- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
Minor anomalies of cardiac development (MACD) in children are minor changes in the structure of the heart and blood vessels, which, as a rule, do not lead to gross disturbances of blood flow and do not cause significant clinical manifestations.
The abbreviation MARS is consonant with the name of the planet, which makes it easier to remember the long, complex term.
In recent years, there has been an increase in the number of children with minor anomalies of cardiac development. This is primarily due to improved diagnostics due to the widespread introduction into practice of ultrasound examination of the heart (cardiac ultrasound or EchoCG - echocardiography).
Causes of minor cardiac anomalies
As a rule, the causes of occurrence are divided into external and internal factors. The first include poor ecology, stress, poor nutrition, and taking medications. Internal indicators include genetic pathologies that can be caused by hereditary predisposition. As a rule, all these deviations arise at conception, and this is the most common option, less often - at the birth of a child. The fetus's heart begins to form early in pregnancy, and if the expectant mother smokes, is exposed to radiation, or drinks alcohol, all of these can affect the baby.
Diagnostics
Acquired heart defect. When diagnosing people, their well-being at rest, exercise tolerance are monitored, and their medical history is clarified.
When diagnosing heart defects in the clinic, palpation reveals the presence of venous pulsation, cyanosis, edema, and shortness of breath. Percussion determines the boundaries of the heart, listens to light and heart sounds and noises (to determine the type of defect). Palpation is also used to determine the size of the liver.
Using the results of phonocardiography, heart valve defects are detected. To clarify the type of disease, an x-ray is performed. Echocardiography helps diagnose pathology, the severity of regurgitation, the area of the atrioventricular orifice, the size and condition of the valves, chords.
Laboratory tests that have the greatest diagnostic value include special rheumatoid tests, determination of cholesterol, sugar, urine and blood tests.
Such diagnostics are carried out not only during the initial examination of patients with suspected disease, but also in dispensary groups of patients with a confirmed diagnosis.
Congenital. The diagnosis is confirmed by visualizing the defect on echocardiography, identifying ECG signs of cardiac chamber overload and hypertrophy, recording noise using phonocardiography, and detecting disturbances in the gas composition of arterial blood. A change in the configuration of the heart muscle is also detected on the corresponding x-ray.
After 3 years of a child’s life, congenital heart pathologies are differentiated from rheumatism, non-rheumatic carditis, cardiomyopathies, bacterial endocarditis, and disorders of the cardiovascular system. The latter are often based on congenital minor anomalies and dysplasia of the connective tissue structures of the heart. It is also necessary to differentiate congenital defects from each other.
Symptoms of minor cardiac anomalies
Basically, a person who has developmental anomalies does not feel any discomfort, so this pathology is most often found during a routine examination by a doctor. When listening, the doctor may hear a heart murmur and will send you for additional tests. In principle, it is difficult to call it a disease, since these are simply some anomalies in the heart that do not have serious consequences. Very often there are cases when a teenager simply “outgrows” it, and everything gets better on its own.
Minor cardiac anomalies
Minor anomalies of cardiac development (MACD) are microdisorders of the development of the cardiovascular system. The most commonly detected abnormalities are mitral valve prolapse, left ventricular accessory chordae, and patent foramen ovale.
Minor anomalies of cardiac development (MACD) are microdisorders of the development of the cardiovascular system. The most commonly detected abnormalities are mitral valve prolapse, left ventricular accessory chordae, and patent foramen ovale.
Unlike heart defects, these anomalies are not accompanied by clinically significant disorders, however, in all periods of life they themselves can cause the development of serious complications or aggravate other diseases.
Minor anomalies of heart development are often combined with such serious conditions as cardiac arrhythmia and conduction disturbances, sick sinus syndrome, right bundle branch block, extrasystole and paroxysmal tachycardia, which can be life-threatening for the child.
The reasons for the formation of MARS are, most often, the improper formation of connective tissue, which forms the basis in the structure of the valves and septa in the heart. This disorder is called connective tissue dysplasia.
MARS appears already in the first year of life. It can be detected when examining a child. The cardiologist pays attention to the appearance of a heart murmur when the body position changes and during exercise.
In adolescents, MARS is often combined with disorders such as scoliosis, flat feet, joint hypermobility, polycystic kidney disease, dilation of the ureters, gastroesophageal reflux, gallbladder abnormalities and various developmental disorders of the genital organs (phimosis, etc.).
If these symptoms are present, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive in-depth examination of the child by a pediatric cardiologist to clarify the diagnosis.
At the First Children's Medical Center, a comprehensive assessment of the child’s health and cardiovascular system is carried out, including all the necessary studies:
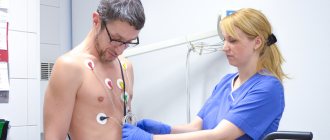
- electrocardiography
- doppler echocardiography
- Holter heart rate monitoring
- functional tests with physical activity
- 24-hour blood pressure monitoring
- laboratory research
Based on the examination results, the pediatric cardiologist makes a qualified conclusion about the state of the cardiovascular system, prescribes treatment and rehabilitation methods. In the future, regular monitoring is carried out by this specialist 2 times a year.
Non-drug treatments for MARS include:
1. Age-appropriate organization of work and rest
2. Rational, balanced diet, rich in protein, microelements, vitamins C and E
3. Therapeutic physical training classes
4. Massage courses – at least three annually with an interval of 1 month
5. Physiotherapeutic treatment, halotherapy (stay in a salt cave) - at least two courses per year
Diagnosis of minor cardiac anomalies
In order to detect this disease, you need to consult a doctor who will first conduct an examination, then listen to the heart, after which he will offer to do an ultrasound of the heart, as well as an ECG. Since minor anomalies in the development of the heart occur in children, the doctor will ask whether the baby has fainted or complains of headaches. The doctor will also listen to the heart and count the heart rate to make sure that the child does not have tachycardia. Thanks to an ECG, you can not only determine whether you have, but also heart rhythm disturbances, which is also an important factor.
It should be added that, although rare, the child may experience pain in the heart area, as well as surges in blood pressure.
Publications in the media
Minor anomalies of cardiac development (MADC) are anatomical congenital changes in the heart and great vessels that do not lead to gross dysfunction of the cardiovascular system. A number of MARS are unstable and disappear with age. Frequency - 2.2-10% in the population, in children with various cardiac pathologies - 10-25%, increases with hereditary connective tissue diseases. The predominant age is children of the first 3 years of life. Etiology. Hereditary determined connective tissue dysplasia. A number of MARS are dysembryogenetic in nature. The influence of various environmental factors (chemical, physical effects) cannot be excluded.
Options. About 40 variants of MARS are described in the literature. Most often observed • Ectopic trabeculae • Mitral valve prolapse • Tricuspid valve prolapse • Patent foramen ovale • Long Eustachian valve (flap) - a non-rudimentary fold of the endocardium (an element of the embryonic circulation), located at the mouth of the inferior vena cava from the side of the right atrium cavity, with a length of 1 up to 2 cm. Usually accidentally found during echocardiography • Aneurysm of the interatrial septum - protrusion of the interatrial septum in the area of the fossa ovale, which does not cause hemodynamic disturbances. Clinically, upon auscultation - systolic clicks • Aneurysm of the interventricular septum - bulging of the interventricular septum towards the right ventricle. On auscultation - systolic murmur and clicks on the left at the base of the sternum • Dilatation of the aortic root and sinuses of Valsalva - expansion of the aortic orifice (in children, normally 1.2–2.4 cm) and sinuses (normal depth, 1.5–3 mm ). Auscultation - inconsistent systolic “clicks”, sometimes a “spinning top” sound on the vessels of the neck.
Concomitant pathology • Marfan syndrome • Ehlers–Danlos–Rusakov syndrome • Primary hypogonadism • Behcet's syndrome • Congenital heart defects (CHD) • Cardiac arrhythmias • Infective endocarditis • Valvular regurgitation.
Diagnostic criteria • Anamnestic data (occupational hazards, maternal alcoholism during pregnancy, connective tissue diseases in the family, etc.) • Signs of dysplastic development (external minor developmental anomalies - short neck, high palate, etc.) • Characteristic auscultatory pattern depending on the variant of MARS • Changes on the ECG • EchoCG criteria • X-ray criteria.
Differential diagnosis • Congenital heart disease • Major anomalies of cardiac development.
Functional significance • Depends on the patient’s age, variant of MARS, presence of concomitant diseases • Marker of dysembryogenetic development of the heart • Predisposes to the development of arrhythmias, valvular regurgitation, left ventricular dysfunction.
Treatment is determined by the type of MARS and concomitant pathology.
Reduction. MARS - minor anomalies of cardiac development
ICD-10. Q20.9 Congenital anomaly of cardiac chambers and connections, unspecified
Note. Major anomalies of cardiac development are anatomical changes in the heart and great vessels, accompanied by gross dysfunction of the cardiovascular system (for example, mitral valve prolapse with grade III regurgitation).
Treatment of minor cardiac anomalies
If, nevertheless, the child is bothered by any of the above syndromes, then care must be taken to ensure that the daily routine is followed. Limiting exercise is not necessary; on the contrary, you need to spend more time in the fresh air and play active games. At the same time, we must not forget about the benefits of proper nutrition, this will help you quickly restore your strength and support your immune system. Surgery is required in very rare cases. In order to remove the anomaly, the surgeon will insert an instrument through large vessels and correct the defect. The operation is not considered difficult, complications are usually not observed and the person quickly returns to their previous lifestyle. The doctor may suggest a course of magnesium supplements in order to improve the functioning and structure of heart tissue.
Types of heart defects
There are heart pathologies of acquired and congenital origin.
Congenital heart defect. With this pathology, defects are observed in the walls of the myocardium, which is responsible for the rhythmic contractions of the heart muscle or the walls of large vessels that are adjacent to the myocardium. Some types of birth defects occur both in various combinations and individually.
Acquired defects are also called valvular defects. With this pathology, one or more valves of the heart muscle undergo changes. The most commonly affected valves are the aortic valve, which is located between the aorta and the left ventricle, and the mitral valve, which controls blood flow between the ventricle and the left atrium.
Prevention
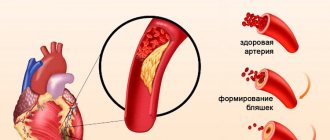
The risk of heart disease can be reduced through timely treatment of diseases caused by streptococci - pharyngitis, sore throat. They are the most common causes of the development of rheumatism. If you already have this disease, then you must take a course of bicillin prophylaxis. It must be prescribed by a competent doctor.
If a person has been diagnosed with mitral valve prolapse or has already suffered from rheumatism, then for the purpose of prevention it is necessary to start taking antibiotics prescribed by a doctor for a certain time before medical interventions. These “interventions” include removal of tonsils, teeth, adenoids and other surgical operations.
The ABC-Medicine clinic provides complete diagnosis and treatment of heart defects of various forms. If you are concerned about the listed symptoms, be sure to sign up for an examination. Highly qualified specialists will individually prescribe treatment for the disease.
Treatment
Therapeutic treatment of heart defects cannot eliminate pathological changes in the heart. It will only ease the course of the disease.
Treatment of heart defects depends on several components:
- type of defect;
- the general health of the patient;
- stage of the disease.
The sooner the disease is diagnosed and treatment of the heart defect is prescribed or surgery is performed, the more the risk of serious consequences will be reduced. Now many defects are being successfully eliminated. But we should not forget that no matter how competently, from a technical point of view, the operation was performed, a healthy heart is much more reliable than a restored one. Therefore, it is important to first reduce the possibility of the disease occurring.