Call the clinic +7 928 828 4001
Prices for services
| Service | Price |
| Phlebologist consultation | 1350* ք |
| Ultrasound (duplex) of the veins of the lower (upper) extremities | 1900 ք |
| Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the lower (upper) extremities | 3800 ք |
| Ultrasound (duplex) of the arteries of the lower extremities | 1900 ք |
| Ultrasound (duplex) of extracranial brachiocephalic arteries | 1900 ք |
| Ultrasound (duplex) of the arteries of the upper extremities | 1900 ք |
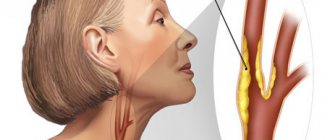
Using this method, blood supply disorders in the brain and neck vessels are determined. The bracheocephalic arteries consist of vessels responsible for supplying blood to the head, brain, shoulders and arms. The aorta is the largest vessel in the body. Large arteries branch off from it. On the right is the brachiocephalic or bracheocephalic trunk. It divides into the carotid and subclavian arteries. And they are already divided into small vessels. On the left are the carotid and subclavian arteries. They extend directly from the aorta and form the brachiocephalic trunk. Next, they divide into small vessels. The internal carotid and basilar arteries, as well as their branches, supply blood to the brain. They are arranged in a circle so that in case of obstruction in some areas, blood flows from other vessels in this circle.
Ultrasound examination of the BCA - what is it?
Are you looking for a research method that will provide the most reliable information about your disease?
With duplex scanning, the specialist receives accurate data on the pathologies and condition of the brachiocephalic vessels of the neck that supply the brain. Duplex scanning of the BCA also examines the dynamics of blood flow: speed of movement, nature of blood distribution. Modern Doppler ultrasound of the brachiocephalic arteries has a number of advantages, including:
- absolute harmlessness;
- painlessness;
- high information content;
- frequency of repeated examinations.
Do you feel frequent dizziness, periodic or constant numbness of the limbs, progressive deterioration of vision, dark spots and “spots” flashing in your eyes? Do you experience short-term fainting or headaches for no reason? Dopplerography of the brachiocephalic arteries is a quick way to visually examine the carotid, vertebral, and subclavian arteries and make a diagnosis. Get an ultrasound scan of the neck vessels if you suffer from diabetes. The examination will protect you from dangerous complications (hypoglycemia, ketoacidosis)!
Indications for use
Ultrasound Doppler Doppler of the BCA – what kind of examination it is, it’s almost clear. You need to figure it out when it's needed.
Headache
There can be many reasons for a person to experience periodic headaches. To eliminate this symptom and the disease associated with it, it is important to correctly determine the cause of the pain. Quite often it turns out that the blood supply to the brain is impaired due to dysfunction of the brachiocephalic arteries and vessels. Using ultrasound scanning of veins and arteries
manages to find out.
Dizziness
Dizziness can be caused by various factors: disruption of the vestibular apparatus, inner ear, fasting, stress, poor diet. Often, this pathological condition, when the patient loses coordination (for example, during sudden movements, walking, and so on), is caused by a disruption in the functioning of the brain. It, in turn, can be caused by disruptions in the blood supply from the brachiocephalic artery (BCA).
Fainting
Fainting is a short-term loss of consciousness. Its main cause is a temporary disruption of cerebral blood flow, which in turn can occur due to disruption of blood flow in the brachiocephalic artery. Systematic fainting is an indication for urgent ultrasound examination of the BCA.
Sleep disorders
The lack of normal rest due to a sleep disorder has a very negative effect on a person’s general condition, his performance, mood, and so on. One of the reasons for this problem may be impaired hemodynamics in the BCA. Doppler ultrasound of BCA arteries for sleep disorders can be prescribed in the presence of other alarming symptoms (fainting, dizziness, and so on).
Permanent or transient visual disturbances
Deterioration of vision is another indication for ultrasound examination of the central nervous system (what it is is described above). The blood supply systems of the brain and eyes are adjacent, therefore, for an accurate diagnosis and treatment, it is important to study the blood flow in all interconnected systems.
Flashing “flies”, a veil before the eyes
“Floaters” and blurred vision can be associated both with purely eye problems (for example, retinal detachment) and with brain pathologies. The most dangerous and, unfortunately, quite common pathology is stroke. Ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic vessels will make it possible to find out exactly what is causing such discomfort in the eyes and, perhaps, will help prevent hemorrhage in the brain.
Tinnitus, ringing in the head
The sensation of noise and ringing in the ears, which interfere with a person’s normal life and work, can also be one of the symptoms of a violation of cerebral blood supply from the BCA. If such a symptom is observed in combination with dizziness, migraines, fainting, then the doctor must prescribe an ultrasound scan of the brachiocephalic arteries (vessels).
What does ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck and neck examine?
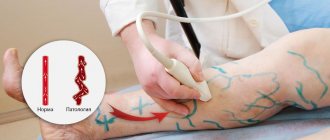
Duplex scanning of blood vessels examines:
- vascular lumen, wall mobility;
- blood clots, plaques, detachments;
- narrowing, expansion of walls;
- deformations, ruptures, aneurysms.
Scanning of the extracranial sections of the brachiocephalic arteries in 99% of cases reveals circulatory disorders in the head area, leading to strokes: arterial hypertension, thrombosis, vasculitis. Timely ultrasound of the neck vessels will save your life and prevent the risk of disability!
Indications and contraindications for ultrasonography of brachiocephalic arteries and vessels:
Mostly people suffering from obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary heart disease, and cervical osteochondrosis suffer. And also if you have previously suffered a stroke, heart attack and people over forty years old. If such diseases are present, then an ultrasound examination must be performed at least once a year.
Also, people suffering from frequent headaches, fainting, sleep disturbances, tinnitus, spots in the eyes, and visual disturbances should also undergo ultrasound examination of the bracheocephalic trunk. And also if there is weakness in the legs and arms and memory becomes worse. There is only one contraindication, and that is the presence of wounds on the neck.
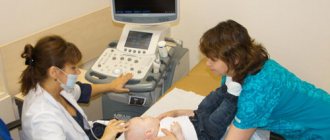
How is ultrasound examination of the BCA performed?
At the CBCP clinic, you will undergo a duplex scanning of the arteries using an expert-level device - the Italian MyLab 50 scanner. It is used to perform in-depth color duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries.
You will sit comfortably on the couch in a supine position. During the examination, the doctor will move the sensor over your skin, lubricated with a harmless gel, in the area of the collarbones, carotid arteries and monitor the image on the screen. You may be asked to breathe deeply, and your doctor may apply gentle pressure with a finger or probe to the blood vessels. You will not experience any unpleasant sensations!
The scanner will record certain indicators, and the doctor will enter them into the protocol for duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries. Decoding of the Doppler spectrum and color cartogram of blood movement is carried out within 10 minutes, and you will immediately receive a conclusion.
Why is the procedure prescribed?
Doppler ultrasound of the brachiocephalic vessels is necessary to assess various parameters of the main arteries, namely for:
- determining the degree of passability;
- identifying places of blockage;
- measuring the traversable diameter of the vessel;
- detection of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots;
- studying the anatomical structure of the vascular system;
- determining the size of the vessel;
- detecting hypoplasia or dilatation.
Ultrasound scanning of the brachiocephalic vessels helps accurately diagnose abnormalities such as aneurysms or wall ruptures.
Additional diagnostics
All data on scanning of the great arteries at the CBCP clinic are archived and stored. In subsequent procedures, the data from duplex scanning protocols of the brachiocephalic arteries are compared: the norm of the vessel lumen, echogenicity, mobility, blood flow velocity. This helps to monitor the dynamics of the clinical picture and adjust therapy.
You may need additional examinations, in particular a duplex scan of the lower extremities, which records deep vein thrombosis in detail. Atherosclerotic blood clots form in them, which threaten life. The procedure also does not require preparation, and its implementation is no different from an ultrasound scan of the neck: the doctor moves the sensor over the skin of the legs. In this case, you can lie down or stand.
Preparation for the procedure
Preparation for the BCA ultrasound (BCA) procedure involves following nutritional rules.
Drinks containing caffeine (tea, coffee, energy drinks)
At least one day before the test, the patient should exclude tea, coffee, and energy drinks from the diet. These are the drinks that can affect the condition of blood vessels and the results of the examination.
Alcohol
Drinking alcohol the day before the procedure is absolutely excluded (it is even better to increase the period of abstinence).
Salty foods
Excessive salt content in the blood can somewhat affect the speed of its flow and the condition of blood vessels, therefore, the day before an ultrasound scan, consuming various pickles is also prohibited.
Examination at the CBCP clinic
At CBCP you will be examined by doctors of the highest category who have 5-20 years of experience, experience in ultrasound, functional diagnostics in government institutions of the Russian Federation (NCSS named after A.N. Bakulev, Central Military Clinical Hospital). To master technologically advanced imported ultrasound equipment, specialists underwent training in German clinics, which is confirmed by professional certificates.
The clinic offers:
- wide range of examinations;
- affordable prices;
- discounts for pensioners, disabled people, children;
- comprehensive examination programs.
The essence of the method
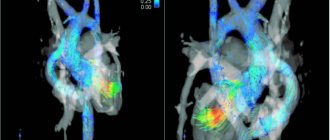
During the procedure, mainly the common, internal and external carotid arteries (CCA, ICA, ECA), as well as the vertebral artery (VA), are examined on both sides. The peculiarity of the CDK of the BCS is that to obtain longitudinal and transverse sections of the vessels, a typical two-dimensional mode (B-mode) is used for ultrasound, and another method is used to assess hemodynamic parameters - Doppler sonography. It is based on the Doppler Effect (named after the Austrian physicist and mathematician Christian Doppler), with the help of which, after appropriate signal processing, blood flow in the brachiocephalic arteries is visualized, its speed and strength are measured.
Most often, ultrasound is performed with color Doppler mapping in conjunction with spectral Doppler. The first allows you to determine the direction of movement and speed of red blood cells through Doppler frequency measurements. Blood flows are color coded in 2D images. The blood flow directed to the ultrasound sensor is mapped in red, and from it in blue. The CDB of the BCS makes it possible to clearly visualize areas of complex vascular geometry and turbulent blood flow.
Typically, the sensor head is turned towards the patient's head, so arteries are highlighted in red and veins in blue. Since color Doppler is used simultaneously with B-mode, it is called duplex sonography. The speed of blood flow is determined by the brightness of the color at individual points. Light indicates high speed and dark indicates slow.
Preparation and carrying out the procedure
As with other ultrasound examinations, no special preparation is required, but it is not recommended before the procedure:
- drink drinks that increase vascular tone: coffee, strong tea, energy tonics;
- take some medications, vitamins;
- smoke, be in a smoky or stuffy room.
Important! The possibility of temporarily stopping medication should be discussed in consultation with a therapist.
Before starting the CDC examination, it is necessary to place the patient in the correct position. He should lie on his back, to the right of the ultrasound device (comfortable for right-handed people). A pillow or cushion is placed under the back of the head to make prolonged lying (about half an hour) as comfortable as possible. A pillow that is too high is not suitable as it will deform the neck.
A contact gel is applied to the skin over the area to be examined to prevent air from entering between the skin and the sensor and distorting the results. Then the doctor moves the sensor over this area, lightly pressing the head towards the body. At least during the first session, both sides of the cerebral arteries should be examined to determine the hemodynamic significance of the stenosis.
First, the patient turns his head 45 degrees in the direction opposite to the one being examined. To find the desired vessels, a linear ultrasound probe is used to obtain cross-sectional images. The probe is then deployed to obtain a longitudinal slice, blood flow velocity is measured, and intima-media thickness (IMT) is assessed. In the longitudinal plane, the CCA is examined until it branches (bifurcation), and then both final branches are examined separately: the ICA and the ECA. Finally, using spectral Doppler, blood flow is measured in these arteries near the bifurcation and in the CCA, 2 cm from the branching.