If excess fluid accumulates in a person’s brain, which prevents the organ from functioning normally, it is called dropsy, or hydrocephalus of the brain. Excess fluid increases pressure on the brain structures, pressing them against the skull. In the absence of timely diagnosis and qualified treatment, the patient may die.
The success of treatment depends on the degree of damage, severity of the process, symptoms and concomitant pathologies. The disease can be congenital or acquired.
Types of dropsy
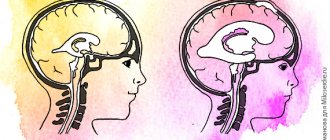
The classification of hydrocephalus of the brain is quite complex, with blurred diagnostic boundaries. Until recently, this disease belonged exclusively to children, but today it has been proven that it is possible to develop dropsy in adults.
Clinical manifestations of dropsy are divided into groups:
- The mixed form is severe, the volume of fluid increases inside and outside the brain. The prognosis is unfavorable. Violations cause epileptic seizures, convulsions, and paralysis of the limbs.
- Atrophic hydrocephalus of the head develops against the background of traumatic brain injury. The ventricles increase symmetrically, the volume of gray and white matter decreases. A month after the injury, changes become noticeable. This is a natural reaction of the body. The prognosis of the post-traumatic form of the disease is unfavorable.
- Hydrocephalus vicarious - the ventricles become enlarged, but the anatomical structure of the brain does not change. The prognosis is favorable if detected at an early stage. In the vast majority of cases, the development of the disease can be stopped and the situation stabilized.
- Hypotrophic hydrocephalus develops as a reaction to a malnutrition of the brain, when soft tissues lack nutrients. A person has a headache and vestibular functions are impaired. The condition is aggravated by nausea and vomiting.
- The compensatory form appears when the acute stage of the disease has passed. The volume of fluid in the ventricles stabilizes, but their volume remains increased. There is no treatment.
- Non-occlusive form - changes do not cause hypertension. The nature of the disorders is not clear, the inflow and outflow of cerebrospinal fluid remains at the same level, the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is within acceptable limits.
- Partial form - an increase in fluid volume causes neurological changes. A characteristic symptom of the disease is epileptic seizures.
- Discirculatory hydrocephalus - a lack of cerebral circulation is diagnosed, often accompanied by atrophic processes.
Whatever the etiology, dropsy remains a dangerous disease, the consequence of which is disruption of brain function, deterioration of thinking ability and perception of information. It is important to identify the disease at an early stage and stop its development.
Pathogenesis
The disease provokes expansion of the cerebral ventricles for various reasons. The main provocateur is a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
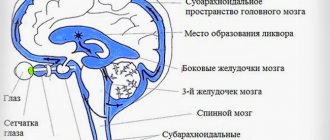
The process of cerebrospinal fluid circulation
The choroid plexuses produce approximately 600–700 ml of cerebrospinal fluid per day. It enters the central canal through special openings, washing the brain and then the spinal cord. Reabsorption occurs through the cerebral hemispheres through the venous sinuses.
Brain damage process
Excessive pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid provokes its leakage into the surrounding substance, which causes the development of edema. The dilated ventricles begin to compress the brain tissue.
The white matter takes the brunt of the attack, causing destruction of the myelin sheaths that transmit nerve impulses to the body.
Up to a certain point, such changes are reversible—after timely surgery, it is possible to almost completely restore neurological functions. Otherwise, atrophy of the brain substance develops, causing spastic paralysis, and the person ceases to control the functioning of the pelvic organs.
In infants, under the influence of such excess pressure, there is a rupture of adhesions inside the subarachnoid space, which opens the way for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and self-healing. In advanced situations, brain tissue ruptures. Timely treatment can prevent the development of neurological disorders.
Reasons for the development of pathology
The human brain consists of soft tissues located in the skull. To protect against damage, cerebrospinal fluid circulates in the cavity - the liquid fills the internal ventricles and grooves. When a person is healthy, the inflow and outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is balanced. The performance of its functions does not affect the patient’s health. If disturbances occur due to the development of tumors, injuries and infections, intracranial pressure increases and the process of cerebrospinal fluid movement is disrupted, causing changes in brain function and neurological manifestations.
Hydrocephalus can develop due to a stroke or tumor development.
Complications
Excess cerebrospinal fluid dilates the ventricles, compresses the medulla - swelling occurs. A closed cranial cavity provokes the development of irreversible changes in blood vessels - in the absence of the necessary treatment, this condition is life-threatening.
Children who develop hydrocephalus are mentally behind their peers. With complications, mental disorders, mental retardation, personality disorders, and inhibited reactions are likely. Irritability, attacks of euphoria or anger appear. Due to brain damage, speech problems, vision or hearing problems occur.
Adult patients complain of a bursting headache and nausea. Only vomiting sometimes alleviates the condition. The organs of vision experience internal pressure, and there is a feeling as if sand has gotten into the eyes. As pressure increases, drowsiness occurs.
Chronic hydrocephalus provokes an increase in intracranial pressure. The pathology develops slowly, appearing several months after the onset of the disease. Its main symptoms:
- cognitive disorders;
- walking disorders.
How does dropsy manifest itself?
With moderate development of the process, minor neurological disorders appear. You can't ignore:
- Nausea;
- Headache;
- Vomiting;
- Deterioration of vision;
- Changes in the appearance of the eyeballs;
- Problems with the vestibular system;
- Mental abnormalities.
The open external form has manifestations similar to mental disorders. If the diagnosis is made incorrectly, the patient will be treated in a psychiatric clinic, and the underlying disease will go unnoticed. To make a correct diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes additional tests:
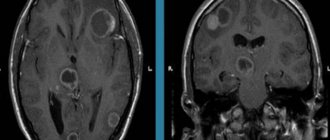
- MRI of the brain is clear - the results of tomographic diagnostics will show the localization of the pathology and the catalyst for the disorders (infants may be prescribed neurosonography instead of MRI);
- puncture - children are tested using general anesthesia;
- fundus examination.
At the initial stages of the development of the process, an accurate diagnosis can only be made using instrumental methods.
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus in adults
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose hydrocephalus using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. These methods make it possible to determine the size and shape of the ventricles, brain cisterns, and subarachnoid space. If doctors at a neurology clinic detect early signs of hydrocephalus on an MRI, they prescribe medication to stop the progression of the disease. X-ray of the cisterns at the base of the brain allows us to clarify the type of hydrocephalus and assess the direction of the cerebrospinal fluid flow.
A trial diagnostic lumbar puncture with removal of 30-50 ml of cerebrospinal fluid is carried out to diagnose the disease. After the procedure, the patient’s condition temporarily improves due to the restoration of blood supply to ischemic brain tissue against the background of a decrease in intracranial pressure. In acute hydrocephalus, lumbar puncture is not performed due to the high risk of brainstem herniation and the development of dislocation syndrome.
To clarify the diagnosis, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe craniography, ultrasound, and angiography. The results of the examination are discussed at a meeting of the expert council, where tactics for managing a patient with hydrocephalus are developed.
What is the danger of the disease?
The consequences of dropsy largely depend on the age at which the disorders occurred and the development of complications:
- Infants experience high excitability, sleep disturbances, and increased muscle tone. The most severe manifestation is developmental delay and mental deviations.
- Preschoolers show aggression, stutter, develop strabismus, and experience developmental delays.
- School-age children experience memory loss and headaches. The learning process is difficult.
- In adults, epilepsy, increased excitability, and hallucinations appear.
The danger of the disease in adulthood is the development of mental disorders, motor functions and motor skills. If urgent measures are not taken, the patient becomes disabled.
Prevention and consequences of hydrocephalus
The prognosis for this disease is difficult to determine. It largely depends on how early treatment is started and the extent of irreversible brain damage.
The consequences of hydrocephalus include delayed physical and mental development. However, with the right rehabilitation program, many children with this diagnosis can lead normal lives with minor limitations.
With a progressive form of pathology, the prognosis is unfavorable.
On the other hand, even bypass surgery is not always accompanied by complete recovery. The factors on which this depends have not been fully established.
Therefore, disease prevention is important:
- if necessary, genetic counseling for expectant mothers;
- protection against infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- prevention of traumatic brain and birth injuries;
- vaccination against pneumococcus, which protects against meningitis;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases causing hydrocephalus in adults.
How to treat dropsy?
This brain pathology is practically incurable. Existing medications are designed only to slow down the process.
The most effective treatment method today is surgical, when the patient undergoes bypass surgery or endoscopic surgery.
Massage plays an important role in the treatment of hydrocephalus. Dropsy helps to increase muscle tone, and stroking and rubbing movements have a relaxing effect, helping to restore motor functions.
Another type of treatment, manual therapy, is used as an addition to the use of medications. Manual influence is aimed at activating the human body’s own reserves. The use of manual therapy for secondary dropsy is especially effective.
Recommendations for the use of treatment methods are given by a neurologist or neurosurgeon.
Treatment of hydrocephalus
The option of surgical intervention for hydrocephalus is quite effective. Two types of operations are used: neuroendoscopy or liquor shunting. They are performed by a neurosurgeon, a specialist who can correct problems in the brain or spinal cord, as well as the peripheral nerve ending system.
Bypass surgery
In this type of surgery, a thin tube is inserted into the brain ventricle. Excess cerebrospinal fluid flows through it to another anatomical zone of the body. If the second end of the drainage system is placed in the peritoneum, the shunt is called ventriculoperitoneal. Then the excess cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed by the abdominal cavity and then enters the blood.
When the draining end is directed into the cardiac chamber, the shunt is called ventriculoatrial. This option is practiced during surgery for children, because their increase in height does not affect the functioning of the organ as much, so the drainage does not have to be changed as often as the ventriculoperitoneal system.
Occasionally, lumboperitoneal shunts are also used. With the help of such drainage, cerebrospinal fluid is drained from the lumbar region into the peritoneal cavity.
Any drainage system contains a valve that is set to a certain capacity. It is selected for a specific patient, taking into account the patient’s cerebrospinal fluid pressure. The doctor performing the surgery determines these values in advance by installing a suitable valve, which then looks like a “bump” protruding under the skin on the head.
Currently, neurosurgeons have two types of valves for drainage systems:
- With predefined characteristics that define a specific throughput.
- Adjustable magnetic fixtures. When choosing them, the doctor remotely, using special equipment, without performing additional incisions, changes the pressure in the device to achieve an optimal result. Thanks to this, it is possible to neutralize adverse side effects in the form of insufficient or excessive cerebrospinal fluid pressure.
Bypass surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The procedure lasts 1–2 hours and after it the patient is kept in the hospital for several days. If the outflow through the shunt is disrupted or the patient becomes infected, a repeat procedure is sometimes performed.
Neuroendoscopy
This operation is an excellent alternative to bypass surgery. Without taking steps to install drainage, the neurosurgeon forms a hole directly in the wall of the cerebral ventricle, after which he creates a bypass path from the vessel through which cerebrospinal fluid flows freely to the surface. There it is absorbed by the brain tissue without obstacles.
This procedure is not universal - it cannot be done on all patients, although this method is often used if the natural cerebrospinal fluid pathways are blocked. In this case, the cerebrospinal fluid flows through the created hole, successfully bypassing all blocked vessels.
The endoscopic procedure is done under general anesthesia. First, the neurosurgeon makes a burr hole with a diameter of 1 cm on the skull. Then, using an endoscope, he examines the inside of the cerebral ventricles. Through the internal channel of the instrument, surgical instruments are inserted, which are used to perform an operation inside the brain. When the endoscope reaches the third ventricle, the doctor creates a hole in its lower wall through which the cerebrospinal fluid penetrates into the subarachnoid cavity. After removing the device, first the aponeurosis is sutured, and then the skin on the skull. The duration of the operation is approximately an hour.
The risk of infection with such an intervention is significantly lower than with cerebrospinal fluid bypass. Neuroendoscopy does not have significant advantages over drainage surgery over long periods of patient observation. After such an intervention, hydrocephalus can also develop again after a few years.
Actions for normal pressure hydrocephalus
When normal pressure hydrocephalus (a common occurrence in older people) is diagnosed, the patient's condition can be improved by performing a cerebrospinal fluid shunt. Although surgery is not effective for every patient. Due to the considerable risks that accompany all operations, certain tests are required to assess how much the potential benefit outweighs the risk of negative consequences.
Almost 80% of patients diagnosed with normal pressure hydrocephalus experienced significant improvement after preliminary testing, so ventriculoperitoneal shunting was recommended for them. Significant clinical postoperative improvement occurs after a few weeks, sometimes even months. Only a timely correct diagnosis guarantees successful recovery even with many years of development of hydrocephalus.
Diet
The patient's nutrition should be aimed at improving the water-salt balance. Foods that cause fluid accumulation should be excluded from the diet. Instead, vegetables and fruits, steamed meat, and cereals are introduced into the menu.
It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, exercise with moderate exercise, and walk a lot. Following these recommendations will help maintain the patient's mental and mental fitness.
Dropsy is a serious disease that does not go away on its own. The patient requires qualified specialist assistance for life. The disease is in an advanced stage and cannot be treated.
Classification of the disease
There are three main forms of pathology:
- occlusive hydrocephalus, or internal, is a condition in which fluid does not flow from the ventricles, while the space around the brain is compressed;
- non-occlusive hydrocephalus, or external - fluid can enter from the ventricles into the space between the brain and its membranes, while they expand and compress the nervous tissue from the outside;
- mixed hydrocephalus is a combination of several blocks of cerebrospinal fluid outflow pathways.
External replacement hydrocephalus is a severe form in which the substance of the cerebral cortex atrophies, and excess fluid takes its place. A synonym for this condition is atrophic hydrocephalus.
The disease is also divided depending on its causes into post-traumatic, post-infectious and post-hemorrhagic forms. Hydrocephalus can be progressive (active) or chronic (compensated). It is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure.
Which doctor should I contact?
Hydrops is treated by neurosurgeons. When you contact the RAS clinic in Moscow, you will be provided with qualified, effective assistance: they will conduct an examination, prescribe tests, make a diagnosis, and determine an effective treatment strategy.
If any symptoms of neurological diseases appear, you must immediately make an appointment with a neurologist to prevent the situation from worsening. We invite you to a consultation with a neurologist in Moscow at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Registration can be made by phone or using the feedback form on the website.
Liquor shunt interventions
CSF shunting is the installation of elastic silicone implant systems to remove cerebrospinal fluid outside the central nervous system. The systems are equipped with catheters in the form of flexible hollow tubes, as well as valves with an anti-siphon (reverse) mechanism and with fixed or adjustable opening pressure.
The operation can be performed in various ways. But surgeons consider ventriculoperitoneal (the most commonly used method) or ventriculoatrial shunting to be the most successful in terms of safety. Interventions are performed under endotracheal anesthesia, manipulations are controlled by intraoperative fluoroscopy, CT, and ECG.
- Ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. The principle of the procedure is based on the implantation of silicone catheters, through which an excess of CBF goes into the intra-abdominal cavity, where it is resorbed between the intestinal loops.
- The procedure begins by making an incision on the scalp, after which a small burr hole is created in the skull. The dura mater is opened sparingly.
- A ventricular catheter is introduced through the created access, its end is placed in the lateral ventricle of the brain.
- The valve element is implanted in the area of the auricle (at the back or slightly above). The ventricular (ventricular) and distal catheter (DC) are fixed to it.
- Next, the neurosurgeon places a distal catheter into the abdominal cavity through a specially formed subcutaneous channel.
- Upon reaching the desired abdominal area, the specialist makes a small incision (no more than 10 mm) and inserts the end of the DC into the abdominal cavity.
- The procedure ends with thorough disinfection of the surgical field, followed by closing the wound areas with antiseptic dressings (sutures are applied if necessary).
- Ventriculoatrial shunting. The essence of this operation is to divert cerebrospinal fluid through installed shunts from the ventricle of the brain into the right atrium.
- Dissection of tissue in the neck along the anterior sternocleidomastoid muscle is performed to open the common facial or internal jugular vein.
- The atrial catheter is removed into one of the indicated veins, fixing it with specially designed ligatures.
- The shunt is directed through the catheterized vein to the right atrium. The end of the atrial shunt is generally located in the superior vena cava.
- For the installation area of the distal end of the vascular catheter, yes, the superior vena cava is often preferred. Here the blood flow is turbulent, and this reduces the likelihood of thrombosis of the drainage system by blood clots.
- The cranial part of the intervention, when the ventricular element of the system is implanted, a valve and two catheters are connected to it, is identical to VP shunting.
For adults, shunts are permanently implanted. In childhood, they are periodically replaced with elongated models. We emphasize that patients after surgery with shunt implantation are shunt-dependent people.
Treatment in the elderly
In the presence of increased intracranial pressure, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe diacarb, mannitol and mannitol to older people in combination with furosemide or lasix. These drugs have a diuretic effect, removing excess fluid from the body. Diacarb temporarily blocks the production of cerebrospinal fluid. To correct potassium levels in the body, use asparkam or panangin. Nutrition of brain tissue in elderly patients improves after using Cavinton, Actovegin, Cerebrolysin, and Semax.
A radical treatment method that affects the cause of hydrocephalus is surgery. Shunting is most effective for the occlusive form of the disease. External drainage operations involve removing the cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles from the outside. They are accompanied by complications, so they are rarely used. The priority direction in neurosurgery for hydrocephalus is endoscopic interventions.
Neurosurgeons at partner clinics of the Yusupov Hospital perform the following endoscopic operations on elderly people:
- aqueductoplasty;
- endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the floor of the third ventricle;
- removal of intraventricular brain tumor;
- septostomy;
- endoscopic installation of a shunt system.
After the operation, the patient's condition improves, and neurological symptoms reverse. Elderly people with hydrocephalus restore their ability to self-care and adapt to social life.
If there are signs of hydrocephalus in an elderly person, call the Yusupov Hospital, where neurologists, using modern diagnostic methods, identify the cause and severity of the disease, concomitant pathologies and prescribe individual treatment. Neurosurgeons perform minimally invasive operations aimed at restoring the physiological flow of cerebrospinal fluid. After treatment, the quality of life of older people suffering from hydrocephalus improves significantly.