CT angiography of the vessels of the head and neck is considered an important part of the examination of this area of the body. With its help, it is possible to visualize the current state of health of not only large arteries. Due to the detailed image, the radiologist will be able to understand even changes in vascular structures of a smaller caliber, if they occur.
The main task of this modern study is to assess blood flow according to several parameters, as well as search for possible pathologies of a congenital or acquired nature. The final visual picture allows you to find deviations of vessels of any size, ranging from their incorrect location and pumping, expansion or narrowing of their lumen. All this data together guarantees an accurate diagnosis at an early stage of the development of the disease, which in the future contributes to a speedy recovery through a properly prescribed treatment program.
Also, diseases detected in the initial phase of development have fewer complications on the body, which is especially important in the case of vascular damage due to severe changes of any type.
Advantages of CT scan of brain vessels
CT not only displays the vascular network in three dimensions, but also allows you to study in detail any large or small vessels. This research method is considered the most useful and effective, since it makes it possible to diagnose almost any dangerous disease at an early stage.
During CT angiography, you can examine the structure of the vascular wall and the tissue that surrounds the veins and arteries. This provides valuable information necessary, for example, for the early detection of hemorrhagic stroke. In the images, you can see the size of the hematoma, study the degree of damage to the brain centers and nuclei, and also assess the level of compression of the brain matter.
There is no pain during the examination.
How is computed tomography performed?
- The patient lies down on a table that will slide into the tomograph ring;
- To inject contrast into a vein, a special cannula is installed, which is connected to a machine for automatically administering a contrast solution.
- The CT machine is controlled by a specialist from the next room. There is a special intercom to communicate with the patient.
- During the tomography, you must stand still so that there is no movement. Any movement distorts not only the currently scanned image, but also all subsequent images. It is necessary to strictly follow the commands of the doctor performing the research. The patient holds his breath every time the specialist gives the appropriate command.
- The examination lasts 3-5 minutes, after which the cannula is removed from the vein. The received data enters the apparatus for computer processing. After studying the materials, the doctor gives a conclusion on the study.
Alternatives to CT scan of the brain
Alternative diagnostic methods include primarily MRI. But it is not recommended if the patient has any metal elements in the body: a pacemaker, vascular clips, etc. X-ray angiography is also sometimes used.
If you want to know where is the best place to get a CT scan of the brain, contact us - we will sign you up for a study at a clinic where they conduct the study using the latest equipment and guarantee high-quality diagnostic results.
When is CT angiography needed?
For the circulatory system to function normally, it is important to have healthy blood vessels. Ekaterina Aleksandrovna Nekhaeva, a radiologist at the Expert Clinic Kursk, told us how CT angiography helps check their condition and the indications for such a study.
— Among the methods of studying blood vessels, CT angiography occupies a special place. Ekaterina Alexandrovna, what is this? What is the point of this research?
— This is a modern and one of the most informative methods for diagnosing vascular pathology, based on the use of X-ray radiation. It is distinguished from ordinary x-rays by much greater information content. Using a special program, the doctor can create a three-dimensional model of the vessels of the area under study.
CT angiography is always performed with contrast, that is, with intravenous administration of a contrast agent. This makes blood vessels more visible on images compared to surrounding tissue. This makes it possible to accurately assess their lumen, location, syntopy (relationship with surrounding anatomical structures) and other parameters. These parameters determine the availability of vessels for the surgeon, for example, when planning interventions. We try to reflect all this information in the protocol in as much detail as possible (especially if the referring doctor asks us specific questions).
— Vessels of which parts of the body and human organs can be examined using CT angiography?
— CT angiography is widely used to evaluate the vessels of the head, neck, large vessels of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space, vessels of the iliac regions, lower extremities, coronary arteries, as well as pulmonary arteries and veins.
Read material on the topic:
Who can benefit from CT coronary angiography?
— When might a patient need CT angiography?
— Basically, the indications for the study are determined by the referring doctor. These are usually vascular surgeons, because CT angiography is often performed immediately before the proposed surgery so that the doctor can take into account the location and size of the vessels when performing the operation.
The most common pathologies and other reasons for which patients come (or are admitted) to us are:
- obliterating atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities (damage to the large arteries of the legs, leading to narrowing of the arteries and poor circulation);
- atherosclerotic lesions of the arteries of the head and neck, coronary arteries, etc.;
- vascular development abnormalities;
- aneurysm;
- aortic rupture;
- arterial thrombosis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- extravasal blood vessel compression syndrome (i.e. when the vessel is compressed by something from the outside);
- vascular damage;
- examination after surgery, etc.
Read materials on the topic:
Find and neutralize. How to protect against blood clots? Coronary heart disease: diagnosis and treatment
— What does CT angiography reveal?
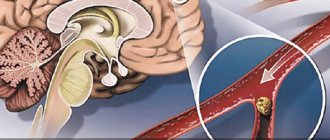
— It helps to detect stenotic changes (areas of narrowing) or aneurysmal areas (areas of expansion) of blood vessels, the presence and prevalence of atherosclerotic changes (with determination of the exact size and structure of plaques), compression of blood vessels by a tumor, etc.
CT angiography also makes it possible to identify abnormalities in the development of blood vessels, the presence of various variants of the origin and relative position of vessels, which are also often clinically significant.
— Ekaterina Aleksandrovna, what are the advantages of CT angiography when compared, for example, with MRI and ultrasound? And can it completely replace these methods?
— CT angiography is definitely more informative than the listed methods, since it allows us to visualize the vascular wall itself, while on MRI and ultrasound we see only the signal of blood flow through the vessels. Also, only thanks to such CT diagnostics we can see atherosclerotic plaques, assess their size, structure, and shape.
With CT angiography of cerebral vessels, intracranial (intracranial) vessels can be seen much better than with ultrasound, since the capabilities of ultrasound are limited due to the screening of ultrasound by the bones of the skull.
CT angiography can completely replace MR angiography, since the latter is inferior to it in sensitivity and specificity. On the other hand, when performing MRI, there is no radiation exposure inherent in computed tomography. The only advantage of ultrasound is the ability to assess the speed of blood flow in dynamics, as well as the absence of contraindications typical for X-ray studies and intravenous contrast.
In any case, the optimal choice of one or another research method, depending on the questions facing the radiologist, always remains with the referring clinician.
Read more about vascular ultrasound in our article: Doppler, duplex, triplex... What is vascular ultrasound?
— Is preparation necessary before CT angiography?
— In general, no special preparation is needed. But if the patient underwent an X-ray examination of the stomach and (or) intestines with barium sulfate a few days before the computed tomography scan, then you should wait 3-4 days until the barium is removed from the body. Also, if the patient uses metformin (a drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes), then, after agreement with the attending physician, it is necessary to stop taking the medication two days before the examination.
— Tell us in more detail how CT angiography is performed
— The person is placed on the retractable table of the computed tomograph. First, a catheter is installed in his cubital vein, through which a radiopaque contrast agent is injected using a special device (injector). First, a “native” (preliminary non-contrast) scan is performed, and then a scan with the introduction of contrast. Some areas may require holding your breath for an average of 10 seconds. During the entire session, the specialist remains in the next room and communicates with the patient via speakerphone. The duration of the procedure is approximately 20 – 30 minutes.
— Can everyone do this research? Or are there contraindications for CT angiography?
- Yes, they are. This:
- impaired renal function;
- thyrotoxicosis (increased levels of thyroid hormones) and thyrotoxic crisis;
- allergy to iodine-containing contrast agents;
- pregnancy.
— Is a referral required to undergo CT angiography?
— Yes, a referral from the attending physician is necessary in the vast majority of cases.
— Ekaterina Aleksandrovna, is this research carried out for children?
- Yes. To perform computed tomography for children, special scanning protocols are used, the use of which implies the maximum possible reduction in radiation exposure to the child’s body. However, CT angiography is performed for children according to strict indications and with a mandatory referral from the attending physician.
If you need a CT angiography, you can sign up for this test here ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
Interviewed by Marina Volovik
The editors recommend:
How will MRI of cerebral vessels help a patient? When is ultrasound of cerebral vessels prescribed? Take care of your vessels! How not to miss vascular diseases of the brain?
For reference:
Nekhaeva Ekaterina Aleksandrovna
In 2013 she graduated from Kursk State Medical University.
In 2015 – residency in general surgery.
Completed professional retraining in radiology.
Currently, he is a radiologist at the Expert Clinic Kursk. Receives at the address: st. Karl Liebknecht, no. 7.
Indications
- Presence of headaches of unknown origin;
- Detection of atherosclerosis, in order to identify the risk of stroke;
- Presence of head injuries;
- If other diagnostic methods do not provide convincing information regarding the diagnosis;
- Systemic and cerebral vasculitis;
- Risk of hemorrhage;
- To assess the patient’s condition after surgery;
- The presence of malignant and benign neoplasms in blood vessels;
- Any abnormalities in vascular development.
How to prepare?
- It is necessary to inform the doctor about the presence of allergies and concomitant diseases. Your doctor may recommend that you stop taking NSAIDs or blood thinners before the procedure.
- It is recommended not to eat or drink 8-12 hours before the procedure
- Women should always inform their doctor and radiologist if there is a possibility that they are pregnant. Many types of imaging are contraindicated during pregnancy, and the use of CT angiography is possible only when there are compelling clinical indications and minimizing the risk to the fetus.
If you are breastfeeding after the procedure, you should avoid breastfeeding your baby for 24 hours after the procedure.
Contraindications for CT scanning
Computed tomography is prohibited at any stage of pregnancy, since X-rays can cause abnormalities in the development of the fetus.
Also, diagnostics are not recommended for people with a body weight exceeding 200 kg.
Since CT is based on the use of contrast, it has a number of additional limitations:
- Since iodine is used as a contrast agent, it can cause allergic reactions in patients. This is why the procedure is not prescribed to people allergic to iodine;
- If the patient has previously been diagnosed with renal failure, this is a contraindication for CT scanning, as it can lead to serious consequences;
- Since the contrast penetrates into milk, the procedure is not prescribed to women during breastfeeding;
- If the patient has severe injuries or shock, computed tomography with contrast is also not recommended.
Contraindications and possible complications
Like all diagnostic methods, CT scan of cerebral vessels has its contraindications. Situations that do not allow the use of CT angiography include:
- allergic reactions that develop as a result of exposure to a contrast agent;
- severe liver and kidney disease (inability to properly remove the contrast agent from the body);
- severe degrees of phlebitis - a contrast agent can provoke a worsening of the pathological process in this disease;
- pregnancy, because there is a risk of intrauterine development disorders of the fetus.
Frequent and regular use of X-rays for diagnostic purposes (with CT) increases the likelihood of developing malignant tumors. However, with a single or rare use of cerebral CT with contrast, there are almost no risks.
Research results
The radiologist's report and the resulting images usually take no more than 2 hours to prepare. But in some cases, the interpretation of images can take longer, sometimes up to a day.
CT can determine:
- atherosclerotic plaques, their size and location;
- the condition of the walls of all vessels (veins, arteries, peripheral system);
- stenosis and occlusion (blockage) of the vessels of the head and neck (risk of developing acute cerebrovascular accident);
- ischemic lesions, heart failure, aneurysms;
- hemorrhages, blood clots, neoplasms, metastases;
- traumatic damage to the walls;
- dissection of the aorta and other large vessels.
Risks
- Although there is some risk associated with x-rays, the diagnostic benefit outweighs this risk.
- There is a possibility of an allergic reaction to the contrast, but it is minimal
- Women should always tell their doctor or radiologist if there is a possibility that they are pregnant
- Nursing mothers should avoid breastfeeding for 24 hours after contrast administration
- If you have diabetes or kidney disease, you are at risk of kidney damage.
- Any procedure in which a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel has certain risks. These include: vascular damage, hematoma bleeding and infection.
- There is a slight risk of a blood clot forming around the tip of the catheter.
- There is a certain risk of stroke, since the catheter removes plaque from the walls of the vessel and this can lead to circulatory problems.
- In very rare cases, the catheter can puncture an artery and cause internal bleeding.
Angiography of coronary vessels
This is a method for assessing blood flow in the coronary vessels, or coronary angiography. Angiography in this case allows you to assess the patency of the arteries that supply the heart. The positive aspect is the possibility of performing diagnostics without hospitalization of the patient and the low invasiveness of the procedure. Angiography of the coronary vessels is possible using computed tomographs that perform 64 slices or more. Indications for CT coronary angiography:
- IHD;
- Various types of arrhythmia;
- Preparation for AV ablation or interventional treatment for additional pathways of electrical impulses in the myocardium;
- Significant disturbance of the electrolyte composition of the blood;
- Malignant arterial hypertension;
- Suspicion of endothelial dysfunction.
general information
Computed tomography (CT) is a cross-sectional imaging technique based on the X-ray principle.
A tomograph's X-ray tube is not static, unlike a conventional X-ray machine. Together with a digital detector, it rotates around the patient at high speed (up to 4 revolutions per second) inside the tomograph body, which is called a gantry. During scanning, the patient moves on a special table along the longitudinal axis of the body into the gantry aperture, so the X-ray beam “draws” a spiral trajectory on his body, hence the name spiral and multispiral computed tomography. From the data obtained by the detector, a three-dimensional model of the area under study is formed, and then sections in various planes are formed.