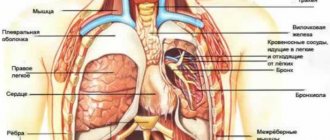
Causes of chest pain when breathing
The most common cause of chest pain when breathing is pleurisy. This disease is characterized by inflammation of the lining around the lungs. There are two layers of pleura: covering the inside of the chest and the pleura covering the lungs. Pleurisy, in addition to pain when breathing, can cause coughing, chest tenderness, and difficulty breathing.
In addition to pleurisy, chest pain during breathing can provoke various diseases. The most common causes of the symptom:
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Lungs' cancer;
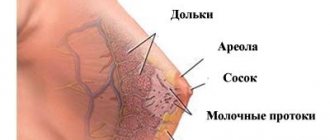
- Mammary cancer;
- Mesothelioma;
- Lupus;
- Pancreatitis;
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Connective tissue disease;
- Viruses, fungi, parasites;
- Pulmonary infarction;
- Injuries to the ribs, sternum;
- Pleural tumors;
- Pulmonary embolism;
- Clogged lungs with particulate matter;
- Congestive heart failure.
Diseases that cause pain in the lungs
Pain in the lungs is most often a manifestation of a certain disease, and ignoring such symptoms means not worrying about your health. People feel pain in different ways: sometimes they cut, sometimes they prick, sometimes they press. The location of the pain is also an important factor. By summing up all the symptoms of pain in the lungs, it is possible to make a correct diagnosis, since there are many diseases in which pain in the lungs is felt.
Diseases in which a person experiences pain in the lungs:
- Pneumonia;
- Bronchitis;
- Acute tracheitis;
- Lobar pneumonia;
- Pleurisy;
- Spontaneous pneumothorax;
- Lungs' cancer;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Pain of bone, joint or muscle origin;
- Heart diseases;
- Pericarditis;
- Pulmonary embolism;
- Aortic diseases;
- Pancreatitis;
- Stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- COPD
Diagnosis of chest pain when breathing
Due to the large number of diseases that can cause chest pain when breathing, diagnosis can take a long time. By contacting a therapist, you can receive a referral for an examination, which will include the following techniques:
- Electrocardiography;
- Radiography;
- Laboratory tests;
- Angiography of blood vessels;
- CT (computed tomography);
- Blood and urine analysis;
- Bronchoscopy;
- Sputum culture analysis;
- Biochemical studies for amylase, glucose and LDH;
- Palpation;
- Biochemical markers for the presence of myocardial damage;
- Echocardiography;
- ECG screening method;
- ECG with exercise and at rest;
- Study of thyroid hormone levels;
- Dopplerography of blood vessels.
Pain when taking a deep breath
Causes of pain when taking a deep breath
The following conditions lead to pain when taking a deep breath:
- inflammation of the pleura (pleurisy), often detected with pneumonia (the pain is more easily tolerated in a lying position, the general condition suffers, weakness and fever appear);
- intercostal neuralgia is a common cause of pain when inhaling, and they have a “shooting” character and sharp severity;
- deformation of the rib frame with limited mobility of the thoracic spinal column (this condition is typical for scoliosis and other postural disorders);
- shortening of the interpleural ligament, which is accompanied not only by pain when inhaling, but also by constant coughing;
- injuries or compression of the chest with damage to the cartilaginous or bony rib structures (the pain is sharp, intense, radiating to the surrounding areas and lower back);
- osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine (manifested by moderate pain of varying intensity, inhalation is difficult during exacerbation of the disease, which is caused by hypothermia, physical activity, and prolonged exposure to a static position).
As a rule, pain occurs not only when inhaling - the patient feels significant discomfort when coughing, sneezing, or laughing. If the discomfort is caused by intercostal neuralgia, numbness or burning of the skin along the branches of the affected nerve is added to the pain.
Treatment at the Posturology Clinic
The main task of a posturologist is to carefully release pinched nerve endings from compression by muscles, ligaments and the ribs themselves. Drug therapy is used according to strict indications and serves as an auxiliary method of treatment for acute, unbearable pain.
Using massage techniques, exercise therapy, reflexology, hirudotherapy, physiotherapy, the specialist achieves a number of effects:
- restores the anatomically correct configuration of the chest;
- relieves muscle blocks in the chest and back;
- restores normal curves of the spine;
- helps the internal organs of the chest to “fall” into place;
- improves blood circulation and nerve conduction in the affected area.
Complex treatment eliminates trigger pain points, relaxes the necessary muscle groups, forms the correct motor stereotype and consistently eliminates all links in the pathological chain of disorders.
There is no need to wait until the pain with a deep breath goes away on its own - it can and should be treated, and a competent doctor will not only relieve you of the pain syndrome, but will also bring all body systems into a state of harmonious balance.
Treatment of chest pain when breathing
Treatment of this symptom is primarily aimed at the cause of its occurrence. Each disease requires a specific approach.
Treatments for the most common causes of chest pain when breathing:
- Pulmonary embolism - a course of anticoagulants is prescribed or the blood clot is removed during surgery;
- Pneumonia - doctors prescribe a course of antibiotics, inhalations and saline solutions;
- Pleurisy - therapy is usually complex. Doctors prescribe anti-tuberculosis and antibacterial drugs in combination with immunostimulants;
- Pneumothorax - in advanced cases, the patient is admitted to the hospital and the air is sucked out of the lungs;
- Rib melancholy - anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants and physical therapy are prescribed;
- Angina pectoris - acute attacks are relieved with blockades and painkillers. In addition, diet, β-blockers and acetylsalicylic acid are prescribed.
Diagnosis of pain in the heart area when inhaling
What to do when I breathe and my heart hurts? Contact specialists at the KDS Clinic. Medical workers will conduct a comprehensive examination, diagnose the disease even at an early stage, and prescribe effective and affordable treatment. Pain in the heart area when inhaling indicates impaired functioning of the internal organs. We are talking not only about the cardiovascular system, but also about neighboring organs that can load the heart, thereby causing discomfort. If the patient feels a sharp nagging pain, he should change his position and take painkillers.
If these symptoms occur regularly, it is worth getting tested. Visit a cardiologist and TB specialist. He will direct the patient to undergo tests, including stool, urine, biochemistry and blood tests. With the help of tests, the condition of all indicators of the body will be diagnosed. The patient may be referred for an electrocardiogram, radiography and ultrasound diagnostics. If we are talking about lung disease, then auscultation of the lungs will be performed at a medical institution. To diagnose the cardiovascular system, the patient remains in the hospital where he undergoes a Holter examination. Over the course of several days, doctors observe changes in the patient’s condition and study the dynamics.
If you feel pain in the heart area when you inhale, do not worry and go to the clinic as soon as possible, where they will conduct a comprehensive diagnosis using modern equipment. In most cases, surgery will not be required. Even in advanced cases, doctors will find an effective solution to the problem. When your heart hurts when you inhale, make an appointment with a specialist by number.
Heart problems
Pain in the chest in the middle or on the left side occurs with various heart diseases:
- IHD, angina pectoris - a violation of blood flow in the heart arteries. Often an attack of sharp pain lasts up to 15 minutes. Occurs during physical activity, stress, anxiety, and goes away after rest.
- Myocardial infarction is the death of cells and the formation of scars on the heart muscle. It is characterized by severe pain in the chest on the left and in the middle, which does not go away after 15-20 minutes. Additional symptoms include weakness and fear of death.
- Pericarditis or myocarditis is an inflammatory process in the muscle or lining of the heart. They are characterized by acute or aching pain in the chest when inhaling in the middle of the chest, which intensifies while eating or lying down.
- Mitral valve prolapse - in addition to chest pain, it causes shortness of breath, dizziness, even fainting.
- Pulmonary hypertension is increased pressure in the pulmonary arteries, an attack similar to a heart attack.
A characteristic feature of heart pain is that it often occurs against a background of emotional or physical stress and is accompanied by a feeling of panic and fear of death.
Principles of treatment
Pain relief is aimed at reducing pain and eliminating muscle spasms in the affected area. If taking NSAIDs orally or by injection does not help, blockades are performed. This is the introduction of drugs into the most painful points, which are projections of the exit of nerves. Local anesthetics, hormones, NSAIDs, and muscle relaxants are used. Diuretics reduce swelling of the compressed nerve and eliminate pain. Drugs are prescribed that improve the conductivity of nerve tissue.
In addition to relieving acute pain, it is necessary to influence the cause of pinching of the intercostal nerve in the thoracic region. Medicines, massages, manual therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, reflexology, and physical therapy help reduce the destruction of bones and joints. Medicines prescribed:
- vascular drugs - improve blood circulation;
- chondroprotectors – restore the properties of the cartilage layer between the vertebrae;
- calcium supplements, vitamin D fight osteoporosis;
- multivitamin complexes with minerals.
Acupressure, lymphatic drainage and classic types of massage are used. The impact on the back muscles helps eliminate spasms, improves blood flow and tissue nutrition. Thanks to this, it is possible to break the pathological circle, when pain causes muscle contraction, which compresses nerve fibers and blood vessels, disrupting blood supply and increasing pain.
In some cases, surgical treatments may even be necessary. For example, to eliminate the consequences of an injury, remove a significant hernia, tumor, or perform spinal stabilization.
Every person should be attentive to their health and not ignore the symptoms of a pinched nerve in the thoracic region if they appear. It is important to seek qualified help immediately. After all, the earlier the problem is identified, the greater the chances of achieving complete restoration of the function of the nerves and all structures of the spinal column, and of avoiding another pinching under the breast in the future.
Injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Thoracalgia appears due to injuries, diseases of the spine, and worsens after physical activity. Main causes and symptoms:
- Osteochondrosis, hernias and protrusions of intervertebral discs in the thoracic spine, scoliosis - cause chest pain, which intensifies with movement or prolonged immobility.
- Rib fractures.
- Muscle spasms, sprains, intercostal neuralgia - cause pain in the chest on the right or left, depending on the location where the pathology occurred.
- Tietze's syndrome or inflammation of the costochondral joints.
- Neurological pain - from “pins and needles” in the chest to severe pain occurs due to mental disorders, with panic attacks.
Pain in the right or left side of the chest may have other causes: tumors in the lungs or mammary gland, herpes zoster and other diseases.
The doctor’s task is to make a timely and correct diagnosis. This will help: heart examinations, ultrasound, radiography and other diagnostic procedures.
Emergency medical care is needed if:
- Acute chest pain does not go away after 15 minutes and after rest.
- There is dizziness, shortness of breath, increased sweating, and palpitations.
In other cases, it is also advisable not to delay consulting a doctor for too long. Who to contact - a cardiologist, a neurologist, a gastroenterologist - depends on the symptoms. But it is not always possible to determine this on your own. In this case, start by consulting a therapist who will help you understand the issue and, if necessary, refer you to a specialist.
In other cases, it is also advisable not to delay consulting a doctor for too long. Who to contact - a cardiologist, a neurologist, a gastroenterologist - depends on the symptoms. But it is not always possible to determine this on your own. In this case, start by consulting a therapist who will help you understand the issue and, if necessary, refer you to a specialist. Be healthy!
Diagnosis of any disease requires modern equipment and extensive medical experience. Especially when it comes to chest pain.
Our clinic offers its patients a full range of medical tests using high-precision equipment. Our doctors select the most informative and safe diagnostic methods.
By contacting us, you can be sure that the cause of the pain will be determined as quickly and accurately as possible. High-tech diagnostic devices allow you to monitor the functioning of all organs and systems without causing you unnecessary discomfort.
We value our patients' time, so all consultations and procedures are by appointment. By booking a visit, you can be sure that the doctor will be waiting for you. Come to the clinic to find out the cause of your pain and discuss treatment options.
Feelings associated with heart disease
More often than others, pain that occurs in the heart area when inhaling is provoked by the following diseases of the cardiovascular system:
- Angina pectoris.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Pulmonary embolism.
Cardiological causes of heart pain are extremely varied and quite often nonspecific. However, there are a number of features that indicate a connection with heart disease.
For example, with myocardial infarction (Fig. 2) and angina pectoris, pain often radiates (“gives”) to the area of the left shoulder and shoulder blade, neck and lower jaw. As a rule, it is associated with exposure to triggers - physical activity, smoking, errors in taking necessary medications. In this case, there is often no connection with respiratory movements.
Also, with a heart attack, severe weakness, shortness of breath, a characteristic “fear of death” occurs, and cold, sticky sweat appears on the forehead. Other possible signs of this pathology are: heart rhythm disturbances, dizziness, nausea.
Figure 2. Symptoms of myocardial infarction. Source: MedPortal
In general, cardiac pain is often accompanied by fluctuations in blood pressure, both towards hypertension (above 140/90 mmHg) and hypotension (below 90/60 mmHg). Also, a clear marker of pain of cardiac origin is a violation of the rhythm of heart contractions and “pulse deficiency” - a phenomenon in which the heart rate does not correspond to the pulse rate in the peripheral arteries.
Cardiac problems are often combined with heart failure, which is accompanied by symmetrical swelling of the extremities and acrocyanosis - bluishness of the skin in areas of the body distant from the heart: fingers and toes, lips, ears, etc.
It is important to understand that cardiac diseases can “masquerade” as other pathologies, which makes them quite difficult to recognize. For example, with myocardial infarction with a focus of ischemia in the region of the posterior-inferior part of the heart, pain may occur in the center of the upper abdomen.
Difficulties in diagnosis are added by concomitant diseases, for example, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, in which pain in the heart, even with the same myocardial infarction, may be absent due to diabetic polyneuropathy (a complication of diabetes mellitus in which damage to peripheral nerves occurs and can be accompanied by both pain and loss sensitivity).
Pulmonary pathologies
The main task of the lungs is gas exchange. In the alveoli, carbon dioxide and oxygen are exchanged between inhaled air and venous blood. This is a vital function, the violation of which causes acute or chronic hypoxia, and when breathing stops, clinical and then biological death quickly develops.
Advertising:
Pleuropneumonia
In some cases, the focus of inflammation during pneumonia may be located close to the pleural cavity. Then the inflammation spreads to the pleura, causing pain. It can be constant, or it can only appear with deep breathing. In any case, coughing and forced breathing significantly increase pain.
In addition to pain, a person is worried about:
- symptoms of intoxication - weakness, fatigue;
- heat;
- cough, usually with sputum.
In the case of massive pneumonia, symptoms of respiratory failure may appear - shortness of breath, cyanosis, decreased saturation. The disease is most severe in the elderly, children and people with immunodeficiencies.
The most common cause of pneumonia is Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Pleurisy
Chest pain when inhaling is more typical of dry pleurisy. Its morphology is very similar to dry pericarditis: fibrinous threads deposited on the surface of the pleura. They make friction of the pleura painful. The pain intensifies when breathing, as well as the slightest cough, or when bending to the healthy side.
The condition is alleviated on the contrary, by tilting towards the affected lung. This reduces the tension of the inflamed pleura. It also becomes easier for a person with pleurisy when he lies on the side of inflammation. This reduces the excursion of the affected side of the chest, thereby relieving pain.
In addition to pain, there may be symptoms of inflammation:
- heat;
- weakness.
Often with pleurisy, a dry reflex cough occurs. The causes of fibrinous pleurisy can be:
Advertising:
- tuberculosis;
- chronic kidney disease;
- Dressler's syndrome;
- systemic diseases.
Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax of the lung is a dangerous pathology in which air penetrates where physiologically it should not be - into the pleural cavity. This condition is becoming more common these days. The injured person needs to begin providing emergency care as soon as possible, since pneumothorax can be fatal. Symptoms of pneumothorax depend on the type of disease, the severity of its course, and the presence or absence of complications. The general symptoms of the disease are:
- the patient has difficulty breathing and has shallow, rapid breathing;
- cold, sticky sweat appears;
- attack of dry cough; the skin acquires a bluish tint;
- cardiopalmus;
- sharp pain in the chest;
- fear;
- weakness;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- subcutaneous emphysema;
- the victim takes a forced position - sitting or half-sitting.
Patients with spontaneous pneumothorax experience chest pain, which is more severe due to the development of the disease. There is also a sudden onset of shortness of breath. At first the pain is sharp, but gradually it becomes dull and aching. In the case of spontaneous pneumothorax, hypotension and hypoxemia are observed. The skin may acquire a bluish tint. In case of spontaneous pneumothorax, the patient should be immediately taken to the hospital.