A heart attack is extremely dangerous. After all, cardiological pathology often manifests itself gradually, and it often happens that it is disguised as others. For example, one of the symptoms is pain that can radiate to the arm, and in some cases to the shoulder. A heart attack can also manifest itself as causeless coughing, sweating, and even fear of death. At the same time, it is extremely important to recognize the disease in time in order to quickly provide first aid and have time to call an ambulance. After all, when a heart attack develops or serious changes in the functioning of the heart muscle, time plays an important role - the faster help is provided, the greater the chances of recovery. Mehman Mamedov, MD, professor, expert of the National Health League, told AiF.ru about how to distinguish a heart attack from other diseases and how quickly to act .
Causes and course of the attack
A heart attack is essentially a violation of the blood circulation of the myocardium, when necrosis of the muscle tissue of the heart can subsequently develop. The attack can be lightning fast - in this case, serious complications appear that require immediate resuscitation measures. Depending on the degree of narrowing of the coronary arteries, the attack may last longer.
As a rule, most often a heart attack develops due to problems with the cardiovascular system. First of all, this is atherosclerotic damage to the arteries. Age is an important factor; in the elderly, the risks of developing pathology increase significantly, as functional changes in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels affect. Although recently there has been a rejuvenation of cardiac incidents. An attack lasting more than 30 minutes can be considered a manifestation of myocardial infarction.
Before and after the disaster. What to do if you have a heart attack Read more
A heart attack can develop against the background of angina pectoris. This is one of the forms of coronary disease, in which paroxysmal pain appears in the heart area. They develop against the background of insufficient blood supply to the myocardium. Angina is provoked by a number of reasons: physical and emotional overload, bad habits (especially smoking, alcohol).
In addition, factors such as diabetes and long-term use of a number of drugs, including non-steroidal ones, can trigger a heart attack.
Causes of myocardial infarction
Etiology of MI
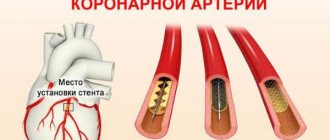
- sudden obstruction to blood flow in the branches of the coronary artery (vessels supplying the heart). Most often, such an obstacle is an atherosclerotic plaque with a blood clot.
Atherosclerosis in the walls of the arteries is the formation of peculiar “growths” - plaques consisting of fatty, fibrous tissue, calcium, and which, as they progress, narrow the lumen of the vessel up to 90% or more. At the time of increased blood pressure, physical effort, or psycho-emotional stress, rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque is possible, the reaction to which is thrombosis.
Less commonly, the cause is a prolonged, prolonged spasm
coronary artery in the absence of significant atherosclerosis, or a complication of other diseases: congenital malformations, trauma to the coronary arteries, vasculitis, embolism, tendency to hypercoagulation (increased blood clotting), syphilis.
There are a number of risk factors
, repeatedly increasing the likelihood of myocardial infarction.
There are non-modifiable ones, that is, those that cannot be influenced:
- male gender (up to 50-55 years, then the incidence levels off),
- age,
- genetic conditioning (coronary artery disease and other manifestations of atherosclerosis in blood relatives);
- low physical activity (hypodynamia),
- obesity or increased body weight,
- smoking (active or passive),
- arterial hypertension,
- diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome,
- dyslipidemia.
And
modifiable, by changing which you can significantly reduce the likelihood of disease:
Acute phase
An acute heart attack is characterized by symptoms such as severe weakness, dizziness, and acute pain in the chest. In this case, it can radiate to the shoulder blade, neck or jaw. The pain does not go away after taking the pills. Indirect evidence of the development of cardiac pathology in such a situation can be cold sweat, shortness of breath and weakness.
The effect of surprise. Who is at risk for sudden cardiac death syndrome Read more
Prevention of myocardial infarction
Prevention of coronary artery disease and its extreme expression - myocardial infarction - comes down to influencing modifiable risk factors, namely: physical activity, nutrition, body weight, bad habits, blood glucose and cholesterol levels, blood pressure.
After a heart attack, it is important to regularly independently measure blood pressure and heart rate, systematically undergo ECG and EchoCG diagnostics, and take daily medications to prevent the progression of heart dysfunction and recurrence of the disease.
Development in advance
Sometimes a heart attack can take an extremely long time to develop—about a month. In this case, the approaching threat may manifest itself as the following harbingers.
A person suffers from fatigue and constant drowsiness. Vessels that are constantly under stress are in a state of tone, that is, they are predominantly narrowed. This means that the body lacks oxygen and nutrition. The nervous system especially reacts to such a shortage. As a result, symptoms such as drowsiness, melancholy and fatigue begin to develop, for which at first glance there is no reason.
Another sign is shortness of breath. If one organ malfunctions, in this case the heart, problems begin in the functioning of the lungs, the gas exchange process is disrupted, and breathing becomes intermittent.
A few days before the attack, many people experience a feeling of internal coldness and begin to shiver. Often even such a condition is confused with ARVI, but if the condition is caused by problems with the heart, the body temperature will be normal. It is also worth remembering cases of hereditary history, and if problems with the heart and blood vessels were observed in relatives, it is worth visiting a doctor even for the purpose of prevention.
The many faces of anxiety. How a panic attack differs from a heart attack Read more
Coughing won't help your body.
Recommendations have appeared on the Internet on how to survive a heart attack when no one is around.
The advice is so simple that people actively forward them to each other, post them in chats and generally express delight: they say, thousands of poor people will be saved! Here's what an anonymous online author writes:
“Let's say you're driving home (alone, of course) after a hard day at work. Suddenly you begin to feel severe pain in your chest, which radiates into your arm and up to your neck. How to survive a heart attack when you are alone? What should a person whose heart is beating abnormally, who is starting to weaken and have 10 seconds before losing consciousness, do? And then the author answers his own question: “Don’t panic, but start coughing quickly and very hard. Be sure to take a deep breath before each cough. The cough should be deep and long, expectorating, from the very depths of the chest. Inhalation and coughing should be repeated approximately every two seconds without rest until help arrives or you feel that your heart is beating normally again.
Taking deep breaths brings oxygen to the lungs, while coughing compresses the heart and helps blood circulate. The squeezing pressure on the heart also helps it restore its normal rhythm. This way, the heart attack victim can get to the hospital.”
Can you trust such advice? We asked the director of the Russian Scientific Center of Surgery of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Doctor of Medical Sciences Sergei Leonidovich Dzemeshkevich about this:
“I’m even embarrassed to comment on such nonsense,” said the professor, having become acquainted with the recommendations of the unknown author. - No person is able to determine for himself what such symptoms mean - a developing heart attack or an attack of angina. Sometimes we, specialists, even in intensive care cannot determine this immediately; emergency tests and monitoring of the patient are necessary. Coughing intensely in such a situation is dangerous - during a heart attack, and even more so during a developing heart attack, any stress is dangerous.
What do we have to do?
- Call an ambulance and lie still.
- If the condition worsens and there is nitroglycerin, take one tablet or capsule (put under the tongue, do not swallow!).
- After 5 minutes, and if it doesn’t feel better, take another tablet, you can take a third, but no more.
- After taking nitroglycerin, you should not get up - a sharp decrease in blood pressure may make you dizzy.
- If you see something on the street, at a bus stop, in a store, etc. the person has become ill, do not pass by - call an ambulance, stay with him until the doctors arrive: unfasten the tight collar and belt, if possible, lay him down, provide air access.
What you need to know
— Signs of a heart attack in which you need to call an ambulance: pain in the heart, which can radiate to the arm, shoulder, lower jaw, stomach, as well as a burning sensation behind the sternum.
- Reaction to nitroglycerin. If after taking it the pain and burning sensation do not go away, this is one of the characteristic signs of a heart attack.
- Fear of death. When the heart feels bad, stress hormones are released, triggering an attack of fear. At the same time, the person turns pale and cold sweat appears.
- Most often, a heart attack occurs in the morning, since at this time the production of hormones, in particular adrenal hormones and stress, peaks. In the morning, be more attentive to yourself and your family - if you feel unwell, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Hidden symptoms
There are also atypical symptoms, which many do not pay attention to, wasting time. For example, chest pain is not the only variant of an attack caused by a malfunction of the heart muscle. There is a variant of the so-called abdominal form. It occurs predominantly in women. The pain in this case is determined throughout the abdomen or collects under the ribs on the right side. At the same time, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, which does not bring relief, and flatulence appear. Doctors even compare the clinical picture to an “acute abdomen.”
Another atypical option is the asthmatic form. There may be no pain at all. The main symptoms include a cough with pinkish frothy sputum, suffocation, and shortness of breath. The patient has to breathe frequently, and this is difficult for him. It is difficult for him to lie horizontally; it is most comfortable to be in a semi-sitting position.
The arrhythmic form of a heart attack also manifests itself predominantly without pain or against the background of minor pain. The main symptom is tachycardia.
The disease of the dissatisfied. What symptoms indicate the onset of heart problems Read more
When to ask for help
Naturally, in the acute phase you need to seek help immediately. In other situations, if some atypical health problems begin that are embarrassing, you should not try to treat yourself. It is necessary to consult a doctor - a therapist or cardiologist. Moreover, you should not practice folk remedies - you can simply waste time. Those who have people in their family suffering from heart disease should be especially attentive to themselves. After all, hereditary risks in the development of cardiovascular pathologies are quite high.
Treatment of myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction
- an emergency disease in cardiology and serves as an indication for immediate hospitalization in intensive care.
The number one task for doctors is to restore blood flow
in a thrombosed vessel. They achieve this in different ways. The priority and most effective is surgical intervention - angioplasty with stenting of the affected area of the artery or coronary artery bypass grafting. In parallel, medications are used that inhibit the development of a blood clot - disaggregants (aspirin, clopidogrel) and anticoagulants (heparin), and if immediate surgery is not possible, thrombolytics - drugs that dissolve the blood clot (alteplase, prourokinase).
Pain relief
carried out with narcotic analgesics, neuroleptics, intravenous infusions of nitroglycerin.
The size of the necrosis zone can be reduced by reducing myocardial oxygen consumption by using beta-blockers (metoprolol, bisoprolol, atenolol), ACE inhibitors (enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril), and oxygen therapy.
For arrhythmias
antiarrhythmics are used (magnesium, lidocaine, amiodarone), atropine for bradycardia. Anxiolytics and sedatives are prescribed to ensure psycho-emotional peace of the patient.
Strict bed rest
in the early stages of treatment and fractional meals, limited in volume and calorie content.