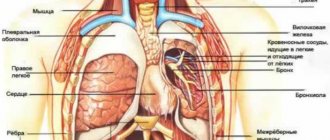
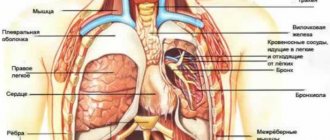
SPECIALISTS Gynecologist Gynecologist-endocrinologist Pediatric gynecologist Mammologist-oncologist Dermatologist Hirudotherapist Intimate plastic surgery Doctor Contour plastic doctor Ultrasound doctor SERVICES AND PRICES Gynecology Mammology Ultrasound diagnostics Paid tests Intimate surgery Contour plastic Treatment for women PROMOTIONS AND DISCOUNTS Students Teams Friends and subscribers am For residents of the region For pensioners Promotions in clinic
Stagnation of blood in the pelvic organs is one of the most common manifestations of circulatory disorders in the female internal genital organs. In the future, this contributes to pathological changes in this area. The main reason for blood stagnation in the pelvis is daily sedentary work without breaks. When a person is in this position for a long time, the ligaments and muscles of the pelvis squeeze the blood vessels passing nearby, preventing blood from circulating freely. And with the advent of computers and the Internet, the number of people suffering from this phenomenon has increased many times...
Mostly women after 30-40 years of age suffer from this, although even in girls over the age of 20, gynecologists detect this condition in 20-25% of cases. After the age of 50, stagnation of blood and lymph in the pelvic organs is observed in almost 80% of women.
☛ Risk factors and reasons why pelvic congestion occurs: • hereditary factors; • sedentary lifestyle; • lack of regular sex life with orgasms; • adhesions in the area of the uterus and appendages; • pathological retroflexion or lateroflexion (bending of the uterus backwards or to the side); • chronic inflammation “feminine”; • protection by interrupted sexual intercourse; • taking contraceptive pills and hormonal drugs. • heavy physical and emotional stress; • pregnancy (repeated, aggravated, multiple); • complicated course of labor.
According to statistics, the problem affects young women and more often those who have 2-3 children. It is believed that during pregnancy, increased estrogen levels can affect the walls of the veins, making them weaker. Blood stagnation often occurs with a disease such as varicose veins of the pelvic organs. These are veins that have stopped functioning properly because something is wrong with the valves.
Cause of lung congestion
- The most common cause of pulmonary congestion is left ventricular failure (eg, due to angina, myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, mitral valve disease).
- Increased pressure in the pulmonary veins (pulmonary artery wedge pressure 12-18 mm Hg),
- pulmonary blood flow is redistributed to the upper parts of the lungs (veins located cranial to the atria collapse at normal pressure)
- When pulmonary artery wedge pressure is >20 mmHg. Pulmonary edema develops.
Conservative therapy
The most common treatment option is conservative therapy with anticoagulants. Drugs used for inferior vena cava syndrome include the anticoagulant warfrin or Xarelto. Detralex or phlebodia are used to improve blood flow from the legs. The main means of conservative treatment is the constant wearing of compression tights of compression class 2-3. They need to be changed every 3 months, as they lose their properties with prolonged wear.
Treating the symptoms of inferior vena cava syndrome with medications and compression can reduce chronic venous insufficiency. Considering the technical complexity of surgical treatment, conservative methods are predominant in modern medical practice.
Which method of diagnosing pulmonary congestion to choose: MRI, CT, radiography
Selection Methods
- Radiography.
What will an x-ray of the lungs show when there is congestion in the lungs?
- The vascular pattern of the upper pulmonary field is enhanced (pulmonary veins are more pronounced), the basal sections are depleted
- An increase in the shadow of the heart and accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity is not always observed.
Is a CT scan of the lungs informative for increased pressure in the pulmonary veins?
- Bronchovascular structures are thickened, the diameter of the vessels is greater than the diameter of the bronchi (normally it is approximately the same).
Distinctive signs of pulmonary congestion
- Cranialization of pulmonary blood flow in the absence of other changes in the lungs.
Prevention of congestion in the lungs
Reducing the risk of pulmonary congestion usually begins during hospitalization in a medical facility. Sometimes these procedures need to be continued at home, along with therapeutic and breathing exercises.
- Congestion in the lungs most often occurs in bedridden patients, in elderly people, with forced limitation of mobility, because the physiology of the respiratory system does not favor long periods of lying down.
- Congestive processes in the lungs lead to a decrease in the amount of air inhaled and insufficient saturation of the blood with oxygen and other equally important gases. An imbalance in the blood gas composition disrupts many chemical reactions occurring in cells and can lead to additional diseases.
What factors provoke the formation of pathologies in the lungs?
- Decreased tidal volume
- Heart diseases
- Hypertonic disease
- Staying in one position for a long time
- Lack of physical activity
- Decreased cough reflex
- Insufficient preventive measures
- Presence of excess fluid in the body
Basic measures to prevent pulmonary congestion 1. Movement
Congestion in the lungs in the initial stage is eliminated only by activity.
- A person forced to stay in bed for a long time needs to make as many movements as possible - roll over, change body position, sit down.
- If it is not possible to move independently, then caregivers need to frequently and promptly change the position of the patient’s body in bed.
- You should not sleep on low pillows or be motionless for a long time, which weakens the functions of breathing and chest movement.
2. Massage and breathing exercises
The use of light manual massage and breathing exercises (even during inflammation) will maintain tissue elasticity and also facilitate expectoration of accumulated mucus. Active spontaneous breathing helps enrich the bronchi and lungs with oxygen and expands the range of motion of the chest, including the diaphragm.
For breathing exercises, you can use both regular balloons and special simulators.
3. Monitoring and maintaining oxygen levels in the blood
To determine the level of oxygen saturation in the blood, a pulse oximeter
.
And to compensate for the lack of oxygen at home, oxygen cylinders
and
oxygen concentrators
.
Oxygen Concentrator
is a device that extracts oxygen from atmospheric air by passing it through a so-called molecular sieve. The device is used both for medical reasons and to maintain health.
The oxygen concentrator must be used strictly in accordance with the instructions and/or doctor's prescriptions. It is unacceptable to exceed recommended dosages.
If you need additional information and specialist help, sign up for a personal consultation.
What diseases have symptoms similar to pulmonary congestion
Redistribution of blood flow caused by pulmonary pathology
— History
— Lung damage (for example, COPD, emphysema, pathology of the hilar region
and etc.
Cardiomyopathy in a 28-year-old man. A plain chest x-ray shows an expansion of the cardiac shadow and a narrowing of the retrocardial space. A significant redistribution of pulmonary blood flow to the upper pulmonary fields indicates left ventricular failure, which is associated with increased pressure in the pulmonary veins. There is an accumulation of fluid in the left cardiophrenic angle.
Severe blood stagnation in the lungs in a 64-year-old man. A plain chest x-ray shows an expansion of the cardiac shadow against the background of mitral stenosis; the roots of the lungs are expanded due to the vascular component and have blurred boundaries. Dilation of the vena cava and azygos indicates that there is also right ventricular heart failure.
What are pelvic varicose veins
How are varicose veins of the pelvic veins formed? The principle of its formation in women is similar to varicose veins in the legs. The valves normally found in the veins that allow blood to be pushed upward towards the heart become less elastic and do not function fully. As a result, the blood in the legs stagnates and the veins dilate. We often see them in others as raised and nodular venous plexuses that can be painful, especially when standing.
These same veins exist in our pelvis, and their valves may also be poor at carrying blood to the heart. This means that the outflow is less than the inflow and some of the circulating blood accumulates inside the pelvic structures due to gravity, causing the veins to swell. These dilated, defective vessels are hidden inside our pelvis, causing pain and other discomfort in the pelvic area, but we cannot see them. Sometimes they become visible around the genitals (vulva, vagina), inner thighs, buttocks, or down the legs.
Fig.1. "Comparison of normal blood flow through a vein and disturbance of blood flow due to valve damage."
Now it is clear that in this condition the blood flow slows down, the blood stagnates in the vessels, the pressure in the veins increases, and they become deformed - they stretch, increase in diameter. Therefore, ultimately, the speed of blood circulation decreases, and this is a direct path to the formation of venous insufficiency. As a result, blood that should flow back to the heart instead remains inside the pelvis, causing what Western medicine refers to as “pelvic congestion” (excess blood flow syndrome). It puts pressure on such important organs as the uterus, ovaries with tubes, bladder and lower intestines with all the ensuing consequences for the intimate and reproductive health of a woman...
Symptoms of blood stagnation in the pelvis
The clinical manifestations of pelvic hyperemia syndrome may vary from person to person. The main symptom is constant (chronic) pain. It is felt by a woman in the lower abdomen and can radiate (spread) to the lower back, sacrum or groin area. The intensity of pain varies and it intensifies during sexual intercourse, after prolonged standing, before or during menstruation, etc.
When visiting a doctor, patients often present the following complaints:
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- Irregular and painful periods;
- Haemorrhoids;
- Varicose veins of the external genitalia and vagina;
- Varicose veins in the legs;
- Lower back pain;
- Urinary problems;
- Chronic pelvic pain;
- Pain during and after sexual intercourse.
If a woman has more than two of the above symptoms, there is an increased likelihood of having pelvic venous stasis and varicose veins.
Possible harm to women's health
Pelvic congestion syndrome (PCS) can cause fertility problems and difficulties in women who have had two or more pregnancies. This condition can also cause the development of venous insufficiency in the lower extremities with varicose veins of the vulva and perineum. This happens because there is a direct connection between the venous plexuses of the uterus and appendages and the superficial network of the legs. This is why, in many cases of impaired blood flow and blood stagnation in the pelvic organs, women develop dilated veins in adjacent areas, especially on the inside or back of the thighs or calves.
Cosmetic defects caused by “protruding veins” and increased vascular patterns on the genitals and lower extremities are not the biggest problem with this syndrome. The danger of poor blood flow in the internal female organs lies in the multifaceted impact on many important functions of the female body.
Possible complications may be:
- Regular nagging pain in the lower abdomen of unknown cause;
- Psycho-emotional instability;
- Constant irritability, weakness, deterioration in performance;
- Decreased libido, anorgasmia;
- Ovarian hypofunction;
- Changes in the nature of menstruation;
- Inflammatory diseases of the uterus and ovaries;
- Problems with conceiving a child and carrying a pregnancy.
Diagnosis of congestion
Initially, a problem with microcirculation in this area can be identified if you perform a “female ultrasound” with a vaginal sensor. This method will allow the specialist to see the exact number, size and distribution of dilated veins in the uterus and ovaries, and optional Doppler measurements will help determine the parameters of vascular blood flow.
In advanced or difficult to differentiate cases, abdominal ultrasound, venography, laparoscopy and MRI are additionally prescribed to identify varicose dilatation.
Increased blood flow in the pelvic organs
The scheme and tactics for treating congestive processes are selected individually by the gynecologist, depending on the severity of this condition and the presence of certain symptoms. In any case, therapy should be comprehensive - aimed at restoring the tone of the venous walls and improving metabolic processes in the pelvic organs.
✅ The main ways to improve blood flow:
- The use of medications - phlebotropic drugs, vitamins and drugs that improve blood flow from venous vessels;
- Surgical intervention. Surgical treatment of the syndrome of “pelvic hyperemia” and varicose veins in the area of the pelvic organs, vulva and vagina is achieved by embolization of the pelvic veins, which can be recommended if conservative methods are unsuccessful or hopeless and only by a specialized specialist.
- Physical exercises, intimate Kegel training at home;
- Physiotherapy, manual techniques, etc.
If with p.p. Nos. 1, 2 and 3 are all more or less clear, we will focus on point No. 4. These include ways to improve blood circulation in the pelvis in women without resorting to invasive methods. The methods listed below to activate the movement of blood and lymph, reduce or eliminate venous stasis in the internal genital organs, can be used either independently or in combination with taking medications.
Only manual and similar treatment techniques, without the use of drugs, are carried out in order to prevent the development of stagnation. They are recommended for all women who lead a sedentary lifestyle or have the risk factors listed above!