A heart attack occurs when the blood supply to the heart is suddenly blocked by a blood clot. Many people recover fully from a heart attack, but there is a serious risk that the heart may stop beating - cardiac arrest. It is very important to provide prompt first aid in case of a heart attack. People with angina are more likely to have a heart attack. It occurs when the arteries leading to the heart become narrow and the heart muscle cannot receive enough blood. It can occur not only during physical activity, but also during a period of rest (a more dangerous condition). Heart pain is usually a tight chest pain that may improve if you calm down and take angina medicine right away. It may only last a few minutes. If the pain lasts longer, a heart attack develops.
What is a heart attack?
A heart attack is commonly referred to as a myocardial infarction.
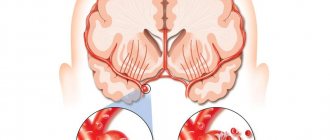
This condition develops when blood flow in the vessels supplying the heart muscle is impaired. For example, due to a sharp spasm or blockage of blood vessels with a blood clot or accumulation of cholesterol. From a lack of oxygen, a section of the heart muscle begins to die. This causes chest pain and cardiac dysfunction. Myths about heart disease
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. However, myths about cardiovascular disease persist. Test your own knowledge.
Heart attack in a woman: features of assistance
Before menopause, women are practically not susceptible to cardiovascular disasters (the hormonal background with the predominance of estrogen protects blood vessels from the formation of atherosclerotic plaques). After 50 years, a sharp decrease in the concentration of steroid hormones increases the risk of developing myocardial infarction.
This category of patients is characterized by precursors of the development of a heart attack, which may bother you for 1-2 months:
- sleep disorders, snoring, sleep apnea;
- causeless fatigue, sudden loss of strength, headaches, anxiety;
- progression of periodontal disease;
- shortness of breath, annoying dry cough, swelling of the lower extremities;
- frequent urge to urinate at night;
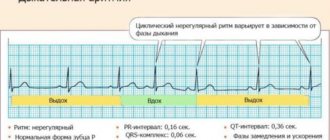
- manifestation of various paroxysmal heart rhythm disturbances.
Instead of the traditional clinical picture, women often develop atypical variants of a heart attack. Symptoms can simulate an exacerbation of gastrointestinal pathology (gastritis, ulcers, pancreatitis, cholecystitis), obstructive pulmonary diseases (bronchial asthma), and cerebrovascular accidents. A high pain threshold and atypical onset make timely diagnosis and treatment difficult.
The difference between a heart attack is the lack of correlation between the extent of myocardial ischemia and the severity of pain, the addition of various arrhythmias, and the gradual progression of the condition.
The care algorithm is identical to that for men, but the doctor should take into account the greater risk of sudden death and fatal complications in the acute period.
How dangerous is a heart attack?
Heart attacks often lead to cardiac arrest
.
At the same time, a person with a heart attack has very little chance of surviving without qualified care in a hospital. That is why, if symptoms of a heart attack develop, you should immediately
call an ambulance, even if the person himself thinks that nothing serious is happening.
Even minor discomfort in the chest can be symptoms of a developing myocardial infarction. Up to a third of heart attacks are not accompanied by severe pain, and people notice heart problems too late
. In addition, women tend to underestimate discomfort in the chest. According to the observations of doctors, even in the hospital emergency room they rarely complain of pain during a heart attack.
First aid and self-help for a heart attack
A heart attack is a serious pathological condition caused by an acute lack of blood supply to the heart muscle with the subsequent development of death of a section of this muscle. Necrosis
heart muscle is called myocardial infarction.
The most common symptoms of a heart attack are:
- Localization: in the chest area (behind the sternum), pain can radiate to the left arm to the forearm, hand, left shoulder blade, left half of the neck and lower jaw, as well as to both shoulders, both arms, upper abdomen
- Nature of pain: pressing, squeezing, burning or aching intense pain
- Stitching, cutting, aching pains that intensify with changes in body position or when breathing are not characteristic of a true heart attack
- Pain is usually accompanied by shortness of breath, weakness, severe sweating
- Duration of pain more than 5 minutes
What should you do if you have a heart attack?
- Sit (preferably in a chair with armrests) or lie in bed with the head of the bed raised
- Free your neck and provide fresh air (open the vents or window)
- Take 0.25 g of aspirin (chew the tablet, swallow) and 0.5 mg of nitroglycerin (put the tablet/capsule under the tongue, first bite the capsule, do not swallow)
- If, after taking nitroglycerin, severe weakness, sweating, shortness of breath, or a sharp headache appears, then you need to lie down, raise your legs (on a bolster, pillow, etc.), drink 1 glass of water and then you should not take any more nitroglycerin
- If after taking aspirin and nitroglycerin the pain has completely disappeared and the condition has improved, you need to call a doctor at home
- If the pain persists, it is necessary to take nitroglycerin a second time and urgently call an ambulance
- If pain persists 10 minutes after taking the second dose of nitroglycerin, it is necessary to take nitroglycerin for the third time.
ATTENTION! If nitroglycerin or aspirin is not available and the pain persists for more than 5 minutes, call an ambulance immediately.
- A patient with a heart attack is strictly prohibited from standing, walking, smoking or eating until specifically authorized by a doctor.
- Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is contraindicated if you are intolerant to the drug (allergic reactions in the past), or if you have already taken it that day, as well as with a clear exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers
- You should not take nitroglycerin if you have low blood pressure, severe weakness, sweating, as well as severe headache, dizziness, acute impairment of vision, speech or coordination of movements.
- If you have been diagnosed with coronary heart disease or, according to your doctor, you have an increased risk of developing a heart attack, you need to be well aware of the rules of first aid for a heart attack and always have aspirin and nitroglycerin in your pocket
How to give first aid to yourself?
There are different situations in life. What to do if a person cannot seek help, finding himself alone with a heart attack, when it is impossible to reach the phone to call an ambulance, and there is no medicine nearby?
In the event of a heart attack, you cannot waste precious time and you must start... coughing! And as strong as possible!
Before coughing, be sure to take a deep breath. The cough should be deep, “chest”.
The frequency of “inhale-cough” is approximately every 2 seconds. You should do this until you feel a little better so that you can take medicine, if you have one, and call a doctor.
The mechanism of action here is very simple. Taking deep breaths brings oxygen to the lungs, and coughing compresses the heart muscle and causes blood to circulate better. This helps the heart restore its normal rhythm.
What else is important to know?
- Keep your heart medications with you, even if you don't consider yourself a heart patient. By the way, a person with heart failure who constantly carries nitroglycerin or valocordin with him is in a better position than someone who considers himself healthy and does not take medications with him
- Learn the rule: heart medications should always be on hand! Keep them in your desk drawer, your nightstand drawer, and your clothing pockets. If you don’t need them personally, they may be useful to someone else who feels ill with their heart in your presence.
- You should always have a phone at hand - landline or mobile. Of course, it’s not a fact that in case of a sudden deterioration in your health you will be able to use it, but still it is at least some kind of safety net
- If you are experiencing severe stress, try to breathe deeply (even if there are no signs of a heart attack)
- If possible, avoid driving
- Take anti-anxiety medications as prescribed by your doctor
Take care of your health!
Valeologist of the prevention department of the healthcare institution “40th GKP” M. Vereshchagina
If you experience discomfort in the chest area, call an ambulance immediately if:
- You are over 40 years old and have one or more risk factors for heart disease: a family history of heart attacks, smoking, obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, high blood cholesterol, diabetes.
- Chest pain can be described as tight, heavy and squeezing.
- The pain is accompanied by weakness, nausea, shortness of breath, sweating, dizziness or fainting.
- The pain radiates to the shoulders, arms, neck or jaw.
- The pain is accompanied by a feeling of despair and doom.
- The pain intensifies within 15-20 minutes.
conclusions
The favorable prognosis after a heart attack is lower in women than in men. With age, the level of estrogen in the blood decreases in the weaker sex, and background pathology (hypertension, diabetes, obesity) is often added. Failure to seek help in a timely manner and attempts at self-medication significantly reduce the effectiveness of therapy and worsen the patient’s quality of life, increasing the degree of disability. Elderly women should be especially attentive to their health, undergo regular medical examinations, and lead an active lifestyle. If two or more warning signs of a heart attack appear, consult a doctor immediately. Timely diagnosed early signs of a heart attack in women and first aid provided in full can save lives.
What to do while waiting for help:
1. Take a sitting or reclining position and relax
.
The greater the load on the heart during a heart attack, the more severe the consequences will be. 2. Unbutton your collar, loosen your belt, ask to open the windows if the room is stuffy. 3. Place a nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue and dissolve it slowly. only take one
before the ambulance arrives , as this medicine can cause a sharp drop in blood pressure in some people.
4. Do not take coffee, alcohol
and other people's “heart” medications. Ethanol, caffeine, and substances found in medications that are not intended for you can be deadly if you have a heart attack.
Algorithm of action in the event of a heart attack
If the above symptoms are observed at any stage of intensity for more than five minutes, you must urgently call an ambulance. During the development of an attack, it is important to provide the patient with rest. Strictly prohibited:
- intake of food and alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- driving a car independently;
- performing any kind of physical activity.
Before the ambulance arrives, you must do the following: record the time of the onset of the attack, measure your pulse, heart rate and blood pressure, take a sitting or lying position, it is important that your head is slightly elevated.
Be sure to open the window and free your neck to allow free access of oxygen. After this, you need to give the patient aspirin - the tablet is chewed and swallowed (important: there should be no allergic reactions or contraindications to the drug). You can take 0.5 milligrams of nitroglycerin (place the tablet under the tongue, inject the spray into the oral cavity, bite the capsule and do not swallow), after taking it you will experience a severe headache, shortness of breath, sweating, severe weakness; to suppress the symptoms, you can drink a glass of water.
If the patient's condition worsens, it is necessary to perform artificial respiration until the ambulance arrives. 15 minutes after taking nitroglycerin, if there is no relief, you should take a second nitroglycerin tablet. The third dose of nitroglycerin is allowed after another 10 minutes - but usually an ambulance arrives before this time.
In our country, up to 80% of deaths occur outside of medical organizations - at home, at work, in the country, in public and other places. Most of them occur suddenly or by the mechanism of sudden death. However, with knowledge of simple first aid techniques on the part of people surrounding a person who finds himself in such a critical condition, as well as everyone’s knowledge of first self-help measures, can in most cases save the patient’s life. In addition, statistics show that many patients themselves (or their relatives) call an emergency doctor late, which delays and reduces the likelihood of rescue.
This leaflet is addressed to almost all people, but especially to patients with cardiovascular diseases, with a high and very high risk of their development and complications, and their relatives and friends, since it is known that often a life-threatening complication, dangerously fatal, can be the first symptom of these diseases.
The leaflet is aimed at preventing and reducing the likelihood of fatal outcomes in life-threatening conditions; it describes clinical symptoms in relation to which one should be especially wary, and provides rational first-aid techniques while waiting for the arrival of an emergency physician.
- FIRST AID FOR HEART ATTACK
characteristic signs (symptoms) of a heart attack (myocardial infarction)
- sudden (paroxysmal) pressing, squeezing, burning, aching pain in the chest (behind the sternum) lasting more than 5 minutes;
- similar pains are often observed in the area of the left shoulder (forearm), left shoulder blade, left half of the neck and lower jaw, both shoulders, both arms, the lower part of the sternum along with the upper abdomen;
- lack of air, shortness of breath, severe weakness, cold sweat, nausea often occur together sometimes followed or preceded by discomfort/pain in the chest
- It is not uncommon for these manifestations of the disease to develop against the background of physical or psycho-emotional stress, but more often with some interval after them.
Uncharacteristic signs that are often confused with a heart attack:
- stabbing, cutting, pulsating, boring, constant aching pain for many hours and not changing its intensity in the heart area or in a specific clearly defined area of the chest
Algorithm of urgent actions:
If you or someone else suddenly has the above characteristic signs of a heart attack, even with weak or moderate intensity, which last more than 5 minutes, do not hesitate, immediately call an ambulance team. Do not wait more than 10 minutes - in such a situation it is life-threatening.
If you have symptoms of a heart attack and there is no way to call an ambulance, then ask someone to take you to the hospital - this is the only right decision. Never drive yourself unless you have no other choice.
In the most optimal scenario, if a heart attack occurs, you must follow the instructions received from your attending physician; if there are no such instructions, then you must act according to the following algorithm:
- Call an emergency medical team.
- Sit (preferably in a chair with armrests) or lie in bed with the head of the bed raised, take 0.25 g of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) (chew the tablet, swallow) and 0.5 mg of nitroglycerin (put the tablet/capsule under the tongue, first bite the capsule, do not swallow); free your neck and provide fresh air (open the vents or windows).
- If after 5-7 minutes. After taking acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) and nitroglycerin, pain persists, you need to take nitroglycerin a second time.
- If pain persists 10 minutes after taking the second dose of nitroglycerin, it is necessary to take nitroglycerin a third time.
- If after the first or subsequent doses of nitroglycerin there is severe weakness, sweating, shortness of breath, you need to lie down, raise your legs (on a bolster, etc.), drink 1 glass of water and then, as with a severe headache, do not take nitroglycerin.
- If the patient has previously taken medications that lower blood cholesterol levels from the statin group (simvastatin, lovastatinfluvastatin, pravastatin, atorvastatin, rosuvoastatin), give the patient his usual daily dose and take the drug with you to the hospital.
Attention! A patient with a heart attack is strictly forbidden to get up, walk, smoke or eat until the doctor’s special permission;
You should not take aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) if you are intolerant to it (allergic reactions), as well as with obvious or worsening peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum;
Nitroglycerin should not be taken if there is severe weakness, sweating, or if there is severe headache, dizziness, or acute impairment of vision, speech, or coordination of movements.