For a pregnant woman, every ultrasound is an exciting event. During the procedure, the doctor will tell you how the fetus grows and develops and whether everything is okay.
Unfortunately, a visit to the ultrasound diagnostic room does not always end on an optimistic note. Sometimes the expectant mother hears words from the doctor that are incomprehensible and therefore alarming for her - “a cyst of the choroid plexus of the brain has been discovered.” What it is? What is the risk of a neoplasm for a baby? How can I help him?
What it is?
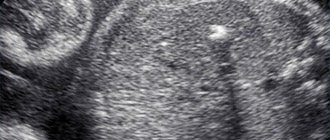
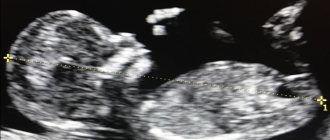
A choroid plexus cyst (CPC) should be distinguished from a vascular cyst - these are different formations that affect the fetus in different ways. Strictly speaking, a choroid plexus cyst cannot be called a cyst in the usual sense of the word, since it is not some kind of pathological formation. What is it?
The choroid plexuses appear at the very beginning of embryonic development. This is an interweaving of vessels that produce cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid. When too much cerebrospinal fluid is produced, it accumulates between the vessels. During an ultrasound, a sonologist sees this accumulation of fluid as an anechoic inclusion in the lateral ventricles of the brain.
Cysts are usually diagnosed during a second routine ultrasound. According to statistics, they are found in 2–3% of babies.
There is an assumption that choroid plexus cysts occur in all children at one or another stage of intrauterine development and growth. They do not relate to pathological formations that threaten the health and life of the fetus or mother, and do not require emergency measures.
Preparation for fetal ultrasound, procedure progress
No special actions are required from the woman to prepare for the ultrasound examination, since all internal organs are displaced by the uterus and do not interfere with the view. But you will have to adhere to several recommendations to make the pregnant woman feel as comfortable as possible.
The doctor will recommend:
- Avoid foods rich in allergens one week before the procedure. Allergies are dangerous not only for the woman - her poor health will certainly affect the behavior of the fetus.
- In a couple of days you need to give up fatty, fried, spicy and salty foods. These products stimulate the secretion of bile and affect the liver - it increases in size.
- For 24 hours, do not consume carbonated water and foods that cause gas formation in the intestines. Air bubbles obstruct vision, distorting echogenicity characteristics.
- Immediately before the ultrasound, control the amount of food and liquid consumed so that the natural urge to empty the intestines and bladder does not constrain the pregnant woman
Failure to follow these recommendations certainly affects the results obtained during the ultrasound, but not so significantly as to refuse diagnosis if you ate a piece of meat or drank a glass of soda the day before.
The procedure is painless. As usual, the woman lies on her back on the couch, and the specialist rubs her stomach, which was lubricated a minute earlier with the gels necessary as conductors. The procedure lasts on average from 10 minutes to half an hour.
Often in the first trimester, a transvaginal ultrasound is performed - a sensor with a condom on it is inserted into the pregnant woman’s vagina. This does not cause pain, the procedure lasts no more than a few minutes. Transvaginal ultrasound may be repeated in the second trimester if a detailed examination of the cervix is necessary.
Causes of choroid plexus cysts
It is generally accepted that choroid plexus cysts can occur under the influence of factors such as:
- infectious diseases of the mother in early pregnancy;
- impaired blood supply to the fetus.
Problems with blood supply can appear due to the incorrect position of the baby in the womb, pathologies of the umbilical cord (absence of one artery, nodes, hematomas, entanglement) and placenta (hypo- or hyperplasia, partial detachment, presentation). It is assumed that insufficient blood supply to the fetal organs and, in particular, to the structures of the brain can lead to excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid and, as a result, its accumulation - the formation of a cyst.
However, there is another opinion, whose supporters consider the formation of choroid plexus cysts to be a normal phenomenon characteristic of brain development. In other words, there is no reason for their formation; they are not a pathology.
Norms of fetal ultrasound indicators in the second trimester in the summary table
| Term | BPR | LZR | coolant | DP | DG | OG | Heart rate | DgRK | DB |
| 20 weeks | From 43 to 53 mm | From 56 to 68 mm | From 124 to 164 mm | From 26 to 34 mm | From 26 to 34 mm | From 154 to 186 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 48mm | From 29 to 37 mm |
| 21 weeks | From 46 to 56 mm | From 60 to 72 mm | From 137 to 177 mm | From 29 to 37 mm | From 29 to 37 mm | From 166 to 200 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 50mm | From 32 to 40 mm |
| 22 weeks | From 48 to 60 mm | From 64 to 76 mm | From 148 to 190 mm | From 31 to 39 mm | From 31 to 39 mm | From 178 to 212 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 53mm | From 35 to 43 mm |
| 23 weeks | From 52 to 64 mm | From 67 to 81 mm | From 160 to 201 mm | From 34 to 42 mm | From 34 to 42 mm | From 190 to 224 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 56mm | From 37 to 45 mm |
| 24 weeks | From 56 to 67 mm | From 71 to 85 mm | From 172 to 224 mm | From 36 to 44 mm | From 36 to 44 mm | From 201 to 237 mm | 120-160 beats/min | About 60mm | From 40 to 48 mm |
Third trimester
The last planned ultrasound examination is the most extensive and consists of measuring and studying the following fetal data:
- BPR – biparietal head size;
- LZR – fronto-occipital size;
- OG – head circumference;
- AB – abdominal circumference;
- DG – length of the tibia;
- DB – length of the femur;
- DP – length of the humerus;
- Height – 430 -470 mm;
- Weights – 1400 – 2400 grams;
- Beclair's nuclei - with normal development less than 5 mm;
- Thickness of placenta;
- The maturity of a child's place;
- Placenta placement, its presentation and the presence of abruption;
- AFL - the amount of amniotic fluid - 1-1.5 l is considered the norm;
- The length of the neck is considered normal to be from 30 to 35 mm.
Diagnosis and treatment
Why even pay attention to choroid plexus cysts and note them during ultrasound? The fact is that such cysts themselves are not dangerous, but they are so-called markers of chromosomal abnormalities (CA) - signs of the possible presence of genetic abnormalities in the fetus. Other markers include:
- hyperechoic intestine;
- enlargement of the ventricles of the brain;
- irregular head shape;
- cystic hygroma of the neck;
- non-immune dropsy;
- dilation of the renal pelvis;
- increasing the thickness of the collar space;
- aplasia or hypoplasia of the nasal bone;
- hyperechoic focus in the heart;
- symmetrical developmental delay.
If one of the listed markers of CA is detected, the probability of the fetus having malformations is no more than 8%. The combination of several signs increases it to 53%. When 8 markers are detected, in 92% of cases a child is born with severe genetic abnormalities.
Choroid plexus cysts are detected most often in children with Edwards syndrome (30–80%), less often they signal Down syndrome (8%) or Patau syndrome (2%). However, the detection of only a choroid plexus cyst does not allow making any specific diagnosis.
When a cyst is detected at 18–20 weeks, doctors take a wait-and-see approach. As a rule, by 24–28 weeks this marker disappears on its own; during this period, the woman is prescribed an additional ultrasound. If there is reason to believe that the cyst arose due to an infection that the mother had, the woman is prescribed tests to check her condition.
The combination of a cyst with other markers of CA is an indication for additional research. A pregnant woman may be referred for an expert ultrasound, aminocentesis, cordocentesis, or recommended to undergo a DOT test. If the risk of having a child with chromosomal pathologies is high, termination of pregnancy is recommended for medical reasons.
Timing of planned ultrasound scans during pregnancy and indications for unscheduled examinations
The content of the article
Routine fetal screenings are carried out within the following framework:
- The first screening is from the 10th to the 14th week.
- The second screening is from the 20th to the 24th week.
- The third screening is from the 30th to the 32nd week.
However, most women undergo the procedure more often. The reasons for non-screening ultrasound are the following:
Up to ten weeks:
- The need to confirm the fact of pregnancy and determine the due date.
- There is experience of miscarriage due to miscarriage, habitual miscarriages, missed pregnancies.
- Pregnancy took place through the use of assisted reproductive technology
- There have been negative experiences with fetal pathologies in the past.
- There was a multiple pregnancy in the family.
- Determination of intrauterine or ectopic pregnancy.
After the first ultrasound, you need to undergo an unscheduled examination if you have:
- Nagging pain in the area of the reproductive organs - lower abdomen.
- Presence of bleeding or unusual discharge.
- The size of the uterus is inappropriate for the given period, the belly is too large.
- Suspicion of leaking amniotic fluid.
- The need to control insufficiency (weakness) of the cervix.
You also need to be examined to confirm or refute the conclusions of doctors from previous ultrasound examinations that showed pathologies.
General indications for all three trimesters:
- Bleeding, discharge.
- Stomach ache.
- A uterine size that is not appropriate for the current week is noticed during an examination by a leading gynecologist - then an ultrasound is necessary to exclude an undeveloped pregnancy
Possible consequences
In nine cases out of ten, such a cyst resolves on its own long before the baby is born. Usually it is not detected at the third planned ultrasound at 30–34 weeks. It does not have any effect on the physical or mental development of the newborn.
If the cyst persists after birth, the baby is examined, including with ultrasound, at 3, 6 and 12 months. Sometimes, if CSS is combined with other neurological disorders, a specialist prescribes drugs to the child to activate cerebral circulation and normalize the production of cerebrospinal fluid. This will help the cyst resolve without consequences for the baby.
Norms of fetal ultrasound indicators in the first trimester in the summary table
| Term | BPR | Yolk sac | Nasal bone | Heart rate | KTR | VP |
| 10 weeks | 14 mm | 4-6 mm, but not less than 2 | Yes, but not measured during this period | From 161 to 179 beats/min | From 41 mm | 1.5 to 2.2 mm |
| 11 weeks | 17 mm | 4-6 mm, begins to decrease | Yes, but not measured during this period | From 153 to 177 beats/min | 1.6 to 2.4 mm | |
| 12 weeks | Not less than 20 mm | Disappears | Not less than 3 mm | From 150 to 174 beats/min | up to 73 mm | 1.6 to 2.5 mm |
| 13 weeks | Approximately 26mm | Disappears | Not less than 3 mm | From 141 to 171 beats/min | 1.7 to 2.7 mm |
Second trimester
The ultrasound report from the 20th to the 24th week contains the following abbreviations:
- BPR – biparietal size of the fetal head;
- LZR – fronto-occipital size;
- BPR/LZR – cephalic index;
- AB – abdominal circumference;
- RS – heart size;
- DG – tibia length;
- DP – shoulder length;
- DB – thigh length;
- OG – head circumference;
- s/b or heart rate - heartbeat;
- IUGR – intrauterine growth restriction;
- DgRK – chest diameter;
- AFI - amniotic fluid index - an indicator of the amount of amniotic fluid;
- ICI - isthmic-cervical insufficiency - the cervix with this pathology is not long enough for full gestation.
Prevention measures
Since the reasons for the formation of CSS are not known for certain, and such a cyst itself is not considered a pathology, there are no specific preventive measures. A woman is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and nutritiously, walk in the fresh air, do gymnastics for pregnant women and do breathing exercises, and take complex vitamin preparations as prescribed by a doctor.
Particular attention should be paid to protection against all kinds of infections. You should not visit crowded places, especially during the seasonal rise in the incidence of ARVI and influenza. In intimate life, it makes sense to use a condom.
Norms of fetal ultrasound indicators in the third trimester in the summary table
| Duration, weeks | BPR | LZR | OG | coolant | DG | DB | DP | Height | Weight | Placenta thickness | Placenta maturity |
| 30 | From 71 to 85 mm | From 89 to 105 mm | From 265 to 305 mm | From 238 to 290 mm | From 49 to 57 mm | From 52 to 62 mm | From 49 to 57 mm | 270 mm | 1400 g | 13.6 to 28.6 mm | 1st degree |
| 31 | From 73 to 87 mm | From 93 to 109 mm | From 273 to 315 mm | From 247 to 301 mm | From 51 to 59 mm | From 54 to 64 mm | 50 to 60 mm | Up to 390 mm | 1500-1600 g | 17.4 to 29.7 mm | 1st degree |
| 32 | From 75 to 89 mm | From 95 to 113 mm | From 283 to 325 mm | From 258 to 314 mm | From 52 to 60 mm | From 56 to 66 mm | From 52 to 62 mm | Up to 400 mm | Up to 1700 g | From 18.1 to 30.7 mm | 1st degree |
| 33 | From 77 to 91 mm | From 98 to 116 mm | From 289 to 333 mm | From 267 to 325 mm | From 54 to 62 mm | From 58 to 68 mm | From 53 to 63 mm | Up to 430 mm | Up to 1800 g | 18.8 to 31.8 mm | 1st degree |
| 34 | From 79 to 93 mm | From 101 to 119 mm | From 295 to 339 mm | From 276 to 336 mm | From 55 to 63 mm | 60 to 70 mm | From 55 to 65 mm | 430-450 mm | Up to 2400 g | 19.6 to 32.9 mm | 1-2 degree |
Characteristics
The formation is an isolated cavity filled with clear liquid.
Structure Features:
- They are small in size and tend to dissolve on their own.
- More often they are localized closer to the caudal part of the choroidal glomus.
- It has clear, even contours.
- Does not show any upward trend.
- The presence of signs of malignancy is not typical. Due to the location, it should be differentiated from choroid carcinoma and choroid papilloma.
- There are no clinically significant symptoms. The exception is the development of occlusive hydrocephalus (disruption of the normal outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and its accumulation in the head). It is extremely rare.
- It is regarded as a stigma of dysembryogenesis (developmental defect). These newborns are at high risk of having chromosomal abnormalities (trisomy 18 - Edwards syndrome).
- The main diagnostic method is ultrasound. Discovered as an incidental finding during screening.
- The pathology does not have serious consequences and does not affect the life and health of the child, therefore it does not require treatment.
- The prognosis is favorable.
Where to get an expert fetal ultrasound in St. Petersburg
You can undergo such an examination only in modern clinics with high-tech equipment. Such a specialized medical center in St. Petersburg is located on Zanevsky Prospekt, 10. The latest device with Doppler, 3D, 4D, etc. functions is installed here. The examination is carried out by doctors of the highest category with extensive experience in maternity hospitals, antenatal clinics and gynecological clinics. The cost of the examination depends on the period and starts from 1000 rubles.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter