Amylase and lipase are digestive enzymes. Their quantity in the bloodstream is used to diagnose the condition of the pancreas if pancreatitis is suspected. Tests can be carried out on the direction of a doctor or at the request of the patient himself, but only a specialist can interpret the results and, if necessary, prescribe treatment. To obtain the most accurate results, special preparation is required before donating blood. For 10 hours before the tests, you must stop eating and avoid significant physical activity and stress.
Detailed description of the study
Pancreatic lipase is a water-soluble enzyme that catalyzes the reactions of digestion of neutral fats (triglycerides) in the initial part of the small intestine - the duodenum. The biochemical feature of lipase is that this enzyme can perform its function without coenzymes - derivatives of vitamins, nucleotides, heme, etc.
The process of digestion of triglycerides begins in the lumen of the stomach with the help of lingual lipase, which is produced in the glands of the tongue and enters the stomach along with saliva. However, the main stage of digestion of neutral fats begins in the small intestine. Pancreatic lipase is formed in the pancreas and, as part of pancreatic juice, is secreted through the duct into the lumen of the duodenum together with colipase. This protein indirectly accelerates the action of lipase, so that fats begin to break down faster.
Before digestion, fats sequentially pass through the emulsification stage. Bile produced in the liver directly produces this process - the integrity of the neutral fat molecule is disrupted, as a result of which triglycerides are repeatedly mixed with water in the lumen of the small intestine and crushed into small fat droplets. After this, the process of hydrolysis begins with the participation of pancreatic lipase.
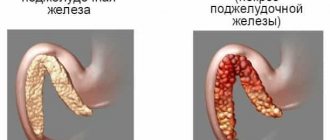
With pancreatitis, the outflow of pancreatic juice into the duodenum is disrupted. The large amount of lipase and other enzymes remaining in the gland, which have pronounced biological activity, leads to inflammation of the “self-digestion” type - the enzymes destroy the anatomical structure of the pancreas and become the main cause of the development of inflammation. In this case, a significant part of the lipase begins to enter the blood. In addition, lipase together with calcium leads to extensive damage to the pancreas (pancreatic necrosis).
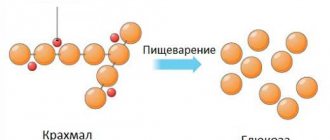
Another enzyme, alpha-amylase, is also a marker of pancreatitis. This protein is formed in the cells of the salivary glands and pancreas; it is involved in the hydrolysis of carbohydrates. With pancreatitis, the pancreatic form of amylase in the blood increases, and salivary amylase levels remain within normal values. Accordingly, hyperfermentemia (increased lipase or amylase in the blood) by more than three times is one of the key signs of acute pancreatitis.
In the context of diagnosing acute pancreatitis, lipase is a more specific enzyme than amylase. An increase in the level of lipase in pancreatitis is observed approximately 4-8 hours after the onset of the disease, amylase - 2-12 hours. In this case, the level of lipase in the blood, as a rule, increases to a greater extent and can remain elevated much longer compared to amylase (7-10 days / 3-4 days). It has also been found that in about 20% of patients, the concentration of serum amylase can remain within normal limits. This property is not typical for lipase.
Also, the level of serum pancreatic lipase may be increased in diseases of the hepatobiliary region and systemic diseases leading to secondary damage to the pancreatic gland.
Taking Pancreatin to compensate for lipase
Enlarge image
In order for food to be completely digested and all the necessary substances to be absorbed by the body, a sufficient amount of enzymes is required:
- lipases;
- amylase;
- trypsin;
- chymotrypsin.
If there are not enough of them, the person requires replacement therapy. One of the most effective drugs is Pancreatin. It helps in the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, and is used in the treatment of pancreatitis. With its help, digestion processes are normalized, and the functional state of the gastrointestinal tract is improved.
On a note! Pancreatin is an international nonproprietary name (INN). Therefore, many manufacturers can produce it under the same name, because The name "Pancreatin" does not belong to anyone.
Cholinesterase (ChE)
An enzyme that is involved in the destruction of acetylcholine, a chemical carrier of impulses in excitable tissues (muscle, nervous).
It binds to the liver and represents the main marker of the functional activity of this organ. That is, if something happens to the liver, then, of course, its ability to synthesize something decreases, and because of this, the content of those substances in the blood that should normally be produced in large quantities decreases. Norm:
5300-12900 units/l.
Increase:
physiological (in the first trimester of pregnancy), pathological (obesity, diabetes mellitus, tetanus, breast cancer, nephrosis, arterial hypertension).
Decreased:
usually in late pregnancy, with the use of certain drugs (anabolic steroids, glucocorticoids), as well as during the period of postoperative rehabilitation.
Important:
a decrease in ChE is a sign of destructive liver diseases, acute insecticide poisoning, and myocardial infarction.
Limits of normal indicators in adults and children
In a healthy person, lipase levels are at a constant level; a feature of this enzyme is that the standard values are the same for both men and women; changes occur only as the person grows older.
Table: dependence of lipase values on age
| Age | Normal lipase concentration, units per milliliter of blood |
| Children and teenagers under 18 years of age | 0–130 |
| Adult men and women | 0–190 |
If we consider the values of only pancreatic lipase, then its correct value will be 13–60 U/ml.
Maintaining digestion and treating enzyme deficiencies
If you have problems with digestion, enzyme preparations (more often called drugs to improve digestion) can help, the main task of which is to compensate for the lack of the body’s own enzymes. It’s not for nothing that this therapy is called “enzyme replacement”. It is critical that the enzyme preparation “mimics” the physiological process as closely as possible.
Today, there are various drugs to improve digestion. How to navigate the variety of means and make the right choice?
An effective enzyme preparation must meet the following criteria5,6:
- have an optimal particle size
- do not break down in the stomach
- quickly activate in the intestines
The drug Creon® meets all these requirements.
To learn more
1) Today, pancreatin minimicrospheres, which are contained only in the drug Creon®5,7, are recognized as the optimal particles. The invention of minimicrospheres was the result of many years of work to improve the effectiveness of enzyme preparations, which left far behind drugs in the form of tablets and capsules with other types of particles inside: pellets, mini-tablets, etc. In addition, Creon® minimicrospheres are produced using patented technology, which prevents other manufacturers from reproducing the same release form.
2) Creon® minimicrospheres are enclosed in a capsule that protects them from the destructive effects of the stomach. But that is not all. Each particle is covered with an acid-resistant coating in order to “reach” the intestines, where its work is necessary, completely intact. At the same time, some other encapsulated drugs can lose up to 30% of their activity6.
3) Creon® begins to work within 15 minutes after entering the intestines, improving digestion and thereby eliminating heaviness and discomfort after eating6.
Creon® has several dosages, including 10,000 IU of lipase - the minimum required dose of lipase to improve digestion in case of dietary errors, eating heavy foods and overeating. To obtain the effect, Creon®10000, like any enzyme preparation, must be taken with every meal - during breakfast, lunch and dinner.
Pancreatin: reviews
Diseases of the pancreas occur at any age, especially in those people who do not particularly monitor their diet, exceed the portions required by the body and abuse alcohol. Pancreatin is extremely necessary in the first aid kit, people with gastrointestinal problems note in reviews. The effect after administration occurs literally within 30-40 minutes. As a rule, it is prescribed by doctors, because this drug has proven itself well. Take Pancreatin alone or in combination with other medications. Many people have known pancreatin since the times of the USSR.
People with chronic pancreatitis take a course of the drug for prevention 1-2 weeks before the holiday feast. The drug helps improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and also replenishes the deficiency of digestive enzymes.
The main contraindication is individual intolerance, but it occurs in only 1% of people taking Pancreatin. If you follow all the recommendations and follow a diet, this will allow you to avoid surgical intervention and quickly return to your normal life.
On average, in reviews in general, people note the positive role of Pankratin in alleviating the gastrointestinal tract after:
- abundant holiday food;
- food poisoning;
- consuming stale or not very clean products from hand in markets, stalls, etc.
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK)
An enzyme that provides energy to muscles, mainly striated muscles (skeletal and cardiac).
It is located inside muscle cells and is responsible for the transfer of phosphoric acid residue to creatine and the resulting activation of energy metabolism. We have already mentioned many times above that intracellular enzymes, increasing in the blood, indicate that destruction of a specific tissue is occurring somewhere. In the case of CC, this tissue is muscle. This is the earliest and most specific marker of myocardial infarction; its activation can be detected within two hours after the occurrence of a focus of necrosis in the heart muscle. Norm:
up to 190 units/l for men, up to 167 units/l for women.
Increased:
myocardial infarction, myocarditis, myocardial dystrophy, heart failure, tachycardia, hypothyroidism, malignant tumors and some diseases of the central nervous system (schizophrenia, psychoses, epilespy, head injury).
It can also increase after operations and diagnostic manipulations on the heart, after physical activity. Decrease:
sedentary lifestyle, severe decrease in muscle mass, cachexia (exhaustion).
Pancreatin: at the pharmacy
In any pharmacy in Moscow and St. Petersburg you can find a variety of drugs containing lipase . Manufacturers promise an almost instant effect. Or vice versa, you need a lot of pills and take them for a very long time. And many people have long noticed that conventional drugs do not always give the expected effect. There are good drugs in pharmacies, but many people prefer to order dietary supplements on iHerb.com, because... All products are shipped from warehouses in the USA. And here many people from Russia and 150 countries around the world regularly place orders for various herbal supplements and vitamins. When purchasing dietary supplements and sports nutrition from iHerb, you can be confident in its quality and originality. iHerb works only with trusted manufacturers.
All products are purchased, stored and delivered in accordance with all GMP and manufacturer safety requirements. Humidity and temperature conditions are regularly monitored. Absolutely all additives have documents confirming the quality of the products.
Main signs of pancreatic enzyme deficiency
Identifying enzyme deficiencies is quite simple. The key symptoms are heaviness after eating, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen and abdominal discomfort. Often these symptoms are accompanied by bloating, rumbling, flatulence, and diarrhea. Most often, such symptoms can occur in ordinary situations: when eating heavy, fatty foods or when overeating, when it was simply impossible to resist eating a lot of tasty dishes. In this case, you should not be afraid of problems with the pancreas or other gastrointestinal diseases. The pancreas simply cannot cope with much work and may need help.
Why does diarrhea occur? Fats are the most difficult components of food to digest. If there is a lack of enzymes in the body, it is with the processing of fats that difficulties arise. As a result, undigested fats that are not decomposed by enzymes contribute to a change in the nature of the stool and the rapid movement of contents along the intestines, which provokes diarrhea8.
If a lack of enzymes and digestive problems persist for a long time, then this does not go unnoticed by the body. Symptoms may worsen and become regular rather than episodic. Constant diarrhea gives rise to vitamin deficiency; protein-energy deficiency and dehydration throughout the body can develop. Significant weight loss may occur. In addition, in severe stages, the following symptoms of pancreatic enzyme deficiency may be observed8:
- nausea and vomiting;
- heartburn;
- a sharp decrease in appetite;
- general weakness.
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
This is an enzyme that is usually localized in the membrane, in contrast to the enzymes described in the first part of the article, which are located in the cytoplasm of cells.
It is mainly contained in the brush border of the mucous membrane of the bile canaliculi (the surface layer of cells forms brush-like outgrowths, hence the name). This is a key enzyme involved in the metabolism of phosphoric acid. Most often, alkaline phosphatase is determined when gallstone disease is suspected and the mechanical origin of jaundice occurs when stones block the lumen of the ducts, bile stagnates, and the pigment bilirubin begins to leak into the blood. The diagnostic value is based on the fact that during obturation the activity of alkaline phosphatase increases 10 times. ALP is often determined by monitoring the healing of bone tissue and the healing of fractures, as well as when tumor processes in the bone are suspected, since the enzyme functions as a marker of osteosynthesis. Norm:
30-90 units/l.
Increase:
with obstructive jaundice, bone tumors and metastases, rickets, to a lesser extent with destructive liver diseases (cirrhosis, cancer), amyloidosis, blood diseases (myeloma, lymphogranulomatosis, mononucleosis), hyperthyroidism.
Decrease:
observed with a lack of certain microelements (zinc, magnesium, vitamins B12 or C), as well as with anemia, placental insufficiency during pregnancy, hyperthyroidism and disorders of growth and bone formation.