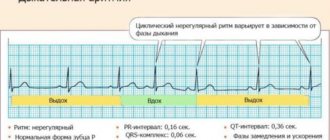
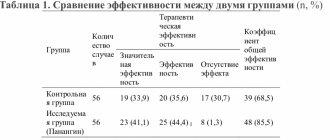
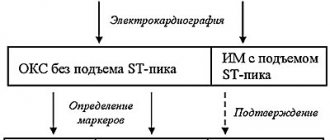
General description of the disease
Tachycardia is an acceleration of the heart rate, which occurs as a reaction to increased body temperature, emotional and physical stress, smoking, alcohol consumption, decreased blood pressure (as a result of bleeding) and hemoglobin levels (for example, with anemia), with increased thyroid function glands, malignant tumors, purulent infection, use of certain medications. Also, tachycardia can be caused by pathology of the heart muscle, disturbances in the electrical conductivity of the heart.
Reasons for the development of tachycardia
- excessive consumption of caffeine-containing products;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (heart disease, ischemia, heart attack, hypertension);
- disease of the thyroid gland and endocrine system;
- infectious diseases;
- pregnancy.
Types of tachycardia
physiological, short-term and pathological tachycardia.
Signs of tachycardia:
darkening in the eyes, pain in the chest, rapid heart rate at rest and without objective reasons, frequent dizziness, repeated loss of consciousness.
Consequences of tachycardia
wear and tear of the heart muscle, heart failure, impaired electrical conductivity of the heart and the rhythm of its work, arrhythmic shock, acute cerebral circulatory failure, thromboembolism of cerebral vessels and pulmonary arteries, ventricular fibrillation.
First aid for tachycardia
The normal heart rate (HR) for a healthy adult is 60–80 beats per minute. To calculate your heart rate, you need to place the index and middle fingers of one hand on the wrist of the other and count the pulse rate for 15 seconds, then multiply the resulting number by 4.
If the heartbeat exceeds 90 beats, tachycardia begins. However, not every attack requires calling a doctor. For example, physiological (natural) causes of increased heart rate go away on their own if the provoking factor is eliminated - reduce physical activity, stabilize the emotional state, quit smoking, etc.
Pathological variants of tachycardia begin for no apparent reason and are accompanied by symptoms of oxygen starvation, decreased blood pressure and a feeling of fear. This condition can stop on its own, but in some cases an attack of tachycardia occurs due to serious pathology (heart or respiratory failure, hypertensive crisis). And then the rhythm of the heart can only be adjusted in the hospital.
Disruption of the normal heart rate (HR) can lead to serious complications such as:
- heart attack;
- stroke;
- acute heart failure;
- thrombophlebitis;
- injuries resulting from fainting.
An attack of tachycardia for no apparent reason requires a visit to the doctor, even if the episode of increased heart rate goes away on its own
What to do during an attack of tachycardia
- 1
Take a horizontal position. This will take the load off the heart and blood vessels. - 2
Release the chest and neck - unfasten the buttons, loosen the collar, remove the tie. Tight clothing restricts breathing, so the pressure needs to be loosened. - 3
Place a pillow under your neck. Throwing back the head can cause circulatory problems, which is unacceptable in conditions of tachycardia. - 4
Provide fresh air flow. When the heart rate increases, the body experiences oxygen starvation, so an open window can alleviate the condition. - 5
Drink a glass of cold water in small sips. Hot drinks, coffee or strong tea are prohibited, and douse yourself with cold water. - 6
Cool your face - for example, place a towel soaked in cold water on your forehead and temple areas. - 7
Perform breathing exercises. A cycle of repeating slow, deep breaths, holding your breath for 5 to 8 seconds, and exhaling slowly can slow your heart rate. - 8
If signs of panic appear, you should take a sedative. - 9
If an attack of tachycardia does not occur for the first time, you should take antiarrhythmic drugs prescribed by your doctor.
For tachycardia at a young age, massage of the neck and back of the head is acceptable. This method is contraindicated for the elderly due to the high risk of heart attack and stroke.
When to call the doctor
If the tachycardia is caused by a serious heart pathology, the first aid measures described above may not be sufficient. If tachycardia does not go away within 15–20 minutes, especially while taking antiarrhythmic drugs, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Other reasons to call a doctor
- Heart rate is 120 beats per minute or higher.
- Intense pain behind the sternum, which is accompanied by pallor, sweating, fear of death and a burning sensation spreading to the left arm, lower jaw or abdomen.
- Tachycardia is accompanied by severe headache and a feeling of numbness in the limbs or half of the face.
- The attack occurred during pregnancy.
Feed your heart right. Rational nutrition for cardiovascular diseases.
Today, heart disease has become a real disaster. But you can prevent and even cure angina pectoris, ischemia, arrhythmia, hypertension, and prevent heart attack and stroke with the help of proper nutrition. Rational nutrition is nutrition that fully satisfies the physiological needs of the body for nutrients and energy, which in turn helps to maintain and strengthen health and prevent diseases.
Nutrition for cardiovascular diseases is based on the following principles: food should be varied, energy consumption should be optimal to maintain ideal weight; the diet should contain a certain amount of nutrients in an optimal ratio (proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, macro- and microelements), taking into account age, gender, climatic and other characteristics; the total fat content in the diet should not exceed 30% of the total energy composition, and the saturated fat content should not exceed a third of all consumed fats; the amount of dietary cholesterol consumed is less than 300 mg/day; the ratio between saturated, mono- and polyunsaturated fats should be 1:1:1; preventive diet; compliance with the diet.
What misconceptions about healthy and unhealthy nutrition do we most often encounter?
Most often, people suffering from cardiovascular diseases believe that a diet that is good for blood vessels, such as the Mediterranean diet, is very expensive, especially now, during a protracted economic crisis. In fact, you can choose products that are good for the heart and blood vessels and are not burdensome on the wallet, even with limited funds. Because the main thing is to eliminate salt and animal fat, switch from expensive lamb, pork, beef, cheese to cheaper and lean chicken, fermented milk products - kefir, cottage cheese. Buying fish doesn't have to be expensive. Vegetables - cabbage, potatoes, zucchini and dried fruits also cost no more than harmful sausages, sausages, baked goods, butter and other products that cause irreparable harm to the entire cardiovascular system.
What dietary restrictions and consumption of healthy foods can be taken to prevent cardiac diseases?
In some cases, we have to enrich the diet with biologically active food additives that compensate for the lack of consumption of certain essential nutrients. Most often these are sources of polyunsaturated acids of the omega-3 family, a number of microelements, such as selenium, and vitamin and mineral complexes. This is necessary for all those who cannot afford to eat sea fish at least twice a week or eat a mostly poor and uniform diet, since these people are at the highest risk of developing a deficiency of much-needed nutrients and associated diseases. In addition, the vast majority of cardiac patients require increased amounts of heart-protective micronutrients. It is important to remember here that for prevention you need to take, for example, at least 200 – 400 mg of omega-3 PUFAs per day.
How does the diet depend on the age and gender of patients?
The older a person gets, the less calories they spend. Firstly, metabolism slows down with age, and secondly, physical activity decreases. Often people do not notice that muscle mass has partially been replaced by fat mass, because the arrow on the scale remains in place. To do this, you need to conduct special studies that will show the ratio of bone, muscle and fat tissue in the body, and adjust the diet based on the results. As a rule, after 50 years you need to reduce your total caloric intake. A lower calorie diet is recommended for women, since energy expenditure in men is initially higher.
How should cardiac patients eat in the summer, in the heat?
Even among cardiologists, there is an opinion that it is necessary to limit fluid, since excess fluid causes swelling and provokes an increase in blood pressure. This is partly true, but there is a mistake here. It is important to limit salt, which retains fluid in the body, not water. Excessive fluid restriction can lead to blood clots. The number of these diseases doubles on hot days precisely because patients drink little fluid. People with diseases of the cardiovascular system need to drink one and a half liters of water daily, and in hot weather - two to two and a half liters. Sometimes sensations can be deceiving; many people mistake thirst for food, overeat, but never get water. Therefore, you need to watch how much you drink. The water should be still. It is worth limiting mineral water to 0.5 liters per day, as it contains a lot of salts that retain water in the body. But you shouldn’t give it up completely, as it contains microelements necessary for the heart.
What is the role of fermented milk products, in particular those enriched with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli?
Microbiocenosis, that is, the totality of all beneficial intestinal bacteria, is of enormous importance for the proper functioning of not only the intestines, but also the heart. Metabolic processes occur daily in the human body, striking in their scale. For example, every day in the human body, about 400 g of protein is normally broken down into amino acids and synthesized again - mainly muscle and blood plasma protein. Many people do not know that there is a so-called muscular-intestinal circulation of amino acids, in which amino acids formed during the natural breakdown of protein enter the intestinal cavity, and are then reabsorbed and used to build new muscle proteins. I would like to remind you that the heart is also a muscular organ in which the same processes of protein self-renewal take place. Therefore, it becomes clear how much the condition of the heart depends on the ability of the intestines to fully perform their work and, not least of all, on the state of the intestinal microflora. If protein breakdown for a long time prevails over its resynthesis, that is, restoration, then gradually this can lead to dysfunction of the muscular system and heart failure. This is especially dangerous if a person has already suffered a myocardial infarction. Intestinal dysbiosis is also dangerous because it is a factor that provokes angina attacks. Accumulated gases cause discomfort and pain, which can reflexively cause coronary spasm and an attack of angina. In addition, the absorption of vitamins, minerals and other beneficial substances depends on the state of the microflora. Therefore, it is imperative to introduce fermented milk products into your diet, preferably additionally enriched with beneficial bacteria. A rational, balanced diet allows for effective prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, and also greatly enhances the therapeutic effect of medications. The diet of patients with heart and vascular diseases should contain a minimum amount of table salt, limited in the content of dietary cholesterol and animal fat, with normal or reduced calorie content. At the same time, the diet of patients should contain a sufficient amount of foods rich in dietary fiber, potassium and magnesium, polyunsaturated fatty acids of the omega-3 and omega-6 families. Such nutrition will slow down the development of atherosclerosis, normalize blood pressure, reduce swelling, shortness of breath, and also reduce the risk of developing such serious complications as myocardial infarction and stroke. The effectiveness of diet therapy has been proven by international and Russian national studies. Some studies have class 1A evidence, that is, highly conclusive. These are studies concerning the effectiveness of consuming fish oil, as well as the effects on the human body of the so-called Mediterranean style of nutrition, which contains large amounts of seafood, fish, vegetables and fruits. These recommendations are approved by the American Heart Association and the European Society of Cardiology, which indicates their high level of evidence.
A balanced diet is a balanced, regular (at least 4 times a day) diet with limited salt intake. Research by scientists has shown that if you limit your salt intake, the risk of myocardial infarction and other heart events can be reduced by 25%. It is very useful to increase the consumption of foods containing potassium and magnesium (seaweed, raisins, beets, apricots, zucchini, pumpkin, buckwheat). All individuals should receive professional advice on food choices and follow a diet that is associated with minimal risk of developing CVD.
General recommendations (determined according to cultural traditions):
- food should be varied, energy consumption should be optimal to maintain ideal weight;
- The consumption of the following foods should be encouraged: fruits and vegetables, whole grains and breads, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, fish;
- consume products containing fish oil and w-omega, which have special protective properties;
- the total fat content should not exceed 30% of the total energy composition, and the saturated fat content should not exceed a third of all fat consumed; the amount of cholesterol consumed should be less than 300 mg/day;
- with an isocaloric diet, saturated fats should be replaced partly with carbohydrates, partly with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats from vegetables and marine animals.
Basic principles of nutrition for cardiovascular diseases:
Diet No. 10 - do's and don'ts
| Can | It is forbidden |
| Dietary salt-free bread, toast, white bread croutons | Fresh bread, pancakes, pancakes, baked goods |
| Vegetable soups with cereals, milk soups | Broths from meat, poultry, fish, mushrooms. Soups with legumes |
| Lean beef, veal, rabbit, chicken, turkey. Boiled or baked without fat | Fatty meat, geese, ducks, offal, sausages, smoked meats, lard and corned beef, canned meat |
| Lean fish and seafood - boiled or steamed | Fatty fish, salted, smoked fish, caviar, canned fish |
| Milk, low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir | Salty and fatty cheese, sour cream, cream |
| Soft-boiled eggs, omelettes. No more than 1 egg per day | Fried eggs, hard-boiled eggs |
| Cereal dishes, pasta made from durum flour | Legumes |
| Boiled and baked vegetables. Raw vegetables rarely and carefully | Pickled, salted vegetables. Radishes, onions, garlic, mushrooms, radishes, green peas, cabbage |
| Fresh ripe fruits and berries, honey, jam, dried fruits | Fiber fruits, chocolate, cakes |
| Weak tea, fruit and vegetable juices | Natural coffee, cocoa, strong tea, alcohol |
| Vegetable oils, occasionally unsalted butter | Cooking fats and margarines, lard |
Head 1st therapeutic department Dedovets E.S.
Prevention of tachycardia
Since tachycardia itself is not a disease, there is no specific prevention for this condition. Primary preventive measures consist of maintaining a healthy lifestyle, daily routine and proper rest - that is, the same as for the prevention of any heart failure.
Secondary preventive measures that should be followed in case of already established heart pathology imply more serious lifestyle adjustments, drug therapy prescribed by a doctor (if necessary, surgical interventions), as well as regular medical examinations.
What foods can you eat if you have tachycardia?
The diet for cardiac tachycardia should be enriched with proteins of animal origin. For this purpose, it is good to include lean varieties of meat and fish in the diet:
- Chicken;
- Turkey;
- A rabbit;
- Pike perch;
- Perch;
- Roach and others.
As for red meat, it is quite acceptable to eat lean beef or pork.
The menu must include milk and fermented milk products, which are easier to digest. They are rich in protein and calcium and at the same time have a moderate calorie content.
Cereals and wholemeal bread should be used as the main sources of carbohydrates. Such foods are digested more slowly than those that contain large quantities of simple sugars. Therefore, they have a more beneficial effect on the digestive system and at the same time have lower calorie content.
In addition, the diet for tachycardia in particular and for cardiac diseases in general involves eating large amounts of vegetables and fruits. If you eat enough of them daily, you can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by almost a third.
MenuRKDC
- Eliminate foods that stimulate the nervous system from your diet. Firstly, there is caffeine and caffeine-containing drinks: cocktails, energy drinks and even all kinds of colas. They increase the heart rate, further loading the heart muscle. Doctors include strong tea, rich broths and dishes containing large amounts of spices as stimulating foods.
- Reduce your intake of animal fat. Fatty foods of animal origin: canned meat, pork, fatty poultry, all types of offal, sausages, smoked meats and lard. They are rich in harmful cholesterol, which is deposited in blood vessels in the form of plaques that can disrupt blood flow, including in the vessels that feed the heart itself. But there is still room on the menu for lean veal, rabbit, chicken and turkey. Boil, steam or bake - any cooking method that does not add additional fat will do.
- Reduce the amount of salt in your diet. This will reduce the amount of fluid that is retained in the body and reduce the load on the heart, which is forced to pump an increased volume of blood. High blood pressure, in particular, develops due to fluid retention. Try to avoid pickles and marinades, and do not buy ready-made sauces, smoked meats and sausages. For the same reason, it is better to avoid fast food, snacks and processed foods, which often have a high salt content.
- Add Omega-3 fatty acids to your diet. These beneficial substances help reduce cholesterol levels in the body, prevent the process of blood clots and lower blood pressure. Omega-3 is most abundant in vegetable oils and fish oil. Experts recommend choosing not too fatty fish and seafood. It is best to boil them, but you can also fry them without fat. But salted, smoked and canned fish are harmful to the heart due to excess salt content.
- Eat small meals. In heart disease, a full stomach and bloating lead to irritation of the autonomic nerves responsible for the functioning of the heart. And this, in turn, leads to interruptions in its work. Doctors believe that 4-5 small meals during the day will be easily digested and will not create additional stress on the nervous, and, therefore, cardiovascular system.
Diet No. 10
| Can | It is forbidden |
| Dietary salt-free bread, toast, white bread croutons | Fresh bread, pancakes, pancakes, muffins |
| Vegetable soups with cereals, milk soups | Broths of meat, poultry, fish, mushrooms, soups with legumes |
| Lean beef, veal, rabbit, chicken, turkey - meat boiled or baked without fat | Fatty meat, geese, ducks, offal, sausages, smoked meats, lard and corned beef, canned meat |
| Lean fish and seafood - boiled or steamed | Fatty fish, salted, smoked fish, caviar, canned fish |
| Milk, low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir | Salty and fatty cheese, sour cream, cream |
| Soft-boiled eggs, omelettes. No more than 1 egg per day! | Fried eggs, hard-boiled eggs |
| Cereal dishes, pasta made from durum flour | Legumes |
| Boiled and baked vegetables, raw vegetables rarely and carefully | Pickled, salted vegetables, radishes, onions, garlic, mushrooms, radishes, green peas, cabbage |
| Fresh ripe fruits and berries, honey, jam, dried fruits | Fiber fruits, chocolate, cakes |
| Weak tea, fruit and vegetable juices | Natural coffee, cocoa, strong tea, alcohol |
| Vegetable oils, occasionally unsalted butter | Cooking fats and margarines, lard |
Potassium is one of the most important microelements for the normal functioning of the human body, especially for the cardiovascular system. The potassium diet is suitable for both an ordinary person who leads a healthy lifestyle and those who suffer from cardiac diseases (hypertension, atherosclerosis, tachycardia) or are trying to lose excess weight. This diet is prescribed even for children who are overweight, and therefore have a greater burden on the heart or have heart problems.
Products for a potassium diet
Among foods rich in potassium, it is worth highlighting dried apricots (apricots), seaweed, prunes, raisins, beans (also contains a large amount of magnesium), baked potatoes and apples, bananas, tea, avocado (contains a lot of magnesium), buckwheat. As you can see, these are mainly vegetables that can be supplemented with leaf salads, mustard, and basil. They, in turn, contain a lot of magnesium, which will bring even more benefits to the body.
While adhering to such a diet, you should stop eating fatty, fried, carbonated drinks, marinades and canned food. It is better to eat sea fish and dietary meat in small quantities. If an adult can even eat a vegetarian diet, then a potassium diet for a child’s heart must necessarily contain meat and fish. You should also reduce your consumption of foods containing a lot of fiber (white cabbage, fresh onions, carrots, sweet corn, bran, white bread, flax seeds). It is very good to consume low-fat fermented milk products.
The most important points of this diet:
- limit salt intake (almost no salt in food)
- reduce fluid intake (1-1.2 liters)
- consume foods containing potassium in natural form.
Why is a potassium diet so beneficial for the heart? With potassium deficiency, salt and liquid are retained in the body, which leads to salt deposits, edema, thirst, high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, and so on. Magnesium is an equally important microelement for the heart, so it is recommended to supplement the potassium diet with foods containing magnesium, which helps to better absorb potassium.
Magnesium is an equally important microelement for the heart, so it is recommended to supplement the potassium diet with foods containing magnesium, which helps to better absorb potassium.
Drinking diet
Water is an important component of nutrition. It is needed for the normal course of all metabolic processes. Therefore, it is necessary that it enters the body in sufficient quantities. However, its excess can increase the volume of circulating blood and increase the load on the heart and blood vessels.
Before moving on to discussing the question of exactly how much water patients with tachycardia need to drink, first you need to decide how to calculate this very volume. The problem is that it is now very popular to consider only pure water, and to recognize the water that is contained in food or, for example, in tea as “inferior”.
In fact, our body does not care at all what kind of water it receives. During the digestion process, any food is broken down into simple components, among which will be that same “pure” water. Therefore, any drinks, soups, fruits - everything that contains water in one form or another should be considered.
Tachycardia as such is not an indication for limiting water intake. Therefore, you can drink it as usual: approximately 2-2.5 liters per day.
If chronic heart failure develops against the background of rapid heartbeat, the amount of fluid should be reduced to 1.5 liters per day.
Some recommend replacing plain water with decoctions and infusions of soothing herbs:
- Valerian;
- Mint;
- Melissa;
- Chamomiles, etc.
This may be useful for people whose attacks of tachycardia are associated with an unstable mental state and are often observed under the slightest stress. If the rapid heartbeat is due to other reasons, then the use of these folk recipes does not make much sense.
In any case, it is better to drink what you like best and not torment yourself with specially “healthy” decoctions.
What fruits and vegetables are good for tachycardia?
People suffering from arrhythmias, including those accompanied by rapid heartbeat, can be recommended to eat almost any vegetables and fruits in large quantities. They are a valuable source of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants, and are therefore very beneficial for the heart and blood vessels.
However, it should be remembered that some fruits and berries are high in sugar and have high calorie content. This:
- Bananas;
- Grape;
- Pomegranate;
- Cherries and sweet cherries;
- Khurma et al.
It is best to include them in your diet in small portions.
Also, you should not “overuse” too exotic fruits. They can cause a severe allergic reaction, which is unnecessary stress for the body. The optimal choice is vegetables and fruits grown directly in the area in which a person lives.
It is believed that nutrition for tachycardia must necessarily include plant foods high in potassium and magnesium:
- Legumes;
- Sea kale;
- Nuts;
- Greenery;
- Beetroot;
- Avocado, etc.
In most cases this is the correct approach. Tachycardia can sometimes develop solely due to a deficiency of these microelements. But it’s better not to start using them “blindly”, but first do an analysis and determine their initial content in the blood.
If it is closer to the lower limit of normal, then vegetables and fruits rich in potassium and magnesium will be very useful. If the indicator is below the threshold values, then it is better to supplement such a diet with potassium and magnesium supplements.
However, there are situations when potassium and magnesium are at the upper limits of the norm and even exceed it. Then such nutrition will be not only useless, but also dangerous.
In general, we can advise you not to “lean” on strictly defined vegetables and fruits, but to adhere to the principle of variety. This approach will definitely not harm the body, and this, as a rule, is quite enough to get the required amount of all useful substances.