Professional athletes spend their lives fighting for results. It takes a lot of time and effort to win prizes. Amateurs also often hang out in the gym. But how can you stay healthy with this rhythm? To do this, you need to ensure proper recovery of the heart rate after physical activity: the norm at rest is 70 beats per minute.
What will happen to the heart rate (HR) during serious power loads? The indicator will increase. The myocardium must not be allowed to wear out. Otherwise, there will be a risk of getting an appointment with a cardiologist. Let's talk about how to find a middle ground and not go beyond what is permitted.
Physiology of increased heart rate
The main function of blood is to deliver oxygen to organs and tissues. The nervous system monitors the state of our body. If in a calm state, it is enough for the heart to “beat” at an interval of 50-70 beats per minute. As activity levels increase, the need for oxygen increases along with it. The myocardium begins to contract 80-90 times per minute.
But as soon as you return to normal physical activity, the brain triggers the restoration of your heart rate after exercise. The heart slows down, the hormonal levels rush towards a state of balance.
How the heart reacts to sports stress
At maximum athletic activity, the heart contracts more than two hundred times, pumping more than 30 liters of blood per minute. Trying to ease the colossal cardiac work, the body distributes blood more efficiently, reducing the resistance of the vascular walls, dilating the vessels of skeletal muscles and opening additional collateral vessels, which were previously in a collapsed state. However, even with such a significant compensatory decrease in blood flow, the heart works on the verge of beyond its capabilities.
Under the influence of loads, the heart changes its configuration - it is remodeled to ensure the viability of all organs under intense load. Morphological - biological changes correct the electrophysiology of the myocardium, that is, the emergence of an electrical potential for contraction of the heart chambers and their relaxation. In four out of ten professional athletes, the ECG recording, reflecting the electrophysiological characteristics of the heart, differs from the normal electrocardiogram in the height and depth of the waves.
Over time, but before that, at least two or three years of regular sports activities will pass, the heart will adapt to constant loads that are excessive for the normal body, so that the skeletal muscles are able to develop strength that is inaccessible to an untrained person.
Normal heart rate
Different people come to sports. The body of a 50-year-old man is difficult to compare with the body of a twenty-year-old boy. But there are other characteristics: the condition of the blood vessels, pathologies of the nervous system, and previous injuries. How to find a “common denominator”, a reference point for measuring heart rate?
There is an equation that allows you to calculate your maximum heart rate. It is called the Haskell-Fox formula:
Hmax = 220 - age
For women the formula is different. This is due to the characteristics of the body. So:
Hmax = 220 – age – 6
Let’s take an example of an athlete – a man who is 28 years old. Let's do the calculation:
Hmax = 220 - 28 = 192 beats per minute
We will focus on this indicator in the future.
Run
Sports medicine experts suggest that while running you should keep your heart rate between 70% and 80% of your HRmax. How much is this in exact numbers? Let's do the math:
- Hmax = 192.
- H optimal = 192 × 0.7 = 134.
- H maximum = 192 × 0.8 = 153.
In order for heart rate recovery after physical activity to occur as quickly as possible, you do not need to run at the limit of your capabilities. If the indicator goes beyond 190, then you should slow down.
A regular fitness bracelet will help you track your heart rate. The ideal option would be a meter with a chest sensor. It can be connected to a monitoring system for HRV - heart rate variability.
Cardio training
Cardio training is a technique based on moderate exercise. It is used for recovery after strength exercises. The ideal heart rate value is 60-70% of Hmax. The values will be:
- Hmax = 192.
- H optimal = 192 × 0.6 = 115.
- H maximum = 192 × 0.7 = 134.
Therefore, during cardio exercise you need to stay within the range of 115-134 beats per minute.
In the same range is the fat burning zone - the fat burning zone. Ideal for drying. Under heavier loads, the body will stop using fat as fuel and switch to glycogen, the building material for muscles. This is bad.
Walking
Walking is the first “full-fledged” exercise that a person begins to perform at a very early age. This is a warm-up necessary to prepare the heart for more serious stress. Doctors recommend keeping myocardial function within 50-60% of Hmax. For completeness:
- Hmax = 192.
- H optimal = 192 × 0.5 = 96.
- H maximum = 192 × 0.6 = 115.
It turns out that 96-115 is the ideal range for a person aged 28 years.
Sport
The body of an active athlete adapts to stress over time. As a result, during intense training, heart rate can reach up to 80-90% of Hmax, and during extreme training, up to 100%.
Much depends on the sport. Long distance runners train for endurance. Therefore, their heart rate recovery time after physical activity is significantly lower than that of bodybuilders and powerlifters.
It should be taken into account that professional athletes have a resting heart rate that can be 10-20% lower than the average person. There have been cases when an athlete’s myocardium contracted only 30 times per minute. This is already 2 times lower than the norm in a calm state.
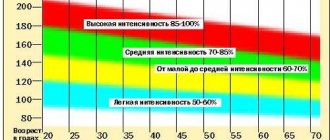
Here is a table with the characteristics of pulse zones:
| № | Heart rate zone (% of Hmax) | Impact | Hmax for 34 years old |
| 1 | 100%, maximum heart rate | Upper limit | 186 |
| 2 | 90-100%, maximum oxygen consumption | Increases energy output and speed | 172-186 |
| 3 | 80-90%, anaerobic strength training | Improves physical endurance | 159-172 |
| 4 | 70-80%, aerobic zone, cycling and running | Improves heart endurance | 145-159 |
| 5 | 60-70%, fat burning zone, gymnastics, walking | Increases stamina and burns calories | 132-145 |
| 6 | 50-60%, light activity zone, warm-up | The aerobic base develops and recovery occurs | 118-132 |
When big sport is prohibited
Changes in the myocardium under high physical loads are inevitable; normal hyperfunction mobilizes all the physiological resources of the heart; in the presence of some anatomical defects of the heart and blood vessels, the loads on the myocardium are not simply summed up, but increase exponentially. With undetected heart disease or arterial hypertension, cardiac hyperfunction is continuous, there is no rest for the heart, as happens with a healthy athletic heart, and cardiomyopathy develops very quickly against the background of exacerbation of a chronic disease.
Exacerbations of chronic heart diseases that are not diagnosed in time are not classified as a pathological sports heart, because they were not formed by sport, but by human nature, and sport only revealed and aggravated them.
People suffering from valvular and other congenital defects and diseases of the heart and blood vessels, heart rhythm disturbances, and heart configuration disorders are completely justifiably not allowed into elite sports, because such a heart is not able to bear excessive loads and may stop.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels seriously threaten human health and even life. Periodic medical examinations are designed to detect the disease in time so that you do not have to deal with the consequences belatedly. Consulting a cardiologist makes it possible to keep your health under control. To make an appointment with a cardiologist, call +7 (495) 120-08-07.
Hmax by age
Age is almost the main factor for playing sports without unnecessary injuries. Let's calculate the Hmax indicator for young and adult athletes and female athletes:
| Age | Hmax, men | Hmax, women |
| 14 | 206 | 200 |
| 15 | 205 | 199 |
| 16 | 204 | 198 |
| 17 | 203 | 197 |
| 18 | 202 | 196 |
| 19 | 201 | 195 |
| 20 | 200 | 194 |
| 21 | 199 | 193 |
| 22 | 198 | 192 |
| 23 | 197 | 191 |
| 24 | 196 | 190 |
| 25 | 195 | 189 |
| 26 | 194 | 188 |
| 27 | 193 | 187 |
| 28 | 192 | 186 |
| 29 | 191 | 185 |
| 30 | 190 | 184 |
| 31 | 189 | 183 |
| 32 | 188 | 182 |
| 33 | 187 | 181 |
| 34 | 186 | 180 |
| 35 | 185 | 179 |
| 36 | 184 | 178 |
| 37 | 183 | 177 |
| 38 | 182 | 176 |
| 39 | 181 | 175 |
| 40 | 180 | 174 |
| 41 | 179 | 173 |
| 42 | 178 | 172 |
| 43 | 177 | 171 |
| 44 | 176 | 170 |
| 45 | 175 | 169 |
| 46 | 174 | 168 |
| 47 | 173 | 167 |
| 48 | 172 | 166 |
| 49 | 171 | 165 |
| 50 | 170 | 164 |
It turns out that the minimum value is 164 beats per minute, and the maximum is 206.
Indicators for women
The female body is more resistant to changes in external factors. It is not for nothing that the life expectancy of the fair sex is 10-15 years higher than that of men.
But where's the catch? Nature doesn't give anything for nothing. Indeed, there are some features that prevent women from gaining muscle mass. This is a hormonal background. It sometimes changes not only during the month, but also throughout the day.
There are a number of factors that influence women’s heart rate:
- Height and weight.
- Age.
- Physical activity.
- Hormonal background.
The average resting heart rate is from 60 to 90 beats per minute.
Calm state
Young female athletes have a resting heart rate in the range of 70-85 beats. For older women, the maximum value drops to 65. This change occurs due to associated factors:
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Problems with the nervous system.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
It is worth noting that a similar process of heart rate slowing occurs in men.
Night
In the dark, the body turns on a recovery program. Organ activity decreases, metabolism slows down. The myocardium also reduces the number of contractions.
By the middle of the night, the heart rate slows to 40-45 beats per minute. By 5 o'clock in the morning the indicator becomes extreme - up to 32 heart beats. This occurs due to the activation of the vagus nerve, which begins to prepare the body for awakening.
Yoga classes
One group of classes helps you relax, while the other, on the contrary, develops strength and endurance. Therefore, you need to watch what a woman does. If through soft, meditative practices, then the heart rate will be similar to that characteristic of a state of rest.
Active yoga stimulates myocardial function. As a result, the pulse can jump to 110-120 beats. These are acceptable indicators. They are about the same as during cardio training.
Yoga is useful. It strengthens the immune system, normalizes blood pressure and speeds up metabolism. The level of cholesterol in the blood decreases, and organs and tissues receive enough oxygen and nutrients.
Return to normal
When physical activity ends, the body strives to restore balance. The nervous system gives a command to the myocardium, the number of heart contractions slowly creeps down. How long does this period last?
To restore your heart rate after a workout, you need to stop doing exercises completely, but you shouldn’t do it suddenly. A runner can gradually reduce the pace, a bodybuilder can reduce the weight and number of approaches.
If a person engages in sports on a regular basis for at least 6 months, his body quickly implements inhibitory functions. Within 15 minutes, the heart rate will drop to 90-100 beats per minute. After half an hour the value will be 60-70.
With low physical activity, doctors call this a state of detraining, one should not expect a quick return to normal values. A typical restoration of heart rate to resting values occurs only 2 hours after the end of the workout. And even later.
Brief summary: with constant exercise, the heart rate becomes normal after 30 minutes; with low activity, the time increases to 2 hours.
Heartbeat in sports
An increase in heart rate during physical activity is generally considered normal, says the cardiologist. “The heart rate reasonably increases when we move and especially when there is active physical activity,” says Tatyana Shalygina.
To prevent problems, you should calculate in advance the optimal values for increased heart rate for physical training and carefully monitor it. “There are certain formulas by which the maximum and submaximal values of heart rate are calculated for a particular patient in accordance with age or gender, as well as weight. These are the parameters that are recommended to be achieved during training,” says Tatyana Shalygina.
There are many such formulas, the cardiologist emphasizes. You can calculate the optimal heart rate for exercise yourself. So, the simplest formula for submaximal values is 200 minus age, for maximum values - 220 minus age. “The only thing is that during exercise we do not recommend reaching the maximum; it is worth working up to 75% of the maximum heart rate,” says the cardiologist.
Therefore, during training, you should constantly monitor your heart rate values and react in time if something goes wrong.
What should a child's normal heart rate be during sleep? More details
If recovery is delayed
The maximum allotted time, which is 2 hours, has passed and your heart rate has not returned to normal values? There could be 3 reasons:
- Detraining. If you go to the gym a couple of times a month, the nervous system and heart do not adapt to the growing load. During a period of inactivity, the body loses all the gains it has gained. Solution: increase the number of workouts to 3 per week.
- Overtraining. The opposite case. Daily work in the gym or stadium, heavy loads without rest and recovery lead to stress. The balance of hormones is disrupted. Solution: reduce the number of workouts and turn to effective recovery methods.
- Diseases. There are hidden disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular or nervous system. These may be congenital heart defects, ischemia, vegetative-vascular dystonia, high blood pressure. Solution: contact a cardiologist and conduct a comprehensive examination.
Pain during exercise, tachycardia, hand tremors and increased sweating are signs of disturbances in the functioning of the body. The problem cannot be ignored. The reason is unlikely to go away on its own.
How to correct the situation?
“If, against the background of physical activity, you feel unwell or have a rapid heartbeat, you should stop exercising. But not sharply, but slowly. Be sure to endure a recovery period when the pulse returns to normal. For example, reduce the load a little if this happened on the treadmill, reduce the speed if you can’t tolerate it well and your heart rate has increased significantly,” says Tatyana Shalygina. Yes, the pulse has the right to rise against the background of the load, it will be scary if it does not react to the load and does not increase. But an overly active heartbeat should also be a signal that something is wrong.
From the point of view of an increase in heart rate and assessing whether this is normal, a person’s fitness also matters. If a person is an athlete, his heart rate will initially be lower, and his pulse will rise more slowly during exercise.
Today, fitness clubs ask for a cardiologist's opinion or a certificate of admission to physical education and sports. You can also get tested at a specialized sports dispensary. This will eliminate contraindications to exercise, the cardiologist notes. “We sometimes ask to undergo a stress test in order to record a cardiogram during exercise and make sure that the person tolerates physical activity well,” says Tatyana Shalygina.
This will allow you to structure your workouts more competently, to know exactly the heart rate values, so that you can correctly monitor it and reduce it in time during the training process.
My heart trembled. When arrhythmia becomes deadly Read more
Speeding up the process
Although the time it takes to restore your heart rate after a heavy load is an individual indicator, it can still be reduced. Some use sports pharmacology for this, but the influence of medications does not always give positive results.
We will give a number of recommendations:
- Monitor your pulse . Any device, like the Mi Band from the Chinese brand Xiaomi, is suitable for this. Have you noticed that your heart rate is outside the normal range? Slow down the pace, change or remove the extra weight on the bar. It seems like obvious advice, but only a few take note of it, especially among amateurs.
- Plan your workouts . You should not move on to the active phase of exercise without warming up, even if you have little time. Prepared muscles become elastic and work much more efficiently. Work one muscle group on one day. Then they will have time to recover for the next classes.
- Eat right . Protein, amino acids, vitamins, fats and carbohydrates are the necessary “building blocks” for the production of muscle tissue. Diet will only worsen the result and cause health problems. It is better to postpone it for the future.
- Drink fluids . A bottle of mineral water without gas is a mandatory attribute for an athlete during training. As soon as classes are over, you need to replenish the water-salt balance. Otherwise, the blood will become thick and the heart will no longer cope with its functions.
- Limit caffeine . This substance stimulates the nervous system. As a result, increased sensitivity occurs, the myocardium begins to work more actively, which can cause tachycardia. You are allowed to drink no more than 1 cup of coffee per day. The drink should not be strong.
It is difficult for a beginner to understand all the intricacies of the training process. Therefore, it is better to contact a professional trainer or instructor. He will select an individual schedule. Things will go much faster. There will be no harm to health.
The heart of an athlete
In medicine there is such a thing as “athlete’s heart.” After active training, the main organ acquires peculiar differences. The myocardium is subjected to constant stress. After all, you need to deliver oxygen to working muscles. As a result, the muscle tissue of the “motor” begins to adapt to difficult conditions.
Changes occur only if you engage in physical exercise for 2 or more years every day for at least 2-3 hours.
Sooner or later, the body realizes that a high heart rate is dangerous and strives to reduce it. To do this, the heart enlarges and pushes out up to two normal volumes of blood in one contraction. Therefore, heart rate at rest can reach extremely low values for a normal person - 30 beats per minute.
Everything seems to be fine so far. But nothing lasts forever under the sun. After 3-4 years, the resources of the “muscular” heart begin to deplete. Areas of healthy tissue replace scars. This is how local foci of ischemia arise - lack of oxygen.
Varieties
There are two states of overtrained myocardium. If the first does not promise problems, then the second can lead to chronic diseases. The types are:
- Physiological . Thickened walls of the ventricles, chambers with increased volume. One hit – double “dose” of blood. There are no symptoms, the body works normally. No complaints of pain, lack of oxygen. Prospects: reversible condition.
- Pathological . The heart is growing too fast. The capillary network does not have time to cover the entire area of muscle tissue. Symptoms of ischemia begin. There is a lack of oxygen. Blood does not nourish the myocardium in the required volume. Prospects: irreversible condition.
Only a cardiologist can distinguish one condition from another. For diagnosis, a doctor may refer you to an ECG and ultrasound of the heart.