Myocardial infarction (heart attack) - symptoms and treatment
A patient with an acute heart attack must be promptly transported to the hospital to prevent complications and increase the chances of survival. The system of care for patients with myocardial infarction includes the following stages:
- Pre-hospital stage. Ambulance teams provide assistance and transport the patient to the hospital.
- Hospital stage. Help is provided in specialized vascular departments.
- Rehabilitation stage. Rehabilitation is carried out in special departments of hospitals or specialized cardiological sanatoriums.
- Dispensary observation and outpatient treatment. Clinical examination in the post-infarction period is carried out in regional or city cardiology centers or in cardiology offices of clinics [6].
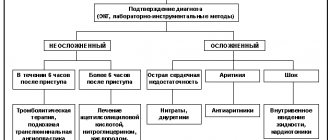
At the prehospital stage, the following tasks are solved:
- an accurate diagnosis is established. If this fails, it is permissible to establish a tentative syndromic diagnosis as soon as possible;
- The patient is given a nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue (or use a nitro-containing spray) and 0.25-0.35 g of aspirin;
- pain is relieved by administering painkillers;
- acute circulatory failure and heart rhythm disturbances are eliminated;
- the patient is brought out of the state of cardiogenic shock;
- in case of clinical death, resuscitation measures are performed;
- transport the patient to the hospital as soon as possible.
Further therapy is determined by the stage (period) of myocardial infarction. In the acute and very acute period, the goal of treatment is to prevent an increase in the focus of myocardial necrosis, eliminate pain and other symptoms. It is important to restore blood flow through the heart arteries and relieve pain. The intensity of pain during this period is so great that the patient may die due to cardiac arrest. It is necessary to prevent severe complications. When the disease passes into the subacute stage and in the post-infarction period, the goal of therapy is to reduce the risk of attack recurrence and possible complications.
For the treatment of acute myocardial infarction, drugs from various pharmacological groups are used:
Painkillers. Analgesics from the group of narcotic painkillers (morphine, promedol, omnopon) in combination with analgin, antihistamines (diphenhydramine). Neuroleptanalgesia is most effective when a combination of the analgesic fentanyl with the strong antipsychotic droperidol is used. The effectiveness of these drugs is noticeable within a few minutes. Not only pain disappears, but also fear of death, unmotivated anxiety and psychomotor agitation. Tranquilizers (diazepam) can be used to relieve psychomotor agitation. To reduce hypoxia (decreased oxygen in tissues), oxygen inhalation is used using a nasal catheter.
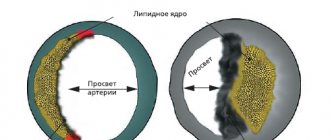
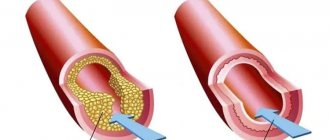
Thrombolytic therapy. It is important to restore blood flow and dissolve blood clots so that the death of the heart muscle does not spread further. The smaller the area of necrosis, the higher the patient’s chances of successful rehabilitation and the lower the risk of life-threatening complications. Immediate use of drugs (preferably within the first hour after an attack) allows you to achieve maximum effectiveness of treatment. A time limit of three hours is allowed. To dissolve a blood clot, thrombolytic drugs are administered intravenously, for example, streptokinase, urokinase, alteplase. The dose depends on the patient's weight.
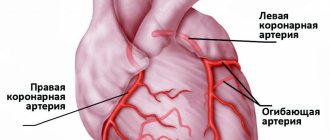
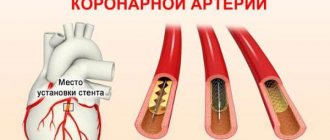
Restoration of coronary blood flow is also possible with the help of surgical treatment - stenting or coronary artery bypass grafting. A balloon catheter is inserted into a narrow section of the artery under fluoroscopic guidance. In this case, the atherosclerotic plaque is “crushed”, and the lumen of the heart artery increases. Then a stent (metal frame) can be installed into the lumen of the vessel.
Antiplatelet agents. Drugs from this group affect blood cells (platelets and red blood cells). The action of antiplatelet agents prevents platelet aggregation, improving blood flow. The main drug used is aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). Contraindications to the use of aspirin: bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, exacerbation of gastric or duodenal ulcers.
P2Y12 platelet receptor inhibitors are also used , which block platelet activation. The main blockers are ticagrelor, prasugrel and clopidogrel.
Intravenous/subcutaneous anticoagulants. , unfractionated heparin intravenously, is used to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) . Enoxaparin , which is also used to prevent venous thromboembolism, is administered subcutaneously.
To limit the area of myocardial ischemia and necrosis, it is necessary, in addition to restoring blood flow in the arteries of the heart, to reduce the hemodynamic load on the heart. Nitrates and beta blockers are used for this purpose.
Nitrates. They have an analgesic effect, reduce myocardial oxygen demand, increase coronary and collateral (bypass) blood flow, reduce the load on the heart muscle, and limit the size of the myocardial lesion. Their combination with beta blockers is especially effective, leading to rapid positive ECG dynamics and reducing the risk of sudden death [10].
Beta-blockers have an antiarrhythmic effect. The purpose of using beta-blockers (propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol) is to reduce the frequency and force of heart contractions, which will help reduce the load on the heart and the myocardial oxygen demand. Beta blockers continue to be used indefinitely in the absence of side effects and contraindications [1].
When to see a doctor
People should see a doctor if they experience chest pain, discomfort, or the following symptoms:
- pain in one or both arms
- pain in the back, neck, jaw or stomach
- dyspnea
- sweating
- nausea
- dizziness
If your blood pressure rises, when the systolic pressure is above 180 and the diastolic pressure reaches 110 or more, you should consult a doctor. Blood pressure in this range puts people at greater risk of heart attack.
Related article: High blood pressure and low pulse - what could be the reason?
Classification of heart failure
Acute heart failure
Characterized by sudden, dynamic and to some extent unpredictable development. An attack can develop in 3-5 minutes or 3-5 hours. The contractile function of the heart is impaired, so blood circulation suffers, and the load on the heart tissue (either the left or right ventricle) increases sharply.
Various types of acute forms are characterized by:
- stagnation of blood in various large veins or pulmonary circulation;
- a sharp decrease in heart rate, which causes a deterioration in the blood supply to organs and tissues of the body;
- sudden deterioration in the condition of a patient suffering from a chronic form of the disease.
Chronic heart failure
The most common form. It is characterized by a progressive course and an increase in functional heart problems. The disease has several stages.
Initially, the heart muscle compensates for the insufficient volume of blood ejection by increasing the number of contractions. At this time, myocardial hypertrophy gradually occurs, the vessels begin to reflexively narrow, and the patient experiences periodic ailments.
This state lasts until the compensation mechanism exhausts its resources. Organs and tissues experience a greater lack of oxygen supplied by the blood, and metabolic products are excreted worse. Dystrophic phenomena develop in the body.
What is heart failure?
The evolution of this disease occurs gradually, problems in the functioning of the heart increase with the age of the patient. In his youth, he does not feel interruptions, because the heart tissues and blood vessels have sufficient tone to supply blood to all parts of the body. Gradually, under the influence of various factors, tissues and blood vessels lose their elasticity, the heart does not fully perform its main function and blood supply deteriorates.
Negative factors include:
- passion for bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
- sedentary lifestyle;
- eating disorders;
- hereditary heart diseases;
- unfavorable environment.
At the initial stage, changes occur in the structure of tissues - the ventricles of the heart and their muscles increase. Accordingly, the volume of blood in them increases. The heart muscle needs to work harder to push blood into the vascular system.
As a result, the heart is exhausted, and the walls of blood vessels, due to overload, lose their elasticity, narrow, quickly wear out and over time lose their ability to pass a normal volume of blood. At the same time, vascular pressure increases, and the person quickly gets tired. And the greater the degree of wear and tear of the heart and blood vessels, the faster fatigue sets in. With a high degree of cardiovascular insufficiency, the patient feels a loss of strength even when stationary.
Not only changes occur in the tissues of the heart and blood vessels. The body replenishes the lack of blood, primarily in the brain and the heart itself. Therefore, patients experience insufficient flow to the limbs and other organs. Peripheral vascular diseases, chronic renal failure develop, joints suffer from lack of blood circulation, etc.
Functional classes of heart failure
- First . The patient is physically active and does not feel obvious signs of the disease.
- Second . The patient experiences well at rest, but physical activity causes symptoms of the disease to appear.
- Third . The patient is comfortable at rest, but much less physical activity is required for signs of the disease to appear.
- Fourth . Already at rest the patient feels discomfort, and with minimal exertion the symptoms increase sharply.
First aid for heart failure
First aid for heart failure is mainly required for acute illness, when the risk of myocardial infarction increases. Only a team of resuscitators with special equipment can provide qualified help. Therefore, you urgently need to call an ambulance.
While you are waiting for doctors, provide first aid for acute heart failure:
- make the patient sit with pillows around him;
- give him a nitroglycerin tablet;
- provide air access.
If the patient has lost consciousness, it is necessary to perform an indirect cardiac massage.
Diagnosis of heart failure
At an early stage, methods are used to detect interruptions in the functioning of the heart under load that are not noticeable in a calm state. At the CBCP clinic, patients are offered the most effective of these methods:
- daily ECG monitoring;
- stress ECG;
- Holter ECG;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- stress echocardiography.
To diagnose chronic heart failure and study various abnormalities in the structure of the heart and blood vessels, CBCP also uses 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM), cardiac rhythmography, and a special cardiac screening program.
Stages of heart failure
In medicine, there are 4 stages (degrees) of heart failure.
- First . Mild manifestations of the disease during physical activity (fatigue, shortness of breath, increased heart rate), which most patients usually do not pay attention to. In a calm state, the symptoms disappear.
- Second . Quite long-term, increasing changes in the functions of the heart occur. The patient begins to feel interruptions in heart rhythm and shortness of breath already at rest, but their degree still remains moderate. Moreover, symptoms may appear suddenly, for example, when trying to get out of bed.
- Third . In the end, interruptions in the functioning of other organs and blood vessels make themselves felt, accompanied by pathological changes in their tissues and the circulatory system.
Qualified care for heart failure at the CBCP clinic
At the slightest suspicion of this disease, undergo diagnostics of the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to determine the true cause of the disease in order to promptly block its further development.
The CBCP clinic has the latest expert-class equipment for diagnosing all types of this disease. Experienced, qualified cardiologists will advise you and give recommendations on how to treat heart failure.
Make an appointment right now on the website or during business hours by phone.