacement of the organs located next to him occurs.
The position of the heart also changes to some extent, which may affect its functioning. The cause of tachycardia may be other factors, namely:
- development of ectopic pregnancy; excess weight;
- severe stress, anxiety, fears;
- increased metabolic rate, leading to a deficiency of vitamins that are necessary for normal heart function;
- anemia;
- hypertension or hypotension;
- severe form of toxicosis;
- taking medications;
- allergies, bronchial asthma;
- thyroid diseases;
- infections and inflammations;
Physiological reasons
In addition to changes in hormonal levels, the causes of rapid heartbeat in pregnant women may be other factors related to the characteristics of female physiology during a given period. These include:
- a progressive increase in the size of the uterus, which, as the fetus grows, stretches and begins to put pressure on the diaphragm and blood vessels, preventing normal blood circulation (less blood and oxygen enter the heart, as a result of which it is forced to contract more intensely than usual);
- increase in body weight, leading to the occurrence of reflex cardiac reactions;
- vitamin deficiency and deficiency of macro- and microelements necessary for the proper functioning of the heart (most of the nutrients, especially potassium and magnesium, enter the fetus’s body for its growth and development);
- toxicosis;
- iron deficiency anemia (to varying degrees in almost all pregnant women).
Often, moderate tachycardia occurs against the background of allergic reactions, in case of violation of the dosage regimen of medications (including vitamin complexes) and the use of drugs prohibited for use during pregnancy. Natural factors that disrupt normal heart rhythm are stress, strong emotional excitement and physical activity, which in pregnant women increases with each trimester. Rapid heartbeat, if the deviation from the reference value does not exceed 10%, is also the norm for pregnant women, since to provide the fetus with the necessary elements and oxygen, an increase in the volume of circulating blood is required, as a result of which the heart begins to contract more actively.
There are several ways to check for coronavirus at home, but few of them are quite informative. The need for self-diagnosis usually arises when a doctor refuses to write a referral for biomaterial and laboratory testing. Read more in the article: “how to test for coronavirus: diagnostic methods.”
Pregnancy and blood pressure
Blood pressure and pregnancy
Pregnancy is a period when the female body uses all its potential, all its reserves, to provide everything necessary for the full bearing of a child.
Blood pressure is one of the main parameters of the intensity of blood flow in the body. During the period of bearing a baby, a woman’s body is faced with the need to provide oxygen and nutrition not only to itself, but also to the unborn child. Changes in blood pressure during pregnancy become an indicator of disturbances in the functioning of the body that threaten the health of the woman and child, and can also complicate the course of childbirth.
When is blood pressure measured?
At every appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist or therapist in the antenatal clinic, the expectant mother's blood pressure must be measured. But visits to the doctor's office should not be limited. It is necessary to measure this indicator yourself in the morning and evening; in order for the results to be compared, they must be written down daily in a special notebook. Particular attention to their blood pressure should be paid to those women who have previously had pregnancy toxicosis, miscarriages, or missed pregnancies. Women with hypertension, excess body weight, neurocircular and vegetative-vascular dystonia, kidney, heart, and vascular diseases should be specially registered and have their blood pressure measured as often as recommended by the doctor.
Hourly blood pressure measurement in high-risk pregnant women is called 24-hour monitoring. It is done three times during the entire period of pregnancy. The first time - at the very beginning of pregnancy, to identify a woman’s tendency to hypertension, the second time - at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy, to identify a predisposition to gestosis or late toxicosis of pregnant women, the third time - before childbirth, to determine the degree of risk for the woman and the fetus , and also resolve the issue of the method of obstetrics.
If problems with blood pressure are detected in a pregnant woman, then it is necessary to visit a cardiologist and a therapist who can advise what needs to be done to solve the problem of blood pressure during pregnancy.
Types of tonometers
There are two types of tonometers (device for measuring blood pressure) - mechanical and electronic.
- Doctors use a mechanical tonometer. It gives the most accurate results. You can learn to use a mechanical tonometer at home. However, measuring your own blood pressure is very difficult, so if you want to use this type of blood pressure monitor, you will need an assistant.
- An electronic tonometer is easier to use. Simply put the cuff on your arm and press the button. The device itself will do the rest, and all you have to do is read the results on the electronic display. The electronic tonometer shows blood pressure and pulse, memorizing the indicators. There are blood pressure monitors whose cuff can be worn on the shoulder, on the wrist, and even on the finger. The most suitable device for home use is one whose cuff is placed on the shoulder. Wrist or finger devices can be used to measure blood pressure at work or while traveling.
Correct blood pressure measurement
You should not immediately panic because of high or low blood pressure during pregnancy; you need to make sure that the measurement is correct.
There are several important rules for correctly determining blood pressure:
- Before measuring, sit down and rest for a couple of minutes, think about something pleasant. Stress is one of the factors that causes short-term increases in blood pressure.
- Place the cuff on your bare arm or thin cloth. It must be selected according to size.
- Measure the pressure on both arms.
- Never round the numbers you get and write them down exactly.
- It is not recommended to determine blood pressure immediately after a meal or after physical activity.
Blood pressure during pregnancy: norm and deviations
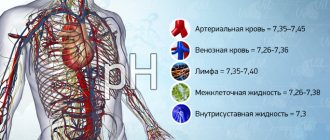
Blood pressure is the force of blood flow on the wall of blood vessels. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and written as two numbers separated by a slash.
The first number shows the pressure value at the moment of maximum contraction of the heart (systolic blood pressure), and the second - at the moment of its complete relaxation (diastolic blood pressure). If blood pressure is normal, we can safely say that the mother’s cardiovascular system is doing its job, which means that all organs receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients brought by the blood flow.
Outside of pregnancy, blood pressure is considered normal in the range from 100/60 to 130/80 mmHg. Art. During pregnancy, the pressure may differ slightly from the original: if it is 10% lower or higher than usual, then such changes are still within normal limits. If the pressure is 15–20% or more lower or higher than usual, then we are dealing with arterial hypotension (low blood pressure) or arterial hypertension (high blood pressure). It is advisable for a woman to know her normal pressure level, which was before pregnancy, so that the doctor can draw the right conclusions.
1.1 What is the danger of changes in blood pressure
During pregnancy, nutrients and oxygen are constantly supplied to the fetus through the vascular network of the placenta, and waste products are constantly supplied back to the mother.
Such an exchange is possible only at an optimal level of pressure. A change in blood pressure in either direction can have adverse consequences.
With low blood pressure, transportation worsens and the amount of substances the child needs decreases, which can lead to fetal growth retardation syndrome. A significant increase in blood pressure can cause damage to microvessels, foci of hemorrhage are formed, which can lead to placental abruption. This is why it is so important to control your blood pressure during pregnancy and maintain it at an optimal level.
Normal blood pressure during pregnancy
The norms of blood pressure accepted in general medicine range from 100/60 to 120/80 mmHg. But during pregnancy, these indicators may change somewhat. Usually in the early stages (the entire 1st trimester and up to 20 weeks), these numbers decrease slightly, which is associated with changes in the hormonal levels of the whole body and the restructuring of metabolic processes.
Later, as the fetus grows and more intense blood flow forms to nourish it, the pressure may increase relative to “non-pregnant” indicators. Because of this, the average norm for expectant mothers lies in a wider range - from 105/60 to 139/89 mmHg.
Significant deviations from this range to a greater extent are called pregnancy hypertension, and to a lesser extent - hypotension.
Low blood pressure during pregnancy or hypotension
In the first months of pregnancy, the hormonal background of the expectant mother undergoes significant changes, works under heavy load, creating a favorable background for the development of the child, and these changes are often accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure and hypotension.
1.1.1 Possible causes of hypotension
Sometimes it is impossible to determine the cause that provoked the appearance of such a disorder, but the following may play a role in its development:
- Hormonal changes;
- NCD of hypotonic type;
- Infectious diseases;
- Liver pathology;
- Taking certain medications;
- Peculiarities of a woman's emotionality.
Hypotension in pregnant women is often not perceived as a serious threat to the health and course of pregnancy. However, it can represent a serious pathogenic factor that provokes various pregnancy disorders:
- Abortion
- Fetal growth restriction
- Oxygen starvation of the baby
- Weakness of labor
- Possible bleeding after placenta separation
- Relaxation of the uterus after childbirth and repeated bleeding
1.1.2 Main symptoms of hypotension:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Headache
- Tinnitus
- Dyspnea
- Dizziness
- Increased fatigue
- Drowsiness
- Pale skin
- Increased sweating
- Loss of consciousness
1.1.3 How to increase blood pressure or what to do with low blood pressure
As a rule, women with low blood pressure are not hospitalized unless there is a risk to the child. Expectant mothers are observed by an obstetrician-gynecologist, a therapist and, if necessary, a cardiologist. Most often, the pressure normalizes in the third trimester.
Pregnant women should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Get at least 8 hours of sleep (9–10 hours is optimal) and rest during the day if possible.
- Spend more time outdoors (at least 2 hours a day).
- You should take food in small portions, but throughout the day.
- Moderate physical activity is recommended - do gymnastics for pregnant women; If possible, swim.
- Water procedures are useful - showers, douches, contrast foot baths, as well as massage; Physiotherapy (electric sleep, salt-pine and mineral baths) and acupuncture are successfully used for treatment.
- If necessary, doctors can prescribe drug therapy: usually pregnant women are prescribed herbal preparations that increase the tone of the autonomic nervous system, for example, eleutherococcus extracts, radiols, tinctures of lemongrass, aralia, zamanikha in combination with sedatives (valerian, motherwort), as well as caffeine-based medications .
If a pregnant woman loses consciousness due to a sharp drop in pressure, first of all she must be laid horizontally on her side and call an ambulance. Then open the door or window, unfasten the collar, and let the ammonia smell. You can massage the area between the nose and lip or work on the tips of your fingers.
High blood pressure during pregnancy or hypertension
Arterial hypertension is a disease characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure. Changes that occur in the body during pregnancy predispose to the development of hypertension and therefore pregnant women are at higher risk of developing hypertension than the general population. Arterial hypertension is a risk factor for various pregnancy complications and ranks second in the list of causes of maternal mortality. At the same time, the diagnosis and treatment of arterial hypertension in pregnant women requires a special approach.
If before pregnancy you noted that your blood pressure was higher than normal, took pills, and visited the appropriate doctors, be prepared that this problem will pop up now. Moreover, most likely it will manifest itself with greater force.
Remember: the situation is completely different now, you don’t need to take the same pills as before pregnancy.
Forms of arterial hypertension during pregnancy
Arterial hypertension of pregnancy is an increase in blood pressure during pregnancy. It is regarded as a persistent increase in systolic blood pressure above 140 mmHg. and diastolic blood pressure above 90 mmHg. in women with normal blood pressure before pregnancy. Women with such elevated blood pressure require close medical supervision.
There are several types of arterial hypertension during pregnancy:
- Chronic hypertension is characterized by the presence of high blood pressure before pregnancy and its persistence after pregnancy.
- Arterial hypertension of pregnancy is a persistent increase in blood pressure that develops after the 20th week of pregnancy, which disappears at the end of pregnancy.
- Preeclampsia/eclampsia is a severe disorder of the cardiovascular system and kidneys during pregnancy, which includes: hypertension and impaired renal function.
In pregnant women, arterial hypertension occurs with a frequency of 4-8%, which is a very high figure, especially if we take into account the young age of most expectant mothers. During pregnancy, a woman’s body adapts to new operating conditions, which include ensuring the vital activity and development of the fetus. The following changes occur in the body of a pregnant woman regarding the cardiovascular system:
- An increase in the volume of circulating blood and the appearance of the placental circulatory system is necessary to ensure the nutrition and development of the child. In pregnant women, the volume of circulating blood increases by 25-30%, which, in addition to providing nutrition for the child, allows women to lose some blood during childbirth, without significant damage to health.
- Increased heart rate.
- An increase in intra-abdominal pressure, an increase in the diaphragm and a change in the position of the heart in the chest due to a significant increase in the size of the uterus.
- Gradual weight gain in a pregnant woman.
Possible other causes of high blood pressure
- Physical exercise
- Drinking strong tea or coffee
- Chronic stress, fatigue, lack of sleep, emotional stress
- Smoking, alcohol abuse
- Unbalanced diet, lack of vitamins and minerals
- Obesity, overweight
- Multiple pregnancy
- Weak physical activity
- Thyroid diseases
- Adrenal diseases
- Diabetes
- Head, brain and spinal cord injuries
- Encephalitis
- Myelitis
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
- Renal dysfunction
- Hereditary predisposition
Main symptoms of hypertension:
- Headache
- Nausea, vomiting
- Dizziness, weakness, powerlessness
- Redness of the skin of the hands and face
- Noise or ringing in the ears
- Deterioration of vision
- Edema
- Protein excretion in urine
- Convulsions
High blood pressure can cause complications such as retinal detachment or retinal hemorrhage, which can lead to partial or complete loss of vision.
If blood pressure begins to increase in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, then we are probably dealing with a serious complication of pregnancy - gestosis.
Preeclampsia is a special condition that occurs only during pregnancy and ends with its completion. Manifestations of gestosis are varied, but the classic symptoms are:
- arterial hypertension
- swelling
- proteinuria (protein in urine)
With gestosis, microcirculation is disrupted in all vital organs: blood supply to the brain deteriorates, kidney failure develops, the blood becomes viscous, and the resulting microthrombi disrupt the functioning of all organs and systems. Particularly dangerous is such damage to the blood vessels of the placenta and brain. The most severe manifestation of gestosis is eclampsia - convulsive seizures ending in cerebral coma.
But gestosis often begins with a pathological increase in body weight. Expectant mothers often wonder why the doctor pays so much attention to weight. Well, just think, I added a couple of extra pounds.
But such an increase is due to fluid retention in the body, or so-called hidden edema.
And if treatment is not started in time, all manifestations of gestosis will not take long to appear. If there was an increase in blood pressure before pregnancy, then its successful course is possible only with good preparation and the correct selection of medications that lower blood pressure. For uncomplicated hypertension and a slight increase in blood pressure, only non-drug measures are sufficient.
More about gestosis
Treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension during pregnancy
Treatment of arterial hypertension during pregnancy is a complex and responsible task. Therefore, the basis of any type of treatment should be close cooperation between patient and doctor.
In the treatment of arterial hypertension in pregnant women, as well as in the treatment of arterial hypertension, the following methods are used: non-drug treatment and drug treatment.
Non-drug treatment, that is, treatment without drugs, is the most acceptable method of treating hypertension during pregnancy, since many drugs used in the treatment of this disease can be dangerous to the fetus.
What to do with blood pressure, how to reduce blood pressure during pregnancy
Non-drug treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension includes:
- Diet. The basic requirements for the diet of women suffering from hypertension are reducing the consumption of table salt, coffee, tea, and giving up bad habits. The permissible amount of salt per day for patients with hypertension is 5 grams, and the calculation must include not only the salt with which we season food, but also the salt contained in various food products.
- Physical activity. Moderate physical activity has a beneficial effect on the general condition of the body, promotes fat burning, normalizes metabolism, improves blood supply to internal organs and the fetus, increases muscle tone and helps to establish the correct position of the fetus in the uterus. For the treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension during pregnancy, daily physical activity in the form of gymnastics (preferably with an instructor), walking in the fresh air, and swimming are recommended.
- Maintaining normal body weight. The common expression that during pregnancy a woman “must eat for two” is not true. In fact, the “energy supplement” during pregnancy should not exceed 350 kcal. At the same time, maintaining a normal body weight during pregnancy is extremely important for maintaining the health of the pregnant woman herself and her child (obesity contributes to the development of hypertension and diabetes). The normal increase in body weight of a pregnant woman by the end of pregnancy should not exceed 12 kg.
Drug treatment of hypertension during pregnancy should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist and only using safe drugs.
- With a single slight increase in blood pressure, treatment begins with the prescription of sedative natural drugs, for example: valerian, motherwort, novopassit and others. In combination with non-drug therapy, these measures are very effective.
- If there is a constant increase in blood pressure, the following drugs can usually be prescribed, but only after the recommendation of a doctor. The main drug or “drug of choice,” the most effective and safe, is Methyldopa (Dopegit), which can be used during pregnancy from early stages of pregnancy.
- A group of drugs that can be prescribed from the second trimester of pregnancy are calcium channel blockers: Verapamil, Nifedipine.
- For persistent hypertension, beta-blockers can be prescribed from the 2nd-3rd trimester; this group of drugs does not have a teratogenic effect.
While taking medications, monitoring of the intrauterine condition of the fetus is necessary.
If the pressure suddenly increases and you feel unwell, urgent hospitalization is necessary. Only in a hospital is full control over the condition of the child and mother and full therapy possible.
The delivery plan and referral to the maternity hospital for pregnant women with high blood pressure are drawn up in advance. If problems arise that cannot be corrected, a caesarean section is performed.
Follow your doctor's advice.
He is a professional, he knows what is best for you and your child! Tags: pregnancy
Features of tachycardia in pregnant women
Advertising:
There are many reasons for frequent heart contractions, so patients with severe discomfort and repeated attacks must undergo examination. Some nuances need to be taken into account:
- In pregnant women in the first trimester, tachycardia occurs due to an increase in circulating blood volume and cardiac output to ensure the necessary blood flow to the fetus.
- Increased production of thyroid and adrenal hormones affects heart rate.
- There is a change in metabolism and a rapid increase in body weight.
- Experiences and stress increase the release of adrenaline, which is manifested by rapid heartbeat.
- Under the influence of progesterone, vascular tone weakens and pressure decreases, compensatory tachycardia occurs.
- As the fetus grows, the diaphragm rises, breathing and heart contractions become faster to deliver the required amount of oxygen.
- Iron deficiency anemia is manifested by dizziness and rapid pulse due to hypoxia.
- A sharp change in position and compression of large vessels by the uterus at a later date lead to sudden weakness and tachycardia, which disappear with a change in body position.
- Some medications affect blood pressure and heart rate. Before taking any medications, you should consult a gynecologist.
- Excessive physical activity worsens the condition.
- Nausea, severe headache and rapid heartbeat during late pregnancy may be signs of toxicosis.
Heart strain during pregnancy
The heart of a woman carrying a child has to work for two, pumping a larger volume of blood. Therefore, among expectant mothers, there are frequent cases of tachycardia - disturbances in heart rhythm in the direction of increased heart rate. The pulse increases for natural reasons:
- Women's weight gain;
- High content of hormones that increase heart rate (heart rate);
- Increased metabolism (metabolic rate);
- Shifting position of the heart under pressure from the growing uterus.
However, there are other factors. Because of them, the increase in heart rate often goes beyond the normal limits for pregnant women. So, other reasons for increased heart rate:
- Severe toxicosis with frequent vomiting;
- Smoking;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Excessive consumption of coffee and other foods and drinks containing caffeine;
- Taking certain medications. In particular, Naphthyzin vasoconstrictor drops can cause increased heart rate. The same goes for some other cold sprays.
When to sound the alarm?
If a woman feels normal and does not experience discomfort, there is no reason to worry. Such attacks occur from time to time in pregnant women and go away on their own. Unfortunately, attacks of rapid heartbeat are not always so harmless. The reasons for contacting a specialist are:
Advertising:
- increased fatigue;
- annoying headache for 2-3 hours;
- weakness and dizziness;
- sharp pain in the heart area;
- dyspnea;
- state of anxiety and fear;
- nausea and vomiting.
All these symptoms can be caused by other reasons, for example, excessive fatigue and drowsiness in the early stages are associated with an increase in the level of the hormone progesterone. If you are not sure whether this is a serious symptom, it is better to play it safe and consult your doctor. To find out the causes of ailments, a specialist will prescribe a professional examination, ECG, EchoCG or ultrasound examination of the heart and competent and effective treatment.
Rapid pulse in the third trimester
In the third trimester (from 28 weeks until birth), tachycardia of varying degrees is detected in almost every woman, since the uterus at this stage is large and compresses the vessels and diaphragm, and the child is rapidly gaining weight, which leads to the development of vitamin deficiency and deficiency conditions and lack of essential elements for the heart. In the third trimester, the so-called “late toxicosis of pregnancy” also occurs, which is called gestosis. All this together can provoke a sharp increase in the load on the heart muscle, a change in heart rhythm and an increase in the number of heart contractions to compensate for pathological reactions.
How to understand that a condition threatens your health
In the first trimester, tachycardia rarely occurs in a pregnant woman, and most often it is associated with the manifestation of early toxicosis. But perhaps this is a sign of a hidden disease. Both can be dangerous for both mother and child; a doctor’s consultation will not be superfluous. In the case of a physiological increase in heart rate, there is no threat to a pregnant woman.
A pathological malfunction of the sinoatrial node indicates the presence of the following abnormalities:
- the heart cannot withstand the increased load upon the birth of the fetus;
- anemia;
- arterial hypotension;
- reflex reaction of the myocardium to compression;
- nervous disorders;
- toxicosis of pregnant women;
- taking certain medications;
- endocrine diseases (in particular, thyrotoxicosis);
- imbalance between maternal energy needs and nutrition;
- water-electrolyte imbalance.
In the later stages of pregnancy, rhythm disturbances often have a natural (physiological) explanation: the uterus grows, the fetus increases in size and requires increased nutrition and oxygen supply. Seizures should not frighten a pregnant woman, but extra caution and attention to your health will not hurt: even a seemingly insignificant deviation from the norm can affect the outcome.
Complications
- Delayed fetal development.
- Premature birth or miscarriage.
- Death of the fetus in the mother's stomach.
- Difficult birth.
Symptoms
Moderate tachycardia is most often clinically mild and has a small number of clinical signs. An important symptom of physiological tachycardia in pregnant women is that the pulse returns to normal within 5-10 minutes after taking sedatives, eliminating provoking factors and at rest. If such attacks occur infrequently and do not affect the well-being of the pregnant woman, any medical assistance is not required (subject to dynamic monitoring).
But there are symptoms that must be immediately reported to your doctor, since their presence is an indication for a comprehensive diagnosis and exclusion of pathological causes of disruption of the normal cardiac cycle. You should seek the advice of a specialist in cases where palpitations are accompanied by the following symptoms:
Advertising:
- pathological pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- instability of blood pressure;
- increased attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- any bleeding (including bleeding from the vaginal tract);
- increased sweating;
- pulsation of blood vessels in the neck;
- severe swelling;
- dyspnea.
Women with heart disease may develop cardiac and acute coronary insufficiency. These are acute conditions with a fairly high risk of mortality, so if an attack occurs, the woman should be immediately hospitalized in the hospital. Pathological changes in heart rhythm are diagnosed using electrocardiographic examination, ultrasound diagnostics and auscultation. If necessary, a set of additional studies and consultations with specialized specialists are prescribed.
What to do if your heart rate is high
True pathological tachycardia in women who do not suffer from myocardial diseases and severe endocrine disorders is extremely rare, so drug treatment with antiarrhythmic drugs is usually not required. Beta blockers - the main drug group for the treatment of tachycardia - are contraindicated during pregnancy, as they can negatively affect the fetus, so they are prescribed only in case of vital need, and treatment is most often carried out in a hospital setting under constant laboratory monitoring of hemodynamic parameters.
In emergency situations, when the heart rate reaches critical values (up to 180-240 beats per minute), the question of the advisability of using lidocaine is decided, which, in addition to an anesthetic effect, also has antiarrhythmic properties and is a cardiac depressant. To relieve acute attacks, a continuous infusion method is used with a solution infusion rate of up to 4 mg/min and a loading dose of up to 1.5 mg/kg. If the attack is accompanied by a hypotensive crisis (the woman is unconscious), norepinephrine is administered intravenously to restore the heart rhythm.
How to provide first aid?
Advertising:
If the palpitations are mild, no special help is required. It usually goes away within a few minutes; the main thing is to avoid physical activity during this time. If tachycardia develops in the form of attacks with deterioration in health (dizziness, darkening of the eyes, difficulty breathing), you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- sit down or half-lie down, try to relax;
- warn others, ask them for help;
- ensure air flow: open the window, unbutton tight clothing;
- take Valerian;
- rinse your face with cool water and/or place a damp towel on your forehead;
- try to cough, take a deep breath and exhale;
- close your eyes and press your palms on your eyeballs (repeat several times).
Most often, all these measures relieve an attack of tachycardia. But if your health does not improve, you need to call an ambulance.
Risks
Tachycardia during pregnancy is considered a physiological phenomenon. Attacks of rapid heartbeat accelerate blood flow through the vessels, which helps provide the fetus with nutrients and oxygen. However, an increase in heart rate to 120 beats per minute and the appearance of corresponding symptoms may indicate a pathology caused by cardiac or extracardiac causes. Tachycardia in pregnant women requires monitoring. It is important to distinguish a physiological norm from a pathological rhythm disorder that requires urgent treatment.
Treatment with folk remedies
Constant tachycardia during pregnancy can negatively affect the course of pregnancy and the development of the fetus, since the work of the heart becomes ineffective when the cardiac cycle changes. Dangerous complications of tachycardia can include bleeding, premature placental abruption, and early onset of labor. For a child, too active heart contractions are dangerous due to various developmental defects, since blood flow to organs, including the placenta, worsens with an increase in the mother’s heart rate.
The danger of the pathology is also that many medications are contraindicated in pregnant women, so it is important to know safe methods of alternative treatment, many of which are quite effective for uncomplicated tachycardia.
Lemon-carrot mixture
This is a very effective remedy that can be used both as an emergency measure to normalize the pulse and for the complex treatment of tachycardia. In one container you need to mix 100 ml of carrot and lemon (natural) juice, then add a tablespoon of pureed cranberries. Mix everything and drink in three doses with an interval of 6 hours. It is best to drink the product after meals, as cranberry and lemon can disrupt the acidity of gastric juice.
The course of treatment is 21 days.
Melissa infusion
Melissa is one of the best herbal remedies to combat stress. Melissa infusion is useful for pregnant women, as it has a positive effect on the psycho-emotional state, is an additional source of vitamins and flavonoids, and has a mild anti-inflammatory effect. To prepare the infusion, you need to pour 2 teaspoons of lemon balm into a glass of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave for 30 minutes.
Drink 1 glass 3-4 times a day for 10 days.
Prevention of tachycardia during pregnancy
Advertising:
If the expectant mother does not have diseases that cause rapid heartbeat, attacks of tachycardia can be prevented. To do this, it is enough to follow simple preventive measures:
- normalize your diet, give preference to a vegetable-dairy diet;
- give up bad habits and sources of caffeine - no cocoa, coffee, chocolate, etc.;
- Minor physical activity is useful - walking in the fresh air, swimming;
- learn to relax and unwind, yoga, breathing techniques, etc. are useful;
- protect yourself from stress;
- drink at least one and a half liters of water per day;
- Get at least eight hours of sleep.
Palpitations in pregnant women in the early stages are not common. As a rule, the symptom bothers you no earlier than the second trimester. The rhythm is gradually disturbed, and closer to childbirth, attacks may become more frequent. In most cases, everything ends well, there are no complications.
If tachycardia is a symptom of the development of some disease, then it is of course impossible to predict in advance how it will affect the pregnancy and fetus. A thorough examination and consultation with doctors is necessary. It is important to identify all diseases at an early stage, preferably at the stage of pregnancy planning.
Diagnosis: tachycardia
If, in a calm, relaxed state, a pregnant woman’s pulse rises to high, doctors, as a rule, already speak of a diagnosis of “tachycardia.” This is the easiest level. The expectant mother does not feel pain in the chest area. Only occasionally she may feel discomfort, which goes away on its own after some time.
A more severe degree of tachycardia is if the pulse periodically jumps above 120 beats/min. Such a strong heartbeat is felt physically. The woman experiences dizziness, headache, nausea, and may even faint. All this happens against the background of general weakness and poor health. There is no need to attribute such symptoms to ordinary ailments of pregnant women. You should seek medical help as soon as possible. The doctor will assess the woman's health. If there are no other pathologies, special medications are prescribed, mainly herbal. These substances gently soothe and relax the nervous system. In addition, minerals are prescribed: magnesium, calcium and others.
Neuroses aggravate the situation with an increase in heart rate. In some cases, to relieve nervous tension, doctors prescribe medications for pregnant women, like Persen or Novo-Passit, and recommend taking valerian, motherwort, and drinking teas with lemon balm and mint.
High heart rate: what to do
It is not difficult to notice the first “bells” in the form of a slight increase in heart rate, which occurs rarely at first, then more and more often. In order not to lead to severe tachycardia, you need to be more attentive to your lifestyle, diet, and emotions.
The simplest means of preventing tachycardia and other heart problems are: walks in the fresh air, good sleep, rest, proper, balanced nutrition, and lack of stress. Don’t forget about physical activity (within the exercises allowed for pregnant women). Sometimes it is enough to do light exercises to relieve the nervousness that sets in.
If the mother's heart beats smoothly and calmly, the likelihood that the baby will be born healthy is much higher. Therefore, it is necessary to follow all doctor’s instructions and monitor your heart rate. The pulse will tell you if something is going wrong in the body.