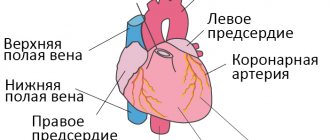
Exudative enteropathy with disaccharidase deficiency is associated with congenital or acquired deficiency of enzymes for the hydrolysis (digestion) of disaccharides - lactase, sucrase, trehalase, etc. Disaccharides - milk sugar (lactose), sugar (sucrose), trihalose (mushrooms). In the future, we will look at this condition using the example of intolerance to milk sugar - lactose, which affects up to 30-70% of the world's population. Russian synonyms for this suffering: lactase deficiency, congenital adult lactase deficiency (with delayed onset), hypolactasia, lactose intolerance, lactase malabsorption.
The enzyme lactase is produced in the small intestine. Lactase digests lactose (milk sugar) from milk and dairy products into simple sugars - glucose and galactose, which are absorbed in the small intestine and enter the blood.
Lactose is the main source of energy in the human body and an activator of the nervous system. 5-6% of the population has a congenital deficiency of the lactase enzyme with normal, intact small intestinal mucosa, associated with a congenital gene mutation. Acquired lactase deficiency occurs when the intestinal mucosa is damaged and its synthetic function is impaired, including the production of lactase.
Insulin, thyroid and glucocorticoid hormones, the state of the autonomic nervous system, and nutritional composition have a great influence on the activity of the lactase enzyme in the small intestine.
If there is a lack of lactase enzyme production in the small intestine, lactose (milk sugar) is not digested, passes further through the small intestine and enters the large intestine. There it is exposed to fermentation processes and the action of colon microflora.
And if the cause of lactase deficiency is in the small intestine, then the clinical manifestations of this condition are noted in the colon. With a lack of lactase, unabsorbed milk sugar (lactose) reaches the colon. Under the influence of anaerobic bacteria, it is broken down to form short-chain acids, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and fatty acids. As a result, along the osmotic gradient, water rushes into the lumen of the colon, which leads to the development of osmotic diarrhea and a decrease in the pH of the stool.
Lactase deficiency - causes
The causes of lactase deficiency in adults may be the following:
- inflammatory bowel diseases of bacterial, viral (rotovirus), parasitic (giardiasis) etiology; for example, a rotovirus penetrates the mature cells of the microvilli of the small intestinal mucosa, destroys and rejects them, the mucosal cells cease to form the enzyme lactase, the dysentery bacillus, entering the intestine, produces toxins, causes inflammation throughout the small intestine, multiplies intensively in the ileum and then passes to the large intestine; Giardia lives in the upper small intestine, attaches to the mucosal villi, multiplies, affects the intestinal wall deeper, and disrupts parietal (membrane digestion) by disrupting enzyme production.
- chronic diseases of the stomach, biliary tract, pancreas,
- operations on the gastrointestinal tract,
- endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hyperparathyroidism),
- Whipple's disease is a rare disease of the small intestine;
- gluten enteropathy (celiac disease), with celiac disease the synthesis of all enzymes is disrupted, including lactase, and lactase deficiency occurs, the manifestations of which are significantly reduced by following a gluten-free diet;
- Crohn's disease is a granulomatous enteritis that affects the entire wall of the small intestine in any part of it. Inflammation develops, then scar tissue, and enzyme synthesis stops; damage to the mucous membrane is based on autoimmune mechanisms;
- food allergy - damage to enterocytes (cells of the mucous membrane of the small intestine), it is called allergoenteropathy, which is based on immunoallergic antigen-antibody complexes, the antigen is the food product, and the body produces antibodies; the antigen-antibody complex in cells causes inflammation, the release of neurotransmitters, which leads to damage to enterocytes, and their ability to secrete lactase is impaired;
- bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine;
- lymphoma of the small intestine.
Causes of ketoacidosis
A number of factors can provoke the development of this condition, among the main ones:
- Disorders associated with injection administration of insulin. This may occur due to incorrect dosage, use of a drug that has expired, or unexpected malfunction of the syringe or pump.
- Wrong choice of therapy by the attending physician. In clinical practice, there are situations when the patient used tableted hypoglycemic drugs, while needing insulin therapy.
- Taking drugs with an effect that is opposite to insulin. Hormones and diuretics can cause high blood sugar levels.
- Associated with an increase in the interval between breakfast, lunch and dinner or an increase in the number of bread units in the diet.
- The use of antipsychotics, which reduce the body's sensitivity to insulin.
- A history of nervous disorders or alcohol dependence, since these diseases may interfere with receiving adequate treatment.
- Use of alternative treatment methods if insulin injections are necessary.
- The presence of concomitant somatic pathologies.
- Traumatization of the pancreas during surgery.
- Pregnancy occurring with severe toxicosis.
In every 4th patient, it is impossible to identify the true cause that served as the trigger for the development of ketoacidosis, since this condition cannot be associated with any of the factors that were listed. An increased need for insulin also occurs due to increased growth of the body, hormonal changes or nervous strain.
Lactase deficiency - symptoms
The severity of clinical manifestations depends on the degree of lactase deficiency, the amount of milk and dairy products, and the severity of the disease, which is recognized as the cause of lactase deficiency. Thus, when consuming more than 200 ml of milk and dairy products, only 5% of people experience pronounced manifestations of intolerance, 10-12% have clinical manifestations only when consuming whole milk, 60-70% of the population suffer from varying degrees of lactase deficiency, 5-10 % can consume milk up to 200 ml and unlimited fermented milk products.
With significant enzymatic deficiency of lactase, approximately 1 to 2 hours after consuming milk or dairy products, a person may develop a complete picture of lactase deficiency:
- heaviness, bloating, rumbling in the stomach, caused by the breakdown of lactose in the colon and the formation of carbon dioxide and hydrogen;
- pain of a bursting nature, due to increased gas formation and distension of the colon and irritation of pain receptors;
- loose frequent stools - copious, watery, light yellow with a sour odor due to the formation of fatty acids, increased osmotic pressure and the attraction of water into the colon;
- nausea, single vomiting.
In addition to intestinal manifestations, general weakness, rapid heartbeat, sweating, and headache may occur.
What to do with ketoacidosis and ketoacidosis coma?
It is important to understand that when this critical condition develops, the patient needs emergency medical care, which can only be provided in a hospital setting. The clinic uses the following areas to stabilize a person’s condition:
- Insulin infusion.
- Rehydration aimed at replenishing fluids, electrolytes, and pH correction.
- Treatment of concomitant somatic diseases.
Insulin therapy is aimed at eliminating biochemical changes in the body that led to the development of ketoacidosis. To increase concentration, it is administered in short doses of 4-6 units every hour. This helps to slow down lipolysis, the formation of ketone bodies and inhibition of glucose release by the liver, which has a beneficial effect on glycogen synthesis.
To rehydrate the body, the introduction of 0.9% saline solution with sodium chloride is used. With an increased level of sodium in the blood, fluid replenishment is carried out using a 0.45% solution. As the deficiency is eliminated, kidney function is restored, and glucose levels decrease due to its active excretion in the urine.
Correction of acidity also remains an important point. With adequate sugar concentration and sufficient fluid supply, stabilization of the acid-base balance occurs independently. The pH shifts toward the alkaline level, the synthesis of ketone bodies stops, and the restored excretory system copes with their removal.
Diagnosis of lactase deficiency
Diagnosis of lactase deficiency largely depends on the anamnestic data of a person who has had poor tolerance to whole milk throughout his life, and the exclusion of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, food allergies, chronic enteritis and other causes of the disease.
The following laboratory data should be noted:
- A genetic blood test, gene determination (LCT, LPA) helps to identify lactose intolerance and predict the development of lactase deficiency in children over 1.5 years of age.
- The oldest scatological analysis of stool has not lost its significance, by which it is possible to identify disturbances in the absorption of carbohydrates (sugars): increased starch, fiber, iodophilic flora, decreased stool acidity less than 5.5, determine carbohydrates in stool.
- Glycemic load test with lactose - a test of lactose tolerance. The blood glucose level is determined on an empty stomach and 15, 30 and 60 minutes after a lactose load of no more than 50 g. If the lactase enzyme is insufficient, within 60 minutes after taking lactose, the blood glucose level increases by less than 1.1 mmol/l, i.e. , no more than 20% of the initial level - a flat glycemic curve. The most accurate research method.
- Hydrogen breath test - an increase in the concentration of hydrogen in exhaled air due to bacterial breakdown of disaccharides in the colon. The study is carried out on an empty stomach after a 14-hour fast. Preparation for the study: the patient follows a diet that excludes slowly digested foods (legumes, bran and carbonated drinks). Immediately before and during the examination, smoking and chewing gum are not allowed, and physical activity is limited 2 hours before the examination. Before the first intake of exhaled air, oral hygiene is carried out - teeth brushing. Then the patient is given 50 g of lactose and the hydrogen concentration in the exhaled air is determined every 15 minutes, if the hydrogen concentration is >20 ppm - a criterion for lactase deficiency. In 20% of cases the result is false positive.
- A biopsy of the small intestinal mucosa, revealing a decrease in lactase activity, is the “gold standard”, but is rarely performed.
Differential diagnosis must be carried out with food allergies, pseudoallergic food intolerance, chronic enteritis and other causes of lactase enzyme deficiency.
Treatment
- Hemodialysis - infusion therapy is used to remove accumulated lactate from the cardiovascular system. Intravenous glucose and insulin injections trigger enzyme and protein activity.
- Artificial pulmonary ventilation (ALV) with intubation of the patient restores gas exchange, maintains impaired respiratory function, and reduces the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood to normal levels. The procedure is carried out until the alkaline balance is restored.
- Cardiotonic drugs are prescribed to stimulate the activity of the heart muscle and normalize heart rhythm.
- Insulin therapy with prolonged effect.
As an emergency aid, the patient is administered sodium bicarbonate with a concentration of 4% or 2.5%, the daily dose is up to 2 liters. The drug is administered as a slow intravenous infusion, with adequate ventilation and calcium supplementation to mitigate side effects.
For patients with septic shock, crystalloid solutions - saline or saline - are prescribed in an amount of 30 mg/kg for the first 3 hours. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are used to combat concomitant infections.
Metformin
In case of lactic acidosis, the prescription of metformin to patients with type 2 diabetes is associated with the risk of complications due to possible overdose.
If metabolic acidosis is suspected, metformin should be stopped immediately and the patient should be hospitalized. It is important to preserve the vital functions of the body by stabilizing blood circulation and ensuring complete saturation of blood and tissues with oxygen. There is no specific antidote for metformin. In case of overdose, the introduction of activated carbon for adsorption may be indicated after a few hours.
Treatment of lactase deficiency. Food selection
Treatment consists of eliminating whole milk and dairy products from the diet. Currently, products with a reduced lactose content are produced and labeled “hyla”; products manufactured by Valio, Parmalat, and President are treated with lactase and labeled with the “laktoosition” symbol, most often for children.
Elimination diets (test consumption of individual foods containing milk sugar) are of great importance in both diagnosis and treatment.
If taking any dairy product - whole milk, fermented milk products, cottage cheese, cheese, coffee with cream, butter, etc. causes clinical manifestations of intolerance, if treatment is not effective, and clinical signs disappear without treatment, then we can talk about dairy intolerance sugar, the product should be excluded.
In products that have undergone lactic acid fermentation, when milk sugar turns into lactic acid, there is little lactose and therefore the use of fermented milk products in nutrition is possible (yogurt, fermented baked milk).
Products with live lactobacilli can be well tolerated, which can be done by preparing a live fermented milk product at home using starter cultures - Narine or Evitalia.
The amount of lactose in a dairy product is inversely proportional to its fat content, so there is practically no lactose in butter, and heavy and half-fat cream contains less lactose than whole milk.
When making some hard cheeses (cheddar, Parmesan, Swiss), the whey, where lactose is concentrated, is separated. Therefore, lactose-poor cheeses are suitable for consumption by lactose intolerant people. But homemade cheese and soft cheeses are rich in lactose.
Products containing lactose should be divided into several doses throughout the day.
Lactose-free products include fruits, vegetables and their juices, cereals, honey, butter, rice, vermicelli, meat, fish, poultry, chicken eggs, salt, nuts.
Prevention of ketoacidosis
With a timely and correct treatment plan, ketoacidosis can be stopped in a hospital setting. However, in the absence of the possibility of therapeutic measures, the pathological condition quickly develops into a coma. Mortality during its development is 5%, and in elderly patients (over 60 years old) - up to 20%.
Prevention of the development of ketoacidosis is based on education of people suffering from diabetes. Patients should know the initial symptoms of this pathological condition, the rules for injecting insulin, and the basics of monitoring glucose concentrations. Obtaining the maximum amount of information about the disease will help a person maintain a healthy lifestyle and adhere to the diet compiled by a nutritionist. It is important to remember that when the first signs of decompensation appear, you need to seek medical help to prevent the development of complications.
Hidden lactase
ATTENTION!
To improve the structure, taste and other properties, lactose is often used in the manufacture of food products. It is “hidden” in dry milk formulas, bread, frozen vegetables, canned soups, dressings and sauces, spaghetti, sausage, jam, sweets, instant foods, fast food, ketchup, mayonnaise, chocolate (except bitter). Read the product ingredients!
Milk sugar (lactose) is an auxiliary component of many drugs, for example, Ganaton, Gastal, Motilium, Cerucal, Imodium, Karsil, Linex, No-shpa, Kvamatela, Dulcolax, Gelusil, Galstena, Wobenzym, Mexidol, Corvalol, Warfarin, Bilobil, Panzinorm -forte, Omeza, and other drugs. Read the annotations for medications! Considering that lactase deficiency is based on a deficiency of the small intestinal enzyme - lactase, there are currently drugs that perform a replacement function for the lack of this enzyme. Dietary supplements Lactase, Lactazar can be taken 1 capsule along with a dairy product and help digest milk sugar, Tylactase taken 1 capsule with food or 2 capsules added per 1 liter of milk, store in the refrigerator, Lactrase 1-2 capsules before taking dairy products.
Forecast. If lactase deficiency is congenital, elimination diets are beneficial. In acquired variants of lactase deficiency, the course of the underlying disease that caused this type of enteropathy is important.