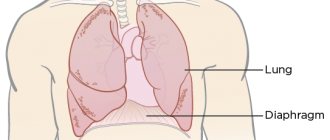
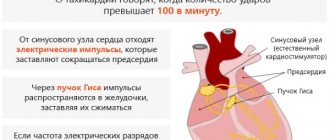
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is a painful feeling of lack of air, in extreme terms taking the form of suffocation.
If shortness of breath occurs in a healthy person against the background of physical activity or severe psycho-emotional stress, it is considered physiological. Its cause is the body's increased need for oxygen. In other cases, shortness of breath is caused by some disease and is called pathological.
According to the difficulty of the inhalation or exhalation phase, shortness of breath is distinguished as inspiratory and expiratory, respectively. A variant of mixed shortness of breath with limitation of both phases is also possible.
There are several types of shortness of breath. Dyspnea is considered subjective if the patient feels difficulty breathing, dissatisfaction with inhalation, but this cannot be measured and there are no factors for its occurrence. Most often it is a symptom of hysteria, neurosis, and thoracic radiculitis. Objective shortness of breath is characterized by a violation of the frequency, depth of breathing, duration of inhalation or exhalation, as well as increased work of the respiratory muscles.
Diseases associated with shortness of breath
In diseases of the respiratory system, shortness of breath may be the result of an obstruction in the airways or a decrease in the respiratory surface area of the lungs.
An obstruction in the upper respiratory tract (foreign body, tumor, accumulation of sputum) makes it difficult to inhale and pass air to the lungs, thereby causing inspiratory dyspnea. Reducing the lumen of the final sections of the bronchial tree - bronchioles, small bronchi due to inflammatory edema or spasm of their smooth muscles prevents exhalation, causing expiratory shortness of breath. In the case of narrowing of the trachea or large bronchus, shortness of breath takes on a mixed character, which is associated with the limitation of both phases of the respiratory act.
Mixed shortness of breath will also be due to inflammation of the lung parenchyma (pneumonia), atelectasis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis (fungal infection), silicosis, pulmonary infarction or compression from the outside by air, fluid in the pleural cavity (with hydrothorax, pneumothorax). Severe mixed shortness of breath up to suffocation is observed with pulmonary embolism. The patient takes a forced sitting position with support on his hands. Choking in the form of a sudden attack is a symptom of asthma, bronchial or cardiac.
With pleurisy, breathing becomes shallow and painful; a similar picture is observed with chest injuries and inflammation of the intercostal nerves, damage to the respiratory muscles (with poliomyelitis, paralysis, myasthenia gravis).
Shortness of breath in heart disease is a fairly common and diagnostically significant symptom. The cause of shortness of breath here is a weakening of the pumping function of the left ventricle and stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation.
The severity of heart failure can be judged by the degree of shortness of breath. At the initial stage, shortness of breath appears during physical activity: climbing stairs more than 2-3 floors, walking uphill, against the wind, moving at a fast pace. As the disease progresses, it becomes difficult to breathe even with slight exertion, when talking, eating, walking at a calm pace, or lying horizontally. In the severe stage of the disease, shortness of breath occurs even with minimal exertion and any actions, such as getting out of bed, moving around the apartment, bending the body, entail a feeling of lack of air. In the final stage, shortness of breath is present even at rest.
Attacks of severe shortness of breath, suffocation that occur after physical, psycho-emotional stress or suddenly, often at night, during sleep are called cardiac asthma. The patient is in a forced sitting position. Breathing becomes noisy, bubbling, audible at a distance. The release of foamy sputum may be observed, which indicates the onset of pulmonary edema; the participation of auxiliary muscles in the act of breathing and retraction of the intercostal spaces are noticeable to the naked eye.
In addition, shortness of breath in combination with chest pain, palpitations, and interruptions in cardiac function can be a sign of acute myocardial infarction, rhythm disturbances (paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation) and is caused by a sharp decrease in heart function, a decrease in perfusion and oxygen supply to organs and tissues.
A group of blood diseases, one of the symptoms of which is shortness of breath, includes anemia and leukemia (tumor diseases). Both are characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells, the main role of which is oxygen transport. Accordingly, oxygenation of organs and tissues deteriorates. A compensatory reaction occurs, the frequency and depth of breathing increases - thereby the body begins to consume more oxygen from the environment per unit of time.
The simplest and most reliable method for diagnosing these conditions is a general blood test.
Another group is endocrine (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus) and hormonally active diseases (obesity).
With thyrotoxicosis, the thyroid gland produces an excess amount of hormones, under the influence of which all metabolic processes are accelerated, metabolism and oxygen consumption increase. Here, shortness of breath, as with anemia, is compensatory in nature. In addition, high levels of T3 and T4 increase the work of the heart, contributing to rhythm disturbances such as paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation with the consequences mentioned above.
Shortness of breath in diabetes mellitus can be considered a consequence of diabetic microangiopathy, leading to impaired trophism and oxygen starvation of cells and tissues. The second link is kidney damage - diabetic nephropathy. The kidneys produce the hematopoietic factor erythropoietin, and its deficiency causes anemia.
With obesity, as a result of the deposition of adipose tissue in the internal organs, the work of the heart and lungs is hampered, and the excursion of the diaphragm is limited. In addition, obesity is often accompanied by atherosclerosis and hypertension, which also entails disruption of their function and the occurrence of shortness of breath.
Shortness of breath to the point of suffocation can be observed with various types of systemic poisoning. The mechanism of its development includes an increase in the permeability of the vascular wall at the microcirculatory level and toxic pulmonary edema, as well as direct damage to the heart with disruption of its function and stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation.
Treatment of shortness of breath as a symptom of cardiac, pulmonary pathology or anemia
Shortness of breath, a feeling of acute lack of air, difficulty breathing is a symptom that accompanies many people. The occurrence of this condition is in most cases associated with manifestations of diseases of the respiratory system, heart, and blood vessels. Shortness of breath can appear at a young age and often accompanies representatives of the older generation. A regularly recurring symptom should be reported to your doctor. Treatment of shortness of breath is preceded by an analysis of the characteristics of the patient’s health status and identification of the pathologies that led to the appearance of the symptom.
What is shortness of breath?
Treatment for shortness of breath depends on its type. Patients can have different forms of it - physiological and pathological. Physiological shortness of breath in most cases is a temporary condition and occurs in the following cases:
- increased physical activity, stress on the body, which is one-time, not systematic;
- due to lack of oxygen, occurs when climbing to a height or staying in closed, unventilated rooms for a long time.
Dyspnea of this type can be easily corrected in most patients. To achieve the goal, a gradual increase in daily physical activity is recommended. If the symptom persists, a medical examination is required, as illnesses can cause shortness of breath. In such cases, the phenomenon becomes pathological. There are several types of shortness of breath, the classification depends on the cause of its occurrence:
- cardiac;
- pulmonary;
- observed in anemia.
Shortness of breath may be sudden or persistent. Doctors classify the condition depending on the characteristics of its form - acute, subacute or chronic.
8
24/7
Causes
The appearance of shortness of breath of a physiological nature is not associated with the development of diseases. Its pathological form indicates that the patient is sick and needs therapy. Treatment of shortness of breath involves getting rid of the disease that caused it.
Cardiac dyspnea occurs with pathologies of the heart and vascular system. This symptom is characteristic of the development of:
- heart failure;
- acute coronary syndrome;
- cardiomyopathy;
- inflammatory processes in myocardial tissues;
- pericarditis;
- cardiac tamponade.
Shortness of breath is a manifestation of heart defects, when the organ has congenital or acquired pathologies of the walls, valves, vessels, and septa, which lead to obstruction of blood flow.
The appearance of pulmonary shortness of breath is provoked by pathologies of the respiratory system. It accompanies diseases:
- bronchial asthma;
- emphysema;
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
- pulmonary embolism;
- aspiration;
- obstructive pulmonary disease of chronic type.
Lack of hemoglobin in the blood leads to the development of anemia. The condition is characterized by the occurrence of shortness of breath. It appears due to a lack of oxygen saturation in the blood - it is this that tissues and internal organs, including the lungs and heart, do not receive enough of.
Shortness of breath, the causes and treatment of which are determined and prescribed by a doctor, requires an examination of the patient and confirmation of the main diagnosis.
Symptoms
Shortness of breath is a condition that has characteristic, pronounced symptoms. The main ones:
- a person suddenly finds it difficult to breathe, he feels that he is beginning to suffocate;
- there is discomfort in the chest area, pain, difficulty or restriction in movement of the chest;
- there is a feeling of lack of air, a feeling of suffocation.
It is necessary to immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment for shortness of breath if the phenomenon has become systemic or occurs suddenly and is accompanied by additional manifestations:
- severe chest pain;
- nausea or vomiting;
- hoarse breathing, cough;
- swelling of the limbs;
- loss of consciousness.
Diagnostics
Depending on the causes of shortness of breath, symptoms, treatment and diagnostic methods will differ. During the initial request for medical help, the doctor conducts an examination of the patient, which is accompanied by questions about the characteristics of shortness of breath:
- how often the symptom occurs;
- what conditions cause it;
- the nature of the process;
- what factors help mitigate or aggravate the manifestations.
8
24/7
During the examination, the doctor will evaluate the functioning of the lungs and heart using a stethoscope. Checks to see if the patient has signs of swelling in the tissues.
The diagnosis can be confirmed by the use of instrumental and clinical diagnostic methods. The doctor can give a referral for the following procedures:
- blood test - general (detailed), biochemistry;
- general urine analysis;
- sputum examination;
- chest x-ray;
- ultrasound examination of the lungs and heart (echocardiography);
- bronchoscopy;
- laryngoscopy;
- spirometry;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- computed tomography of the heart and blood vessels;
- ECG - normal or with stress;
- cardiac catheterization;
- coronary angiography.
The choice of diagnostic method depends on the dysfunctions of the heart or lungs identified during the initial examination, and the availability of equipment at the medical institution. Features of the treatment of shortness of breath, the choice of method depends on the diagnostic results, and involves excluding the manifestation of symptoms of the underlying disease.
Treatment
Treatment of shortness of breath will be effective if the causes of its occurrence are reliably established. Self-medication is unacceptable, since the causes of the symptom are dangerous dysfunctions of the human body. Individual treatment measures are prescribed for a specific patient:
- drug treatment;
- surgical operations;
- Traditional medicine recipes are used.
To quickly normalize their health, the patient must adjust their lifestyle - switch to the correct daily routine, change their diet, and eliminate bad habits.
How is cardiac dyspnea treated?
When cardiac dyspnea occurs, treatment is aimed at combating heart disease and pathological vascular changes. Depending on the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed medications:
- diuretics - to reduce tissue swelling, normalize blood pressure, reduce cardiac stress;
- ACE inhibitors – have a vasoconstrictor effect;
- beta blockers are used to normalize cardiac activity and lower blood pressure;
- angiotensin receptor blockers with antihypertensive properties;
- Aldosterone antagonists - used to get rid of edema, preserve potassium in the body, and normalize blood pressure;
- cardiac glycosides – are cardiotonics, normalize metabolic processes in the myocardium, prevent blood stagnation in the vessels;
- antiarrhythmic drugs - necessary to restore the rhythmic functioning of the heart.
Depending on the characteristics of the patient’s condition, the doctor prescribes natural remedies that can improve the performance of the cardiovascular system, relieve shortness of breath in heart failure, treatment is also possible using recipes from plants:
- hawthorn;
- valerian;
- lemon balm;
- mint;
- calendula.
Defects of the heart, its valves and blood vessels cause severe shortness of breath; treatment for patients requires surgery - surgery. The main types of assistance are:
- coronary stenting;
- coronary artery bypass grafting;
- heart valve replacement;
- installation of a pacemaker;
- surgery to replace a patient's heart with a donor one.
Treatment of pulmonary dyspnea
To treat shortness of breath that occurs as a result of lung pathology, the principle of an integrated approach is used. Therapeutic actions should be aimed at relieving the causes of shortness of breath, preventing complications and relapses of the underlying disease. Drug therapy, physiotherapy, and surgery are used.
The patient is prescribed medications:
- beta2-adrenergic agonists, m-anticholinergics, methylxanthines - their action is aimed at expanding and relaxing the walls of the bronchi and their muscle tissue;
- antibiotics - indicated to destroy or suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms;
- glucocorticosteroids - have an anti-inflammatory effect, reduce swelling of the mucous membranes, reduce the formation of fluid in the bronchi.
Oxygen inhalation is often used to treat shortness of breath in the elderly. The procedure is carried out under the supervision of specialists.
Shortness of breath when walking, causes and treatment are often associated with serious pathology of the respiratory system. In such cases, one of the types of surgical operations is used - puncture of the pleural cavity, thoracotomy, drainage of the pleural cavity, lung volume reduction, organ transplantation from a donor.
Treatment of anemia
If shortness of breath is caused by anemia, therapy involves the following measures:
- treatment of the underlying disease that provokes a decrease in hemoglobin;
- taking iron and folic acid supplements;
- normalization of hematopoietic function;
- stopping bleeding, preventing its recurrence;
- treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Prevention
Difficulty breathing, especially shortness of breath in older people, requires individual treatment. To mitigate symptoms and prevent their recurrence, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- use physical activity in volumes recommended for certain age groups;
- learn to breathe correctly, train breathing with the help of gymnastics;
- prevent the development of stressful situations, control the emotional state;
- Completely quit smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Only timely consultation with a doctor in case of regularly occurring shortness of breath will help to make a correct diagnosis and begin effective treatment. Otherwise, some diseases can be fatal.
8
24/7
Deep breathing
The technique is performed to ventilate all respiratory tracts, helps relieve symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections, and restores and straightens the lungs after infections. Doctors in Rostov speak positively about the benefits of daily practice as a preventive measure.
The exercise has contraindications:
- pregnancy,
- dry non-productive cough.
To perform this, you need to take 3-4 deep breaths only through your nose so that the air is warmed and moistened in the nasopharynx. It is worth taking a break between breaths to prevent hyperventilation.