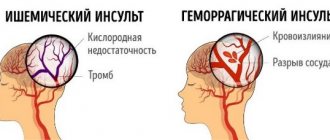
The heart is one of the most important human organs. Thanks to its stable and proper functioning, other organs are saturated with oxygen and nutrients. Supporting the vital functions of the body is possible only if the compressor capacity of the heart muscle is normal. This especially applies to people involved in sports, both professional and amateur. Even if you go to the gym and your workouts are far from exhausting, you should know your level of maximum load or the so-called effective heart load index.
How does the heart work normally?
How does exercise affect the heart?
Is it possible for heart damage due to exercise?
How to avoid heart problems?
What is the effective heart load index (VIDEO)
What are the contraindications to physical activity?
Dynamic loads
The most beneficial thing for the body is dynamic load - that is, movement. This type of physical activity includes running, swimming, walking, as well as such popular exercises as lunges, squats, and crunches.
What do regular dynamic loads give?
- A well-developed exercise program helps build the body;
- Exercise promotes muscle growth;
- Energy consumption increases - not only during load, but also at rest;
- Lung volume and depth of breathing increases;
- All tissues of the body are more intensively supplied with oxygen;
- Metabolism improves;
- The risk of developing diseases of the musculoskeletal system is reduced.
Static loads
Load is not necessarily movement. Staying in one position for a long time can also be a strain on the muscles. If your health does not allow you to practice dynamic loads, you can resort to static ones. They do not require active movement; on the contrary, during the process you must maintain a certain position or change it very slowly (as, for example, in yoga or Pilates). Such loads are indicated even for diseases of the cardiovascular system or musculoskeletal system, which do not allow dynamic activity.
Basic principles of dosing and control of physical activity during physical education
Excess body weight, decreased physical performance, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption - all this contributes to the occurrence of cardiovascular and many other diseases. Despite the powerful development of drug therapy, dosed physical activity remains a universal method for the prevention of coronary heart disease, arterial hypertension, obesity and other diseases. Recently, there has been a certain increase in the population's interest in regular physical education.
People who want to receive practical recommendations on building, planning and controlling loads during physical education seek medical advice. The doctor should recommend a certain regimen of physical activity that corresponds to the level of fitness of the body, taking into account the existing chronic pathology.
We present to your attention information material that reveals the main goals, objectives and principles of physical training.
- Physical health assessment
If your client is under 35 years of age and has no signs of any illness, then there is generally no need for him to consult a doctor before starting regular physical activity. But if he is over 35 years old, and he has not been involved in sports or physical activity over the past few years, then a medical examination is necessary, especially if the following health abnormalities occur:
- high blood pressure;
- a history of heart attacks;
- presence in the family history of indications of the early development of cardiac pathology or deaths from cardiovascular diseases;
- frequent attacks of headaches or dizziness;
- significant degree of shortness of breath with little physical exertion;
- arthritis and various pathologies of the musculoskeletal system;
- other possible chronic diseases.
Physical activity is practically safe for people with an initially good level of physical health, who have undergone a full medical examination and received adequate medical recommendations.
- Basic concepts of physical health
Physical fitness can be characterized as the body’s ability to comfortably endure everyday physical activity and successfully cope with suddenly occurring stressful situations. The individual level of physical performance is influenced by factors such as age, gender, heredity, bad habits, and nutritional patterns. The concept of physical health, or fitness of the body, includes several components.
Fitness of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems (cardiorespiratory endurance)
- a component of the general fitness of the body, reflecting the ability of these systems to adequately ensure the vital functions of the body during physical activity of varying intensity and duration. In practice, this indicator can be assessed taking into account a person’s ability to withstand prolonged physical activity, such as running, swimming, skiing, etc.
Muscular strength
- the ability of muscles to perform the maximum possible mechanical work in a short time. In practice, this component of the body’s fitness is assessed, for example, for the upper limb belt, by the maximum amount of weight lifted.
Muscular endurance
- the ability of muscles to perform mechanical work of varying duration and frequency. For example, repeated lifting of a certain weight is used to determine muscular endurance of the upper shoulder girdle.
Flexibility
- the ability to perform mechanical work using the maximum possible range of motion. Seated trunk flexion is a simple and objective method for assessing the flexibility of the lumbar spine and lower extremities.
Body composition
- the ratio between body fat and the total mass of skeletal muscle, bone tissue and internal organs. Individually selected physical exercises help reduce fat mass and increase muscle mass in certain areas of the body.
- Structure of training sessions
The duration and number of workouts per week, as well as the intensity of physical activity, are determined by the level of fitness of the body, age, the presence or absence of any chronic diseases, as well as the social needs of the person.
Any individual training program should include exercises aimed at the harmonious development of all the main components of physical health. Any training session should consist of a warm-up (warmup), main load and cool-down (cooldown).
Below is the structure of a training session, designed for the average healthy person and aimed at maintaining a minimum level of physical health of the body. It includes the most popular types of training exercises.
Warm-up lasts five to ten minutes and includes low-intensity physical activity (walking, slow running, flexibility exercises, rotational and swinging movements of the upper and lower extremities). It is aimed at preparing the cardiovascular, respiratory and musculoskeletal systems for the main training load. Below are the main types of core training load.
Training to develop muscle strength (muscular strength) is carried out at least twice a week for 20 minutes. The most effective way to develop muscle strength is to lift weights.
Training to develop muscular endurance should be carried out at least three times a week for 30 minutes and include exercises for the main muscle groups: rhythmic and plastic exercises, push-ups, squats, pull-ups, repeated weight lifting.
Training to develop fitness of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems (cardiorespiratory endurance) is carried out three times a week for 20 minutes and includes prolonged physical activity performed in an aerobic mode. The most common types of such exercise are fast walking, running, cycling, rowing, skiing, as well as team sports (basketball, handball, etc.).
Flexibility training should be done daily during the warm-up or cool-down and include flexibility and stretching exercises. A cooldown involves low-intensity activity (such as walking or running at a slow pace) and five to ten minutes of flexibility exercises.
- Basic principles of fitness
Specificity
- the need to select a certain set of physical exercises aimed at developing and strengthening muscle groups that are most involved in a certain type of muscle activity. It is advisable to combine different types of physical activity (swimming, running, walking, skiing, etc.) for more harmonious development of the body, as well as for the prevention of injuries.
Physical activity must be of sufficient intensity and duration to ensure growth or maintenance of the body's optimal level of fitness.
Regularity of physical activity.
Training sessions should be regular. A minimum of three training sessions per week is required to maintain optimal fitness levels.
Progression.
A gradual increase in the intensity, duration and/or frequency of training sessions is a necessary condition for optimally increasing the body's fitness level.
- Exercise intensity and heart rate control
Physical activity comes in varying intensity and duration. Four main zones of physical activity intensity have been identified (see Fig. 1), each of which corresponds to a certain level of bioenergetic processes and a range of heart rate (HR):
1.
Low-intensity physical activity with a heart rate less than 75% of its maximum value (HR max.);
2.
Physical activity of a maintenance nature with a heart rate from 75 to 85% of the maximum heart rate, carried out in an aerobic energy supply mode;
3.
Physical activity of a developmental nature with a heart rate from 85 to 95% of the maximum heart rate.
and transitional aerobic-anaerobic energy supply regime; 4.
Physical activity of submaximal and maximum intensity with a heart rate of more than 95% of the maximum heart rate. and anaerobic energy supply.
Each person has his own individual boundaries of load intensity zones. To more accurately determine these boundaries for the purpose of subsequent monitoring of sports loads, special testing is used. It is based on a test load that increases stepwise to the maximum possible (“work to failure”) level.
Such testing is contraindicated for untrained and poorly prepared people. To determine intensity zones in this case, a simpler calculation method is used. You can easily calculate the boundaries of each intensity zone, knowing the age value of heart rate max., which is determined by the formula 220 minus age.
For health purposes, as a rule, physical activity is recommended within intensity zones I and II. Loads of greater intensity are a privilege of sport and require a fairly high level of preparedness.
Studies have shown that exercise with an intensity of 60-70% of heart rate max. is most effective for burning fat, so it is used to correct excess body weight:
| Target zone | |
| Age (years) | Heart rate (bpm) |
| 20 | 120-140 |
| 30 | 114-133 |
| 40 | 108-126 |
| 50 | 102-119 |
| 60 | 96-112 |
To increase the fitness of the cardiovascular system, a load with an intensity of 60-80% of max heart rate is used:
- Monitoring heart rate during training sessions and during rehabilitation programs
Heart rate monitoring is a universal method of monitoring and regulating the intensity of physical activity. Heart rate monitoring is a prerequisite for the safe and dosed use of physical activity in a certain group of people: the elderly; suffering from cardiovascular pathology; undergoing rehabilitation after myocardial infarction and other serious illnesses.
| Target zone | |
| Age (years) | Heart rate (bpm) |
| 20 | 120-160 |
| 30 | 114-152 |
| 40 | 108-144 |
| 50 | 102-136 |
| 60 | 96-128 |
Recently, heart rate monitors, which continuously record heart rate, are most often used for this purpose. The operating principle of heart rate monitors is similar to recording the electrical biopotentials of the heart on the surface of the chest, used when recording an ECG. The heart rate monitor consists of two parts: a chest belt with electrodes and an ECG signal transmitter, and the heart rate monitor itself or receiver, which looks like a wristwatch. The transmission of signals from the chest transmitter to the heart rate monitor is carried out telemetrically. There are several models of heart rate monitors, differing in the range of special functions. Mandatory for all monitors is continuous recording of the heart rate value, as well as audio and visual alarms when the heart rate goes beyond the boundaries of a preset target heart rate zone. These functions are necessary for dosing the intensity and duration of physical activity, when strict adherence to the pulse regime is necessary.
The information provided to your attention reveals only the basic principles of planning and controlling loads during physical education. We hope that the proposed material will help you in your practical medical activities.
How to calculate heart rate for sports
The abbreviation HR stands for “heart rate,” in other words, it is the pulse. The easiest way to measure it is to place your finger on your wrist about 3-5 cm below the bend of the hand and count your heart rate for 15 seconds. Multiply the result by 4 to get the number of heartbeats per minute.
The same work can easily be done by modern fitness bracelets and smart watches. If you just started playing sports, these devices will help you track your daily activity and heart rate.
Measuring your pulse during exercise is very important: this allows you to understand how your heart reacts to physical activity and prevent overload.
In an adult, the resting pulse should vary from 60 to 80 beats. When under load, the norm is considered to be up to 200 beats - and the figure of 100-130 beats per minute belongs to the zone of moderate loads, during which fat is intensively burned. 130-170 beats per minute are already intense loads that are suitable for training the heart. Above are high-intensity workouts, which are stressful for the body. You can only exercise with such a pulse under the guidance of an experienced trainer.
Please note that your heart rate may be higher if you exercise in a stuffy room, get sick, or drink coffee shortly before your workout. In this case, monitor your well-being - the higher the pulse, the harder the load is tolerated.
If recovery is delayed
The maximum allotted time, which is 2 hours, has passed and your heart rate has not returned to normal values? There could be 3 reasons:
- Detraining. If you go to the gym a couple of times a month, the nervous system and heart do not adapt to the growing load. During a period of inactivity, the body loses all the gains it has gained. Solution: increase the number of workouts to 3 per week.
- Overtraining. The opposite case. Daily work in the gym or stadium, heavy loads without rest and recovery lead to stress. The balance of hormones is disrupted. Solution: reduce the number of workouts and turn to effective recovery methods.
- Diseases. There are hidden disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular or nervous system. These may be congenital heart defects, ischemia, vegetative-vascular dystonia, high blood pressure. Solution: contact a cardiologist and conduct a comprehensive examination.
Pain during exercise, tachycardia, hand tremors and increased sweating are signs of disturbances in the functioning of the body. The problem cannot be ignored. The reason is unlikely to go away on its own.
Blood pressure and sports
Normally, a person’s blood pressure should be approximately 120/80. But people who lead a healthy lifestyle may have lower blood pressure - for example, within the normal range, blood pressure is 100/60.
Sports are not contraindicated for people with hypertension - but they need to carefully monitor the level of stress and start exercising in a gentle manner. You can start with walking - first accustom yourself to walking more, then increase the pace. Later you can switch to running or swimming.
It is better to start training after consulting with your doctor.
IMPORTANT! If your blood pressure exceeds 190\110 at least periodically, if during physical activity you experience a burning sensation or pressure in the chest, intensive training, unfortunately, is contraindicated for you. But you can do static exercises, such as yoga.
Speeding up the process
Although the time it takes to restore your heart rate after a heavy load is an individual indicator, it can still be reduced. Some use sports pharmacology for this, but the influence of medications does not always give positive results.
We will give a number of recommendations:
- Monitor your pulse . Any device, like the Mi Band from the Chinese brand Xiaomi, is suitable for this. Have you noticed that your heart rate is outside the normal range? Slow down the pace, change or remove the extra weight on the bar. It seems like obvious advice, but only a few take note of it, especially among amateurs.
- Plan your workouts . You should not move on to the active phase of exercise without warming up, even if you have little time. Prepared muscles become elastic and work much more efficiently. Work one muscle group on one day. Then they will have time to recover for the next classes.
- Eat right . Protein, amino acids, vitamins, fats and carbohydrates are the necessary “building blocks” for the production of muscle tissue. Diet will only worsen the result and cause health problems. It is better to postpone it for the future.
- Drink fluids . A bottle of mineral water without gas is a mandatory attribute for an athlete during training. As soon as classes are over, you need to replenish the water-salt balance. Otherwise, the blood will become thick and the heart will no longer cope with its functions.
- Limit caffeine . This substance stimulates the nervous system. As a result, increased sensitivity occurs, the myocardium begins to work more actively, which can cause tachycardia. You are allowed to drink no more than 1 cup of coffee per day. The drink should not be strong.
It is difficult for a beginner to understand all the intricacies of the training process. Therefore, it is better to contact a professional trainer or instructor. He will select an individual schedule. Things will go much faster. There will be no harm to health.
Charging at the workplace
Everyone knows that a sedentary lifestyle has a negative impact on health. It is not without reason that most office workers, who sit for up to 10 hours a day, have musculoskeletal diseases.
To prevent the development of illnesses, experts recommend doing a short warm-up at the workplace every two hours. It looks like this:
- First, pay attention to your neck. Slowly rotate your head back and forth, up and down. Repeat this at least 10 times.
- Then stretch your arms. Lift them up, clasp your palms together and stretch as high as possible. Next, make circular movements with your shoulders, 10 times.
- Pay attention to your wrists. Make 15 circular movements with your brushes.
- Stand on the floor and try to reach your palms to your feet without bending your knees. If it doesn't work, stretch as far as you can. Hold the position for 15 seconds.
- Sit on the edge of a chair with your legs extended in front of you without bending your knees. Keeping your back straight, pull your feet towards you and then back.
This complex must be carried out every 2-3 hours at work.
Calorie counting
If you want to not only become healthier, but also lose weight, it is important to pay attention to nutrition. Diet determines 70% of weight loss success. The most effective way to lose weight is to count calories. In order to accurately calculate them, you need to purchase a kitchen scale. It is convenient to use various applications for counting - they automatically calculate calorie content depending on the weight of the product. To maintain healthy and comfortable digestion, an adult should consume about 1700 kcal for women and about 2200 kcal for men. To lose weight, it is enough to reduce this number by 20%.