In this article we will look at different types of examination of the human brain. We will tell you what this or that scanning procedure allows you to study in the human body.
Depending on the reason why a person turned to a qualified specialist for a brain examination, various techniques are used, the most popular of which we will consider below in this article.
Echoencephalography
Echoencephalography, or, as it is also called, EchoEG, is a unique method in the field of ultrasound diagnostics aimed at analyzing brain pathologies.
The echoencephalography procedure involves recording ultrasound signals reflected from the brain, the results of which are clearly displayed on the device’s display.
In general, the EchoEG procedure gives a clear and reasonable reasoning about the presence, extent and displacement of all brain structures in the case of traumatic brain injury or tumor.
It should be noted that the echoencephalography procedure is simple, harmless and does not require specialized training.
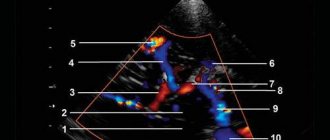
Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels
Another extremely effective operation is Doppler ultrasound, or, as it is also called for short, the Doppler ultrasound procedure.
It is necessary for a correct assessment of blood flow in the area of large and medium-sized vessels of the neck and head.
In addition, the USDG procedure is used to monitor the general condition of the patient, as well as to identify initial pathologies in the vascular bed.
The ultrasound examination procedure in most cases has no contraindications, and it is also painless. In addition, it is performed on an outpatient basis and does not require special preparation.
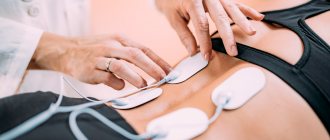
REG of cerebral vessels
REG, or, as it is otherwise called, Rheoencephalography, is another way to examine the vessels in the brain area for its functional state.
Rheoencephalography is based on recording all changes in the total or partial electrical resistance of living tissues.
This method of studying the brain is determined by pulse fluctuations of its vessels. In fact, the REG procedure is a very promising method for treating injuries and brain tumors of varying severity, as well as epilepsy and migraine. The method is also prescribed as a research method for fetal hemodynamics.
The examination takes place using a special multi-channel device called a rheograph. Of course, the greater the number of channels, the larger the area under study.
What does the REG procedure look like step by step:
- The patient being studied is placed on the couch;
- Metal plates are placed on his head, which are pre-treated with gel;
- The plates are also attached with a special rubber band where it is necessary to assess the general condition of the vessels.
CT head with contrast
Also prescribed for strokes (depending on indications). The advantage of contrast is a more accurate assessment of soft tissue and vascular bed.
Brain tumors are visualized much better with contrast than without it. In areas where malignant tumors are localized, blood circulation is more or, conversely, less intense, which affects the distribution and accumulation of the contrast agent, that is, the “staining” of tumors on CT scans.
Benign tumors on CT with contrast are homogeneous. Oncology is characterized by alternation of foci of more and less high density, signs of necrosis. Tumors are described in medical classifications and have their own characteristics. For example, a benign hemangioma has a round shape and high density (about 50).
Malignant tumors of the brain and skull bones detected on CT include: astrocytomas, gliomas, osteomas. The most common benign neoplasms detected on CT scans with contrast include hemangiomas and cysts.
In other words, when studying soft tissues, blood vessels, as well as for oncological alertness, preference is given to CT with contrast.
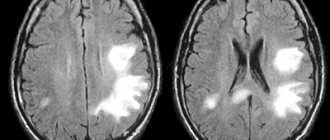
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, allows you to fully diagnose the location and nature of lesions, as well as accurately determine the direction of blood in different parts of the brain.
In addition, this examination of the brain using magnetic resonance imaging brings quite good results in the case of vascular diseases.
For example, if a person gets sick with cerebral atherosclerosis. In addition, magnetic resonance imaging is of great help in the case of a critical period of stroke, since this particular procedure is capable of detecting thromboembolic infarction, as well as ischemic patterns of blood circulation.
How does the procedure work?
MRI examination is completely painless. Immediately before the procedure, you must remove any metal items from yourself. The patient lies down on the tomograph couch, which is placed inside the device.
Brain MRI procedure
Before carrying out the procedure you need to know the following:
- High-resolution (high-field) magnetic resonance imaging scanners create a fairly high noise level. At our center, patients are provided with headphones to reduce discomfort from these sounds;
- the doctor conducting the study always remains in touch with the patient, the patient has an alarm button;
- The patient must remain absolutely still throughout the procedure to avoid motion artifacts.
The duration of an MRI of the brain is usually about 15 minutes. If you plan to use a contrast agent, the study will take a little longer - about 30 minutes.
Magnetic resonance angiography
In addition to magnetic resonance imaging, which is known to everyone, there is also another procedure, magnetic resonance angiography.
Today, it is one of the most promising methods among all types of vascular bed diagnostics. In addition, magnetic resonance angiography does not require arterial puncture.
In the process of conducting magnetic resonance angiography, a qualified specialist is given a unique opportunity not only to diagnose the brain, but also to examine all possible structural and pathological changes in the vascular brain, as well as to competently and most accurately assess the physicochemical and pathophysiological processes of both the entire brain and and its shells and individual structures.
In addition to all of the above, this procedure for examining the brain helps to build a three-dimensional reconstruction of the vascular network, obtain thin sections and isolate individual trunks and nerve vessels.
Today, magnetic resonance angiography has gradually moved to its honorable first place among all types of brain diagnostics.
Contraindications for MRI
Despite its high safety, MRI also has a number of contraindications.
Absolute contraindications include:
- the presence in the body of implants, pins, brackets made of magnetic metal;
- presence of a pacemaker, neurostimulator;
- weight exceeding the technical specifications of the tomograph;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- inability to remain still due to neurological or psychiatric diseases.
Relative contraindications are:
- second and third trimester of pregnancy;
- children under 5 years of age;
- fear of being in a confined space.
If contrast agents are used during the procedure, the following may be contraindications:
- renal failure;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- allergy to contrast agents used.
If there are objective restrictions on magnetic resonance imaging, the patient may be prescribed other types of diagnostics that do not have the above restrictions.
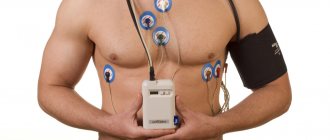
Electroencephalography
EEG, or, as it is also called, Electroencephalography, is a specialized recording of all, even the most insignificant, fluctuations in brain potentials, which are very simply recorded using a special device - an electroencephalograph.
The procedure goes approximately as follows: all electrical potentials of the brain are removed using special, controlled electrodes. And all the results of the procedure are recorded on paper or on a monitor. Electroencephalography is performed in case of delayed psycho-speech development, as well as in the case of a person having epileptic seizures or injuries.
In addition, modern equipment equipped with the latest technology allows for detailed EEG monitoring, that is, a long-term recording of all biocurrents in epileptics.
Neurosonography
Another brain examination procedure is neurosonography, which is aimed at examining the head of young children for the presence or absence of an overly open fontanel. It is through this very enlarged fontanel that the dimensions of the liquor-conducting system are examined with the help of ultrasonic sensors, to determine the optimal parameters of blood flow and the structure of the brain.
This method is very informative and, of course, safe. In addition, it allows the effectiveness and reliability of treatment to be assessed at the optimal time and during follow-up. Neurosonography also helps to identify any pathologies in children.
Methods for diagnosing brain diseases
The quality of our life depends on many nuances of the state of the body. The most important of these is the functioning of our brain. Stress, depression, poor ecology are constant companions of almost every inhabitant of the Earth, so many diseases, including brain diseases, are much more common than a hundred years ago. In addition, diseases are “getting younger” and are observed in a huge number of adolescents and even children. Sometimes we no longer pay attention to the symptoms, get used to frequent headaches, ignore dizziness, try once again not to “listen” to our feelings, and mindlessly take pills. It is important not to numb the pain with medications, but to understand the cause by examining the brain for the presence of structural and functional disorders. Maria Yuryevna Alekseeva , a functional diagnostics doctor, a doctor of the highest category, told how to do this
If you have any complaints, you should immediately consult a doctor. It will help determine the necessary path of examination. But, there are a number of studies that can be done before the consultation to save time. I would like to remind you a little about such diagnostic techniques as EEG, REG and ECHO-EG.
All of them are screening tests, as they have a number of positive properties: painless, harmless, without age restrictions, low cost, quick, and informative. With the results of these studies, the specialist will have a more complete picture of what is happening in your body.
What is EEG?
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method for studying the functioning of the brain, based on recording its electrical activity. Brain activity can be normal and pathological. So, when recording an EEG, we provide a description of normal brain activity taking into account age-related assessment criteria, and also indicate the presence or absence of pathological activity, which includes epileptic activity.
What are the indications for an electroencephalogram?
Mainly it is the diagnosis of epilepsy.
It can also be any complaints about the head (headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, loss of consciousness, panic attacks), seizures, any sleep disorders, a constant feeling of fatigue.
EEG is prescribed for various brain diseases: traumatic brain injuries, meningitis, encephalitis, strokes, brain tumors, autism, speech disorders, delayed psychomotor development, tics, neuroses, Down syndrome, cerebral palsy, vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In addition, EEG allows you to observe the dynamics of the disease, adjust treatment methods and evaluate the effect of drugs. It is also included in the screening program when passing a medical examination.
Is EEG performed on children?
This examination is very common in childhood, since the onset of many diseases of the nervous system occurs in children. Even for an infant, this technique is completely safe and does not harm health. Thanks to a timely EEG, it is often possible to defeat a serious illness at the earliest stages of its development.
How is the procedure performed?
No special preparation is needed, the procedure will not take much time and will not cause any discomfort. A special cap is placed on the head, to which electrodes are attached. Before applying them, the electrodes are moistened with a special gel so that the contact with the scalp is more dense.
The procedure lasts approximately 15-20 minutes. When recording an EEG, functional tests are usually carried out, “provocations” of hidden pathological conditions, convulsive attacks: photostimulation (light flashes at different frequencies), hyperventilation (deep breathing). These are different types of stress for the brain, which help to identify violations of its functioning.
What is REG? What is the essence of the method?
Rheoencephalography is a study of cerebral circulation, namely the functional state of blood vessels, their walls (tone), how they (quickly or not) fill with blood, venous outflow. The reaction of blood vessels to turning and tilting the head and holding the breath is also assessed. The procedure is based on recording the electrical resistance of brain tissue.
What are the indications for the procedure?
This study has wide application in childhood. After all, vascular disorders, unfortunately, are often found in modern children.
Rheoencephalography is advisable to use in the diagnosis of cerebrovascular pathology of a functional nature (vegetative-vascular dystonia, migraine), in atherosclerosis, acute and chronic cerebrovascular disorders, as well as in assessing the effectiveness of certain medications and non-drug treatment methods. REG studies are highly informative in identifying the effect on cerebral vessels in pathologies of the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, spondylitis, consequences of injury, etc.).
REG can be prescribed both for diagnostic purposes and routinely, since it is absolutely safe. This is especially true for mature and elderly patients, since over time the characteristics of blood vessels only worsen, and any pathology is best recognized in advance.
How is the examination carried out?
REG does not require special training. In general, the procedure is similar to an EEG: electrodes are installed on the patient’s head and connected to a machine that records the results. The whole procedure lasts 5-10 minutes.
What are the advantages of REG?
There is an opinion that REG research has been used for quite a long time and can be considered obsolete, especially with the advent of ultrasound and tomographic techniques. However, the simple conditions for the procedure and its painlessness for the patient are the main advantages of REG. At the same time, the device takes readings about the work of arteries and veins separately, which simplifies diagnosis at any stage of the disease.
Magnetic resonance and computed tomography, as well as Doppler ultrasound, are more detailed, but not as accessible to the public. In addition, there are categories of patients who need to undergo such research regularly, for example, during the postoperative period.
REG in childhood is especially relevant, since sitting in a rubber cap for 5 minutes in the presence of parents is much easier for a child than being alone inside a huge humming device (tomograph). Therefore, doctors do not stop turning to rheoencephalography.
What is ECHO-EG of the brain?
Echo-EG of the brain (ECHO-ES or Echoencephalography) is a method of one-dimensional ultrasound diagnosis of the brain followed by computer processing.
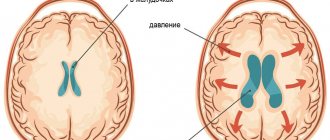
ECHO-EG reveals displacement of the midline structures of the brain, which occurs due to head injuries or neoplasms. The midline structures include the ventricles of the brain (these are natural cavities between the hemispheres). In case of pathological processes on the right or left, they shift to the healthy side.
This method also helps in diagnosing increased intracranial pressure.
In what cases should an ECHO-EG be done?
Mainly traumatic brain injuries.
Also, ECHO-EG is indicated:
- for severe regular headaches,
- general weakness, the causes of which are not clear;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- fainting.
In addition, echoencephalography allows you to see indirect signs of increased intracranial pressure.
How is the procedure performed?
No special preparation is required. The doctor places small ultrasound sensors on the patient’s head and periodically moves them during the examination. In this case, the patient does not experience any discomfort. It is done very quickly (5-10 minutes), the result is given immediately.
What are the advantages of ECHO-EG?
Echoencephalography is a simple, safe and harmless diagnostic method that has no contraindications or age restrictions. It is especially relevant in patients with contraindications to MRI (for example, an installed pacemaker, or built-in metal structures). Or in early childhood with head injuries, which happen quite often. In such cases, global examinations such as MRI are not always justified, and ECHO-encephalography comes to the rescue.
What are the features of conducting EEG, REG and ECHO-EG at the Center for New Medical Technologies?
To conduct these studies, our Center uses the latest equipment, and modern computer programs are used for analysis. Patients are received by highly qualified specialists by appointment, without queues. We have extensive experience working with children of different ages (including newborns), and with various pathologies. Research results are prepared quickly.
In conclusion, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that, whatever the reason why you or your child needs an EEG, REG or ECHO-EG, after the examination you must consult a neurologist to interpret the results and treatment. Be healthy!
Craniography
Using modern equipment, craniography allows for a quick and painless examination aimed at identifying birth defects and bone fractures.
During craniography, the dose of X-ray radiation is extremely small, and it is selected individually for each person.
Pictures are taken in two projections - in profile projection and in front projection.
The craniography technique includes a number of specialized radiographs, that is:
- Survey direct, axial and lateral radiographs;
- Images in the area of the temporal bones;
- Oblique photographs of orbits;
- Detailed pictures of the sella turcica.
Craniography must be performed in case of injury or disease of the cranial bones, brain and paranasal sinuses.
When is a head CT scan recommended?
A neurologist, traumatologist, surgeon, oncologist, or general practitioner can refer the patient for this examination. But a head CT scan can be done without a doctor’s referral. Tomography is also recommended if the patient is bothered by headaches, dizziness, fainting of unknown etiology after injuries, in particular those received during an accident.
In what situations is it recommended to do a CT scan of the head?
- Traumatic brain injuries. A CT scan will show fractures, hematomas, joint dislocations, and hemorrhages.
- After a stroke or if acute cerebrovascular accident is suspected. In case of hemorrhagic stroke, it is important to exclude hemorrhage in the brain; diagnosis is carried out immediately. The consequences of an ischemic stroke are best assessed after 4-5 hours, since the signs of this type of stroke are visualized later.
- If tumors and brain metastases are suspected. Neoplasms can compress nerve endings and blood vessels; their compression can cause chronic pain and disorders of the central nervous system and vision.
- Before operations and surgical interventions. A CT scan of the head is prescribed before the removal of tumors and cysts, reconstructive operations for injuries and fractures of the skull bones, removal of hernias and cysts of the cervical spine, and some types of operations on the facial bones of the skull (before septoplasty, rhinoplasty, osteotomy).
- After surgery and chemotherapy. Follow-up CT is necessary to monitor treatment results.
- If vascular diseases, malformations, or thrombosis of cerebral vessels are suspected. Blockage of the arteries can cause ischemia, atrophic changes, and poor health.
- Foreign objects. A CT scan of the head will show foreign bodies in the scanned area and traumatic changes. The examination can be performed on patients with internal metal structures and implants.
- With frequent otitis. An ENT doctor may prescribe an examination of the temporal bone and paranasal sinuses.
- Before aesthetic surgeries (rhinoplasty, septoplasty, Olivari surgery).
- In case of disruption of the salivary glands. A CT scan of the neck is prescribed as part of the examination for salivary stone disease (sialolithiasis).
Computed tomography of cerebral vessels
CT scan, or computed tomography, is a detailed examination of the blood vessels in the brain using a special scanning device.
The device allows you to measure the intensity of X-ray radiation flows and their subsequent passage into the brain tissue, thereby allowing you to obtain a visual image of sections in the brain at different levels of horizontal planes.
This procedure is carried out using scanning equipment that makes one full revolution around the head. The step size of the device is 1 degree.
The final collected information is recorded on a personal computer, where calculations are made.
Computed tomography helps to identify any congenital abnormalities and malformations, as well as determine the nature and location of various pathological formations.
Decoding MRI of the brain
You can receive the test result immediately upon completion of the procedure.
It will take the doctor about 15-30 minutes to decipher the results. Recording images is possible both on a disk (it is provided free of charge), and on film or a flash drive, at the request of the patient.
The patient will be given a disc, as well as a doctor’s report, which will describe in detail the anatomical features of the area under study and possible pathological changes.
The resulting conclusion must be provided to the attending physician to determine a further treatment plan.