Laboratory and clinical testing of diastase in the blood is prescribed at the Sensitive LCC in Yeysk, mainly for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diastase is a pancreatic enzyme involved in digestion. This enzyme enters the duodenum as part of pancreatic juice, and diastase is broken down into complex carbohydrates in the intestine.
If the pancreas is healthy, the concentration of diastase is always at a small but constant level. But if there are changes in the functioning of the organ, then the level of diastase also changes.
What is diastasis?
The enzyme alpha-amylase or diastase is produced by the pancreas, takes an active part in the functioning of the digestive organs and is involved in food processing. Amylase is part of pancreatic juice.
The process of carbohydrate breakdown occurs in the duodenum. Diastasis is within standard limits in the healthy body of any person.
If the main organ of the endocrine system does not have pathologies, then the concentration of amylase is at a constant level. Changes in diastase saturation indicate disorders in the body. An increased level of amylase is a consequence of pathology of the endocrine and digestive organs.
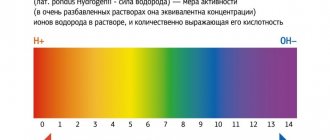
Urine reaction (pH)
The pH of urine in a healthy person on a mixed diet is acidic or slightly acidic.
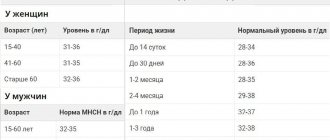
| Children under 1 month | 5,4 — 5,9 |
| Children 2 – 12 months | 6,9 — 7,8 |
| Children 1 year - 6 years | 5,0 — 7,0 |
| Children 7 - 14 years old | 4,7 — 7,5 |
| Children 15 - 18 years old | 4,7 — 7,5 |
| Men | 5,3 — 6,5 |
| Women | 5,3 — 6,5 |
Interpretation
The urine reaction may vary depending on the nature of the food. The predominance of animal proteins in the diet leads to a sharply acidic reaction; with a vegetable diet, the urine reaction is alkaline.
- An acidic urine reaction is observed with fevers of various origins, diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation, fasting, and renal failure.
- An alkaline reaction of urine is characteristic of cystitis, pyelonephritis, significant hematuria, after vomiting, diarrhea, and drinking alkaline mineral water.
Normal for adults and children
To measure the content of this enzyme, a coefficient per liter of blood is used.
The enzyme content index changes during different life periods. And the patient’s age is of great importance for the diagnostic result.
The standard values for the diastase enzyme in the male body and the standard levels for the enzyme in the female body are the same. The female body is resistant to pancreatic disorders.
Table of normative indicators of amylase in the blood during different life periods:
| age | norm in units/l |
| newborns up to 12 months | no more than 8 units/l |
| from one year to ten years | about 30 units/l |
| from ten years to eighteen years | no more than 40 units/l |
| adults up to 70 years old | up to 125 units/l |
| older than 70 years old | up to 160 nd/l |
In women, while carrying a child, the diastase index does not change and corresponds to the coefficient that was before pregnancy. An increase or decrease in the enzyme indicates that there may be pathologies in the digestive organs.
There is also a fluctuation in amylase, which is temporary and occurs after the operation. The density of the enzyme in the blood can change after constant overeating.
The indicator in children should be within the corridor of up to 40 units/l. If the numbers reach an index of 100 units/l, then we can confidently talk about pathology in the body.
Urine color
The color of urine normally ranges from light yellow to deep yellow and is due to the pigments it contains (urochrome A, urochrome B, uroethrin, uroresin, etc.).
Reference values:
| Children | Various shades of yellow |
| Men | Various shades of yellow |
| Women | Various shades of yellow |
Interpretation
The intensity of the color of urine depends on the amount of urine excreted and its specific gravity. Rich yellow urine is usually concentrated, excreted in small quantities and has a high specific gravity. Very light urine is slightly concentrated, has a low specific gravity and is excreted in large quantities.
Discoloration may be the result of a pathological process in the urinary system, the effects of dietary components, or medications taken.
How is a diastasis study performed?
To diagnose diastasis, only blood from a vein is needed.
In order for the test rate to be as accurate as possible, it is necessary to prepare for this procedure and follow the rules for donating blood for testing:
- Biological fluid is collected in the morning,
- The procedure takes place on an empty stomach,
- 5-7 calendar days before submitting biological fluid for analysis, it is advisable not to eat fatty foods, sour and smoked foods, pickled vegetables and sweets, and not to take medications,
- Do not smoke 4 hours before the procedure,
- Do not drink alcoholic or low-alcohol drinks for two days,
- If you are taking vital medications, inform your doctor.
The methodology of this study is not complicated: carbohydrates are added to the blood and the process of breaking down these carbohydrates by the enzyme amylase is monitored. The effectiveness of the enzyme is determined by the time of cleavage and is reflected in the blood test.
Specific gravity of urine (g/l)
In a healthy person, it can fluctuate over a fairly wide range throughout the day, which is associated with periodic food intake and loss of fluid through sweat and exhaled air.
| Children under 1 month | 1002-1020 |
| Children 2 – 12 months | 1002-1030 |
| Children 1 year - 6 years | 1002-1030 |
| Children 7 - 14 years old | 1001-1040 |
| Children 15 - 18 years old | 1001-1030 |
| Men | 1010-1025 |
| Women | 1010-1025 |
Interpretation
The specific gravity of urine depends on the amount of substances dissolved in it: urea, uric acid, creatinine, salts.
- A decrease in the specific gravity of urine (hyposthenuria) to 1005-1010 g/l indicates a decrease in the concentrating ability of the kidneys, an increase in the amount of urine excreted, and drinking plenty of fluids.
- An increase in the specific gravity of urine (hypersthenuria) of more than 1030 g/l is observed with a decrease in the amount of urine excreted, in patients with acute glomerulonephritis, systemic diseases, and cardiovascular failure; it may be associated with the appearance or increase of edema, large loss of fluid (vomiting, diarrhea ), toxicosis of pregnant women.
Reasons for increasing the diastase index
A mandatory biochemical blood test for amylase is necessary when diagnosing pancreatitis in the acute form of the disease, as well as chronic pancreatitis and at the time of relapse of the disease.
An elevated enzyme level indicates problems in the main organ of the endocrine system, as well as the digestive organs.
Reasons for elevated amylase levels in the blood:
- Pancreatitis is an acute form of inflammation of an organ or a chronic inflammatory process. During the period of inflammation, the function of the pancreas is disrupted, the outflow of pancreatic juice is difficult, which contributes to its accumulation in the organ. Because of this, its concentration increases,
- Oncological neoplasms in the endocrine organ . The secretion of the enzyme increases, which contributes to the accumulation of diastase in the blood and urine. If the neoplasm is localized in the organ itself, then the level of diastase will be maximum,
- Gallstones. When stones migrate into the bile ducts, difficulty occurs in the process of outflow of pancreatic juice and in this case, diastasis is increased,
- Renal failure in the acute form of the disease and in the chronic stage of the disease. The enzyme is excreted from the body with the assistance of the kidneys. Any deviation from the norm in the functioning of this organ leads to the accumulation of amylase in the body,
- Inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity peritonitis . Any inflammation negatively affects the functionality of internal organs. The pancreas suffers from inflammation in the peritoneum and disorders occur in it that provoke increased production of amylase,
- Hyperglycemia (diabetes mellitus) is a disease of the body that is directly related to disturbances in the carbohydrate metabolic process. With this pathology, not all amylase is consumed in the breakdown, a small part of it accumulates in the body and this causes an increase in its level,
- Mumps is an inflammatory process in the parotid gland, which is responsible for the production of saliva. Diastase is produced by the pancreas, and the salivary glands also take part in the process of its production. With mumps, an increase in diastase occurs.
Diastasis increases with pancreatic disease
For any diseases of the pancreas, the diastase coefficient will be increased. The results of a diagnostic study either confirm pancreatitis, or, according to tests, there is no inflammation in the pancreas.
How does a doctor determine the presence of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscle?
If any of the listed symptoms appear, as well as if there are predisposing factors such as recent pregnancy and childbirth or increased physical activity, you should consult a doctor for examination. You can’t delay your visit; it’s better to see a specialist for prevention than to wait until dangerous complications appear.
Many people do not know which doctor determines the presence of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles. You need to contact a surgeon. In most cases, an experienced specialist will be able to determine the pathology using only palpation examination.
For diagnosis, the patient lies on his back, slightly bends his knees and rests his feet on the surface. After this, the surgeon asks you to tighten your abdominal muscles. At the same time, you need to raise your shoulder blades and head. The doctor feels the abdomen, measures the width of the discrepancy, and determines the presence and stage of the pathology. In this case, pronounced diastasis of the third degree is noticeable even in a standing position.
In some cases, the study of the width of the white line is complicated by excess body weight. The doctor refers such patients for an ultrasound examination. This procedure is also prescribed if there is a suspicion of the development of complications: hernial protrusions, displacement of internal organs. In rare cases, radiography or computed tomography is necessary.
Reasons for reducing the diastase ratio
When checking diastase, low amylase concentrations are rarely diagnosed. If there is a decrease in amylase concentration, then this indicates quite serious and severe diseases of the body.
Such diseases require long-term and complex therapy with surgical intervention:
- Growth of pancreatic tumor cells . When diagnosed with oncology, the pancreas can produce quite a lot of amylase or completely stop the synthesis of this enzyme,
- Necrosis of endocrine organ tissue. When diagnosed with necrosis, the main organ of the endocrine system is not able to produce diastase,
- The disease mucoviscytosis is a congenital disease. The activity of the endocrine glands is disrupted. This disease develops in the lungs and digestive organs, but the pancreas is most affected.
In order to establish an accurate diagnosis of pancreatic disease, a blood test for diastasis is not enough. It is necessary to conduct additional examination of the digestive organs and endocrine system. Conduct diagnostics using ultrasound.
The totality of all diagnostic results can either confirm the pathology in these organs or reject the alleged diagnosis.
If diastase indicators are within normal limits or have minor changes, then we can say that there are no disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas and internal digestive organs.
Deviations of the index from the norm become a reason for additional examination and establishment of the correct diagnosis.
Transparency (turbidity)
Normal urine is clear. Cloudiness of urine can be the result of the presence of red blood cells, leukocytes, epithelium, bacteria, fat droplets, precipitation of salts, pH, mucus, urine storage temperature (low temperature promotes the precipitation of salts).
In cases where the urine is cloudy, you should find out whether it is immediately cloudy, or whether this cloudiness occurs some time after standing.
| Children | Full transparency |
| Men | Full transparency |
| Women | Full transparency |
Chemical examination of urine
Currently, chemical testing of urine is carried out on automatic analyzers using the dry chemistry method.
Chemical testing includes determination in urine:
- squirrel
- glucose
- ketone bodies
Protein in urine, normal protein in urine
Normal urine contains a very small amount of protein (less than 0.002 g/l), which is not detected by qualitative samples, so it is considered that there is no protein in the urine. The appearance of protein in the urine is called proteinuria.
| Children under 1 month | absent |
| Children 2 – 12 months | absent |
| Children 1 year - 6 years | absent |
| Children 7 - 14 years old | absent |
| Children 15 - 18 years old | absent |
| Men | < 0,1 |
| Women | < 0,1 |
Interpretation
Physiological proteinuria includes cases of temporary appearance of protein in the urine that are not associated with diseases. Such proteinuria is possible in healthy people after eating a large amount of protein-rich food, after severe physical stress, emotional experiences, and epileptic seizures.
Functional proteinuria associated with hemodynamic stress can occur in children with fever, emotional stress, congestive heart failure or hypertension, or after cooling.
Pathological proteinuria is divided into renal (prerenal) and extrarenal (postrenal):
- Extrarenal proteinuria is caused by an admixture of protein secreted by the urinary tract and genitals; they are observed in cystitis, pyelitis, prostatitis, urethritis, vulvovaginitis. Such proteinuria rarely exceeds 1 g/l (except for cases of severe pyuria - detection of a large number of leukocytes in the urine).
- Renal proteinuria is most often associated with acute and chronic glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis, nephropathy in pregnancy, febrile conditions, severe chronic heart failure, renal amyloidosis, lipoid nephrosis, renal tuberculosis, hemorrhagic fevers, hemorrhagic vasculitis, hypertension.
False-positive results when using test strips can be caused by severe hematuria, increased density (more than 1.025) and pH (above 8.0) of urine.
Determination of glucose (sugar). Normal level of glucose in urine.
Also, urine normally contains traces of glucose not exceeding 0.02%, which, like protein, is not detected by ordinary qualitative tests.
| Children under 1 month | absent |
| Children 2 – 12 months | absent |
| Children 1 year - 6 years | absent |
| Children 7 - 14 years old | absent |
| Children 15 - 18 years old | absent |
| Men | 0 – 1,6 |
| Women | 0 – 1,6 |
Interpretation
The appearance of glucose in the urine (glucosuria) can be physiological and pathological.
- Physiological glucosuria is observed when eating large amounts of carbohydrates (alimentary glucosuria), after emotional stress (emotional glucosuria), after taking certain medications (caffeine, glucocorticoids), and in case of poisoning with morphine, chloroform, phosphorus.
- Pathological glucosuria can be of pancreatic origin (diabetes mellitus), thyroid (hyperthyroidism), pituitary (Ishchenko-Cushing syndrome), hepatic (bronze diabetes). To correctly assess glucosuria, it is necessary to determine the amount of sugar in daily urine, which is especially important in patients with diabetes.
Ketone bodies in urine
Ketone bodies (acetone, acetoacetic acid, (B-hydroxybutyric acid)) can sometimes be detected in the urine of a healthy person with a very small intake of carbohydrates and a large amount of fats and proteins.
| Children under 1 month | none |
| Children 2 – 12 months | none |
| Children 1 year - 6 years | none |
| Children 7 - 14 years old | none |
| Children 15 - 18 years old | none |
| Men | none |
| Women | none |
Interpretation
Ketone bodies appear in the urine during fasting, alcohol intoxication, diabetes mellitus, in children with vomiting and diarrhea, neuro-arthritic diathesis, as well as during severe infectious processes accompanied by a prolonged increase in temperature.
How can diastasis be treated?
As we said above, diastasis is not a disease, rather a postpartum condition leading to an aesthetic and functional defect of the anterior abdominal wall. Accordingly, we prefer to replace “treatment” with “correction.”
A properly selected set of exercises can often correct external manifestations. We must remember that not all exercises can be performed with diastasis. All types of exercises that can contribute to an increase in diastasis are prohibited - these are all basic exercises with weights (deadlifts, squats), many exercises for the abdominal muscles - crunches, hanging leg raises, etc. The classic plank is also not recommended for patients with diastasis.
What exercises do we recommend for diastasis? Anything that strengthens the “deep core muscles”: side plank, abdominal tucks, cat exercises, Kegel exercises.
They cannot reduce the width of the linea alba (we remember that this is not a muscle, but connective tissue that cannot be “pumped up”), but can often improve the appearance of the abdomen and the quality of life of its owner, as shown by a recent study by Thabet and Alshehri, although the level The evidence for this thesis is low. However, we recommend a training program of at least 6 months before considering diastasis surgery.
NB! This does not apply to situations where diastasis is combined with hernias - the umbilical or white line. It is impossible to eliminate hernias with physical exercises; we immediately move on to the surgical treatment option (here, namely treatment).