Coronavirus infection leaves many unwanted side effects. People who have had this terrible disease are unable to recover quickly. They constantly feel weak and tired. They have headaches and numbness in their upper and lower limbs. Memory fails, speech is impaired. As a result, a stroke or other disorders related to brain function may develop.
Free consultation right now!
Online consultation with a specialist on your issue!
License number: LO-77-01-019036
All the symptoms described indicate serious changes in the person’s condition. Leading neurologists have studied the effects of this disease on the brain and central nervous system. Coronavirus has a detrimental effect on the most important cells of these systems of the human body. Namely, astrocytes and microglia are affected. The reason is that the brain is unable to recognize the infection because SARS-CoV-2 is very similar to these cells.
Varieties, reasons
Brain edema occurs:
- vasogenic;
- cytotoxic;
- interstitial;
- osmotic.
The signs of cerebral edema depend on the type of developing pathology.
Causes of disease progression:
- Vasogenic edema occurs due to increased cerebral vascular permeability.
- Cytotoxic is the “swelling” of brain cells due to an increase in the amount of fluid inside them.
- Interstitial edema develops when there is increased pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles of the brain.
- Osmotic edema - with an increase in the osmolarity of brain tissue.
The most common reasons that cause brain swelling are: brain injury and disruption of its tissues in various pathologies.
Brain edema most often occurs in the following pathological conditions of a traumatic nature:
- brain contusion;
- fracture of the base of the skull;
- intracerebral hematoma;
- subdural hematoma. The prognosis of surgery for cerebral edema depends on its size.
The described pathology develops against the background of such organic brain lesions:
- ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke;
- hemorrhage under the arachnoid membrane;
- tumors;
- infectious diseases - encephalitis (inflammation of brain tissue) and meningitis (inflammation of the meninges).
Extracranial causes of cerebral edema can result from:
- Quincke's edema is a severe allergic reaction of the body;
- infectious diseases - scarlet fever, measles, mumps;
- diabetes;
- liver failure;
- alcoholism.
On our website Dobrobut.com you will find more information about the causes of cerebral edema in a newborn child, the development of pathology in the elderly and other facts.
Description of the disease
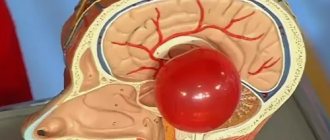
The pathological process is characterized by the rapid accumulation of fluid in the brain tissue, leading to a rapid deterioration of the patient's condition. If this process is not diagnosed and stopped in time, the disease leads to complete dysfunction of the cerebral areas and death of the person. Swelling of intracranial structures was described back in the mid-19th century by scientist N.I. Pirogov. During the study of this anomaly, it was determined that swelling of cerebral fibers is not an independent disease. The accumulation of a liquid substance inside the skull is provoked by other ailments and is their critical complication.
Since the cranium is a limited space, the expanding internal tissues do not have the opportunity to expand indefinitely. With uncontrolled swelling, compression of areas of the organ, displacement, and strong compression follows. Multiple diseases from various areas of medical practice lead to this result. Both neurologists and traumatologists, oncologists, neurosurgeons, neonatologists and toxicologists can encounter such an anomaly.
In scientific theory, there are four described types of cervical swelling:
- Vasogenic. Is the most common type. The nature of edema is the gradual transition of fluid from the vascular network into the internal white matter. The cause of fluid metabolism disorders may be a tumor neoplasm, a focus of neuronal death, ischemic damage, or surgical procedures.
- Cytotoxic. It develops as a result of the loss of the protective function of glia - sheath cells and connective fibers. The main areas with affected cells are formed in the gray matter of the brain. The main causes of dysfunction of the glial membranes can be past infections, prolonged oxygen starvation, the effects of toxins, severe poisoning, stroke, etc.
- Osmotic. With this type of edema, fluid forms in the cerebral tissues independently without disrupting the functions of the fibers of the neural membranes. The provoking factor is metabolic imbalance and impaired hemodialysis.
- Interstitial. It is formed mainly around the ventricles of the brain as a result of excessive penetration of the liquor substance through its outer membranes.
Signs of cerebral edema
Symptoms depend on how quickly brain swelling develops.
Signs of acute cerebral edema:
- disturbance of consciousness - from slight stupor to a state of coma with cerebral edema;
- convulsions – occur as swelling progresses;
- muscle atony – develops after seizures;
- membrane symptoms.
Gradual increase in edema – additional symptoms of cerebral edema in adults:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting that does not bring relief;
- movement disorders;
- visual and speech disorders;
- hallucinatory syndrome.
Signs indicating critical development of the condition:
- paradoxical breathing (deep breaths with long gaps between them);
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- unstable pulse;
- increase in body temperature above 40 degrees Celsius.
The appearance of such signs indicates compression of the brain stem, which leads to death.
Contraindications to the use of Dexamethasone
- For short-term use for “life-saving” indications, the only contraindication is hypersensitivity; systemic mycosis;
- simultaneous use of live and attenuated vaccines with immunosuppressive doses of the drug;
- sucrose intolerance, isomaltase/sucrase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption; breastfeeding period; children up to 3 years old.
Carefully:
Parasitic and infectious diseases of a viral, fungal or bacterial nature (currently or recently suffered, including recent contact with a patient) –
- herpes simplex, herpes zoster (viremic phase), chicken pox, measles;
- amebiasis, strongyloidiasis (established or suspected);
- active and latent tuberculosis.
Diagnostics
Cerebral edema should be suspected if impairment of consciousness increases, meningeal symptoms are observed, and the patient's condition worsens.
Instrumental methods that are used to confirm the diagnosis of cerebral edema:
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This is an important diagnostic method - you can detect swelling of the spinal cord on MRI, and not just the brain.
Of the laboratory research methods, general and biochemical blood tests are important.
It is dangerous to perform a lumbar puncture for diagnostic purposes - displacement of brain structures and jamming of the brain stem in the occipital foramen of the skull may occur.
Composition and release form
Tablets - 1 tablet:
- Active ingredient: Dexamethasone – 0.0005 g
- Excipients: potato starch – 0.0340 g; sucrose (sugar) – 0.1140 g; stearic acid – 0.0015 g.
Tablets weighing 0.15 g.
Tablets 0.5 mg.
10, 14 tablets in a blister pack made of polyvinyl chloride film and aluminum foil.
5, 10 blister packs of 10 tablets each or 4 blister packs of 14 tablets each with instructions for use in a cardboard pack.
Treatment of cerebral edema
The main principles of treatment for cerebral edema are:
- dehydration;
- improvement of metabolic processes in the brain;
- etiotropic treatment;
- symptomatic therapy.
What consequences of cerebral edema during stroke and other pathologies will accompany the patient depends on the timeliness and competence of the therapy.
Dehydration therapy
Its purpose is to remove excess fluid from brain tissue. Based on the appointments:
- osmotic diuretics (diuretics);
- magnesium sulfate and glucose solution - they enhance the effect of diuretics and also improve brain nutrition;
- L-lysine escinate - the drug is not a diuretic, but removes fluid.
Improving brain processes
For this purpose the following are appointed:
- metabolic drugs;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- oxygen therapy.
Etiotropic therapy
When treating cerebral edema, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of the development of the pathology and “destroy” the mechanism of edema formation. Destination:
- antibiotics;
- removal of tumors and hematomas;
- shunt operations, after which cerebral blood supply improves
This treatment is carried out after the patient’s condition has stabilized.
Symptomatic therapy
It is aimed at eliminating cramps, vomiting, pain, and so on. In addition to conservative therapy, surgical treatment can be used:
- decompression craniotomy;
- Ventricular drainage.
How to deal with the disease?
At the first suspicion of illness, the patient is immediately hospitalized. The final diagnosis and research manipulations are carried out only in a hospital or intensive care unit. The main areas of therapeutic influence are:
- Removing excess fluid.
- Normalization of metabolism.
- Identification and elimination of the root cause of edema.
- Relief from associated symptoms.
To remove excess fluid, diuretics are prescribed, which are initially administered intravenously. To normalize metabolic processes, oxygen therapy is performed. The local temperature regime in the head area is restored. If the development of the disease occurred as a result of toxic exposure, detoxification measures are prescribed. In case of infection, antibiotics, antiviral, and antifungal agents are introduced into treatment. If cysts or tumors are detected, they are surgically removed and hematomas are eliminated.
When the patient's condition is stabilized, symptomatic treatment is carried out, antiemetic pharmaceuticals, analgesics, anticonvulsants, and antispasmodics are prescribed. To urgently reduce intracranial pressure, a decision may be made to perform surgical trepanation.
Dexamethasone dosage
Orally, in individually selected doses, the amount of which is determined by the type of disease, the degree of its activity and the nature of the patient’s response.
The average daily dose is 0.75-9 mg. In severe cases, large doses can be used, divided into 3-4 doses. The maximum daily dose is usually 15 mg. After achieving a therapeutic effect, the dose is gradually reduced (usually by 0.5 mg every 3 days) to a maintenance dose of 2-4.5 mg/day. The minimum effective dose is 0.5-1 mg/day.
Children (depending on age) are prescribed 83.3-333.3 mcg/kg or 2.5-10 mg/sq.m/day in 3-4 doses.
The duration of dexamethasone use depends on the nature of the pathological process and the effectiveness of treatment and ranges from several days to several months or more. Treatment is stopped gradually (at the end several injections of corticotropin are prescribed).
For bronchial asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis – 1.5-3 mg/day; for systemic lupus erythematosus – 2-4.5 mg/day; for oncohematological diseases – 7.5-10 mg.
For the treatment of acute allergic diseases, it is advisable to combine parenteral and oral administration: 1 day – 4-8 mg parenterally; Day 2 – orally, 4 mg 3 times a day; 3, 4 days – orally, 4 mg 2 times a day; 5, 6 days – 4 mg/day, orally; Day 7 – drug withdrawal.
Dexamethasone test (Liddle test). It is carried out in the form of small and large tests. For a small test, dexamethasone is given to the patient 0.5 mg every 6 hours during the day (that is, at 8 a.m., 2 p.m., 8 p.m., and 2 a.m.). Urine for the determination of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids or free cortisol is collected from 8 a.m. to 8 a.m. 2 days before the administration of dexamethasone and also 2 days at the same time intervals after taking the indicated doses of dexamethasone. These doses of dexamethasone inhibit the formation of corticosteroids in almost all apparently healthy individuals. 6 hours after the last dose of dexamethasone, plasma cortisol levels are below 135-138 nmol/l (less than 4.5-5 mcg/100 ml). Reducing the excretion of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids below 3 mg/day, and free cortisol below 54-55 nmol/day (below 19-20 mcg/day) excludes hyperfunction of the adrenal cortex. In persons suffering from Cushing's disease or syndrome, no changes in the secretion of corticosteroids are observed during a small test.
When conducting a large test, dexamethasone is prescribed 2 mg every 6 hours for 2 days (that is, 8 mg dexamethasone per day). Urine is also collected to determine 17-hydroxycorticosteroids or free cortisol (if necessary, determine free cortisol in plasma). With Itsenko-Cushing's disease, there is a decrease in the excretion of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids or free cortisol by 50% or more, while with adrenal tumors or adrenocorticotropic-ectopic (or corticoliberin-ectopic) syndrome, the excretion of corticosteroids does not change. In some patients with adrenocorticotropic-ectopic syndrome, a decrease in the excretion of corticosteroids is not detected even after taking dexamethasone at a dose of 32 mg/day.
Use of Dexamethasone during pregnancy and children
Dexamethasone crosses the placenta (can reach high concentrations in the fetus) and into breast milk. During pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, or in women planning pregnancy, the use of Dexamethasone is indicated only if the expected therapeutic effect outweighs the risk of negative effects on the mother or fetus. GCS should be prescribed during pregnancy only for absolute indications. With long-term therapy during pregnancy, the possibility of fetal damage cannot be excluded. If used in the third trimester of pregnancy, there is a risk of atrophy of the adrenal cortex in the fetus, which may require replacement therapy in the newborn. If it is necessary to carry out treatment with the drug during breastfeeding, breastfeeding should be stopped.