They pricked the baby’s finger, took blood, and the next day, after standing in a long line, you took the test. Is it time to take another turn to show the test to the doctor? Let's take a look there ourselves and try to figure out what all these Latin words and mysterious numbers mean.
Whatever happens, doctors prescribe the same thing - a general blood test. Kidneys hurt - a general blood test, chest pain - the same thing, the temperature has risen - again a general blood test, and then we'll see. At least we are adults, but what if a child is sick? Why should he prick his fingers in vain - he’s crying!
In addition, doctors, having looked deeply into this analysis, always prescribe the same thing - antibiotics. Thirty years ago they prescribed oletethrin, ten years ago - smallpox, now augmentin and suprax are in fashion. I’ll tell you a secret: smallpox, suprax and augmentin, although different in chemical composition, work exactly the same, and even against the same bacteria.
Let's decipher the blood test together.
Leukocytes - what are they?
Leukocytes are the body’s protective army. They make up a large group of white blood cells whose purpose is to rid the body of infections. Leukocytes take part in allergic, autoimmune and tumor processes. White cells are divided into types, which are responsible for their specific function.
A complete blood count shows the total number of cells. The leukocyte count is responsible for accurately identifying the cell types that cause an increase (leukocytosis) or decrease (leukopenia) in white cells in the blood. The formula can be found in an expanded form of a blood test. There are five types of cells, their number and relationship to each other.
The blood test is assessed using an automatic analyzer, which calculates the percentage of each type of the total number of cells. The device also calculates the white blood cell count per liter of blood.
Additionally, a visual assessment of the blood smear using a microscope may be required. A “manual” check of analyzes may be necessary in the following cases:
• Changes in the leukocyte formula; • There are altered or immature cells; • Signs of anemia are visible; • Reduced platelet count.
If the analysis is processed manually, only the percentage will be visible. Each type of assessment allows you to correctly diagnose diseases, understand their causes and prescribe the correct treatment.
Preparation and conduct of analyzes
The leukocyte test is highly sensitive and requires careful preparation. To avoid getting false results, parents must follow the rules.
2-3 days before donating blood, you should pay attention to the child’s nutrition. The diet should not contain food:
- fat;
- high protein.
There should be a calm environment at home. Strong emotions and tears should not be allowed. It is especially important to ensure that the child does not cry, since strong emotions lead to increased production of white blood cells.
Strenuous physical activity on the eve of the analysis distorts the results of the analysis. It is worth reducing physical activity 2 days before your visit to the laboratory.
The test is taken on an empty stomach in the morning. At least 8 hours must pass from the last meal to blood sampling.
You are allowed to drink water before the test, but you cannot take medications without the approval of your pediatrician. In the queue in front of the office, it is advisable to keep the child occupied so that he does not run up the stairs, cry, or worry.
What do granulocytes say?
Part of the leukocytes are granulocytes, which get their name due to the presence of granules. There are three types of cells: neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils. The types of granulocytes differ from each other due to the color of the granules and the structure of the nucleus.
The granules store immune substances that are important for protecting the body. Thanks to them, cells participate in inflammatory processes. The job of granulocytes is to absorb proteins and chemicals. Granulocytes also digest them.
The cells mature in the bone marrow, where the resulting quantity is stored for another 3-4 days. Mature cells enter the blood, where they circulate for 6 hours. After the end of the cycle, granulocytes enter the tissues, where they perform their functions.
The largest number of leukocytes are neutrophils, of which there are always about 1010 in the blood. If a bacterial infection enters the body, neutrophilia begins - an increased amount of neutrophils in the blood. The number of cells that appear depends on the number of harmful bacteria.
The duration of stay of neutrophils in the body is only 4 days, which is why still immature cells (band cells, metamyelocytes, and others) enter the body. This phenomenon is called a “shift of the leukocyte formula to the left.” With neutropenia (reduced number of neutrocytes), the body is less protected from infections.
About 5% of leukocytes are eosinophils, the number of which depends on adrenal hormones. In the morning there are the largest number of them. They are stored in the layer under the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. A quantity above the norm indicates that the following processes are occurring in the body:
- Infestation with parasites;
- Allergy;
- Autoimmune processes.
Medical offers to sign up for diagnostics and tests. In our laboratory it is possible to take all types of tests in Tula. Tel. for recording.
The smallest number (less than 1%) are basophils. They play a role in the release of histamine during allergic reactions. It is these cells that are responsible for itching, redness, irritation and bronchial spasms.
Depending on the location of basophils in the body, the following reactions differ:
- Bronchial asthma;
- Rashes
- Hives;
- Quincke's edema (swelling of the larynx).
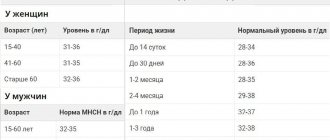
Normal indicators
Leukocytes provide an immune barrier against infection, inflammation, and the growth of a malignant tumor. Immune functions are carried out by the most numerous populations of white blood cells:
- neutrophils (NEU);
- lymphocytes (LYM).
The concentration of leukocytes is measured as a percentage. The indicators reflect the amount of total leukocytes that accounts for each cell group.
Important information: Why are leukocytes in the blood elevated after childbirth?
The leukocyte norm in children differs from the norm in adults. The newborn has elevated white blood cells due to a high concentration of neutrophils. Their LYM levels, compared to the norm in adults, are reduced.
After 7 days, the parameters of the LYM and NEU cells in the newborn are equalized. This balance is called leukocyte crossover. From 7 days to 5 years, the LYM value should normally be greater than neutrophils.
This distinguishes the leukocyte proportions in children and adults. Parents, not knowing this feature, often get scared and begin to worry.
At 5-6 years, the LYM analysis and the number of NEUs again become approximately the same, as was observed at 7 days in newborns. This phenomenon is called second leukocyte crossover and reflects normal immune development.
Neutrophils
Neutrophilic white blood cells increase during inflammation caused by bacterial infections. There are 2 groups of neutrophils present in the blood:
- immature rod forms (NEUp);
- mature segmented forms (NEUc).
An informative indicator is the number of segmented NEUc cells.
Normal NEUc in children depending on age (in%):
- 1-2 — 28-48;
- 2-3 — 32-55;
- 3-6 — 32-55;
- 6-9 — 38-58;
- 9-12 — 43-60.
Lymphocytes
The group is responsible for the production of antibodies to foreign proteins. A significant increase in these blood elements is observed in viral diseases.
Normal lymphocyte counts in children depending on age (in%):
- 1-2 — 37-60;
- 2-3 — 33-55;
- 3-6 — 33-55;
- 6-9 — 30-50;
- 9-12 — 30-46.
Monocytes are killers in the body
Monocytes make up 10% of white blood cells and perform the main “destructive” function of the immune system. Also called tissue macrophages. They are formed in the bone marrow within 5 days and immediately go out to “hunt” without leaving a reserve. They quickly penetrate tissues and destroy foreign proteins. A large number of monocytes are found in the liver, spleen and lungs. They exist for about 60 days and process foreign proteins into antigens, which are subsequently dealt with by immune cells.
An increase in monocytes in the blood, or monocytosis, indicates that there are chronic infections in the body. They can also talk about infections that are located in the cells themselves: viruses, chlamydia and mycoplasma.
What are neutrophils?
Neutrophil granulocytes are blood cells produced in the human red bone marrow. Their main purpose is to protect against infection. They can live for several hours or days, depending on whether there is a focus of inflammation in any system of the human body.
As a rule, the content of these bodies in an adult should fluctuate between 47% and 72% of the total number of leukocytes. As the child grows older, their concentration gradually increases, given that their number will still be at approximately the same level.
The percentage of this type of leukocyte in a child who is about a year old will be from 30% to 50%. At seven years old, this ratio increases slightly and is 35%-55%, and in adolescence it will vary from 40% to 60%.
If the analysis showed an increased concentration of these cells in a person, this indicates neutrophilia. The increase factor is usually considered to be the development of the inflammatory process. Depending on the percentage of increase in these cells during inflammation, you can determine its approximate extent and how actively the body itself counteracts it.
Lymphocytes are the final link
Lymphocytes are responsible for the final action of the immune system, processing antigens already prepared by monocytes and other cells. They are responsible for acquired immunity, which will prevent the infection from acting again. Lymphocytes produce antibodies and memory cells. Like other cells, lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow but circulate in both the blood and the lymphatic system. Cell maturation is influenced by the thymus and lymph nodes. The group of lymphocytes is the second most numerous in the blood.
To identify cells in the blood, a special test called immunophenotyping is used. Thanks to this study, it is possible to determine the specific number of this type of cell. Determining specific types of lymphocytes makes it possible to diagnose and treat diseases of the immune system, HIV infections and others.
The leukocyte formula indicates the increase and decrease in the number of lymphocytes. Both indicators are very important. Lymphocytosis, or an increase in the number of cells, indicates viral infections, as does a decrease (lymphopenia). A decrease in the number of lymphocytes significantly reduces the protective function of the body, which is typical for people with immunodeficiency.
Characteristics of analyzes
Neutrophils are determined according to certain standard standards. The discrepancy characterizes the high activity of blood cells and signals the onset of pathological processes. The presence of mature and immature neutrophilic granulocytes is studied. There is no dependence on gender; it is determined by age category.
In adults, band neutrophils should not exceed the level of 1-4, segmented neutrophils - from 40 to 60. Important indicators include the ratio in percentage and numbers.
An increased level of lymphocytes indicates the onset of inflammation in the body. The doctor determines the location of the disease by analyzing accompanying manifestations. Lymphocytosis in acute pathology is characterized by an increase in neutrophils, observed in the formation of:
- Internal inflammation with the appearance of purulent content - sepsis, peritonitis, tonsillitis and cholera, scarlet fever, pyelonephritis.
- Processes of a necrotic nature - stroke, frostbite, gangrene or large-area burns.
- Lead or alcohol intoxication.
- Oncological neoplasm.
A formula is used to determine the white cell ratio in a blood test. Leukocyte count allows you to calculate the number of leukocytes per 100 cells. The crossover is observed in childhood, when immune barriers are lowered.
Decreased neutrophils with increased lymphocytes are the norm in a child. The cause is vaccination. The immune system reacts to the vaccine as if it were a foreign body, the process of producing antibodies starts, but the granulocytes do not react due to the incapacitated microorganism.
- Why are neutrophils elevated in an adult, what does this mean, what to do?
Few neutrophils and many lymphocytes in an adult are characterized by the following pathologies:
- the body is exhausted;
- typhus, brucellosis;
- infection with bacteria that led to the death of granulocytes;
- blood diseases;
- treatment with chemotherapy, radiation therapy.
Such indicators are typical for the body’s fight against the disease, after the pathogen has been eliminated. Gradually, deviations from the norm will disappear in the analyzes.
Functions of neutrophils and lymphocytes
Neutrophils and lymphocytes perform various functions in the body.
Are neutrophils elevated?
The life activity of neutrophils (neutrophilic granulocytes) in the bloodstream continues for several hours. Cells are constantly renewed, due to which there is an obstacle to foreign microorganisms in the body.
The fight comes in the form of a process called phagocytosis. Moreover, any of the segmented neutrophils (mature) captures and digests pathogenic microorganisms. Having completed their work, the neutrophils die, and others are immediately formed in their place.
Occasionally, immature (band) neutrophils are detected in the bloodstream in a small volume. In comparison with segmented ones, their maturation occurs not in the bone marrow structure, but in the vascular system.
See if the hematocrit is low
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are blood cells that are a type of white blood cell. The percentage of lymphocytes with other cells in the bloodstream: in adults - approximately 40%, in childhood - up to 50%.
Experts divide lymphocytes into 3 groups: B cells, T cells, NK cells. Each of them does its own job. The number of these blood cells is precisely normalized, but if their levels are too high or too low, this sometimes indicates the onset of a disease.
B cells
B cells are called "helpers". Their main purpose is to signal other immune cells to increase or slow down their functions.
They are involved in the synthesis of immunoglobulins (antibodies) of special bodies located on the surface of B cells and used by the immune system to identify and destroy the pathogen. This process is called an immune response. Taurus helps in supporting the humoral immune system.
T cells
Such blood cells are called killer cells. They are involved in the destruction of foreign bodies at an early stage (when pathogenic agents enter the human body). These bodies recognize their enemies, which can be in the form of viruses, bacteria or microbes.
When, for some reason, T cells cannot cope with their functions, B cells begin to work. “Killers” help maintain immunity at the cellular level.
NK cells
They are otherwise called “natural killers”. They are characterized by toxicity towards cancer and viral microorganisms. If they are absent, the innate immune system is considered abnormal.
The main goal of NK cells is the destruction of those pathogenic agents that, for some reason, are closed to T lymphocytes.
Elimination of deviations
If neutrophils are low and lymphocytes are high, the body weakens and becomes defenseless against viruses and bacteria. If such indicators are detected in the results of a blood test, the doctor is obliged to take immediate action. Initially, an additional examination is prescribed to identify the cause of this condition.
The choice of medications depends on the final diagnosis. If indicators deviate from the norm during drug treatment, they will have to be completely replaced. In some cases, the reason for the malfunction of blood cells lies in an imbalance of vitamins and minerals.
In this case, it is necessary to replenish the missing nutrients in the body - vitamin B9 and B12. For this purpose, medications or a special diet are prescribed. Most often, when the cause of the disorder is eliminated, lymphocytes and neutrophils return to normal in the bloodstream within a few weeks.
What is the danger
If the blood level of indicators such as lymphocytes and neutrophils deviates from the norm, then the body is infected with an infection. When interpreting data from a general blood test, the clinical picture should be taken into account. When there are no symptoms of pathology, there is a risk that the person is a carrier of the virus. If neutrophils are low and lymphocytes are simultaneously increased, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, since the possibility of developing dangerous diseases such as hepatitis and HIV infection cannot be ruled out.