September 3, 2010
Doctors are confident that a special diet can improve blood circulation and cope with the first signs of heart disease.
The heart is the only muscle in the body that works continuously and pumps blood, which supplies nutrients and oxygen to the entire body. How effectively it will work also depends on what we eat. Doctors are confident that the nutritional system developed a long time ago called “diet No. 10” can improve blood circulation and cope with the first signs of heart disease.
Introduction
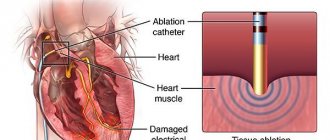
Chronic heart failure (CHF) is a complex syndrome caused by one or another disease of the circulatory system, the essence of which is an imbalance between the hemodynamic needs of the body and the capabilities of the heart.
Clinically, CHF is manifested by five main signs:
- shortness of breath;
- rapid heartbeat;
- fatigue;
- decreased physical activity;
- fluid retention in tissues (edema).
Simply put, CHF is the inability of the heart to provide blood to tissues in accordance with their metabolic needs at rest and under moderate stress, in the absence of hypovolemia and reduced hemoglobin.
Features of diets against edema
- Uncontrolled and prolonged use of diuretics can lead to dehydration and disruption of water-salt balance.
- Abuse of a decongestant diet is fraught with the appearance of severe weakness. At risk are patients with liver and kidney failure.
- To improve the taste of salt-free food during a therapeutic diet, table salt substitutes are used.
- In case of severe swelling, fasting days will help to cope with the malaise. But without control, they can worsen the problem, so it is important to listen to the opinion of your doctor. The most physiological are curd, milk and rice fasting days.
Modern principles of nutrition for a patient with CHF
An essential factor in the treatment and prevention of cardiac diseases is a rational and balanced diet. An incorrectly composed daily diet is a fundamental link that causes the development of excess body weight, lipid metabolism disorders and carbohydrate tolerance, hypertension, and atherosclerosis. Which in turn increases the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, arrhythmias and, as a consequence, CHF.
Chronic heart failure is not an independent pathology. This is a consequence of a long-term illness that has weakened the myocardium.
The main causes of CHF are one or a combination of the following pathologies:
- consequences of coronary heart disease (CHD), caused by atherosclerosis;
- arterial hypertension;
- valve defects (mitral, aortic, tricuspid);
- cardiomyopathies, inflammatory heart diseases;
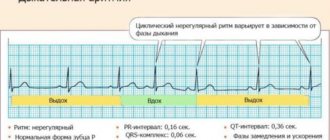
- rhythm disturbances (usually atrial fibrillation);
- diseases of the endocrine system: diabetes mellitus, hypo-, hyperthyroidism, Addison's disease, Conn's disease);
- alcoholism.
The diet of a person with cardiovascular diseases can contribute to:
- reducing the load on the myocardium and blood vessels;
- slowing down pathological changes in the vascular wall, improving their elasticity;
- reducing blood cholesterol levels;
- preventing the appearance of edema, which significantly impedes the normal functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- improving metabolism;
- reducing the required daily dosage of drugs for the treatment of CHF.
Nutritional therapy is determined by a combination of many factors:
- food selection;
- determining the ratios of individual products and nutrients;
- optimal cooking methods;
- degree of grinding;
- meal schedule;
- calorie intake.
In order for nutrition for CHF to create an optimal background to enhance the effect of the main types of treatment and prevent the progression and complication of the disease, it is necessary to create a daily menu in such a way that:
- the patient fully received the necessary nutrients, taking into account existing diseases;
- a set of recommended products could be purchased at a reasonable price;
- the dishes were varied and relatively easy to prepare;
- individual intolerance and preferences of the individual patient were taken into account;
- the diet was divided into 4-6 meals, and no more than 25% of the daily amount of food should be consumed in the evening.
I recommend that my patients buy scales for home and monitor their body weight 2-3 times a week. Gaining 2-3 kilograms in 3 days indicates fluid retention and requires consultation with a doctor and adjustment of the treatment regimen.
Weighing is also necessary for patients with concomitant obesity. A loss of 10% of initial body weight leads to a decrease in blood pressure by 5 mm. rt. Art., reducing the load on the heart, shortness of breath, joint pain, increasing tissue utilization of glucose.
Changes in the body and principles of diet
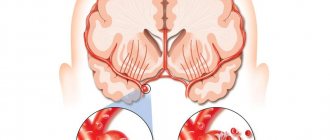
Atherosclerosis and hypertension are the main causes of heart attacks and strokes. What changes occur in the body during the development of cardiovascular diseases?
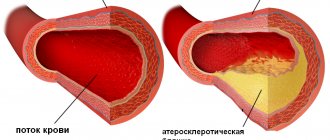
Increased pressure “wears out” the walls of blood vessels. They become more dense. Aneurysms (expansion of the lumen) occur; the wall in these places becomes thinner and can easily “rip” when blood pressure fluctuates.
The process of formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels begins already in infancy, but their size and stability depend on age, lifestyle, and hereditary characteristics. The trend towards a negative attitude towards cholesterol is already a thing of the past, but the stereotype that “it’s better without it” is still alive. Endocrinologists say that about 85% of cholesterol circulating in the blood is synthesized in the body by liver cells and only about 15-20% comes from outside.
Fats are not only a “filler” for cholesterol plaques, but also a material for the construction of all cell membranes and hormones. These are vitamins and natural protection of internal organs from displacement (shock absorption), and the person himself from hypothermia. This means that a complete abstinence from animal foods may not improve, but worsen, your health. But what can be changed? You can influence the amount and composition of fats entering the body.
Speaking about damage to the walls of blood vessels during hypertension and atherosclerosis, we must remember the proteins collagen and elastin. They are responsible for their firmness and elasticity, the smoothness of the inner layer of the vascular wall. The development of atherosclerosis leads to the fact that the walls of blood vessels become more rigid, blood flow decreases, and the heart “has” to put in more effort to push through the required volume. Blood supply deteriorates, the load on the heart increases. The process of restoration of the vascular wall is associated not only with a sufficient amount of protein in food, but also with the presence of ascorbic acid, which takes part in the synthesis of its body structures.
The body needs carbohydrates, first of all, as a quick way to replenish energy. But the excess amount of sugars does not “go away”: they become material for fats. A person’s weight increases, and along with it, the load on the heart increases.
According to the latest WHO recommendations, the amount of table salt (or sodium chloride) that a person receives per day should not exceed 5 g. A larger amount leads to edema and increased stress on the heart. Unfortunately, people are accustomed to considering only the contents of a salt shaker as salt. They forget that sodium chloride can easily “hide” in mayonnaise, ketchup, a piece of sausage, or even in cream cheese.
Having listed the changes that occur in tissues, we can say that the diet for the heart and blood vessels must meet the following requirements:
- Supply the body with all nutrients.
- Do not go beyond the recommended daily caloric intake.
- Prevent fluid retention (edema).
- Contain a minimum amount of “harmful” fats.
- Provide the body with enough protein.
Vitamin therapy, the intake of minerals and trace elements are justified only in cases where the diet does not provide them with food in sufficient quantities.
Potassium and magnesium deserve special attention: these ions have a beneficial effect on the heart and “calm” the nervous system. This means that you need to take care to include foods rich in them in your diet.
What products to exclude
The American Heart Association (AHA) identifies sodium and water as the main substances to limit in heart failure.
Sodium is a mineral that is found in many foods, especially processed foods, fast food, and salt. It promotes water retention in tissues, volume overload of the vascular bed, increased blood pressure, and cardiac decompensation.
The AHA recommends consuming no more than 2,800 mg of sodium daily (and ideally less than 1,500 mg).
Even a salt-free diet does not guarantee that a person does not exceed the daily amount of sodium.
The most hidden salt is found in sausages, marinades and pickles, canned food, ready-made frozen dishes, cheeses (Parmesan, Cheese, Feta, Russian, processed), soy sauce, mayonnaise.
Water. Limitation of fluid intake for patients with hemodynamically stable CHF is moderate - up to 1.5-2 liters per day. In case of cardiac decompensation and edema syndrome, requiring intensive use of diuretics, the daily amount of water should not exceed 1-1.2 liters.
Patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system are recommended to exclude:
- fast food, semi-finished products, canned food;
- fried in oil, hot, spicy food;
- pickles and marinades;
- concentrated meat broths;
- fatty meats, offal, sausages, frankfurters;
- strong tea, coffee;
- alcohol, tobacco.
Eight rules of a heart-healthy diet
Control your portion sizes
How much you eat is just as important as what you eat. Regular overeating is a direct path to obesity. Obesity is the shortest path to disruption of the heart muscle and blockage of blood vessels. There is probably no need to explain what consequences such a scenario might entail.
Content:
- Eight rules of a heart-healthy diet
- Benefits of different types of products
- Food as medicine
Eat more vegetables and fruits
Vegetables and fruits are good sources of vitamins and minerals. They also tend to contain a minimum of calories and a maximum of fiber. In most products of plant origin, scientists find beneficial substances that prevent cardiac diseases.
| Healthy vegetables and fruits | What to refuse |
|
|
Give preference to whole grains
Whole grains are a good source of fiber and other beneficial components that play a significant role in maintaining healthy blood pressure.
Increasing your whole grain intake is easier than you might think.
| Healthy grains | What to refuse |
|
|
Limit unhealthy fats
Limiting saturated and trans fats is an important step to lower blood cholesterol levels and therefore prevent ischemia.
High cholesterol leads to the formation and accumulation of lipid plaques in the blood, which can lead to atherosclerosis and increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
| Type of fat | Recommendation |
| Saturated fats | Less than 7% of total daily calories or less than 14 g based on a total daily calorie intake of 2000 kcal |
| Trans fats | Less than 1% of total daily calories or less than 2 g per 2000 kcal per day |
The best way to reduce your intake of saturated and trans fats is to limit the amount of solid fats (butter, margarine) you consume. To do this, you can slightly reduce the portions of fat in sandwiches, porridges, soups, and also trim the fat from meat as carefully as possible, giving preference to lean varieties. Also, instead of fried potatoes, use baked ones, and instead of baked goods with creams, use less high-calorie cookies.
When cooking, it is better to give preference to monounsaturated fats, such as olive oil, and polyunsaturated fats, which are found in some types of fish, nuts, seeds, and avocados. Eating these fats instead of saturated fats helps regulate cholesterol levels.
| Healthy fats | What to refuse |
|
|
Focus on proteins without fats
Lean meat, fish, poultry, low-fat dairy products, and eggs are considered the best sources of protein. Meanwhile, it is important for people prone to cardiovascular diseases to choose leaner versions of these products. For example, instead of whole milk, choose skim milk, and replace fatty meat cutlets with boiled chicken breast.
Fish is also an excellent choice for a heart-healthy diet because it is an exceptional source of beneficial Omega-3s, which lower triglyceride levels in the blood. The best choices in this regard are salmon, mackerel, and herring. Plant sources of Omega fats: flaxseeds, walnuts, soybeans.
Good sources of low lipid and cholesterol-free proteins are legumes such as beans, lentils, and peas.
| Healthy proteins | What to refuse |
|
|
Minimize sodium intake
Eating large amounts of sodium can cause high blood pressure, which increases the risk of heart disease. Limiting your sodium intake is an important part of a heart-healthy diet.
Doctors recommend that healthy adults consume no more than 2,300 mg of sodium per day, which is equivalent to 1 teaspoon of table salt. People over 50 years of age, as well as people with high blood pressure, chronic kidney dysfunction, and diabetes are advised not to exceed the 1500 mg sodium limit.
And it is important to remember that most of the excess salt does not come from freshly prepared food, but in canned food, instant food, and semi-finished products. It is also important to choose your seasonings carefully to reduce sodium portions.
| Low salt foods | What to refuse |
|
|
Plan your menu
Now you know which foods are good for your heart and which you should avoid. Use this knowledge to plan your menu. But it is important to introduce foods from different categories into your diet, focusing on healthy foods from the list. Make sure that the menu is varied and not repeated from day to day. Consider the recommendations listed above.
Sometimes you can relax
It would be better, of course, if foods on the list of heart-harmful foods do not appear in your diet. But a piece of chocolate or a few chips won't harm your heart if included in your diet from time to time. Give yourself a little indulgence when you really want it. But remember: this is just a small indulgence, not a rejection of a healthy eating plan.
Take our advice and review your menu. Let not only your stomach rejoice, but also your heart, which also has its own favorite and hated dishes.
Important Diet Elements
The daily menu of a patient with CHF must first of all be balanced with respect to proteins, fats, carbohydrates, cover energy costs, and be rich in microelements important for the heart.
Squirrels. An important structural element of cells. It is recommended to eat 2-3 servings of protein daily.
Equivalent to one serving:
- 100 grams of fish, meat (lean beef, veal, poultry);
- ? cups of boiled beans or peas;
- 1 egg.
It is necessary to limit proteins in the diet only in case of renal failure and azotemia.
Dairy products. The optimal amount is 2-3 servings:
- 100 grams of cottage cheese;
- 1 glass of milk with 1-2% fat content;
- 1 glass of kefir, fermented baked milk, yogurt, yogurt without additives;
- 2 tbsp. l. sour cream with a fat content of no more than 15%.
Vegetables and fruits. This is an important part of the diet, which provides the body with fiber, pectin, microelements, vitamins and is low in calories.
You need to eat 5 servings per day:
- ? cups chopped fruit (fresh or baked);
- ? cups of boiled or baked vegetables.
Porridge and bread . This part of the diet is responsible for energy saturation of the body. Preference should be given to slow carbohydrates, eating 5 servings daily:
- 1 slice of whole grain bread;
- ? cups of pasta;
- ? cups of rice, buckwheat, oatmeal and other cereals.
Unsaturated fats and oils. The body needs to get the “right” fats, as this is the building material of all cell membranes. For cooking and dressing salads, it is optimal to use refined oils (olive, corn, sunflower, flaxseed).
A good source of healthy fats are nuts (dried, unseasoned). You can consume 1 handful (40 grams) per day.
To give food a brighter taste, salt can be replaced with aromatic herbs (parsley, basil, oregano, rosemary, cumin, cilantro), garlic, onion, lemon juice, paprika.
Patients with atherosclerosis should pay special attention to the amount of dietary fiber in the diet (as they prevent the absorption of fatty acids from the intestine). Men need 76 grams per day, and women – 28 grams.
Also, if it is impossible for my patients to fully saturate their diet with the necessary vitamins and microelements, I recommend taking courses of beekeeping products and nutritional supplements enriched with potassium, magnesium, zinc, calcium, phosphorus (vitamins A, C, E, B1, B2, B6).
Regarding temperature treatment: it is better to boil, stew or bake foods for heart failure. Cooking on a grill and in a Teflon-coated frying pan is allowed, without oil.
Reviews and results
This therapeutic diet is well tolerated, but many people find it difficult to get used to the reduced amount of salt. However, this is the main nutritional condition for losing excess fluid in the body and facilitating cardiac activity. Using salt substitutes as directed by your doctor or adding lemon juice, apple cider vinegar and herbs will slightly improve the taste of food. Limiting carbohydrates (simple) and fatty foods has a positive effect on excess weight.
- “... I suffered from myocarditis, and they discovered mild heart failure. The doctors were worried about how the pregnancy and childbirth would proceed, so she was hospitalized several times. She gave birth safely, but after the birth her insufficiency began to progress. This forced me to watch my diet (limit salt and fatty foods, don’t overeat), exercise, and walk daily. Be sure to eat dried apricots and raisins every day. Nutritional therapy helped me lose weight. I periodically drink Panangin, Pumpan and Mildronate. Today my condition is normal, I live a full life, I just can’t stand the stuffiness well”;
- “... Tricuspid and mitral valve insufficiency was discovered in childhood. Against this background, insufficiency developed. I absolutely cannot get hypothermic and get sick. That's why I always dress warmly, and before cold seasons I take a course of vitamins and echinacea. In good weather - walks in the fresh air. The doctor said that it is important to eliminate stress and get good sleep. I try to eat healthy: chicken, fish, beef, vegetables and fruits all year round, dried fruits, as I need vitamins for my heart. A low-salt diet helps. Shortness of breath immediately disappears, it becomes easy to walk and breathe. Therefore, limiting salt is very important to me. At first it was difficult to eat unsalted food, and I was tempted to eat forbidden sausage and salted fish, but then I got used to it. I’m losing weight well on a salt-free diet”;
- “...Heart defect since childhood. With a small load, shortness of breath, constant swelling in the legs and pressure began to increase. Therefore, limiting salt in my diet is a vital necessity for me. If I increase the amount of salt for 3-5 days and eat something salty, the swelling returns and shortness of breath increases. I’ve been used to this kind of food for a long time. The only difficulty is that you need to cook for yourself separately. I cook some dishes to share, and then my family add salt to taste. In addition to the fact that everyone eats dried apricots, prunes, raisins, bananas, I always take vitamin and mineral complexes, omega-3, Panangin for 2 months. This is necessary to maintain the heart muscle.”
Sample menu for the week
The DASH nutrition system, developed by the American Heart Association, is considered optimal for heart failure.
When drawing up an approximate 7-day menu for a patient with CHF, it is necessary to take into account the root cause of the disease and concomitant pathology. For example, if the causes of heart failure are coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis, special attention should be paid to limiting saturated fats and enriching the diet with pectin and fiber. And if you have diabetes, focus on eliminating foods with a high glycemic index.
There are low-sodium substitutes (Himalayan salt, Saga) that can give the dish a salty taste. Potassium chloride should only be used after consulting a doctor and monitoring serum K levels.
For my patients, I provide a list of recommended dishes, and they combine the diet themselves, taking into account taste preferences, the available range of products and individual culinary skills.
Diuretic foods and drinks
Prescribing pharmaceutical drugs - diuretics - does not always make sense: it all depends on the nature of the occurrence of edema. So, say, if this is associated with a decrease in the absorption of amino acids due to a stomach ulcer, it is necessary to work with this part of the digestive system and the factors that cause disruption of its functioning (for example, high susceptibility to stress, which leads to spasm of the blood vessels supplying the stomach wall due to secretion by the bark adrenal cortisol).
In addition, any medications must be prescribed strictly by a doctor and only for certain indications. However, this does not mean at all that it is necessary to remain inactive until specialized assistance is provided: a nutritionist always has many levers of influence on the client’s diet that can not only improve the course of the disease, but also significantly alleviate the external manifestations of the pathology.
We recommend
“Nutrition during exacerbation of gastritis: general recommendations and example of a diet” Read more
We have compiled a list of foods that have a diuretic effect. Believe me, they are not inferior in effectiveness to the most fashionable biological supplements.
- Turnip
- this root vegetable was used long before the emergence of modern medicine as such. Our ancestors attributed to it not only diuretic properties (they were provided mainly by decoctions from the leaves of the plant), but also analgesic ones. It was also used to relieve joint pain, as well as to stimulate peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract - the latter was provided by the irritating effect that the essential oil prepared on its basis had on the mucous membrane.
Interestingly, its known anti-inflammatory effect, as recently discovered, is associated with the inhibition of nuclear factor-kappa B, which, when activated, binds to parts of the DNA molecule, triggering the expression of genes, whose products actually implement the inflammatory process.
Turnip seeds also contain biologically active compounds: precursors of vitamin A, tocopherols, fatty oils.
Study
: Turnip is a food and medicinal plant
- Dill
is another well-known diuretic product used in folk medicine for centuries. Previously, by the way, it was assumed that its combination with honey is an effective antidote for poisoning by all types of poisons.
A decoction prepared from this plant helps strengthen the hair roots and also reduces the itching that accompanies allergic reactions. The use of dill was also associated with the normalization of the lipid spectrum in rats, helping to reduce “bad” cholesterol in the serum, as well as providing a cardioprotective effect.
Dill herb and juice are still used in Ayurveda for edema caused by kidney pathologies.
Study
: Promising medicinal plant dill
- Turmeric
- a hemostatic, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial agent, beloved and often used in folk medicine of different peoples of the world. She was credited with diuretic, choleretic and analgesic effects.
Turmeric was also used in the treatment of jaundice and dropsy, as well as for the treatment of tumors.
Study
: Use of turmeric in ancient and modern folk medicine
- Juniper
- a coniferous evergreen plant, which is considered sacred by some peoples. Thus, there are even beliefs that by eating seven cones, a person will be reliably protected for seven years not only from various eye diseases, but also from typhoid fever, which is known for its rather severe course.
It must be said that there are still theories about its ability to lead to miscarriages, so use by pregnant women, as well as during lactation, should be strictly discussed with a doctor.
In folk medicine, decoctions based on this plant are used in the treatment of edema caused by kidney disease, liver disease and heart failure. In addition, juniper is also used in the treatment of gout, as well as an antifungal and bactericidal agent.
We recommend
“Carbohydrate deficiency: signs and causes” Read more
Its berries contain a wide range of antioxidant substances, including sterols, tannins and flavonoids. Some compounds are also capable of inhibiting the activity of one of the key enzymes in the synthesis of melanin, therefore they are used for hyperpigmentation.
- Common thyme
- a plant known since the times of the ancient world and used as a diuretic, anticonvulsant, antispasmodic, and wound healing agent.
Its extracts are also effective in the treatment of helminthic infestations, especially against tapeworms. In addition, it also has a pronounced antifungal effect, which makes it widely used in the context of the treatment of candidiasis.
Clinical case
My patient N. is 64 years old.
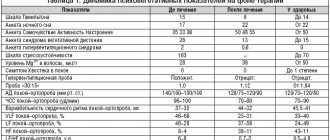
History of hypertension stage III, 2nd degree. In 2015, he suffered an acute Q-myocardial infarction of the anterior wall of the left ventricle, complicated by cardiogenic pulmonary edema. At the time of the first visit in 2021, the patient complained of shortness of breath, worsening with physical exertion, rapid heartbeat, and swelling in the legs. Objectively: N. had class I. obesity (BMI - 34.4 kg/m2), blood pressure - 145/100 mm. rt. Art., heart rate - 89 beats/min. According to the examination results, hypercholesterolemia, hypokinesia of the anterior wall of the left ventricle, ejection fraction 40%. The patient constantly took Enap N, Concor, Furosemide, Cardiomagnyl, and drank Nitroglycerin during attacks. A diagnosis was made: CHF IIA, IIFC. It was recommended to adjust the lifestyle, give up tobacco and alcohol, and select a diet for heart failure for every day. Over the course of 2 years, the patient gradually adapted to the new diet. At the last appointment: BMI - 28.9 kg/m2, blood pressure - 136/85 mm. rt. Art., heart rate - 79 beats/min. Complaints of shortness of breath have decreased; episodes of using Nitroglycerin are no more than once a week. The patient notes a significant increase in physical activity. Based on the results of the consultation, Fr.
From the list, the patient selects 3 main meals and 2-3 snacks.
Breakfast
- Oatmeal, buckwheat, corn, rice porridge, 40 grams, cooked in milk and water in a 1:1 ratio with 1 tsp. honey, 1 boiled egg, herbal tea.
- Omelette of 2 eggs with milk 1-2% (100 ml), a slice of whole grain bread, an apple, tea.
- 300 grams of pumpkin-rice (or millet) pudding, 30 grams of hard cheese.
- 200 grams of cheesecakes with berries and 1 tbsp. l. sour cream or honey, cocoa and low-fat milk.
- Oatmeal pancake with 2 tbsp. l. oatmeal, 1 egg with 30 grams of hard cheese, fresh cucumber, tea.
- Vegetable muffins with green peas, green beans and bell peppers, tea.
Lunches
- Vegetable puree soup (300 grams), 100 grams of boiled meat, 1 slice of bread.
- Lenten borscht (300 grams), 100 grams of stewed or baked poultry, a slice of bread.
- Vegetable salad with vegetable oil, steamed cutlet with a side dish of porridge, compote.
- 100 grams of pasta with vegetable sauce, 100 grams of meat, fresh vegetables.
- Lentil soup, 300 grams, 100 grams of baked fish with vegetables.
Dinners
- 200 grams of baked fish with vegetable garnish.
- Peppers, eggplants or zucchini stuffed with chicken and baked in the oven.
- Vegetable salad with squid with lemon-mustard dressing, 1 slice of whole grain bread with 30 grams of cheese.
- Salad of boiled beans with vegetables, seasoned with vegetable oil or yogurt with herbs, whole grain bread.
- Vinaigrette with beans, dressed with olive oil.
- Steamed poultry cutlets with stewed cabbage.
- Baked potatoes in their skins with a sauce based on yoghurt, herbs and garlic with vegetable salad.
- Omelet with green beans, fresh vegetables.
Snacks
- A handful of dried nuts.
- Apple baked in the oven with honey, cinnamon and cottage cheese.
- 100 grams of cottage cheese and 100 ml of fermented baked milk or 1 tbsp. l. sour cream.
- 1 banana, apple or pear.
- 1 cup chopped fruit.
- 200-250 ml of fermented milk drink.
- A slice of bread with 30 grams of cheese.
- 200 grams of milk pudding.
- 10 pieces. prunes or dried apricots.
- 1 handful of raisins.
- 1 glass of kefir, yogurt or fermented baked milk.
This “backbone” allows the patient to program a weekly menu, and over time, enter new recipes from the list of permitted products.
Fully or partially limited products
- Fresh bread, pastry and cream products.
- It is not allowed to consume meat/fish/mushroom broths or legume soups.
- Prohibited are fatty varieties of pork, cooking fats, kidneys, liver, goose, sausages, duck, canned smoked foods, very fatty fish, canned food, fish caviar, salted and smoked fish products.
- Fatty dairy products.
- Vegetables with coarse fiber (radish, radish, turnip, rutabaga), mushrooms, sorrel and spinach due to their high uric acid content.
- Strong tea and coffee are prohibited; they can be consumed weak and with milk. Chocolate can be consumed very rarely.
- Mustard, horseradish and pepper.
- The consumption of dishes made from legumes, grape juice, and cabbage is limited, as they cause bloating.
- In case of obesity , simple carbohydrates (sugar, honey, jam, sweet fruits, grapes and dried grapes, ice cream, sweet confectionery) are significantly limited.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| pickles | 0,8 | 0,1 | 1,7 | 11 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| red radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 20 |
| black radish | 1,9 | 0,2 | 6,7 | 35 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 3.6% | 2,8 | 3,6 | 4,7 | 62 |
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 11% | 16,0 | 11,0 | 1,0 | 170 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Doctor advises
Lifehacks for adapting your diet:
- In the store, carefully study the label. Most manufacturers indicate the sodium concentration per 100 grams. Choose foods that contain less than 350 mg Na per serving. It is also worth paying attention to calorie content, amount and ratio of fats.
- Give preference to simple dishes with minimal cooking.
- Print out the recommended and prohibited foods on separate sheets of paper and hang them on the refrigerator.
- If possible, buy a slow cooker and a grill pan. This will simplify the cooking process and reduce the amount of fat in the dish.
- For frying, use cookware with Teflon or ceramic coating. Apply vegetable oil to the surface with a silicone brush.
- Inspect the shelves, throw away all harmful semi-finished products and fast food.
- Replace the salt shaker with a bowl of salt with a teaspoon. This will make it easier to count sodium.
- Salt food on your own plate.
- Remove salt from the table. Place jars of dried herbs, onions, garlic, lemon. This diversifies the taste of the dishes.
Nutrition during IVF embryo transfer
A protein diet during IVF after follicle puncture remains relevant. At this stage, proteins are required primarily to mediate receptor interaction. Embryo transfer must result in complete implantation. And in order for the blastocyst to penetrate the endometrium, interaction between receptors located on its surface and on the surface of the uterine mucosa is necessary. Receptors are proteins. If the interaction stage goes smoothly, then all receptors become associated with the ligand, and the fertilized egg is completely immersed in the uterus.
The receptor and ligand fit together like a “key to a lock.” This is the basis of their interaction.
conclusions
Undoubtedly, lifestyle, nutritional culture and physical activity significantly influence the course of cardiovascular diseases. A serious approach to organizing your diet will allow the patient to improve their well-being, reduce the risk of complications and hospitalizations, and in the long term improve their quality of life and give up some medications.
Nutrition for heart failure is a balanced, varied, nutrient-rich menu that a person must adhere to throughout his life.
Recommendations after IVF transfer
A protein diet during IVF after embryo transfer is especially relevant. At this time, cell division is more active than ever. From 2 cells (sperm and egg) a full-fledged child’s body must be formed. In order for all reactions to proceed without disturbances, a sufficient content of amino acids is necessary, both non-essential and essential. The difference between them is that the body cannot synthesize essential ones. To replenish their reserves, supply from the outside is required, which is carried out at the expense of food products.
The list of protein diet products for IVF may look like this:
- eggs (primarily egg white);
- fish;
- seafood;
- cottage cheese;
- cheese;
- lean meats.