Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method that is used to study the state of the human brain and is based on recording its electrical activity. This examination allows you to detect the spread of pathological processes and signs of epilepsy.
The average duration of the procedure is about an hour, but it is highly informative and makes it possible to track functional changes in the brain, the dynamics of the disease, and evaluate the impact of the therapy.
Since the procedure does not cause any pain or discomfort, EEG can be called one of the most accurate and gentlest methods of examining the brain.
EEG principle
The human brain consists of millions of special cells called neurons. Each of them generates its own electrical impulse. Within individual areas of the brain, impulses must be consistent. They can also strengthen each other or make each other weaker. Their strength and amplitude are not stable and are constantly changing.
Content:
- How EEG works
- Historical reference
- Significance of EEG
- Benefits of an Electroencephalogram
- Indications for the procedure
- Contraindications
- How to prepare for an EEG
- Performing an EEG
- Purpose of EEG video monitoring
- Conclusion of electroencephalography
This is the bioelectrical activity of the brain. To register it, special electrodes are applied to the intact scalp, which will pick up vibrations, amplify them and record them in the form of special curves, so-called waves. The latter, depending on their shape, frequency and amplitude, are divided into five types: α- (alpha), β- (beta), δ- (delta), θ- (theta) and μ- (mu) waves. Each of the waves reflects the work of a specific part of the brain and is named by the first letter of its Latin name.
Their registration in real time is the essence of encephalography.
Very often, patients confuse these studies. Let's figure out together what these methods are, how they differ, to whom and why they are prescribed.
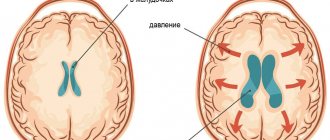
EchoEG (echoencephalography or echoencephaloscopy) is a method of studying the brain using ultrasound. Can be used by both children and adults. But do not confuse it with neurosonography! Neurosonography is also an ultrasound method that can only be performed on small children with an open fontanel. At the same time, the doctor sees the brain structures on the screen and can measure and evaluate them. The essence of EchoEG comes down to the fact that, propagating inside the head, the ultrasound beam is reflected from media of different densities and returns back. In this case, the doctor sees on the screen not the anatomical structures of the brain, but a kind of graph, according to which he can assess: the position of the median structures, which, in the presence of a pathological formation (tumor, hematoma, abscess), will be displaced. The space-occupying lesion will shift the midline structures to the unaffected side. A displacement of more than 2 mm is considered a reliable sign. The EchoEG method is used to assess the strength and nature of the pulsation of the echo signal in real time, which is necessary to determine whether intracranial pressure is increased or not. The study indirectly allows us to judge the presence of hydrocephalus (excessive accumulation of fluid in the ventricular system of the brain). The versatility of EchoEG lies in the fact that this method has no contraindications and can be used in both adults and children of any age. The research does not take much time and does not require preparation. Performed in a supine position. The head must be motionless, therefore, when examining the child, it is advisable for the parents to be present to help hold the head and distract the child. A special gel is applied to the scalp at certain points, where the doctor installs sensors and outputs the necessary echo signals, which are displayed on the screen in the form of a graph.
Thus, this study is most often prescribed by a neurologist for traumatic brain injuries, strokes, suspected tumors, abscesses, hydrocele in the brain in conditions where other methods of brain imaging, such as CT/MRI or neurosonography, are not available or not can be performed for various reasons (for example, the patient’s serious condition, a closed fontanel). But it should be remembered that the method is essentially “blind”: it is impossible to see the hematoma, abscess or tumor itself and measure the exact dimensions; only the displacement of the median structures is determined (it is possible to determine on which side the pathological process is).
But for measuring intracranial pressure, the EchoEG method is the most popular, safe and, most importantly, applicable to adults and children. There are 3 degrees of increased intracranial pressure (depending on the severity of the echo signal pulsation): normal - 10–30%, mild - 30–50%, moderate - 50–75%, severe intracranial hypertension - 75–100%. Some neurologists are skeptical about measuring intracranial pressure, considering this method not always accurate and indicative. Indeed, several factors may influence the reliability of the results. First of all, this is the emotional state of the child at the time of the study (when crying and screaming, a higher percentage of echo signal pulsation is recorded than it would be recorded in a calm state). Also important is the experience of the doctor conducting the study (correct installation of the sensor, correct interpretation of the changes seen...). Therefore, if all conditions are met, the method has the right to exist and is one of the simplest methods for non-invasive diagnosis of intracranial pressure.
To conduct electroencephalography (EEG), or as patients are accustomed to calling this study, a “cap,” a kind of cap is actually put on the patient’s head. It can look different (different colors, can be made of any materials - fabric, rubber, be solid or consist of interconnected flagella). Using a cap, electrodes are attached to the scalp, which capture electrical impulses arising in the brain and transmit them through wires to a computer, where they are displayed in the form of waves. During the study, the patient undergoes various tests, most often “opening and closing the eyes”, photostimulation (flashes of light at a certain frequency) and a test with hyperventilation (asking to breathe deeply). Based on the nature of the electrical impulses, where they occur, with what frequency and amplitude, how they behave during tests, the doctor makes a conclusion about the presence or absence of epileptic activity, pathological foci, and the correspondence of the frequency-amplitude characteristics of the impulses to age. An EEG helps the doctor determine the cause of the patient’s neurological disorders (functional or organic brain damage?). Using EEG, it is possible to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for a number of diseases (for this, the EEG is first taken before treatment, then during and after treatment). An EEG must be taken in patients who have suffered a head injury (traumatic brain injury), after brain surgery, in the presence of fainting, convulsions, paroxysmal headaches (migraines?), attacks of dizziness, panic attacks, suicidal tendencies, depression, sleep disorders (nighttime nightmares, frequent awakenings, sleepwalking...), with delayed speech development, with stuttering, with tics, with encephalitis, with strokes. There are no contraindications to EEG. There may be difficulties with fixing the electrodes due to open wound surfaces of the scalp after injuries; in this case, whether or not to conduct the study is decided individually. It may also be difficult to take an EEG in patients with mental disorders, in young children and in children with behavioral characteristics, since it is difficult for them to remain calm during the study and follow the doctor’s instructions when conducting tests. At the time of the study, the patient is in a dark room and his eyes must be closed almost constantly, which can also be an obstacle to conducting an EEG in children. The way out for such children is video-EEG monitoring (recording EEG during sleep for several hours under video control).
Preparation for the EEG: before undergoing the study, it is recommended to limit the use of sedatives (sleeping pills) and invigorating drugs (coffee, strong tea, energy drinks) for 3 days; before the procedure, the head must be clean (well washed, without gels, oils, varnishes and foams). We should also talk about preparing for an EEG with sleep deprivation. This study is prescribed to identify hidden foci of epileptic activity and is more often prescribed to patients with seizures in whom the epileptic focus could not be identified using a conventional EEG. In order for the focus to “manifest” itself, it must be provoked by creating certain conditions for the brain (in this case, the brain is in a state of excitement). The essence of the method is that the patient should not sleep for some time before the study, for example, a 2-3 year old child is woken up at 3-4 o’clock in the morning and is not allowed to sleep any more, and they come for the study at 9 o’clock. For older children, the time without sleep increases (up to 18 hours in children over 12 years old). The study is carried out sitting or lying down, the patient performs a more expanded range of tests. You need to understand that during an EEG with sleep deprivation, an epileptic seizure may develop.
Dear patients, I hope now you will easily navigate these studies and will no longer confuse them!
Historical reference
One of the founders of the electroencephalography method is considered to be the physiologist and psychiatrist from Germany Hans Berger. In 1924, using a device for measuring small currents called a galvanometer, he was the first to perform a procedure resembling an EEG recording.
Later, a special device called an encephalograph was created to conduct electroencephalography. Today, there are stationary encephalographs, which make it possible to conduct research exclusively in a special room, and portable ones, which are designed for long-term monitoring and can be moved.
It is noteworthy that initially EEG was considered exclusively as a method for identifying mental disorders in a person. Only over time it became clear that the technique also makes it possible to detect deviations not related to psychiatry.
Significance of EEG
EEG is a highly informative diagnostic method that allows:
- assess the nature of brain dysfunction and how severe they are;
- determine the localization of the pathological focus;
- clarify information obtained during other diagnostic procedures (for example, computed tomography);
- monitor how effective the therapy is;
- identify areas of the brain in which epileptic activity is present;
- assess brain function in the periods between attacks;
- identify the causes of panic attacks and fainting;
- study the sleep-wake cycle.
It should be taken into account that if a person has seizures, the study will be informative only if it is carried out after about a week.
Benefits of Electroencephalography
Today, electroencephalography is widely used in neuropathological practice. It makes it possible to clarify a huge number of problematic situations that are associated with the diagnosis and differentiation of neurological diseases. One of the undeniable advantages of encephalography is the fact that it not only helps to identify certain problems, but also helps to distinguish true disorders from hysterical manifestations or simulation.
In addition, the procedure is not as expensive as examination using a tomograph or other similar devices. EEG equipment is available in most hospitals.
The procedure does not have any negative impact on human health and condition. The patient remains fully functional. The study can be carried out even on patients in serious condition, children and adults of any age, since it does not cause deterioration of the condition, discomfort or pain.
Indications for the procedure
Today, electroencephalography is widely used in the practice of neurologists to solve a number of problems.
EEG is recommended:
- for prolonged insomnia and other sleep disorders, including apnea, somnambulism and talking during sleep;
- during a convulsive attack;
- for diseases of the thyroid gland;
- with signs of developmental disorders in children or mental disorders in adults;
- after recently experienced traumatic brain injury;
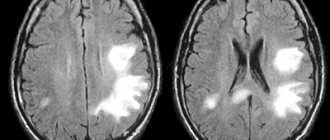
- in case of pathological changes in the vessels of the neck and head, brain tumors detected during ultrasound;
- with frequent migraines, complaints of regular dizziness, feeling of constant fatigue;
- for panic attacks, autism, Asperger's syndrome, stuttering, nervous tics, delayed speech and mental development in children;
- for meningitis, encephalitis, after a stroke and micro-stroke;
- after neurosurgical operations.
How to choose an examination technique?
Ultrasound does not require special conditions for placement of equipment. This is the easiest way to diagnose. The purchase and installation of devices for CT, MRI or PET require considerable costs. In this regard, not all medical institutions can afford to carry out such procedures. For this reason, prices for these types of diagnostics will be high.
However, the popularity of the equipment and the price of diagnostics should not be the determining factors. First of all, you need to follow the recommendations of your doctor. The scope of application of the examination method should also be taken into account:
- PET detects a tumor, including a malignant one, with absolute accuracy, long before its manifestation.
- MRI is most effective in neurosurgery and neurology.
- CT is useful in detecting vascular damage and head injuries.
- From the point of view of the absence of ionization and X-ray radiation, MRI is the safest procedure. However, modern equipment for radiography and ultrasound significantly reduces the risk of gene mutations.
It is important not to forget about contraindications. Thus, PET and CT scans are strictly prohibited for pregnant women. MRI is used for expectant mothers if the potential benefit to the woman is higher than the possible risk to the baby.
Children require special preparation for the procedure. Parents should allegorically explain to their children the need to lie still. The youngest require anesthesia.
Only the attending physician can determine the need for a particular diagnosis. In some cases, different types of scanning may be required at the same time.
Contraindications
It is noteworthy that there are no absolute contraindications for electroencephalography. If a person suffers from convulsive attacks, is diagnosed with coronary heart disease, hypertension, or mental disorders, an anesthesiologist must be present during the diagnosis.
The procedure should be postponed if there are open wounds, traumatic injuries, postoperative sutures or any signs of an inflammatory process in the area where it is necessary to install electrodes. Also, the study is not carried out for patients with ARVI.
Where to get a magnetic resonance imaging scan
The search for a clinical diagnostic center can be significantly speeded up if you use the help of our website. The service contains information about a large number of clinics, ranging from contact details to discount offers. If necessary, our specialist will advise you free of charge over the phone about operating hours, the availability of tomographs of the required type and the time available for making an appointment.
A patient who wants to undergo magnetic resonance imaging of the vascular system of the head and neck can independently filter the list of medical institutions by rating, cost and features of the procedure (24-hour clinics, pediatric MRI).
How to prepare for an EEG
It should be noted that there are no special restrictions that must precede the procedure. However, there are a number of rules that are recommended to be followed to ensure that the examination is successful and informative.
First of all, inform your doctor if you are taking any medications. You may need to stop taking them for a while or change the dosage.
At least twelve hours before the procedure, or even better, a day before, eliminate from your diet foods that contain caffeine, carbonated drinks, chocolate and cocoa, as well as foods that contain them, foods with energy components, for example, taurine. You should also avoid products with sedative effects.
Wash your hair before the procedure. It is not recommended to use additional styling products (oils, gels, balm, varnishes, etc.) as this may affect the quality of contact of the electrodes with the skin.
If the main purpose of the procedure is to detect seizure activity, you need to sleep before the study.
In order for the result to be as reliable as possible, the patient should avoid stressful situations and refrain from driving for twelve hours before the procedure.
Eating is recommended two hours before the procedure.
If the patient is prescribed EEG sleep monitoring, the night before should be sleepless. Immediately before the procedure, the subject will receive a special sedative, which will enable him to fall asleep during the electroencephalography.
If a child is to undergo an examination, parents should first psychologically prepare him for the manipulations, explaining that there will be no pain or discomfort. You can practice putting on a pool cap under the pretext of playing pilots or astronauts, teach your child to breathe deeply, showing him how to do it by personal example. On the eve of the procedure, the child should wash his hair without using any additional styling products. Before leaving the house, the baby should be fed and calmed down. Just in case, parents are advised to take with them tasty food and drink, and a favorite toy that will help calm and distract the baby.
Please note that if the above rules are not followed, the EEG result may not be very accurate or very informative. In this case, the procedure will have to be repeated.
Contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging of the vascular system of the head and neck
The ban on MRI of head and neck vessels is due to the peculiarities of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with certain metals and magnets. The examination is prescribed with caution in certain patient health conditions.
MRI of cerebral vessels is contraindicated if the patient has the following devices in the body:
- pacemaker and other stimulating implants and pacemakers, cochlear implant - implants may fail under the influence of a magnet;
- metal intravascular stents, artificial heart valves;
- endoprostheses, foreign metal bodies in the body;
- metal clips installed in the vessels of the brain after surgery - under the influence of a magnetic field they can move and cause bleeding.
Not every material prohibits MRI of vessels and arteries of the neck and head. Metals that react to a magnetic field by displacement and heating: stainless steel, iron, nickel, cobalt. In other cases, the procedure is not prohibited.
In some patient conditions, examination is allowed by the doctor’s decision on an individual basis:
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks - the fetus is especially sensitive to external factors;
- serious condition of the patient, severe pain;
- epilepsy, seizures, mental illness;
- body weight should not be more than 130 kg - the devices have restrictions on the patient’s weight and waist circumference.
The procedure can be performed in patients who find it difficult to maintain a stationary body position under general anesthesia or in an open-type apparatus. During the entire period of using MRI, there have been no cases of fetal pathology developing after the procedure in the first trimester of pregnancy, however, doctors are careful. If the patient suffers from a mild form of claustrophobia, he may take sedatives before the examination.
MRI of the vessels of the head and neck with the use of contrast agents is contraindicated in pregnant women at any stage, as well as in patients with renal failure.
Performing an EEG
Electroencephalography is performed in a special room, which is completely isolated from light and sound. The patient sits in a chair or is asked to lie on the couch. A special cap with electrodes is first placed on his head. During the procedure, the patient is alone in the room, contact with doctors is maintained using a camera and microphone. If the diagnosis is performed on a child, one of the parents remains in the office.
Before starting the procedure, the patient is asked to close and open his eyes several times to adjust the equipment. During the diagnosis, the eyes must be closed. If during the procedure the patient needs to change position or visit the restroom, he can inform the doctors about this, after which the diagnosis will be suspended.
It is extremely important that the patient lies with his eyes closed and does not move during the procedure. In the event that a person opens his eyes slightly or moves, the doctor makes a corresponding note, since these actions must be taken into account when deciphering the electroencephalogram.
After the resting EEG is recorded, so-called “stress tests” are performed. Their goal is to test how the brain will react to situations that are stressful for it.
So, a hyperventilation test can be performed. The patient is asked to breathe frequently and deeply for three minutes. Photostimulation with a stroboscopic light source can also be used. It flashes frequently, and this allows you to evaluate how the brain reacts to bright light.
Stress tests can trigger convulsions or an epileptic seizure. The doctors who conduct the study have the appropriate skills to provide emergency care to the patient if necessary.
After the study is completed, the physician should remind the patient to resume taking medications that were stopped the day before the EEG.
The total duration of the procedure is from forty minutes to two hours.
What the results look like
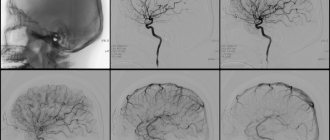
After performing an MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck and head, the doctor receives layer-by-layer images of the vascular pattern with the ability to construct a three-dimensional model. The patient can pick up the images on electronic media or in printed form. The photographs are accompanied by a report from a radiologist.
Normally, the internal carotid arteries are located symmetrically, have clear contours, are not displaced, and are not compressed. The cerebral arteries arise in a typical place, the diameter is not changed, and there is no pathological tortuosity of the vessels. The cerebral veins and sinuses should be of normal diameter, without areas of blood flow disturbance, filling defects or deformations.
On MRI images of the vessels and arteries of the neck you can see signs inherent in certain diseases:
- an aneurysm is a round formation with a high signal intensity; when a thrombus attaches, a layered structure appears;
- vascular malformations appear as linear or tortuous structures with dilated vessels;
- dissection of the arterial wall is characterized by the appearance of a crescent-shaped hematoma located along the vessel, while the lumen of the artery is narrowed evenly or in the form of a rosary;
- atherosclerosis of the vascular system looks like an area of increased intensity on the vessel wall, the lumen is narrowed;
- hemangioma is a high-intensity formation with clear edges and a lobular structure.
Despite a detailed description of all identified pathological formations, the conclusion of a radiologist is not a diagnosis. The MRI result of the area of the cerebral vascular system should be shown to the doctor who ordered the study. Clinics offer the opportunity to consult with the radiologist who performed the procedure. If necessary, he will recommend contacting specialized specialists - a neurologist, oncologist or surgeon.
Purpose of EEG video monitoring
One of the types of electroencephalography is EEG video monitoring. This is a long-term recording of electroencephalography, usually lasting several hours, which can be performed during sleep. The duration of the procedure in each specific case is determined by the attending physician and the personnel of the laboratory that conducts the examination.
EEG video monitoring is prescribed if a short standard procedure does not reveal pathologies, but they are present.
Also, this type of examination allows you to evaluate the EEG during wakefulness and sleep.
Many patients are interested in the question of whether they should necessarily sleep during the study. The answer to this question cannot be unambiguous, because it depends on the specific situation. So, for example, if the reason for the examination is a tic that bothers the patient while awake, there is no need to sleep during the examination.
At the same time, EEG video monitoring during sleep sometimes helps to identify conditions that neither the patient nor his loved ones may even be aware of.
The peculiarity of this procedure is that it can be carried out not only during the day, but also at night. In the event that sleep EEG is required, night monitoring is more rational. Not everyone can fall asleep without problems during the daytime.
At the same time, we should not forget that carrying out a multi-hour procedure in a completely isolated room can be extremely tiring for the patient, especially if we are talking about a child. Most pathologies can be detected during a relatively short recording of a conventional EEG.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Also, overnight EEG video monitoring is much more expensive.