The human brain is the crown of development of human nature, allowing us to develop and transform our own lives in accordance with our goals. We owe most of the body functions responsible for our life to the work of the central nervous system. The human brain is an incredibly complex organ that leads to the coordinated functioning of almost all systems in the body. not to mention the higher nervous activity responsible for cognitive skills and thought processes. Unfortunately, a fast pace and far from the healthiest lifestyle slowly undermine the body, depleting its reserves and compensatory mechanisms. Today, the world faces an acute problem associated not only with high morbidity, but also with disability and even mortality from cardiovascular diseases. Among such diseases, organic brain damage of an ischemic and hemorrhagic nature is in the first place. It is important to note that despite the significant preponderance in the morbidity structure of people in the older age group, namely 45 years and older, organic brain damage can also occur in children.
A brief excursion into the anatomy of the central nervous system
The human brain is a complex organ responsible for the functioning of the entire organism. There is a clear hierarchy in the structure of the brain, which allows the entire body to work effectively. The central nervous system can be divided into several main parts:
- The cerebral cortex is responsible for higher nervous activity, i.e. thought processes, speech, memory, writing, hearing and many other functions.
- Subcortical structures that form the midbrain. The midbrain is responsible for the primary reflex units and the formation of unconditioned reflexes.
- The bridge is a connecting link between all parts of the central nervous system and the cerebral cortex.
- Cerebellum. It is located in the lower occipital part of the head and is responsible for human coordination in space.
- The medulla oblongata connects the brain with the spinal cord and is its continuation. The medulla oblongata contains vital centers: vasomotor and respiratory.
Diagnostics and differential diagnostics
Cerebral arthrosis is a disease for which diagnosis may require a detailed history of the patient.
The medical history is studied and the patient is interviewed about his living conditions and well-being.
But to make an accurate diagnosis, professionals send the patient to undergo the following diagnostic tests:
- CT head;
- diffuse optical tomography;
- MEG (measurement and visualization of magnetic fields);
- two-photon or single-photon emission tomography;
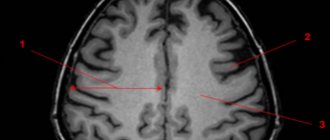
- MRI of the head.
And also in rare cases, differential diagnosis is possible. Having a patient's medical history, using a specially created computer program, a diagnosis can be made by exclusion. Based on the facts and symptoms that appear in the patient, the computer reduces the range of all possible diseases to one.
If it is impossible to carry out a complete diagnosis, a partial differential diagnosis can be made.
What is brain damage?
Organic brain damage is primarily a symptom of a disease, manifested by disruption or loss of a number of functions as a result of the pathogenic effect of some factor on brain tissue. The etiology of brain damage can be very diverse, and this will be discussed in more detail later in the article. Organic damage means that brain cells - neurons - are exposed to a variety of influences, which lead to the formation of dystrophic processes inside neurons and disrupt their functional activity. In the most serious cases, neurons simply undergo first necrobiosis and then necrosis, i.e. are dying. The death of a large number of neurons localized in a single anatomical space leads to the loss of one or another function in the body of the affected person, and the identification of a disturbed function allows specialists to understand in which part of the brain the catastrophe occurred - this is called topical diagnostics. Symptoms of organic brain damage in children manifest themselves differently than in adults, since the full activity of the higher nervous system has not yet been formed. Children may experience delays in mental, mental and physical development, unstable mood and behavioral abnormalities.
Pathogenetic mechanisms of neuronal damage
A number of mechanisms of different nature can lead to organic damage to the brain. This pathological condition can be provoked by both external and internal factors, and this must be taken into account, since therapeutic measures, depending on the pathogenetic type of development of damage to brain neurons, will differ radically.
Violation of energy supply
The most common pathogenetic variant of brain damage is associated with an imbalance between the need of neurons for energy and its entry into the cell. Energy deficiency can develop due to insufficiency:
- Nutrients in the victim's body, for example as a result of hypoglycemia, when there is not enough glucose in the blood;
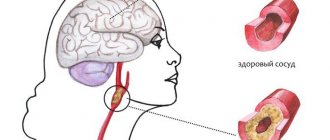
- Oxygen, which causes a condition such as hypoxia. Brain hypoxia causes damage to nervous tissue and often occurs in acute ischemic or hemorrhagic cerebrovascular accidents. In children, brain hypoxia can develop in the antenotal period and during childbirth, which leads to anoxic brain damage in the child.
- When the concentration of potassium, calcium, sodium and chlorine ions increases or, conversely, excessively decreases, transmembrane proteins may malfunction, which also entails energy deficiency inside the cell.
It is worth noting that energy deficiency leads to rapidly progressive damage to brain tissue and within 5-7 minutes, in the absence of sufficient oxygenation, neurons begin to experience acute hypoxia and die. Damage to the blood vessels of the brain has the following symptoms:
- The patient notes memory impairment;
- There is a decrease in vision and hearing;
- The synthetic activity of the brain slows down;
- When performing angiography of cerebral vessels, multiple stenoses of cerebral vessels can be detected;
- MRI of the brain shows dystrophic disorders and a decrease in the volume of the cerebral cortex.
All of the above symptoms are signs of systemic atherosclerosis, which affects most older people. Atherosclerosis leads to the formation of discirculatory encephalopathy.
Traumatic injuries
Injuries are always associated with mechanical damage to the brain and the subsequent development of edema, which leads to an increase in intracranial pressure. Since the brain is located in the cranium and literally floats in the cerebrospinal fluid - intracerebral fluid, the consequences of blows and bruises become serious. Despite. The cerebrospinal fluid plays a protective and shock-absorbing role; with the development of a brain contusion, an increase in intracranial pressure occurs, since the fluid is not physically compressible. Brain cells are exposed to excessive pressure and begin to die. Brain tissues occupy up to 96% of the volume of the cranial cavity, which makes this organ very sensitive to changes in intracranial pressure.
It is very important to note that quite often injuries are accompanied by internal hemorrhage, which can lead to the formation of an extensive hematoma and displacement of the brain. Dislocation of the brain leads to wedging of its subcortical structures into the foramen magnum, which inevitably leads to the death of neurons located in the nuclei of the vasomotor and respiratory centers, without which the life of the victim is impossible.
Infectious
Brain damage can be caused not only by physical factors. But also biological. Conditions such as meningitis, encephalitis, and ventriculitis can significantly impair the functional activity of the brain.
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining of the brain. Etiological factors can be very diverse, so the brain can be affected by many bacterial and viral diseases. Inflammation of the membranes of the brain can occur primarily through direct infection through the wound gate. And secondarily – as a result of an immunodeficiency state.
- Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain tissue itself. Encephalitis is an even more severe infectious disease than meningitis. As a result of encephalitis, purulent melting and liquefaction of areas of the brain can occur, which leads to the formation of persistent disturbances in the functioning of various organs of the victim. With encephalitis, brain damage very often leads to disability or even death.
- Ventriculitis is an inflammation of the integumentary tissues lining the ventricles of the brain. This disease occurs in newborns and infants and leads to increased intracranial pressure and the development of hydrocephalus due to insufficient drainage function of the cerebrospinal fluid.
The brain can be affected by both specific and nonspecific infectious agents; this is important to consider when prescribing treatment, since antibacterial therapy regimens will vary.
Congenital pathology
Anomalies of brain development can form in the very early stages of a child’s development. The first trimester of pregnancy is the most dangerous for the woman and the fetus, since the pregnant woman’s body and the fetus are unprotected from external factors, and at the time of the initiation and formation of organs, the most dangerous anomalies and gross developmental pathologies can form, for example micro or acephaly.
Toxic damage
Not the most common type of brain damage, but nevertheless it does occur. Brain damage occurs if the chemical has neurotoxic properties and is able to cross the blood-brain barrier. Neurotoxic agents lead to organic damage in various parts of the nerve cell; most often, neurons suffer from disruption of the transmembrane transfer of nutrients and disturbances in the synthesis of neurotransmitters. Toxic injuries of varying severity can lead to both persistent encephalopathy and complete loss of some functions of the person affected by intoxication. Most often, gross organic damage to the brain is caused by substances such as arsenic and nitrogen metabolism products, with excessive accumulation of the latter in the blood plasma.
Oncological diseases
Brain damage in oncology can be primary. When a tumor develops directly from brain tissue or secondary - when atypical tumor cells are metastatically introduced into the brain.
Common Causes
At the initial stages of diseases, it is very difficult to detect them, since most of them occur without visible symptoms, or are manifested by minor pain.
The following internal and external causes can lead to the disease:
- severe infections that entered through wounds, insect bites, respiratory tract or blood/lymph from other infected areas of the body;
- trauma to the skull;
- chemical poisoning;
- excessive exposure to radiation;
- adherence to bad habits, systematic intoxication with alcohol, tobacco, drugs or certain medications;
- poor quality of food;
- genetic predisposition to brain destruction;
- congenital disorders.
Types of brain lesions
Brain damage can be either focal or disseminated. Let's figure out what focal brain damage is. This is a condition in which there is a clearly demarcated single focus with necrotic tissue, i.e. This is a local brain lesion. This type of damage often occurs during acute cerebrovascular accident.
Disseminated or multifocal brain damage is a type of injury in which multiple scattered foci of damage to brain tissue are detected. The multifocal form occurs in infectious diseases of the brain, for example, when an infectious agent is introduced hematogenously into the medulla or with an oncological lesion.
When is it time to go to the doctor?
Only a medical specialist can understand what is happening. If discomfort in the head, neck or upper back appears sporadically, for example, when the weather changes, and then disappears without a trace for a long time, there is usually no cause for concern. If you suspect a cold, headache from fatigue, physical or mental stress, just rest. But if you experience the following symptoms, you should definitely go to the doctor:
- previous head injuries with and without complications;
- feverish condition;
- blurred perception;
- muscle tension in the neck or back of the head;
- sudden painful shootings;
- loss of sensation in the arms or legs;
- convulsions;
- problems concentrating your eyes or thoughts;
- bulging of the fontanelle in the newborn period.
Even short-term loss of vision or hearing is also a serious reason for medical intervention.
Treatment tactics
Treatment of organic brain damage can be very diverse and depends on the pathogenetic mechanism of development of the damage and the immediate cause.
Treatment of organic brain damage can be surgical and conservative. For example, the development of high intracranial pressure, which poses a threat to life, can be treated both surgically and conservatively. Surgical treatment - the application of a burr hole for brain decompression is applicable in the formation of a severe hematoma due to trauma or hemorrhagic stroke, and conservative therapy is possible with a moderate increase in intracranial pressure without brain dislocation. For conservative therapy, diuretics are used that cause forced diuresis, allowing for the rapid elimination of edema.
Treatment of cerebral artery atherosclerosis can also be either surgical or conservative. Surgical – angiography with the installation of stents to widen the lumen of the arteries. Conservative – antithrombotic therapy and correction of dyslepidemia.
How to correctly identify the disease?
As soon as a preliminary history is collected, complaints are heard, first assumptions about a possible disease are made, a comprehensive diagnosis is prescribed, which includes the following procedures:
- Laboratory blood analysis.
- Radiography.
- Electroencephalography.
- Angiography.
- MRI of the brain.
- CT scan of the skull or cervical spine.
- MRI of soft tissues of the neck.
The most informative techniques are tomographic sessions. They give a complete picture of the existing changes in tissues and the root cause of the pathology. Even microscopic abnormalities, precancerous stages, and vascular abnormalities clearly appear on scans in one short procedure.
To undergo a full examination at a specialized tomography center, just contact our service, which works free of charge. Choose CT or MRI services, consider offers from different clinics in the city, compare options based on prices, equipment, ratings and other criteria. Here you can remotely consult on existing questions and sign up at your favorite institution with discounts from the service. Contact us, we will be happy to help you.