Pathogenesis
In accordance with the modern, so-called vascular theory, hypercapnia plays a key role in the pathogenesis of edema syndrome in CLS. Carbon dioxide, being a vasodilator, with an increase in its content in the blood, reduces peripheral vascular resistance and increases the capacity of the arterial bed. Due to the reduction of precapillary tone, the filtration equilibrium point in the capillaries shifts distally, which leads to the movement of fluid outside the vascular bed and loss of plasma volume. Of great importance in the development of edema in CLS is compensatory erythrocytosis in response to hypoxemia, an increase in hematocrit with a violation of the rheological properties of blood, the formation of erythrocyte aggregates, the development of capillary stasis, which causes perfusion disturbances and the movement of the liquid fraction of blood outside the vascular bed. The occurrence of edema is also facilitated by extrathoracic deposition of blood due to increased intrathoracic pressure and prolongation of exhalation, which significantly worsens the conditions for venous return of blood to the heart and creates the preconditions for stagnation in the systems of both the superior and inferior vena cava.
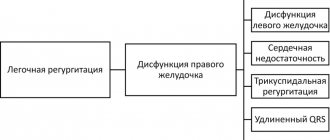
As the resistance load increases due to pulmonary hypertension (PH), hypoxemia, and metabolic disorders in the myocardium, hypertrophy, dilatation and failure of the right ventricle of the heart develop. In patients with diseases that primarily affect the pulmonary vessels (idiopathic PH, postthromboembolic PH, etc.), the leading cause of the development of peripheral edema is right ventricular heart failure (HF) due to hemodynamic overload caused by high PH.
Causes
Factors stimulating the development of pulmonary heart failure are persistent pulmonary hypertension and hypertrophy. As a result of increased pressure in the pulmonary artery, the hypertrophied right ventricle can no longer cope with pumping the venous blood entering it. The disease can develop as:
- complication of obstructive bronchitis, bronchiectasis, bronchial asthma, pneumonia;
- a consequence of damage to the pulmonary vascular bed that occurred due to thromboembolism, compression of the pulmonary veins and arteries by tumor formations;
- the result of conditions accompanied by limited mobility of the chest and diaphragm: chest deformation, spinal diseases, rib fractures, myasthenia gravis, polio, botulism, paresis and paralysis of the diaphragm.
Clinical picture
The basis for the clinical diagnosis of CHL is the addition to the clinical symptoms of the underlying disease (cough, wheezing in the lungs, etc.), manifestations of pulmonary insufficiency (shortness of breath, cyanosis), pulmonary hypertension (emphasis of the second tone over the pulmonary artery, Graham-Still noise) signs of blood stagnation in the large circle - peripheral edema and hepatomegaly. Swelling initially occurs on the feet and legs, progressing to the upper parts of the body. In the evening, as a rule, they increase. The liver is enlarged mainly due to the left lobe, has a rounded edge, is sensitive or moderately painful on palpation. In some cases, the liver can protrude from under the edge of the costal arch even if its size is normal, which is often observed with pulmonary emphysema and a low position of the diaphragm.
Swelling of the neck veins is often a consequence of increased intrathoracic pressure, with the veins swelling during exhalation and collapsing during inspiration. With the development of right ventricular failure, the dependence of the filling of the jugular veins on the respiratory phase decreases.
Cardiopulmonary failure
The diagnostic search for the development of cardiopulmonary failure is aimed at identifying the underlying disease, as well as assessing the degree of decompensation. For correct interpretation of physical and instrumental data, the patient needs to be examined by a pulmonologist and cardiologist. An objective examination of patients with cardiopulmonary insufficiency reveals a barrel-shaped deformation of the chest, hepatomegaly, and pasty feet and legs. Palpation of the precordial region reveals a cardiac impulse, and percussion reveals an expansion of the boundaries of the relative dullness of the heart. Typically decreased blood pressure, frequent arrhythmic pulse. Auscultatory data are characterized by muffled heart sounds, emphasis of the second tone over the pulmonary artery, splitting or bifurcation of the second tone, the appearance of pathological third and fourth sounds, systolic murmur, indicating tricuspid insufficiency.
The most valuable laboratory criteria for cardiopulmonary failure are blood gas indicators: decreased p02, increased pCO2, respiratory acidosis. Chest X-ray can detect not only lung damage, but also signs of cardiomegaly and pulmonary hypertension. Pulmonary angiography and ventilation-perfusion lung scintigraphy are indicated for suspected pulmonary embolism.
The study of respiratory function in cardiopulmonary failure is used to assess the nature and severity of ventilation disorders and identify bronchospasm. Electrocardiography in acute LS allows one to reliably determine signs of overload of the right heart, and in chronic LS - to identify direct and indirect markers of right ventricular hypertrophy.
EchoCG serves as the main non-invasive method to assess intracardiac hemodynamics, determine the size of the heart cavities and the wall of the right ventricle, and determine the degree of pulmonary hypertension. In some cases, if it is impossible to establish the fact of increased pressure in the pulmonary artery, catheterization of the right heart is resorted to. Sometimes, to verify the genesis of cardiopulmonary failure, a transbronchial or transthoracic lung biopsy is performed.
Decompensation of drugs should be differentiated from heart defects, cardiosclerosis, dilated cardiomyopathy and other cardiac pathologies.
Classifications and examples of diagnosis formulation
The severity of circulatory failure (CI) is assessed according to the classification of the Association of Phthisiologists and Pulmonologists of Ukraine (2003). The classification involves dividing patients into groups according to three stages of NC:
1) NC stage I: the presence of mild signs of blood stagnation in the systemic circulation - swelling in the legs, enlarged liver, which disappear under the influence of therapy only for the underlying disease or in combination with diuretics;
2) NC stage II: the presence of pronounced edema and hepatomegaly, requiring intensive, often combined treatment with diuretics; at this stage, as a rule, disturbances in the contractile function of the myocardium are observed, and therefore complex treatment using drugs to correct vascular tone, inotropic drugs, and antiplatelet agents is advisable;
3) NC stage III: terminal stage, characterized by secondary damage to other organs and systems; the only remedy that can at least slightly prolong the life of these patients is continuous oxygen therapy.
The above division of patients into groups depending on the stage applies only to NK in the systemic circulation, since post-capillary stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation (left ventricular failure in the form of cardiac asthma and pulmonary edema) in patients with chronic lung diseases, as a rule, is not observed.
The formulation of the diagnosis consists of four components: the name of the disease (indicating the degree of severity and phase of the course), LN (indicating the degree), chronic pulmonary heart disease, NC (indicating the stage). For example: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stage III, exacerbation phase, stage II pulmonary disease, chronic pulmonary heart disease, stage I NC.
Symptoms
Acute pulmonary heart failure occurs suddenly. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply - within a few minutes or hours. The attack is accompanied by:
- pain in the heart area, rapid heartbeat;
- severe shortness of breath, suffocation;
- panic attack;
- blue nails, nasolabial triangle;
- a sharp drop in blood pressure.
Symptoms are especially severe in sitting and standing positions. Chronic pulmonary heart failure develops gradually, due to stagnation of blood in the venous system of the systemic circulation. This pathology provokes:
- constant shortness of breath;
- painful attacks in the heart and chest, for which nitroglycerin does not help;
- blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, tip of the nose, nails;
- fatigue, fatigue, drowsiness, fainting during physical activity;
- peripheral edema, edematous syndrome, ascites, exhaustion.
Diagnostics
The purpose of using laboratory and instrumental research methods is to determine the treatment tactics for patients.
The main tasks of conducting diagnostic studies:
— diagnosis of possible concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system;
— diagnosis and assessment of the degree of impairment of the contractile function of the right ventricle when determining the feasibility and volume of therapy with inotropic agents;
— assessment of the degree of hemoconcentration when prescribing infusion therapy;
— assessment of the degree of hypoxemia when determining the feasibility and selection of oxygen therapy regimens.
Instrumental and other diagnostic methods
X-ray of the chest organs. In patients with chronic lung diseases, small sizes of the atria and ventricles are usually observed; there may be signs of hypertrophy of the outflow tract from the right ventricle - bulging of the pulmonary cone. In severe cases, the second arch of the pulmonary cone protruding along the left contour can imitate the mitral configuration of the heart. In subsequent stages of development of CHL, a progressive enlargement of the right ventricle due to hypertrophy and dilation is determined. In patients with the vascular form of CHL (idiopathic and chronic post-embolic PH), the trunk and main branches of the pulmonary artery are significantly dilated. A reliable sign of high PH is an increase in the diameter of the right descending branch of the pulmonary artery by more than 18 mm. Sometimes the expansion of the right descending branch becomes aneurysmal in nature, and the aneurysm on the radiograph is mistaken for a neoplastic or tuberculous process. The sizes of the right atrium and right ventricle are sharply increased, while the left parts of the heart may be reduced.
Electrocardiography (ECG) allows you to confidently diagnose right ventricular hypertrophy in patients with the vascular form of CHL (Rv1 > 7 mm, often in combination with complete right bundle branch block, Rv1 + Sv5 > 10.5 mm and other direct signs of hypertrophy). In patients with CLS caused by primary damage to the bronchi and lung parenchyma, an S-type electrocardiogram is usually recorded. However, it should be noted that hypertrophy is a normal reaction of the myocardium to hyperfunction (compensatory increase in cardiac output in response to hypoxemia and resistance load due to PH), which is observed in patients without signs of circulatory decompensation, that is, without CHL. An ECG can be useful if concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system are suspected, for example, coronary artery disease (depression of the S-T segment, changes in the T wave, etc.), in diagnosing metabolic disorders in the heart muscle, manifested mainly by disorders of myocardial repolarization processes.
Echocardiography (EchoCG) is the most accurate method for diagnosing hypertrophy, dilatation and failure of the right ventricle of the heart; measurement of the thickness of the anterior wall of the right ventricle is carried out in M-mode using a standard anterior approach. In healthy individuals, this figure usually does not exceed 0.3 cm, in patients with chronic lung diseases, the thickness of the anterior wall ranges from 0.3 to 0.45 cm, in vascular forms of CHL - more than 0.5 cm. Assessment of the degree of dilatation of the right ventricle based on determining the anteroposterior size of its cavity is not reliable enough; a more reliable way is to analyze orthogonal sections from the apical approach based on the Simpson method. The main sign of impaired contractile function of the right ventricle is a decrease in the ejection fraction (normal - 46.8 ± 1.48%).
The study of the gas composition and acid-base state of the blood allows you to diagnose and assess the severity of arterial hypoxemia (PaO2 < 65 mm Hg, SaO2 < 93%), hypercapnia (PaCO2 > 40 mm Hg), and respiratory acidosis. Signs of compensated respiratory acidosis are an increase in PaCO2, bicarbonate content and excess buffer bases at normal blood pH. Signs of uncompensated acidosis are an increase in PaCO2, a decrease in the level of bicarbonates, excess buffer bases and blood pH. In idiopathic and post-embolic PH, right ventricular heart failure often develops against the background of hypocapnia and respiratory alkalosis.
What is chronic heart failure
When the heart does not provide sufficient blood supply to the body, it causes swelling and oxygen starvation of tissues and internal organs. This condition is called heart failure and has two forms - acute and chronic.
The acute form occurs due to a sharp disturbance in the contractile activity of the myocardium, is accompanied by severe pain in the chest and always requires emergency medical care. An attack can be triggered by: exacerbation of a current cardiovascular disease, sudden damage to the heart muscle, poisoning, trauma, stroke, etc.
Chronic form of heart failure
, unlike acute, it begins asymptomatically and develops gradually. The initial stage of the disease does not have obvious symptoms, and heart problems can only be identified during a medical examination. Over time, the patient develops shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat during physical activity. In later stages, these symptoms persist even at rest.
Structure of the heart: atria, ventricles and heart valves