Treatment methods
Treatment of chronic coronary insufficiency comes down to eliminating the cause that causes occlusive-stenotic processes in the vessels. How is conservative treatment of cardiac ischemia performed? It includes taking medications that reduce blood clotting and cholesterol levels and lifestyle modifications. The patient is prescribed drugs that normalize blood pressure, aspirin, calcium channel blockers and beta blockers, which are used in the treatment of angina.
It is recommended to give up bad habits (smoking), physical activity, and diet. Treatment is carried out for atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, the main disease that causes coronary insufficiency.
Surgical methods for treating diseases accompanied by coronary insufficiency are not always characterized by a long recovery period. Modern methods of endovascular treatment are practiced today. These are minimally invasive operations to restore blood vessels. Under the control of the latest equipment, a special stent endoprosthesis is implanted into the damaged vessel through a small puncture in the artery, which eliminates the narrowing and supports the vascular walls in the future. This percutaneous coronary intervention is performed without general anesthesia or incisions—patients return to their normal lives within a week.
Classification of the disease
In ICD 10, chronic heart failure is coded 150, divided into systolic and diastolic forms. This is not the only division of pathology; there are other bases for classification. One of the most common divisions is by stages :
- Stage I - primary changes, decreased functionality of the left ventricle of the heart. At this moment, there are still no serious disturbances in blood flow, so symptoms of chronic heart failure do not appear.
- Stage II A - blood moves along the bed more slowly and can form areas of stagnation in the pulmonary fields or lower segment of the body.
- II B - hemodynamics suffer, affecting both circles of blood circulation at once. This stage is already characterized by noticeable changes in blood vessels and the heart muscle itself. The doctor can identify signs of the disease by recording extraneous whistling in the lungs and swelling of the lower extremities.
- Stage III - swelling spreads throughout the body. Now they appear not only in the legs, but also become noticeable in the hips and lumbar area. Fluid can accumulate in the peritoneum and spread throughout the body. At this stage, irreversible changes affect vital organs: the brain, heart, bronchopulmonary system, kidneys and liver.
There is a well-known classification by functional units or classes, which is determined by the general well-being of a sick person in response to physical activity. There are 4 stages of chronic heart failure. At the first stage, activity does not cause major changes. Shortness of breath may occur during intense activities, although in many situations there is no shortness of breath.
The second functional class can be determined by normal well-being during the period of rest and increased heartbeat under light loads. When moving to stage 3, the patient experiences significant limitations in physical activity. And at the 4th stage, loads are practically inaccessible, as they cause acute discomfort. Another popular gradation is the division by zones of heart damage. Thus, experts distinguish between left-, right- and two-ventricular heart failure.
Causes and symptoms
Acute coronary insufficiency is caused by occlusion or blockage of the coronary vessels. Acute coronary insufficiency often becomes the cause of death, because in this condition there is a high probability of myocardial infarction. Correctly provided first aid saves a person's life.
Symptoms of acute coronary insufficiency are chest or heart pain that does not stop for 15 minutes. In this condition, the patient needs urgent professional help in a cardiology clinic equipped with special equipment. In the hospital, the patient receives emergency care and undergoes a cardiac examination to prescribe effective therapy.
Risk factors for chronic heart failure
The causes of the disease are various factors: from serious heart pathologies to poor diet. Let's highlight the main ones :
- ischemic disease, in which the muscle does not receive the oxygen it needs;
- recent heart attack;
- essential hypertension (high blood pressure);
- diabetes mellitus, which doubles the risk of developing chronic heart failure in men and increases the likelihood of developing the disease in women by 5 times;
- dilated cardiomyopathy - a condition in which the heart becomes larger and wider for no known reason;
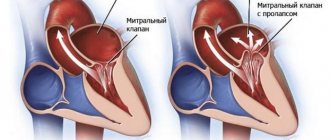
- heart valve disease, especially aortic stenosis, when blood cannot pass through one of the heart's main valves;
- mitral and aortic regurgitation, when blood can flow in the opposite direction;
- alcoholic cardiomyopathy - large amounts of alcohol makes the heart larger and less efficient;
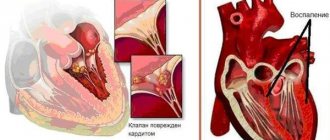
- inflammation of the heart muscle or myocarditis (usually of viral origin);
- chronic arrhythmia;
- HIV AIDS.
The causes of the disease are also certain types of medications, endocrine diseases, vitamin deficiency, obesity and other conditions.
Treatment
Further actions are taken by qualified specialists at the medical institution. The hospital carries out diagnostics: tests, ECG, ultrasound, coronary angiography. Based on instrumental studies, test results and examination, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Treatment of coronary insufficiency is aimed at normalizing blood supply to the myocardium. Drug therapy is used, which includes drugs for stopping attacks, thinning the blood and normalizing blood pressure, or angioplasty and stenting of heart vessels - the decision is made in each case individually. In addition, do not forget about secondary prevention: the patient is recommended to get rid of bad habits, engage in physical therapy and adjust their diet.
The essence of chronic heart failure
The term is used to describe a condition in which the heart is unable to adequately pump blood throughout the body. The disease forces the organ to work under extreme stress, causing irreparable damage to itself. Partial performance of functions ceases, the efficiency of work is disrupted, up to the complete stop of the organ in particularly critical situations.
CHF makes it impossible for the heart muscle to contract normally and empty its chambers. The myocardium fails when filling the ventricles and atria with blood. This creates an imbalance in systems and provokes a deterioration in well-being. The pathology can begin suddenly due to some important event, for example, a heart attack.
Sometimes chronic heart failure develops slowly. The heart tries to adapt to the overwhelming load, without showing acute signs of the disease for a long time. But then malfunctions appear, for which you should immediately consult a doctor to prescribe effective treatment.
General information
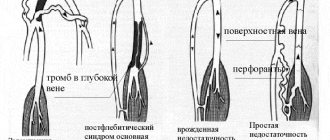
Coronary insufficiency is a pathological condition that develops as a result of a partial or complete cessation of blood flow through the coronary arteries, which ultimately leads to inadequate provision of cardiomyocytes with oxygen and nutrients. , coronary heart disease develops . With coronary insufficiency, a local zone myocardial ischemia hypoxia is observed with severe anemia , respiratory failure, pathological structure of hemoglobin and other non-vascular factors.
Diagnosis of chronic heart failure
Patients with chronic heart failure are most often evaluated using transthoracic echocardiography. The method allows you to confirm the presence of systolic dysfunction, determine the ejection fraction, and exclude signs of other structural heart diseases (valve stenosis, atrial regurgitation, ventricular septal defect, congenital anomalies).
When an etiology cannot be established and coronary artery disease is suspected, cardiac catheterization is considered so that the physician can determine the anatomy of the coronary artery and evaluate for the presence of obstructive disease. A thorough history and physical examination are mandatory procedures to determine pathology.
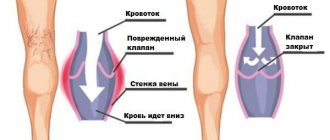
Our clinic’s specialists perform a comprehensive diagnosis of chronic heart failure. Doctors study different body systems. A general examination is performed to see how comfortable the person is in terms of their breathing rate and heart rate. This is especially important in a lying position, since with CHF, shortness of breath usually worsens in a horizontal position of the body. The doctor may examine the veins in the patient's neck as they can show how the right side of the heart is working. They can also provide information about whether blood is being pushed out in the veins when the valves are faulty.
After all these manipulations, the cardiologist examines the patient's chest, where sometimes the heart can be seen beating through the chest. By external signs, the doctor is able to determine how large the heart muscle is. Listening will help determine the characteristics of blood flow and valve function. It is important to exclude the risk of developing pulmonary edema. The legs, back and other places are checked for tissue swelling. This fluid accumulates because blood is not pumped efficiently through the heart. This causes a lot of pressure in the veins, which return blood back to the heart, pushing moisture out of the blood vessels and into the tissue.
There are many tests to make a diagnosis. These tests help identify the disease and serve to determine the severity of the disease. The doctor will refer the patient for blood tests to check the general indicators and function of the liver, kidneys, thyroid gland, and also to determine the number of cells in the blood.
Hormonal analysis is useful. The test focuses on two hormones found in the chambers of the heart (ANP and BNP). They are released when the organ expands. The doctor can also check the physical condition by giving the patient small sets of exercises, which he must perform in a specialist’s office.
The patient is sent for functional diagnostics of chronic heart failure, where he will undergo :
- ECG (electrocardiogram) - measures the electrical activity of the heart, the method shows deviations in the functioning of the heart.
- Chest X-ray - taking x-rays to view internal organs and structures.
- Echocardiography is a technology that can provide valuable information about the circulatory system and the functions of the heart valves.
- Coronary angiography - injection of a certain amount of special dye into the veins, further study of the characteristics of blood flow.
- Nuclear cardiology - scanning gamma rays that are caused by intravenous administration of a radionuclide to reveal information about blood flow.
In addition, spirometry may be prescribed - a test to check the functioning of the lungs and the characteristics of the respiratory system. Based on the data obtained, recommendations for the treatment of chronic heart failure and related diseases are being developed. The list of diagnostic procedures is individual for each patient. The need for a particular technique is explained in more detail by the doctor at the first consultation.
Prevention
Preventive methods are aimed at eliminating factors that contribute to the occurrence and progression of coronary insufficiency. Main directions:
- complete cessation of drinking alcoholic beverages;
- to give up smoking;
- healthy eating;
- physical education classes;
- elimination of emotional and mental overload;
- support of normal body mass index;
- blood pressure control .
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of formation of coronary vascular insufficiency is determined by the interaction of a number of factors:
- presence of atherosclerotic plaque ;
- spasm of the coronary arteries;
- extracoronary thrombosis.
It is known for certain that the appearance of an atherosclerotic plaque is the morphological basis of ischemic myocardial damage in 90% of cases. Severe attacks of angina occur when the coronary vessels are damaged by 70-80%. When an artery spasms, a contraction of the smooth muscle vascular wall occurs, which creates an obstacle to normal blood flow in the myocardium. Coronary artery spasm is influenced by the sympathetic nervous system .
Thrombosis is of utmost importance . Thrombi form mainly on the surface of an atherosclerotic plaque at the site of disruption of the integrity and structure of the endothelial layer in the form of destruction and ulceration of the plaque.
Sources
- Coronary Heart Disease - nhlbi.nih.gov.
- Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention, 2016; 15(2): 93–99 https://dx.doi.org/10.15829/1728-8800-2016-2-93-99.
- Kurdgelia T. M., Kislitsina O. N., Bazarsadaeva T. S. Sudden cardiac death: epidemiology, risk factors and prevention // BMIK. 2014. No. 3.
- Guide to faculty therapy: textbook / S. A. Boldueva, I. V. Arkharov, E. L. Belyaeva, E. G. Bykova, T. V. Ermolova, M. I. Ivanova, I. A. Leonova, A. P. Makhnov, N. S. Shvets, O. Yu. Chizhova; edited by S. A. Boldueva. — 3rd ed., add. and processed - St. Petersburg: Publishing house of North-Western State Medical University named after. I. I. Mechnikova, 2021. - p. 6-32; 64-76.
- Picard F., Sayah N., Spagnoli V., Adjedj J., Varenne O. Vasospastic angina: A literature review of current evidence. //Arch Cardiovasc Dis - 2021 - Vol.112 - No. 1 - p.44-55