The table shows possible deviations (the norm is presented below)
| Index | Characteristic | Diagnosed pathology |
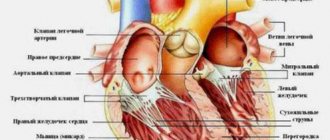
| Heart sizes | Increased | Cardiomegaly, chamber hypertrophy, cardiosclerosis, myocarditis |
| Myocardial characteristics | Thickened | |
| Compacted, heterogeneous | ||
| Istonchen | Organ failure, dilated cardiomyopathy | |
| Volume of ventricles and atria | Increased | |
| Reduced | Restrictive cardiomyopathy | |
| Valve condition | Thickened | Endocarditis |
| They don't close | Failure | |
| Do not open | Stenosis | |
| Pulmonary artery | Enlarged, expanded | Aneurysm |
| Dense | Atherosclerosis | |
| Emission volume | Reduced | Developmental defects, organ failure, cardiomyopathy |
| Residual volume | Increased | |
| Pericardial cavity | Thickened | Pericarditis |
| Liquid is visualized | ||
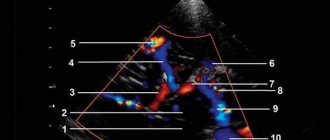
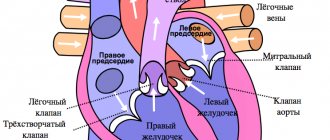
| Movement of blood between cavities and vessels | Regurgitation (backflow of blood during contraction) | Defects (congenital, acquired) – valve insufficiency |
| Shunt (shunt) between the aorta and pulmonary arteries | Congenital malformation | |
| Reset (shunt) at the level of the oval window | Open window | |
| Interventricular shunting | Defect (congenital, acquired) - ventricular septal defect | |
| Additional education | Nodes, thickenings, additional shadows | Neoplasms, blood clots, accessory chord, ventricular aneurysm |
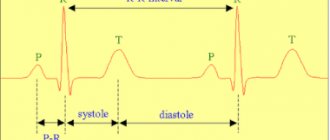
The study does not allow assessing the nature of the rhythm and electrical activity (an ECG is required), the condition of the coronary arteries (coronary angiography is performed), and the blood supply to the myocardium.
Depending on the equipment and assessment methods, the following types of echocardiography are distinguished:
- Standard . Transthoracic option: the sensor is placed on the chest. The study can be one-dimensional, two-dimensional or three-dimensional.
- Doppler . Aimed at assessing the characteristics of blood flow in the cavities of the heart and large vessels.
- Stressful . Ultrasound examination during stress tests.
- Transesophageal . Examination of the heart through the wall of the esophagus.
The gold standard for examination is two-dimensional Doppler-enhanced echocardiography.
Atrial flutter - symptoms and treatment
Drug treatment
Drug therapy involves taking drugs that restore sinus rhythm.
The main antiarrhythmic drugs are:
- amiodarone (cordarone);
- sotalol (sotahexal);
- propafenone (ritmonorm);
- verapamil;
- cardiac glycosides.
The combination of these antiarrhythmic drugs increases the effectiveness of treatment.
Amiodarone and sotalol are class III antiarrhythmic drugs.
Amiodarone is most effective in preventing the development of atrial fibrillation, as well as arrhythmia after a heart attack. It has been proven to improve survival in patients with severe circulatory failure. May improve myocardial contractility [5]. Contraindicated in hypo- and hyperthyroidism.
Sotalol, as a means of preventing atrial fibrillation, is less effective than amiodarone. The safest dose of this antiarrhythmic drug for atrial flutter is 120 mg twice a day. But for life-threatening heart rhythm disturbances, the dose of sotalol can reach 640 mg per day. The most common side effects of the drug include symptoms of digestive tract disorders: abdominal pain and diarrhea [5]. Contraindicated in COPD and severe bronchial asthma.
Propafenone is a class I antiarrhythmic drug. Its preventive effect is weaker than that of amiodarone and sotalol. Long-term use of this drug increases the risk of repeated attacks of arrhythmia. It can lead to side effects such as shortness of breath, dizziness, vomiting, changes in taste, constipation, headaches, abdominal pain, blurred vision, ataxia and diarrhea [5].
Verapamil is a class IV antiarrhythmic drug. Its effectiveness is lower than that of amiodarone and sotalol, and fairly high doses are required to prevent flutter attacks. Side effects include a decrease in heart rate to 50 beats per minute, hypotension and progression of heart failure.
Among cardiac glycosides, digoxin is most often used. Typically, this drug is prescribed for a combination of atrial flutter and circulatory failure.
The antiarrhythmic effect of glycosides does not develop immediately: after about two weeks from the start of treatment. Long-term use increases the risk of overdose. Other reasons that increase the risk of overdose include low levels of potassium, magnesium, oxygen and high levels of magnesium in the blood, kidney and liver failure, old age, poor general condition of the body and taking diuretics.
If it is necessary to take diuretics, preference should be given to potassium-sparing diuretics, for example veroshpiron. At the same time as taking diuretics, you need to monitor your heart rhythm [5].
Considering that atrial flutter most often occurs against the background of low potassium levels in the blood, potassium supplements are added to standard drug therapy:
- 4% potassium chloride solution;
- asparkam;
- Panangin.
Among other things, all patients with atrial flutter and fibrillation are advised to take anticoagulants to prevent the formation of blood clots [5][13].
Electropulse therapy
When symptoms of heart failure appear, preference is given to electrical pulse therapy - EIT. It is carried out using a special device - a defibrillator. One of its electrodes is fixed slightly outward from the apex of the heart, the other to the right of the sternum. If atrial flutter is present and the patient is stable, start with a 25 J shock.
After the procedure, the patient must remain in bed during the day. He is prescribed antiarrhythmic and antithrombotic therapy. Atrial function is restored within a few days after the flutter attack has stopped.
If there are no complications, the patient is discharged from the hospital 6-7 days after EIT [5]. In rare cases, complications are possible: systemic embolism, ventricular tachycardia, acute left ventricular failure, ventricular fibrillation, myocardial damage, extrasystole, hypertension, sinus tachycardia and bradycardia.
When atrial flutter is combined with sick sinus syndrome, permanent pacing . This effect on atrial rhythm significantly reduces the risk of developing flutter attacks.
Ablation
With typical atrial flutter, preference is given to ablation - the destruction of pathological electrical foci.
Ablation, which is carried out using high-frequency currents, is called radiofrequency. The destruction of pathological foci using low temperatures, down to −70 °C, is called cryoablation.
In radiofrequency ablation, a catheter is inserted into the atrium through the common femoral or subclavian vein. Using electrical signals sent through the catheter, the doctor finds the arrhythmogenic zone and begins to influence it through the electrode. After this, the doctor re-checks the electrical activity of all chambers of the heart to ensure the effectiveness of the procedure and ends the operation. The effectiveness of this method is 95% [14].
Open heart surgery aimed at isolating the atrium is also possible However, they are difficult to perform and are not performed in patients with severe heart failure.
How is cardiac ultrasound interpreted?
- Competent ultrasound doctors with many years of experience
- Expert device with high resolution
- All types of ultrasound (ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs, ultrasound of blood vessels, ultrasound of the heart, ultrasound of the joints)
Conclusion during the study.
Burning to disc
Sign up for an ultrasound
Prices for ultrasound
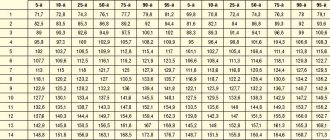
Echo-CG interpretation occurs by comparing normal indicators with the indicators of the study. What are these indicators:
- Myocardial mass
- Volume and dimensions of the left and right ventricles
- Wall thickness of the left and right ventricle
- Aortic diameter
- Thickness of the interventricular septum
It seems simple, but in reality everything turns out to be much more complicated. For competent decoding, it is necessary to know the individual characteristics of the patient, his medical history and many other factors. Therefore, to interpret echocardiography, contact a specialist!