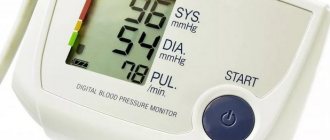
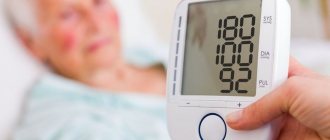
Arterial hypertension is a common disease among older people. When people are aware of their illness, they take certain medications on a regular basis. These medications help keep blood pressure within normal limits. But it happens that a person experiences an exacerbation of the disease. It all starts with a headache, nausea appears, and the vision becomes dark. Such symptoms accompany a hypertensive crisis, which can only be stopped by emergency doctors. It is very important to know when you can do without doctors, and when calling an ambulance cannot be avoided and it is better to do this in a timely manner.
What to do if you have high blood pressure
It should be noted that there are no strict recommendations regarding calling an ambulance in case of high blood pressure. It all depends on the patient’s condition and the deterioration of the condition. If sudden changes for the worse have occurred, it is not recommended to hesitate; life may be in danger at any moment. A hypertensive crisis often causes stroke and other complications that can cause death.
It happens that nothing bothers a person, but the numbers on the tonometer go off scale. And in this case, it is these indicators that need to be taken into account, and not your feelings. Here are some tips from doctors:
- If the upper readings are from 110 to 139, and the lower pressure is within 70-89 units, no action should be taken. Take a lying position.
- If the indicators are above 140 to 90, then this indicates hypertension and measures are already being taken from such indicators. You don’t always need to take medication right away; sometimes it’s enough just to create calm conditions, apply warm mustard plasters to the muscles of your legs (on your calves) and the back of your head.
- If your blood pressure is above 160 over 95, this is a serious reason to think about having you examined by a doctor. Before visiting the doctors, take Capoten.
It is necessary to realize that such an increase is dangerous for the body and should not be ignored. Also rely on your feelings.
Example of cost of hospitalization for hypertension
Patient:
woman 64 years old
Length of stay in the hospital:
18 days
Hospital:
NCC JSC Russian Railways on the street. Hour, 20
Diagnosis:
Hypertension stage III, degree 2, risk 4. NRS: Paroxysmal form of atrial fibrillation, continuously relapsing form.
Complications:
Chronic heart failure (CHF) 1 FC.
Concomitant diseases:
Cerebrovascular disease (CVD). vertebrobasilar insufficiency (VBI). Discirculatory encephalopathy (DE) 2 tbsp. Nodular goiter, euthyroidism. Chronic cholecystitis, remission. Chronic gastritis, remission. Kidney cysts. Common osteochondrosis of the spine. Varicose veins of the lower extremities.
Symptoms of hypertensive crisis
There is a list of symptoms that require help:
- rapid pulse;
- headache and tinnitus;
- visual impairment;
- spots in the eyes;
- goosebumps and numbness in the limbs;
- speech disorders;
- the muscles of the face or tongue become numb;
- breathing problems, wheezing is possible.
If you have at least one of the above symptoms, you should take a reclining position, move less, call an ambulance and open the door if you are alone at home.
Memo for patients on the procedure for calling emergency medical teams
1. Emergency medical care for the population of Mosty and the Mostovsky district is provided by the emergency department of the Mostovskaya Central District Hospital free of charge and around the clock; transportation of patients who do not require medical care is provided on a paid basis.
2. Emergency medical care in the event of a sudden illness or injury, childbirth can be called from any landline telephone, pay phone, mobile phone at the number “103” free of charge, in person when citizens contact the emergency medical service station.
3. Emergency medical care is called for adults and children in case of accidents, life-threatening conditions and sudden illnesses, regardless of the place of their occurrence (home, street, public places, institutions, etc.). The emergency medical team is dispatched to a public place on a first-come, first-served basis.
Accidents include : automobile and other transport, street, industrial and household injuries (wounds, fractures, dislocations, burns, frostbite, electric shock or lightning), drowning, suffocation, foreign bodies in the respiratory tract, bleeding resulting from injury, suicidal attempts, acute non-food poisoning, mental disorders when the patient poses a danger to himself and others.
threatening conditions include: loss of consciousness, respiratory distress, convulsions, sudden acute pain in the heart, cardiac arrhythmia, cerebrovascular accident.
Sudden diseases include : acute abdominal pain accompanied by vomiting, an attack of bronchial asthma, acute poisoning (food poisoning).
4. The emergency department delivers women in labor who need emergency hospitalization to the maternity ward of the Volkovysk Central District Hospital or to the regional perinatal center in Grodno. Hospitalization of patients and victims in accordance with the profile of the disease is carried out in the district hospital of Mosty, Grodno Regional Clinical Cardiology Center, Grodno Regional Clinical Hospital (department of neurology), Grodno Regional Clinical, Grodno Regional Clinical
5. The caller of the emergency medical team is obliged to calmly and clearly inform the paramedic for receiving and transmitting calls to the emergency department by calling “103” the following data:
- reason for the call;
- last name, first name, patronymic (if known
- age (approximately) of the patient;
- the exact address of the patient’s location (street, house, apartment number, entrance, floor, home phone number, entrance door code) and its landmarks, the most convenient access to the house;
- the patient's main complaints;
- does the patient suffer from chronic diseases or have complications (if known)
- tell who is calling;
- accurately answer the questions asked;
- ensure that the ambulance team meets on the street, near the house;
- prepare available medical documents, passport.
Clear and accurate answers to the dispatcher’s questions will significantly speed up the reception of a call and the timely arrival of an ambulance.
6. Persons guilty of intentionally calling an emergency medical service without justification or reporting false data out of mischievous or hooligan motives, as well as committing antisocial acts towards the staff of field teams, are subject to administrative or criminal liability.
7. In situations that threaten the life and health of medical staff when servicing a call (the presence of vicious animals in the room, aggressive people around, a group of people in a state of alcoholic, toxic or drug intoxication and other antisocial elements, etc.) the emergency medical team assistance has the right to attract police officers to service the call.
8. In situations that threaten the life and health of patients, if they refuse medical care and hospitalization, the team has the right to involve police officers to provide emergency medical care and, if necessary, hospitalization.
9. Emergency medical calls are divided into the following groups depending on the reason for the call:
Group 1: emergency calls - are transferred by the dispatcher for service to the ambulance (emergency) medical team, in accordance with its specialization no later than 4 minutes from the moment of its registration.
These include:
- emergencies;
- accident, traffic accident with victims;
- loss of consciousness by the patient;
- rash with high fever in children;
- patient poisoning with chemicals or drugs;
- hanging;
- fire;
- extensive burn;
- deep and extensive wounds;
- convulsions;
- acute breathing disorders;
- dies;
- falling from a height higher than one's own height;
- drowning;
- electrical injury.
Group 2: urgent calls - are transferred by the dispatcher for service to the ambulance (emergency) medical team, in accordance with its specialization no later than 15 minutes from the moment of its registration.
These include:
- arrhythmia;
- heart attack;
- asthma attack;
- injury;
- foreign body;
- bleeding (gastrointestinal, uterine, nasal);
- frostbite;
- childbirth;
- sudden disturbances in motor activity;
- call to the emergency medical services team associated with a sharp deterioration in the patient’s health condition when it is impossible to clarify the reason for the call.
Group 3: emergency calls - can be transferred by the dispatcher for service to the ambulance (emergency) medical care team during non-working hours of the city clinic and rural medical stations; during working hours (Monday-Friday from 8-00 to 18-00) such calls are transferred to service to local doctors no later than 60 minutes from the moment the call is registered.
These include:
- significant change in blood pressure;
- allergies;
- headache;
- pain in the abdomen, back, chest;
- hemophilia;
- inappropriate behavior;
- renal colic;
- vomit;
- rash;
- high body temperature (if the temperature is not reduced by oral medications);
- acute urinary retention;
- food poisoning;
- anesthesia;
- transportation of a patient upon call received from a medical professional.
10. Accompanying a sick or injured person to the hospital is allowed to one person and only with the permission of the doctor of the emergency medical team.
When transporting children under 18 years of age, the accompaniment of parents and relatives is mandatory!
11. The doctor of the clinic must make an ambulance call regarding the delivery of patients to the hospital. Ambulance teams transport only patients who require transportation on a stretcher (heart attacks, strokes, bleeding, comas, severe injuries to the musculoskeletal system). In other cases, delivery is made by the clinic’s transport, or independently.
12. Ambulance medical personnel provide emergency and emergency medical care, but do not prescribe treatment for patients, do not adjust the treatment prescribed by the APU, do not provide medical care to patients as prescribed by specialist doctors from other healthcare organizations, except for the administration of painkillers to patients with cancer in non-working hours of outpatient clinics, does not have the right to issue certificates of incapacity for work and preferential prescriptions, forensic and expert reports, medical examinations to establish the fact of use of alcohol, narcotic and psychotropic drugs, written certificates to patients and relatives.
13. The paramedic for receiving and transmitting calls is obliged to give his work number at the beginning of receiving a call. In the event of a call for a reason that is not subject to an emergency medical team, the paramedic responsible for receiving and transmitting calls is obliged to give advice on where to go for medical help in this case. From 8-00 to 18-00 on weekdays, emergency medical calls are transferred to the reception of the city clinic for service by the emergency service of the clinic or by rural medical districts. The paramedic on duty for receiving and transmitting calls has the right to give consultations without visiting the patient by telephone, using algorithms.
14. No certificates are issued to the public by calling “103”. Written certificates for calls from emergency medical teams can only be issued by the administration of the Mostovskaya Central District Hospital at the written request of organizations and institutions or upon direct application from the patient with the provision of an identification document in accordance with Article 46 of the Law of the Republic of Belarus “On Health Care”.
Compiled on the basis of Resolution of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus No. 110 dated October 12, 2009. “On approval of the Instructions on the procedure for organizing the activities of the emergency (emergency) medical care service.”
Timing and duration
To undergo a routine examination in a hospital, 3-5 days will be enough.
If it is possible to conduct the study on an outpatient basis, a certificate of incapacity for work will be given for each day spent visiting diagnostic rooms. It may take up to 10 days to select a drug therapy regimen. If hypertension is malignant and insensitive to first- and second-line medications, the period of hospitalization may be extended by decision of a special commission.
Sick leave for hypertensive crisis
Most often, sick leave for high blood pressure is obtained in the event of a hypertensive crisis. People seek help because of severe symptoms. The duration of removal from official duties depends on the type of crisis, the stage (degree of target organ damage) of hypertension and the complications that arise.
| Stage of hypertension | Length of sick leave for the first type of crisis (days) | Duration of disability in the second type of crisis (days) |
| I | 3-5 | Not typical |
| IIA | 7-10 | 18-24 |
| IIB | 10-20 | 20-30 |
| III | Not typical | 25-30 |
The duration of hospitalization for a hypertensive crisis depends on the presence of complications:
- hypertensive encephalopathy (initial degree of damage to brain tissue);
- acute cerebrovascular accidents (stroke);
- angina pectoris;
- acute heart failure;
- dissection of a pre-existing aortic aneurysm;
- myocardial necrosis (infarction);
- pulmonary edema.
conclusions
The need to issue a certificate of temporary disability for hypertension is determined, first of all, by the complaints and condition of the patient. Outpatient treatment is possible, but inpatient observation is more effective. The degree of risk of complications and the need for hospitalization is determined by the attending physician.
Most often, temporary disability is established during hypertensive crises.
The average duration of hospital treatment for patients with arterial hypertension is 11-14 days.