In order for the prevention of vascular complications to be effective, everyone needs to know the general symptoms of cardiovascular diseases:
- Burning, sharp, dull or aching pain in the chest . More often occurs during physical, emotional stress, and climate change. Sometimes it radiates to other parts of the body (for example, to the left arm, neck, back).
- Heart rhythm disturbance . Tachycardia (rapid heartbeat) or bradycardia (decreased heart rate) is observed.
- Shortness of breath occurs during physical activity . Indicates excessive stress on the heart muscles and vascular system.
- Swelling . It is observed in the face, arms, lower extremities, and is sometimes accompanied by spider veins on the legs. Swelling usually appears in the evening. They indicate stagnant processes in the vascular system. Prevention of spider veins on the legs should be comprehensive: hardening, compression garments, etc.
- Dizziness and headache may indicate insufficient oxygen supply to the brain. Prevention of vascular diseases of the brain in this case includes taking vasodilating medications that improve blood circulation, for example, Papaverine, Eufillin.
- Changes in blood pressure, weakness, nausea.
Primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Primary prevention of heart disease in men and women is aimed at preventing pathology and creating optimal conditions for the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system. The following factors increase the risk of disease:
- high blood cholesterol;
- increased blood pressure;
- smoking, alcohol;
- poor physical activity;
- excess weight;
- excessive physical and psychological stress.
To minimize the likelihood of developing cardiovascular diseases, the above factors should be eliminated or limited (quit smoking, alcohol, monitor excess weight, etc.).
Diabetes mellitus is an independent risk factor. The incidence of cardiovascular pathologies in patients with diabetes occurs 4-6 times more often than in the general population. Therefore, prevention in such individuals should be mandatory and be based on the correction of arterial hypertension, hypoglycemia, dyslipidemia, and control of the rheological properties of the blood.
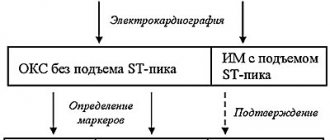
Primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases includes the following diagnostic methods:
- laboratory tests (genetic tests, blood tests for biochemistry);
- instrumental diagnostics (ECG, ultrasound, ultrasound, ABPM, MRI or CT, etc.).
It is recommended to take a referral for a preventive examination from a general practitioner; he will tell you which diagnosis is best to choose, taking into account the patient’s complaints and medical history.
Climatotherapy will help strengthen the cardiovascular system. Dosed use of climatic conditions for health purposes has training, hardening and rehabilitation effects on blood vessels and the heart:
- gelotherapy (sunbathing);
- aerotherapy (air therapy);
- speleotherapy (cave treatment);
- thalassotherapy (the totality of the influence of marine factors on the body: mud, water, algae, etc.).
The nurse's role in the prevention of cardiovascular disease is important. Nurses help:
- overcome barriers for patients to prevent cardiovascular diseases - reluctance to undergo treatment, distrust of traditional medicine, etc.;
- assess the level of knowledge deficit about the prevention and treatment of vascular pathologies in patients;
- conduct surveys of citizens at risk.
In addition, the medical staff carries out:
- conversations on the prevention of cardiovascular diseases;
- distribution of leaflets, leaflets and booklets on the prevention of vascular pathologies;
- screening programs for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases;
- hotline for the prevention and treatment of vascular diseases.
The importance of a healthy lifestyle for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases
A healthy lifestyle plays a decisive role in the primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases, which consists of:
- proper nutrition;
- regular moderate physical activity;
- reducing stress;
- giving up alcohol and smoking.
The role of nutrition in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases
The abundance of fatty, spicy, salty and smoked foods in the diet causes excess weight, high cholesterol in the blood and, as a result, disruption of the cardiovascular system. To prevent cardiovascular diseases, it is not necessary to follow a strict diet; it is enough to limit unhealthy foods and include the following foods in your diet:
- Vegetables, greens, fruits, berries (blueberries, broccoli, pumpkin, pomegranate, spinach, avocado, tomatoes, garlic, olives, etc.).
- Fish (mackerel, trout, salmon, tuna, herring, sardines, etc.).
- Black chocolate.
- Oatmeal, bran, legumes.
- Olive, corn, linseed oil.
- Nuts, dried apricots, almonds.
It is recommended to cook food by steaming, boiling, stewing. Take food often, in small portions. All this will help reduce cholesterol levels by 10-15%, which will improve the condition of blood vessels and prevent atherosclerosis.
Physical education in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Physical education is an integral part of the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. To strengthen the cardiovascular system, improve the body's adaptive abilities and increase the immune system's resistance to adverse factors, physical activity is recommended.
Cardio exercises will help with this to prevent cardiovascular diseases. They speed up the heart rate, saturate the body with oxygen, burn fat deposits, and strengthen the cardiovascular system. These include:
- run;
- intense walking;
- stepping;
- bike;
- jump rope, etc.
If you can’t go to the gym, get off a few stops earlier every day and walk home instead of using the elevator.
Excessively intense physical activity can be harmful to health, especially in the presence of hidden CVDs. Therefore, the prevention of cardiovascular diseases in athletes should be based on regular laboratory and instrumental examinations of blood vessels and the heart (ultrasound, CT, ultrasound, blood tests for biochemistry, etc.).
Major heart and vascular diseases
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels constitute a very large group, so the list below represents only the most basic and common pathologies:
- IHD (coronary heart disease), as well as its complications - heart attack, angina pectoris, cardiosclerosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- congenital and acquired heart defects;
- heart failure;
- infectious and inflammatory pathologies of the heart - endo-, myo-, pericarditis;
- inflammatory vascular pathologies;
- atherosclerosis;
- systemic vascular pathologies;
- bleeding disorders.
Secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases
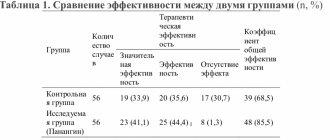
Secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases consists of timely detection of the disease, preventing the progression of an existing disease, disability and improving the patient’s condition. Most diseases require a separate approach.
For example, secondary prevention of heart attack includes timely medical care. If a person once had a heart attack, then in the first aid kit for prevention it is necessary to have nitroglycerin or aspirin to prevent sudden cardiac death. In addition, secondary prevention also includes:
- control of blood pressure and cholesterol levels;
- weight normalization;
- to give up smoking;
- physical exercise.
Secondary prevention of cardiac asthma (acute shortness of breath, apnea, facial cyanosis, swelling of the neck veins, tachycardia, cough, high blood pressure) includes taking medications:
- nitroglycerin to dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow;
- diuretics to lower blood pressure;
- narcotic analgesics for severe pain (Omnopon, Morphine).
As well as oxygen inhalation, application of tourniquets to the legs and arms (to create artificial stagnation of blood).
Secondary prevention of vascular dementia (cognitive impairment, epileptic seizures, walking impairment, instability, urination disorders, slow reaction, narrowing the range of interests, etc.) consists of taking drugs from different groups:
- neurotrophic (Cerebrolysin);
- nootropics (Piracetam);
- antioxidants (vitamins E, C, flavonoids);
- neuropeptides (Actovegin, etc.).
Secondary prevention of vegetative-vascular dystonia (panic attacks, changes in blood pressure, lack of oxygen, facial redness or pallor, muscle stiffness, etc.) includes taking sedatives (Fitosed, Barboval), drugs that improve metabolism in brain tissue (Cavinton); stabilization of emotional health (psychological trainings, auto-trainings, etc.).
European recommendations for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases:
- monitor your blood pressure (systolic blood pressure below 140 mmHg;
- stop using tobacco products;
- walk about 3 km a day or do 30 minutes of moderate physical activity;
- maintain blood cholesterol levels no higher than 5 mmol/l;
- eat foods low in cholesterol, salt and sodium;
- Eat at least 5 fruits and vegetables daily.
Physical activity to prevent heart disease
Modern man is becoming less and less mobile: work, thanks to the automation of processes, requires less and less effort, transportation takes him to his place of work, even laundry, washing dishes, turning on the TV no longer require real physical activity. Sedentary weekdays flow into similar weekends spent watching TV. This lifestyle contributes to excess weight gain and poor blood circulation in the tissues. In order to avoid developing heart disease, you need to increase physical activity. The best solution would be reasonable exercise in the fresh air - walking, Nordic walking, skiing, cycling. Cardio exercises in the gym (exercise bike, treadmill) are also useful. Swimming and gymnastics have proven themselves well.
An important condition for such physical activity: it should not be excessive and should not provoke overwork.
At the same time, it is important that the loads be regular: it is much better to walk 2-3 km every day, that is, half an hour, than to arrange a grueling two-hour session in the gym.
Prevention of cardiovascular diseases in children
Prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system in children is to improve the body's defenses. Various vitamin complexes will help strengthen the immune system:
- Directs – helps stabilize blood pressure, normalize cholesterol in the blood, improve heart function;
- Duovit – improves cellular metabolism, regulates the tone of the heart muscle, strengthens blood vessels;
- Doppelhertz Kinder - improves the functioning of the heart muscle, reduces the likelihood of diseases.
Other measures to prevent cardiovascular disease in children:
- Balanced diet.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Body weight control.
- Limiting negative emotions.
Prevention of heart disease with folk remedies
You can improve your cardiovascular system using folk remedies. Plants such as mint and fennel have a vasodilating and antispasmodic effect. Brew the fruits of these plants as tea and take once a day.
Motherwort, lemon balm, and hawthorn have sedative (calming) properties. Pour 1 tbsp. ground fruits of the plant with a glass of boiling water and take it as a tea decoction once a day.
Green tea will help reduce cholesterol levels in the blood. Its use also maintains the elasticity of blood vessels, tones the heart muscles and stops the overall aging of the body. To prevent cardiovascular diseases, it is recommended to take it in dosage, no more than 2 times a day, because green tea is rich in caffeine, which can cause insomnia and excessive excitability of the nervous system.
Treatment
Treatment methods for heart disease:
- Conservative (integrated approach) - the patient is prescribed a special diet, prescribed medication, and lifestyle adjustments. Therapeutic courses are also used in sanatoriums.
- Surgical – if the conservative method is ineffective or unacceptable. During the operation, the heart valves and blood vessels are replaced, and various types of organ damage are eliminated.
To avoid long-term treatment for heart disease or complex, expensive surgery, prevention is necessary. This should not become a periodic set of events, but an integral part of life.
Memo for the population on the prevention of cardiovascular diseases
- Balanced diet. Reduce your intake of fried foods, fatty foods, coffee, salt and sugar. Add as much fresh vegetables and fruits, sea fish, lean poultry, and whole grain cereals as possible.
- Body weight control. If you become overweight, stick to a low-calorie diet and exercise.
- Fighting physical inactivity. Play sports under the supervision of experienced instructors, walk in the park or forest. If possible, avoid traveling by car and use the elevator less often.
- Rejection of bad habits. Get rid of alcohol, tobacco and drug addiction on your own or with the help of special treatment.
- Protection from stress. Respond adequately to problems and minor issues, communicate more with friends, engage in your favorite hobby, and maintain a work-rest schedule. If necessary, use herbal sedatives.
- Self-monitoring of blood pressure. Measure your blood pressure regularly if you are at risk for developing cardiovascular disease. If alarming symptoms occur, take prescribed antihypertensive medications.
- Regular preventive examinations. Visit your doctor in a timely manner, undergo preventive examinations and take the necessary tests.
- Cholesterol control. If you are over 30 years old, get a blood test every year to check your cholesterol levels.
- Constant control of blood sugar. Upon reaching 40-45 years old, take a blood sugar test every year.
- Prophylactic use of blood thinning medications. Patients at risk should take blood thinners prescribed by their cardiologist.