Hypertension
You are experiencing increased blood pressure. Arterial hypertension is a syndrome of increased blood pressure (BP) in hypertension and symptomatic arterial hypertension .
Depending on the etiology, arterial hypertension is divided into two groups:
1. Primary (hypertension).
2. Secondary (symptomatic arterial hypertension).
Hypertonic disease
– a chronic disease of the cardiovascular system, the leading manifestation of which is the syndrome of high blood pressure in the absence of a connection with diseases that cause symptomatic arterial hypertension.
Secondary (symptomatic) arterial hypertension
– increased blood pressure levels due to the manifestation of a specific disease (kidney disease, thyroid disease, pheochromocytoma, etc.).
Important to remember
that high blood pressure does not return to normal on its own and without treatment, high blood pressure leads to serious complications such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Currently, blood pressure levels can be successfully controlled using non-drug and medicinal means. If you are diagnosed with high blood pressure, it is important to immediately understand that a large proportion of successful treatment depends not only on the doctor and medications, but also on your own attitude towards the disease and strict adherence to recommendations. Increased blood pressure is caused by a number of factors closely related to lifestyle and habits: unhealthy diet, smoking, lack of physical activity, psycho-emotional stress, etc. As a result of medical monitoring, specific risk factors for increased blood pressure are clarified, as well as the risk of complications and the need to fully follow the prescribed recommendations .
The main areas of prevention that help normalize blood pressure levels:
1. Regular self-monitoring of blood pressure levels by patients.
2. Non-drug methods of prevention.
3. Antihypertensive therapy, which is prescribed and adjusted only by a doctor.
- Self-monitoring of blood pressure levels by patients
To assess the effectiveness of preventive and therapeutic measures, self-measurement of blood pressure levels by the patient at home is of great importance. The reliability of blood pressure self-monitoring results depends on patient training in the correct measurement technique and the use of devices that meet international accuracy standards.
Regular self-monitoring of blood pressure levels promotes the patient's active participation in controlled treatment of hypertension, increases his adherence to preventive measures and therapy, and expands awareness of his health status.
Blood pressure levels should be measured twice a day - morning and evening - in a sitting position after resting for 5 minutes. The morning measurement is carried out within an hour after waking up (before breakfast), the evening measurement - before dinner or at least 2 hours after dinner.
In patients with frequently recurring hypertensive crises, in addition to routine measurements, additional monitoring of blood pressure levels is necessary during periods of deterioration in health. Such episodes, as well as the results of routine measurements, should be recorded by the patient in a diary.
2. Non-drug prevention methods that help normalize blood pressure
2.1.Smoking cessation. Under the influence of nicotine, the heart rate increases, vasospasm occurs, and as a result, blood pressure increases, which significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular complications (stroke, myocardial infarction, etc.).
2.2. Reducing table salt consumption. You should limit your consumption of table salt as much as possible - to 5 grams per day or less. Salt retains fluid in the body and weakens the effectiveness of all antihypertensive drugs.
2.3.Reduction of excess body weight.
Weight loss is accompanied by a decrease in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels.
2.4. Increase physical activity.
Increased physical activity has a positive effect on blood pressure levels.
Even a little physical activity is better than no physical activity at all. Fast walking, aerobic exercise, and swimming, when performed regularly, can reduce high blood pressure.
For this purpose, 3-4 classes per week at an energetic pace for 30-45 minutes are enough. 2.5. Reduce or stop drinking alcohol.
You need to limit, and if possible completely stop, alcohol consumption. Alcohol causes an increase in blood pressure both during chronic use and during withdrawal syndrome, which is a risk factor for the development of complications of the disease.
2.6. Comprehensive diet modification.
A healthy diet based on increasing the consumption of vegetables and fruits, including fish and seafood, as well as limiting animal fats, helps lower blood pressure levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
2.7. Elimination of psycho-emotional stress.
Psychoemotional stress, which is typical for most patients with arterial hypertension, plays an important role in increasing blood pressure levels. In the conditions of the intense rhythm of modern life, reduction and, if possible, complete elimination of psycho-emotional stress on the basis of adequate psychological support, becomes an essential element in the prevention of hypertension and hypertensive crises.
Antihypertensive therapy
If the effect of non-drug methods of normalizing blood pressure is insufficient, drug antihypertensive therapy is indicated. With the help of your doctor, you need to select medications to maintain normal blood pressure levels and constantly take them in recommended doses. Remember that hypertension cannot be cured, so you cannot take breaks from taking medications or take them in “courses”!
The most important requirement for normalizing high blood pressure is regularly visiting your doctor. Most cases of hypertensive crises and cardiovascular complications develop against the background of unauthorized withdrawal of antihypertensive drugs. Medicines recommended by your doctor to normalize blood pressure should always be with you!
In some cases, an acute increase in blood pressure takes on a crisis course - a hypertensive crisis.
Hypertensive crisis -
This is a sudden, sharp rise in blood pressure, accompanied by a deterioration in health and the development of complications.
Unlike arterial hypertension, during a hypertensive crisis there is a sudden (from several minutes to several hours) increase in blood pressure, to individually high values, accompanied by clinical symptoms, requiring an immediate, controlled decrease in blood pressure to prevent damage to vital organs (heart, brain, kidneys).
The main symptoms of a hypertensive crisis:
● headaches of various types, dizziness, nausea, vomiting;
● blurred vision in the form of a veil or flickering “flies” before the eyes;
● heaviness or pain in the heart area;
● feeling of shortness of breath, chills, trembling, sweating, etc.
You must call an ambulance and do the following before it arrives:
● place the patient in a bed or chair so that the head is elevated;
● unbutton the collar and remove clothing that restricts the chest;
● open the window for fresh air;
● measure blood pressure.
You need to remember that you cannot sharply lower your blood pressure on your own! Relieving a hypertensive crisis involves a gradual decrease in pressure, otherwise organ ischemia may develop.
Further actions are determined by the emergency medical personnel!
Causes of high blood pressure can be:
- refusal to take antihypertensive drugs
- inappropriate use of medications for hypertension
- diseases of the thyroid gland, kidneys, adrenal glands
- heart diseases
- preeclampsia in pregnant women
- traumatic brain injuries of the head
- severe burns
- abuse of nicotine, alcohol
- psycho-emotional stress
- significant physical activity
- large meal
- changes in atmospheric pressure
Hypertensive crisis - first aid
As a rule, all cardiologists try to teach their patients suffering from hypertension the primary actions necessary at the onset of a hypertensive crisis.
However, many people themselves know how to cope with this dangerous condition and do not even seek medical help. Sometimes the development of a hypertensive crisis may be the first manifestation of the development of hypertension, which people were not aware of before.
So, what needs to be done as an emergency when a hypertensive crisis develops:
- It is important to move the patient to a sitting or horizontal position and ensure maximum peace and quiet.
- Be sure to provide fresh air by opening a window and freeing your neck.
- It is extremely important for the patient to breathe correctly. To this end, he is recommended to take several deep, slow breaths.
- Unfortunately, in this situation, an increased feeling of anxiety can only contribute to a further increase in blood pressure. To calm the patient, you can give him a tincture of Corvalol or Valerian or another sedative and sedative. Panic is a bad ally not only during a hypertensive crisis, but also in any other emergency situations.
- Place a cold towel or a heating pad with ice on the patient's forehead. Mustard plasters can be placed just above the feet and on the back of the head for fifteen to twenty minutes.
- If a crisis is triggered by switching from one antihypertensive drug to another, it is recommended to take a drug that lowers blood pressure. Also, if the patient experiences severe chest pain or severe shortness of breath, it is recommended to take half a tablet of nitroglycerin and, of course, call an ambulance.
While waiting for the medical team to arrive (if necessary), it is important to take one nitroglycerin tablet at intervals of at least ten minutes (you should not take more than three tablets at a time).
In this case, it is necessary to measure blood pressure every twenty minutes. If blood pressure, despite the measures taken, does not decrease, and the patient’s general condition noticeably worsens, it is necessary to urgently seek emergency medical help.
In some cases, the crisis will be stopped only by administering intravenous or intramuscular medications, which are prescribed by the doctor, based on the general condition of the patient. Sometimes, in the presence of complications of a crisis, urgent hospitalization is required.
Healthcare of Mogilev
Risk factors for developing arterial hypertension:
- men over 55 years old,
- women over 65 years old, men over 55 years old
- smoking, drinking alcohol
- cholesterol level (CH) more than 6.5 mmol/l,
- family history of early CVD (women under 65 years of age, men under 55 years of age).
- excess salt intake
- physical inactivity
- stress
- obesity
Method of measuring blood pressure:
- after a 5-minute rest, avoid eating, caffeine (tea, coffee) or smoking (if the patient smokes) for half an hour; after active physical or emotional stress, blood pressure can be measured no earlier than half an hour later;
- in a sitting position, in a comfortable position: the arm is placed freely on the table, supported by the back of the chair, the legs are relaxed and do not cross;
- exclude conversation while measuring blood pressure;
- in the presence of stable asymmetry in both arms (SBP/DBP >10/5 mm Hg), measurements should be taken on the arm with higher blood pressure numbers; in the absence of asymmetry, measurements should be taken on the non-working arm;
- air injection into the cuff should be fast, release should be slow (2 mm Hg per 1 second);
- You should perform at least 2 measurements with an interval of 1-2 minutes and evaluate the average value of the measurements obtained;
- use standard cuffs of three appropriate sizes, and the cuff must cover at least 80% of the patient’s shoulder circumference;
- the middle of the cuff should be located at the level of the heart (approximately at the level of the 4th intercostal space), the cuff should not be placed on the fabric of clothing, a distance the size of a finger should remain between the cuff and the surface of the shoulder, its lower edge should be 2 cm above the ulnar fossa;
- A record of the obtained blood pressure values should be made with an accuracy of 2 mm Hg. Art.
The most common errors leading to incorrect blood pressure measurements:
- using a cuff that does not fit the shoulder;
- little time for the patient to adapt to the conditions of the doctor’s office;
- high rate of pressure reduction in the cuff;
- lack of asymmetry control
The measurement should be carried out for 7 days - 2 times a day, morning and evening. Measurements should be taken before eating and taking antihypertensive medications. At least 2 measurements should be taken with an interval of 1-2 minutes and the average value of the obtained measurements should be assessed. The average value of blood pressure and heart rate is recorded by the patient in a diary, unless a memory function is provided in the device. It is not recommended to include the measurement results on the first day in subsequent medical analysis. An increase in blood pressure measured at home is diagnosed at a level above 135/85 mm Hg. Art. The blood pressure self-monitoring method can be used initially to select antihypertensive treatment and 7 days before a subsequent visit to the doctor to assess the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy.
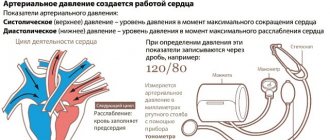
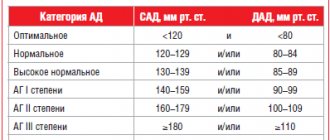
Blood pressure level classification:
| Blood pressure categories | GARDEN | DBP |
| Optimal blood pressure | < 120 | < 80 |
| Normal blood pressure | 120-129 | 80-84 |
| High normal blood pressure | 130-139 | 85-89 |
| AG 1st | 140-159 | 90-99 |
| AG 2st | 160-179 | 100-109 |
| AG 3st | ≥180 | ≥110 |
| Isolated systolic blood pressure | ≥140 | <90 |
Principles of treatment of arterial hypertension
The goal of treating a patient with arterial hypertension is to maximally reduce the overall risk of cardiovascular morbidity and death, which involves not only lowering blood pressure, but also correcting identified risk factors.
Principles of non-drug treatment of arterial hypertension Non-drug measures are aimed at lowering blood pressure, reducing the need for antihypertensive drugs and enhancing their effect, primary prevention of arterial hypertension and associated cardiovascular diseases at the population level.
A non-pharmacological BP lowering program should be recommended to all patients, regardless of the severity of hypertension and drug treatment.
It includes:
- smoking cessation;
- reduction of excess body weight;
- reducing the consumption of table salt;
- reducing alcohol consumption;
- comprehensive diet modification;
- increase in physical activity.
Drug therapy should be started according to the recommendations of the attending physician.
When drug therapy is discontinued on its own, blood pressure may increase, leading to hypertensive crises. A hypertensive crisis can also be triggered by:
- excessive consumption of salt and water;
- self-cancellation of medications;
- meteorological influence (the predominant number of crises occur in the spring and autumn months with a sharp temperature change, heat and extreme cold);
- stress
- colds, kidney and bladder diseases. If you do not take certain measures to prevent the disease, it can provoke a crisis.
- emotional or physical overload;
- weather changes, meteorological changes (“magnetic storms”);
- smoking;
- consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- large meals, especially at night;
- consumption of food or drinks containing substances that increase blood pressure (coffee, chocolate, cheese, caviar, etc.).
A hypertensive crisis is a sudden, sharp rise in blood pressure, accompanied by a deterioration in health and the development of complications.
Signs of a hypertensive crisis
| Symptom | Availability |
| Sharp headache in the back of the head | |
| Diffuse headache without clear localization | |
| Noise in the ears, head | |
| Nausea, vomiting | |
| Deterioration of vision: fog, grid, veil, floaters before the eyes | |
| Dyspnea | |
| Heaviness, pain in the heart area | |
| Anxiety, fear | |
| Trembling in the hands, throughout the body | |
| Dry mouth | |
| Facial hyperemia | |
| Frequent urination | |
| Depression, drowsiness | |
| Swelling of the face and fingers | |
| Palpitations, irregularities in the heart area | |
| Numbness of tongue, lips, face | |
| Goose bumps all over your body | |
| Loss of consciousness | |
| Symptoms that you have but are not reflected in the table |
The duration of the crisis varies: from several hours to several days. It is important not to get confused.
The rules of behavior and the implementation of first aid during a hypertensive crisis must be learned by all patients with arterial hypertension; moreover, their relatives should also know these rules in order to come to the rescue and provide first aid in difficult times.
Rules of behavior and self-help for patients with arterial hypertension during crises and complications:
Rule 1. If you suffer from hypertension, then you must always be prepared for the fact that your blood pressure may periodically increase.
Rule 2. Consult with a doctor how to reduce blood pressure at home, what medications to take in this case before the ambulance arrives.
Rule 3. Do not escalate the situation, because panic and fear lead to an even greater increase in pressure.
Self-help for hypertensive crisis at home:
- Stop physical activity.
- Sit or lie down with your head elevated, measure your blood pressure; You need to calm down and not panic. You can take valerian, motherwort.
- Restore your breathing - take a few deep breaths and exhales.
- When experiencing a hypertensive crisis for the first time in your life, be sure to call an ambulance. For the ambulance dispatcher, clearly formulate your complaints and give your blood pressure number.
- In case of repeated hypertensive crises, emergency care should be provided taking into account the existing experience in treating previous GCs.
- Regardless of the type of HA, you should use medications recommended by your attending physician as self-help.—
- Monitor the decrease in blood pressure after 30 minutes. A good effect is a reduction in blood pressure by 20-25%. from the initial blood pressure within 2 hours.
- If the expected effect is not achieved, you can repeat the medication.
- Control of blood pressure reduction should also be carried out after 30 minutes. If such a reduction in blood pressure has been achieved, then additional doses of blood pressure-lowering medications should not be taken. It is necessary to contact your local general practitioner (call a doctor at home or attend an appointment at the clinic) to correct antihypertensive therapy.
- If the blood pressure level does not decrease or, on the contrary, continues to increase, it is recommended to call an ambulance.
ATTENTION! It is imperative to call an ambulance in the following cases:
- first-time hypertensive crisis;
- the appearance of chest pain, severe shortness of breath, dizziness, weakness, interruptions in heart function, impaired movement of the limbs;
- lack of effect from the drug therapy.
Symptoms of arterial hypertension:
- intense headache
- dizziness
- nausea, vomiting
- visual impairment, transient blindness
- double vision, flashing spots before the eyes
- numbness of hands, face
- decreased pain sensitivity in the face, lips, tongue
- crawling sensation
- mild weakness in the distal arms
- convulsions
- pain in the heart area
- heartbeat
- feeling of interruptions
- dyspnea
- chills, tremor
- feeling of fear
- irritability
- sweating
- feeling hot
- thirst
June 26 marks the International Day against Drug Addiction and Illicit Drug Trafficking, which is of global significance. It was established in 1987 as an expression of the determination of the UN General Assembly to strengthen its activities and create a world society free of drug abuse. The basis for this decision was the recommendations of the International Conference on Combating Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking, which adopted an extensive action plan to combat drug addiction.
In 1998, a special session of the UN General Assembly was held, which set the goal of significantly reducing such a harmful phenomenon in the world as drug addiction by 2008. But the UN has released figures showing that more than 185 million people currently use drugs around the world. This represents 3% of all humanity and 12% of people aged 15 to 30 years. The number of people who inject drugs worldwide has exceeded 13 million. Every day the consequences of drug addiction are becoming more and more threatening in demographic terms. Minors and teenagers are becoming addicted to drugs, and the number of women using drugs is increasing.
Narcologists are especially concerned about this problem, since they have data that 3 years ago the average age of drug addicts was 16-17 years old, and now it has dropped to 13-14 years old. Over the past decade, the number of women taking narcotic and psychotropic drugs has increased sevenfold!
Without exaggeration, drug addiction can be called the most terrible phenomenon of our century. Every day more and more people are falling into its insidious network, trying to escape from problems and stress. But the price of such an “escape” turns out to be too high, and the results of the self-experiment for the most part turn out to be irreversible. Even a special course of treatment for drug addiction is not always able to free a person from this addiction. After several years without drugs, a former drug addict often relapses. And those sensations that seemed like salvation from real problems and failures become an endless nightmare and absolute emptiness. Therefore, initially choosing drugs as a means of escaping life’s problems is an unforgivable and disastrous decision for every person.
People around the world who care about the health of their nation are uniting in the fight against such a terrible phenomenon as drug addiction. That is why World Drug Abuse Day was established, reminding all humanity of this terrible disease.
The fight against drug addiction in Russia
In Russia, the phenomenon of drug addiction is relatively new. More recently, reminders of such means as drugs were found only in books about the civil war and post-war devastation, or in some foreign films.
In our country, the task of the Federal Service for Control of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (FSKN) includes identifying crimes and taking measures to combat drug addiction, and preventive work to reduce drug use in society. In Russia, under the slogans “NO to drugs!” There are numerous sports and recreational events, meetings with students, schoolchildren, teachers and parents.
After the collapse of the USSR, the level of drug crime in Russia and neighboring countries increased significantly. According to data from the Federal Drug Control Service, there are 6 million drug addicts in Russia; 1.8 million people are drug addicts; 350 thousand are registered in drug treatment clinics; The number of drug addicts in Russia has increased 9-fold over the past decade. From 900 thousand to 1 million 100 thousand drug addicts are teenagers and young people aged 11-24 years. Every year from 70 to 100 thousand Russians die from drugs. The problem of drug addiction is directly related to the increasing prevalence of infection caused by the human immunodeficiency virus. From 60% to 80% of HIV carriers became infected by injection, i.e. due to drug use. 25% of all crimes in the country are, in one way or another, related to drug addiction.
Drug addiction statistics in Russia
(UNODC World Drug Report June 22, 2017):
- the number of consumers of psychoactive substances (PAS) in Russia has exceeded 18 million;
- 5 million use them systematically;
- 30% of addicts take surfactants by injection;
- Russia is in 5th place among heroin consumers.
Drug addiction is the main problem of modern society
Unfortunately, drug addiction in our time is an incredibly profitable business. Numerous drug dealers do not disdain the opportunity to profit from someone else’s misfortune. It is known that the drug trade is concentrated in Asia, the countries of the Near and Middle East, and Latin America. Afghanistan is a global heroin supplier.
Currently, the situation has worsened significantly, and methods of combating drug addiction must necessarily include widespread dissemination of information about drugs, the emergence of painful dependence on drugs and the consequences of their use. This is the only way to protect the younger generation from this disaster.
It is young people who become victims of drug addiction to a greater extent. Drug addiction turns into a tragedy for both the young man and his family. But despite its seriousness, this problem is very delicate, and therefore requires a balanced approach.
Drug addiction leads to total personality damage and serious complications of physical health. Many experts in the field refer to drug addiction as a “biopsycho-socio-spiritual” disorder. That is, a drug addict gradually loses self-respect, loses his moral qualities and mental balance. Due to an abnormal psyche, he cannot communicate with family and friends, is unable to find a profession, and even loses the skills in the business that he had before his illness. Having become involved in a criminal environment, he brings nothing but misfortune to the people around him, and slowly but inevitably destroys his life.
Another dangerous feature of drug addiction is the irreversibility of this pathological condition. That is, some of the changes that the body has undergone due to the effects of drugs remain forever. If a drug addict who has managed to live without heroin for a long time decides to experience the “high” once, then he will have to go through the entire circle of drug hell. It is for this reason that doctors usually do not use the phrase “recovered drug addicts”; they say “inactive drug addicts” - that is, those who are not currently using drugs. It’s good if this “moment” lasts a lifetime. Unfortunately, for most drug addicts, mental disorders remain a lifelong diagnosis, although the consequences of drug addiction in the human psyche are compensated to some extent.
International Day Against Drug Abuse promotes a massive solution to such a serious problem of our time as drug addiction. This question should not leave any person on Earth indifferent. Only through joint efforts can positive results be achieved in solving the global problem of our day - drug addiction.