CT angiography of various vessels in St. Petersburg is becoming an increasingly popular appointment for neurologists, vascular surgeons, cardiologists and doctors of other specialties. Often, in order to examine the vessels, ultrasound or X-ray methods are used before CT angiography, but it is the angiography study that is the most informative and indicative, allowing one to accurately identify the cause of vascular disease and begin treatment as soon as possible.
Angiography
|
CT angiography: what is it?
Multislice computed tomography is a modern method of radiological diagnosis of the pathology of organs and their systems. During the study, several processes take place simultaneously:
- Forward movement of the table with the patient on it;
- Movement of the X-ray tube in a spiral around the subject being examined;
- Registration of an X-ray image by a sensor located on the opposite side and transferring it to a computer screen.
As a result, the doctor receives a series of layer-by-layer images of the examined area of the body, after which the information is processed by a computer and a two- or three-dimensional image is built. It often happens that after a standard study, contrast enhancement of the vessels of the pathological focus is necessary to determine the nature of its blood circulation - then CT angiography of the vessels appears in the diagnostic plan. This study is aimed at obtaining reliable data on the patency of blood vessels, the direction of their course and disturbances in blood flow.
The medical diagnostic center “Medicine of the Northern Capital” uses a modern multislice tomograph Siemens Somatom installed in 2016.
Types of angiography and purposes of the study
Angiography is based on the examination of blood vessels using X-rays and a contrast agent injected into the patient’s bloodstream, which is capable of blocking X-rays and thus enhancing the signal from the blood circulating in the vascular bed.
Depending on the organ that supplies blood to the vessel examined by angiography, it can be called cerebral, vertebral, superior and inferior cavagraphy in the study of the vena cava, celiacography in the study of the celiac trunk, aortography, etc.
Depending on the vascular imaging technique used, angiography can be:
- Classic X-ray;
- Digital subtraction;
- CT angiography;
- Magnetic resonance scanning.
Classic angiography
Classic X-ray contrast angiography, depending on the vascular area to be examined, is divided into:
- General is a type of angiography when you need to examine the entire vascular system or most of it;
- Selective - if you need to inspect the branches of the basin of a specific medium-sized vessel. To conduct selective angiography, a contrast agent is injected into the blood vessel that is planned to be examined;
- Superselective - this angiography is prescribed to study pathology in small vessels.
However, this type of vascular angiography is used quite rarely in modern medical practice. This is due to the need for hospitalization, the introduction of contrast into the puncture directly in the diagnostic area, the overlay of soft tissue shadows on the images of blood vessels, and the frequent development of complications. All these consequences of angiography in its classic version force doctors to choose three more modern varieties for diagnosing the vascular bed.
Digital subtraction
It differs from the classic one in that there is no overlay of shadows from soft tissues and organs, because The digital angiography processing method allows you to “remove” them from images. However, such angiography is an invasive procedure that requires mandatory hospitalization and observation by doctors for at least one day. After the angiography procedure, the patient is prohibited from getting out of bed, since iodine-containing contrast is injected through a catheter into the femoral artery, a reliable stop of bleeding from which requires several hours of immobility.
CT scan
For scanning, instead of a conventional X-ray machine, a multislice computed tomograph is used. With this type of angiography, a radiopaque contrast agent is injected into the cubital vein, like a regular injection. This significantly reduces the risk of adverse reactions associated with bleeding. After a successful angiography, the patient can immediately go about his business - no bed rest is required.
CT angiography examines vessels of almost any location, and its information content is comparable to the results of digital angiography. Therefore, in recent years the method has become increasingly popular.
Indications for prescribing angiography
Despite the significant information content when examining vessels of a particular location, strict indications are needed in order to perform CT angiography. All indications for angiography can be divided into:
- General, which determine the choice of research method;
- Particular ones, characteristic for the study of a certain vascular bed, which we will discuss below.
General indications for angiography include the need to:
- determining the exact location of the pathology;
- clarification of its nature: narrowing, blockage, compression of the vessel, aneurysm;
- calculating the effective lumen of the vessel;
- selection of the best treatment in this particular case: surgical or medicinal;
- assessing the effectiveness of the blood flow bypass.
Contraindications for angiography
Contraindications to manipulation are divided into relative and absolute.
However, if manipulation is necessary for health reasons, almost any contraindication can be circumvented. Limitations to diagnosis are associated with the presence of chronic or acute pathology, which may be aggravated by the administration of a contrast agent. Before angiography, you should tell your doctors if you know you have the following diseases or conditions:
- Acute or chronic kidney pathology;
- Increased thyroid function;
- Pregnancy at any stage;
- Weight more than 150 kg;
- Compounded allergic history;
- Pathology of blood clotting;
- Neurological diseases that do not allow a person to remain motionless while an angiography procedure is performed.
Ultrasound price. Sign up for a paid ultrasound in Moscow
The cost of ultrasound depends on the organ being examined and the method used. Usually it is in the range from one to four thousand rubles. On the Diagnostic and Treatment website you will find a detailed price list indicating the price of each service, you can make an appointment by phone and do a paid study at a convenient time.
Dopplerography Duplex ultrasound of the kidneys Ultrasound of the pelvic organs Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity Ultrasound of the breast Ultrasound of the soft tissues Ultrasound of the musculoskeletal system Ultrasound of the thyroid gland Ultrasound of the bladder Ultrasound of the mediastinum Ultrasound of the pancreas Ultrasound of the salivary glands Ultrasound during pregnancy
Ultrasound of the gallbladder Ultrasound of the lymph nodes Ultrasound of the uterus and fetus Ultrasound of the adrenal glands Ultrasound of the liver Ultrasound of the spleen Ultrasound of the prostate Transabdominal ultrasound Transvaginal ultrasound Transrectal ultrasound Ultrasound of the pleural cavity Ultrasound of the hip joints Ultrasound of the eyeball
How is vascular angiography done?
CT examination of blood vessels (angiography) is performed as prescribed by a doctor if there are indications, so the very first thing you need to do is visit your doctor. During this visit, the specialist will explain the purpose of the study and prescribe the necessary laboratory tests, including the mandatory determination of kidney function. If renal function cannot be assessed in advance, patients can have a rapid test done at our center.
If there is a concomitant pathology that may complicate diagnosis, consultation with specialists may be required before prescribing CTA. You should also tell your doctor if you are taking medications on a regular basis, because some medications must be stopped before the test.
Before the manipulation, you need to rest; if you have increased anxiety, you can take mild sedatives. You should have a light snack, but not overeat - the contrast is best tolerated after eating a light meal about a couple of hours before the procedure.
The study is carried out in a specialized equipment room in compliance with all rules of asepsis and antisepsis. The procedure takes place in several stages:
- The doctor or laboratory assistant instructs the patient, tells how the procedure will take place and answers questions;
- The patient is placed on the retractable tomograph table in a comfortable position; special cushions are placed under the head and arm to make lying comfortable throughout the entire scan;
- The healthcare worker treats the skin with an antiseptic drug in the area of vascular access, usually the elbow or forearm;
- The X-ray contrast agent is administered using a special device - an injector, which is synchronized with the operation of the tomograph and ensures that the contrast enters the bloodstream at a certain speed;
- The contrast is distributed along the vascular bed and a series of images is simultaneously taken;
- Once completed, the laboratory assistant helps the patient stand up and clarifies how long it will take to prepare the results.
Due to the fact that contrast is injected into the cubital vein, the way carotid artery angiography is done is no different from CT angiography of cerebral or limb vessels. Angiography is usually not accompanied by any unpleasant sensations and no more than 30 minutes pass from the start of the introductory briefing to the end of the scan.
If the examination is planned for a nursing woman, then on the eve of the examination it is necessary to express a sufficient amount of milk, because it is impossible to feed the child after a computed tomography scan for 2 days. You will need to pump at least twice after the procedure.
Features of the study of vessels of various locations
When prescribing examinations of vessels of various locations, there are some nuances that you should be aware of.
Examination of the vessels of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis
Indications for CT angiography of abdominal and pelvic vessels
- Anomalies in the development of blood vessels and organs;
- Neoplasm of vascular origin;
- Arterial hypertension presumably of renal origin;
- Signs of vascular obstruction.
When examining the renal artery, excretory urography is simultaneously performed, through which the functional abilities of the kidneys are assessed.
To whom is it assigned?
Other arteries in the body already have atherosclerosis
If the patient has previously been diagnosed with atherosclerosis, for example, of the abdominal region, renal arteries, upper extremities, experts recommend examining the lower extremities for the same pathology. The fact is that atherosclerosis is a disease that can affect the entire body. It is important to detect it in time and assess the degree of development.
Pain occurs in the calf muscles
Pain in the calf muscles (sometimes turning into cramps) causes serious discomfort to a person. They interfere with normal walking, do not allow you to endure long, intense physical activity, make it difficult to climb stairs, and even at rest constantly remind you of yourself. Often the cause of pain in the calf muscles is a violation of hemodynamics in the vessels of the legs, and pathologies such as atherosclerosis, thrombophlebitis, varicose veins, ultrasound scanning will allow us to find out for sure.
Pain occurs with exertion and walking short distances
When a person begins to feel pain in his legs after just 10-15 minutes of walking, and intense exercise becomes completely beyond his strength (in terms of walking or running), an ultrasound with Doppler will help you figure out what exactly is the cause of the problem. If it is atherosclerosis or venous stagnation (varicose veins), an ultrasound scan will show a disturbance in the speed of blood flow and indicate those segments where patency is impaired. At the same time, pain when walking can be caused by completely different reasons: osteomyelitis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteochondrosis, that is, diseases not related to blood flow. In such cases , ultrasound examination of the vessels of the lower extremities
allows you to exclude those diagnoses that are associated with hemodynamic disorders and prescribe other specific studies (for example, X-rays, MRI, CT, and so on).
Feet turn blue and cold or red and swollen
Swelling of the legs, their redness, blueness or the effect of “cold legs” are symptoms that may indicate the presence of vascular pathologies of the lower extremities. Such pathologies are atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular inflammation.
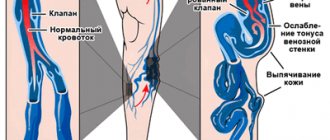
Vessel nodes are visible on the surface and varicose veins appear
When varicose veins enter the active stage of development, they become visible to the naked eye. Veins appear on the legs (most often under the knee). Seals and nodes may be visible on the veins. Ultrasound examination and Dopplerography of the veins of the lower extremities in such cases can be used both for the primary diagnosis of pathology and for planning surgical intervention.
Angiography of coronary vessels
This is a method for assessing blood flow in the coronary vessels, or coronary angiography. Angiography in this case allows you to assess the patency of the arteries that supply the heart. The positive aspect is the possibility of performing diagnostics without hospitalization of the patient and the low invasiveness of the procedure. Angiography of the coronary vessels is possible using computed tomographs that perform 64 slices or more. Indications for CT coronary angiography:
- IHD;
- Various types of arrhythmia;
- Preparation for AV ablation or interventional treatment for additional pathways of electrical impulses in the myocardium;
- Significant disturbance of the electrolyte composition of the blood;
- Malignant arterial hypertension;
- Suspicion of endothelial dysfunction.
When is routine Doppler sonography necessary?
Doppler of both extra- and intracranial arteries and veins should be performed at least once a year as a routine study (even before the appearance of any complaints):
- all women over 45 years old
- all men over 40 years old
- those who have close relatives suffering from hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease
- for diabetes
- smoking
- antiphospholipid syndrome
- for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
- metabolic syndrome
- arterial hypertension
- if you have had a stroke or transient cerebrovascular accident
- if a person suffers from rhythm disturbances (the likelihood of cerebral thromboembolism with subsequent stroke is increased)
- increased levels of cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoproteins in the blood (signs of atherosclerosis)
- had surgery on the spinal cord or brain
- before planned heart surgery.
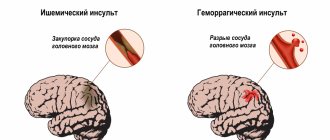
Angiography of the arteries of the neck and brain
Two related vascular studies are related by the fact that the carotid (localized in the neck) and vertebral arteries are the main ones for the blood supply to the brain, so the indications for their examination are similar:
- Headache that persists for a long time;
- Dizziness of unknown etiology;
- Severe causeless drowsiness;
- Frequent or prolonged fainting;
- Traumatic injuries to the neck and skull;
- Presence of vascular pathology in the past.
Decoding the results
Indicators for deciphering ultrasonography:
- systole size;
- diastolic blood flow velocity;
- the ratio of the above indicators;
- resistivity index.
Standards for Doppler ultrasound results for pregnant women:
| Pregnancy time (weeks) | Systole-diastolic ratio | Resistance index |
| 12-13 | 2-3,5 | 0,52-0,71 |
| 14-16 | 1,9-3,1 | 0,48-0,68 |
| 17-19 | 1,7-2,6 | 0,44-0,62 |
| 20-24 | 1,6-2,5 | 0,41-0,61 |
| 25-31 | 1,7-2,4 | 0,4-0,58 |
| 32-37 | 1,6-2,3 | 0,35-0,58 |
| 38-40 | 1,4-2,1 | 0,32-0,55 |
Norms of Doppler ultrasound indicators:
| Index | Group | Norm |
| Vessel diameter | vertebral artery | 3.5 mm |
| carotid artery | 5.5 mm | |
| internal carotid artery | 4.6 mm | |
| external carotid artery | 3.7 mm | |
| Blood flow speed | young | 0,663-0,71 |
| elderly | 0,685-0,73 |
Pathologies:
| Index | Stages of development |
| Narrowing of the lumen of the vessel |
|
| Artery deformation |
|
| Aortic change |
|
| Vascular diseases |
|
Only a specialist in this field can accurately decipher the results of an ultrasound scan.